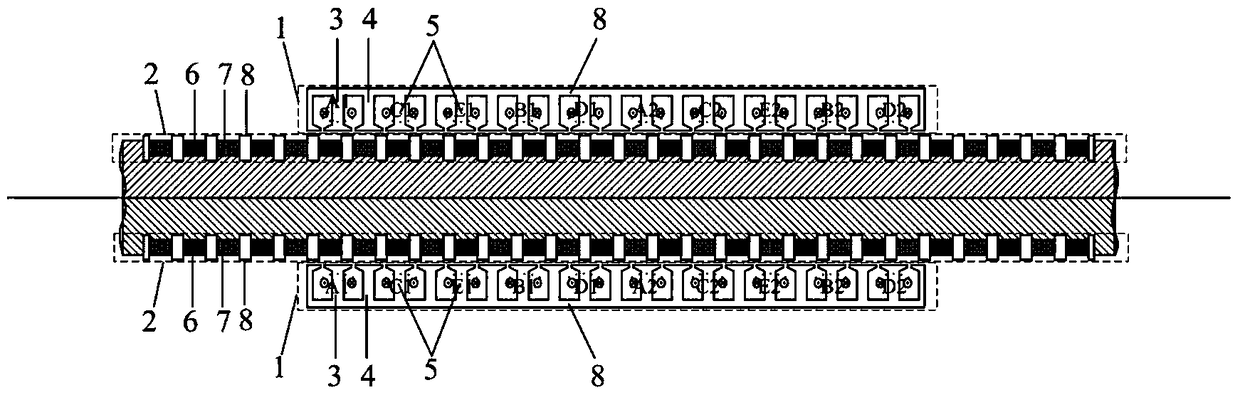
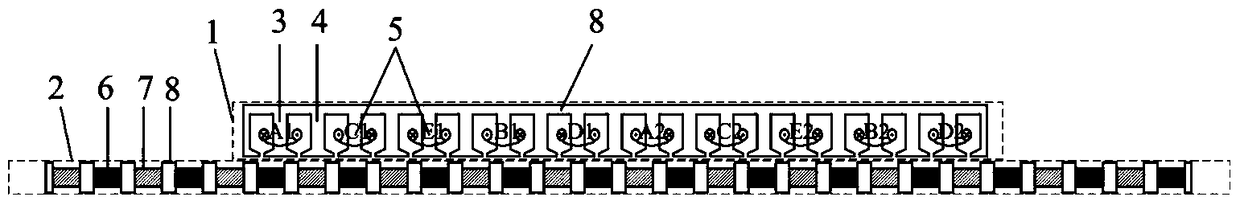
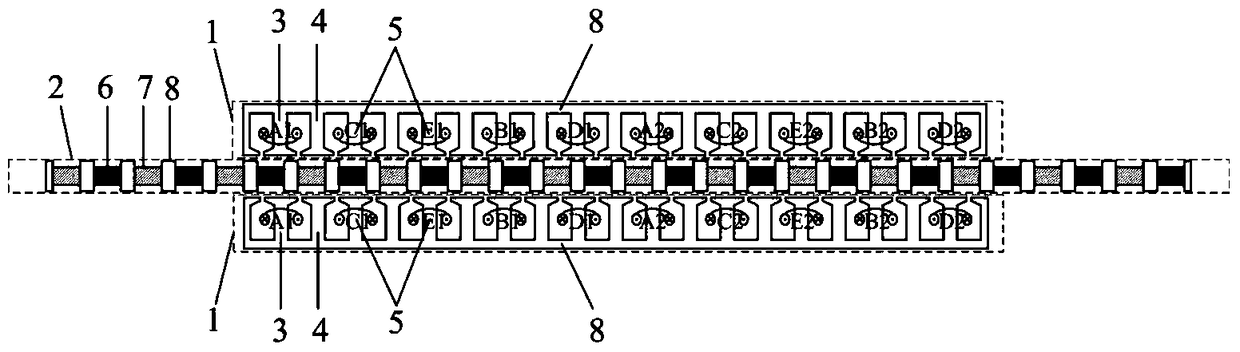
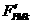Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Suppression of thrust fluctuations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
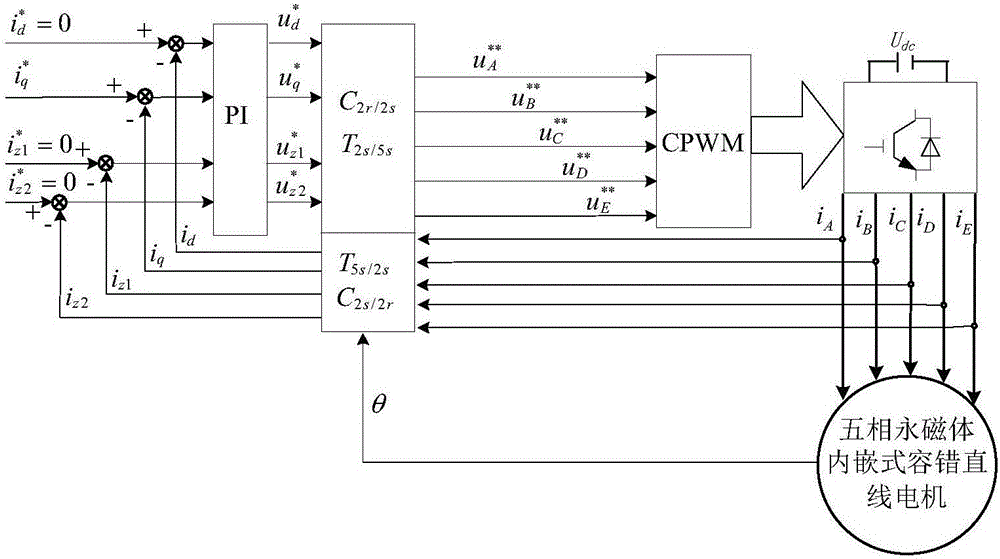
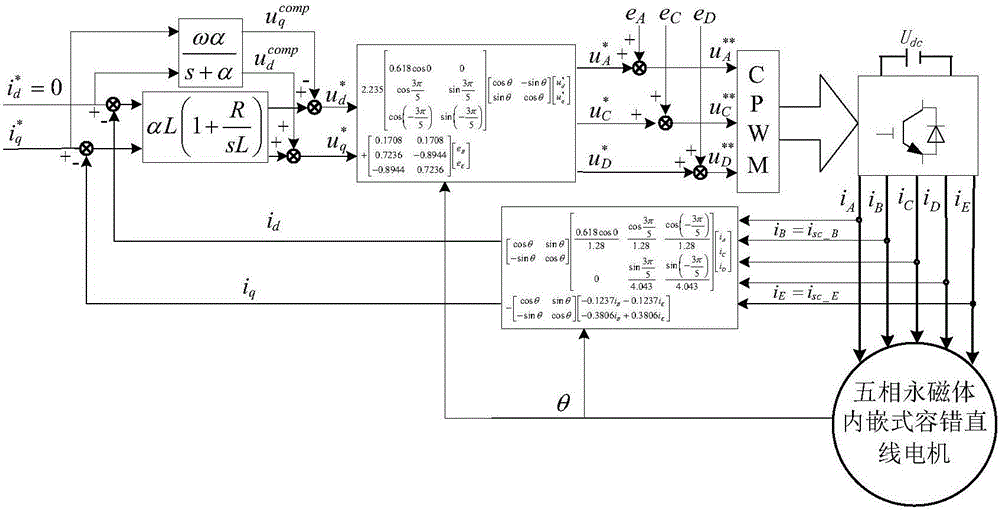
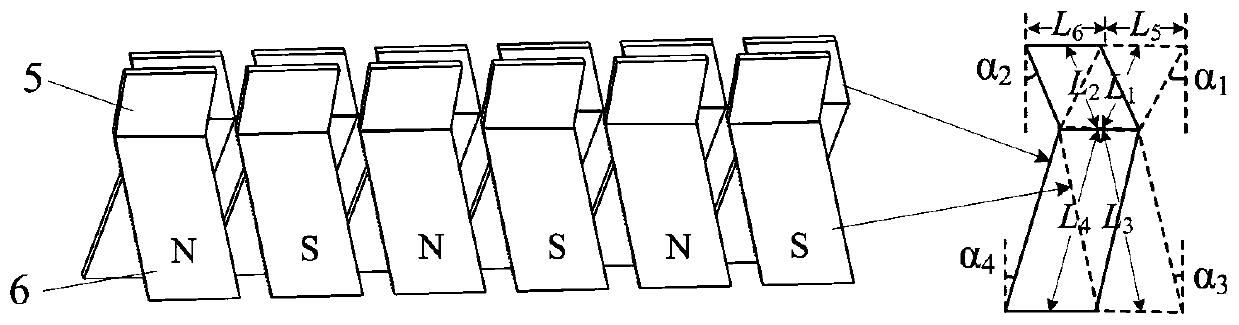
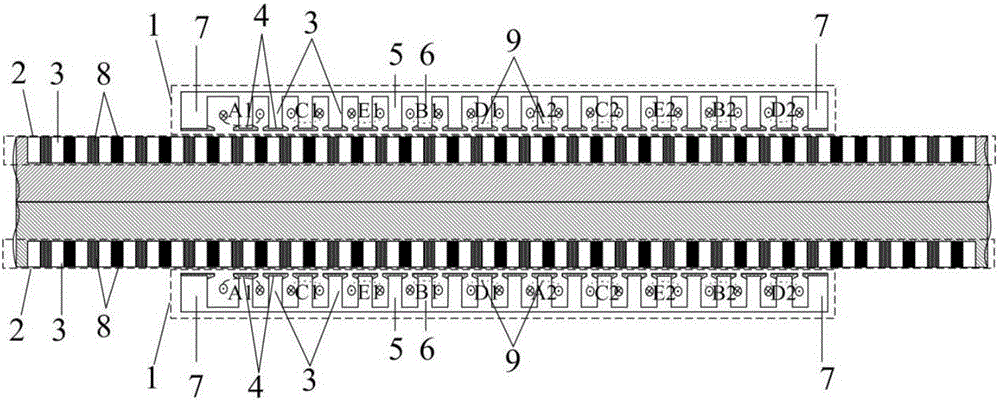
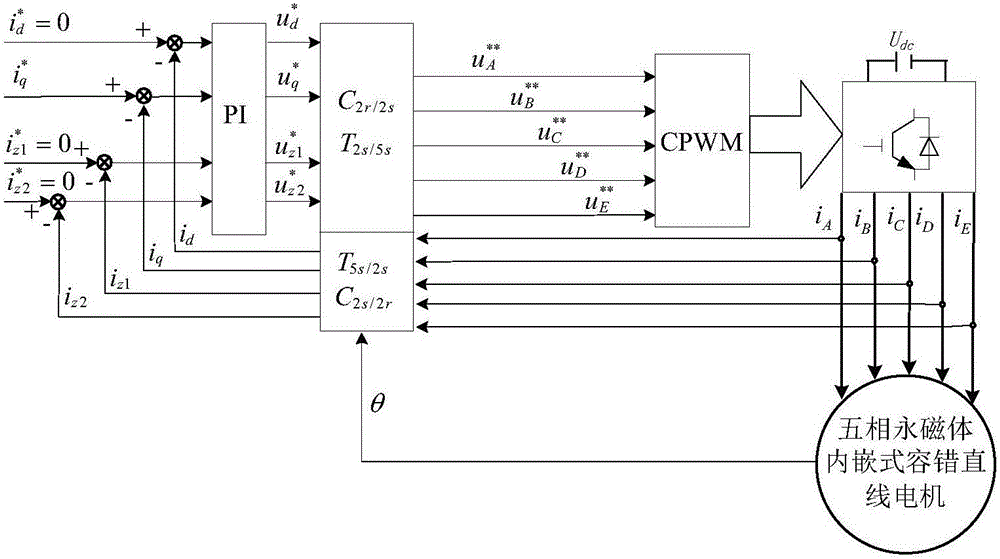
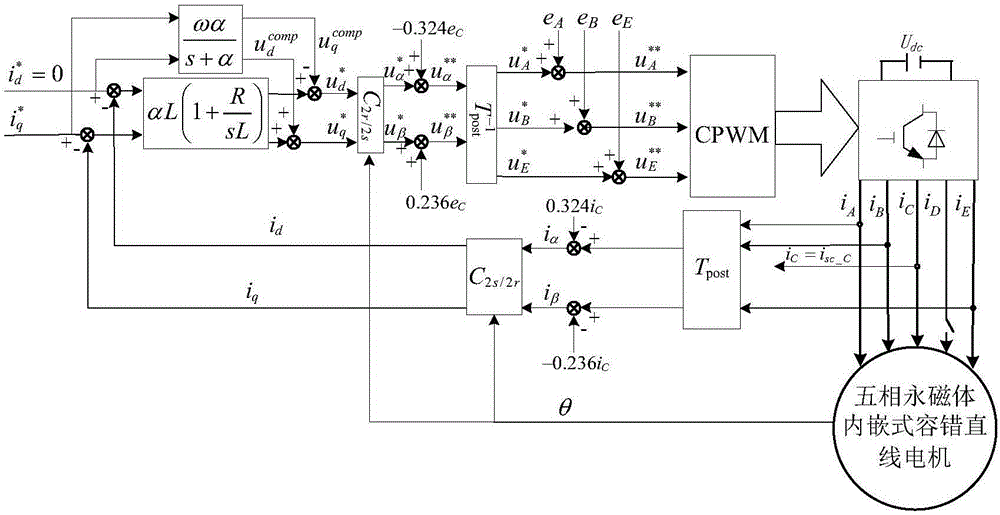
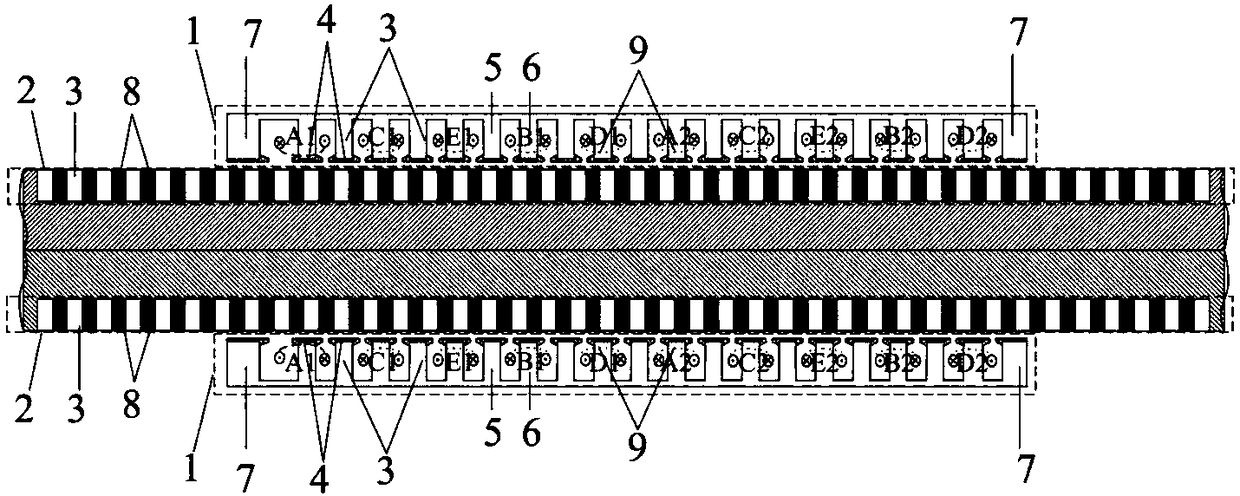
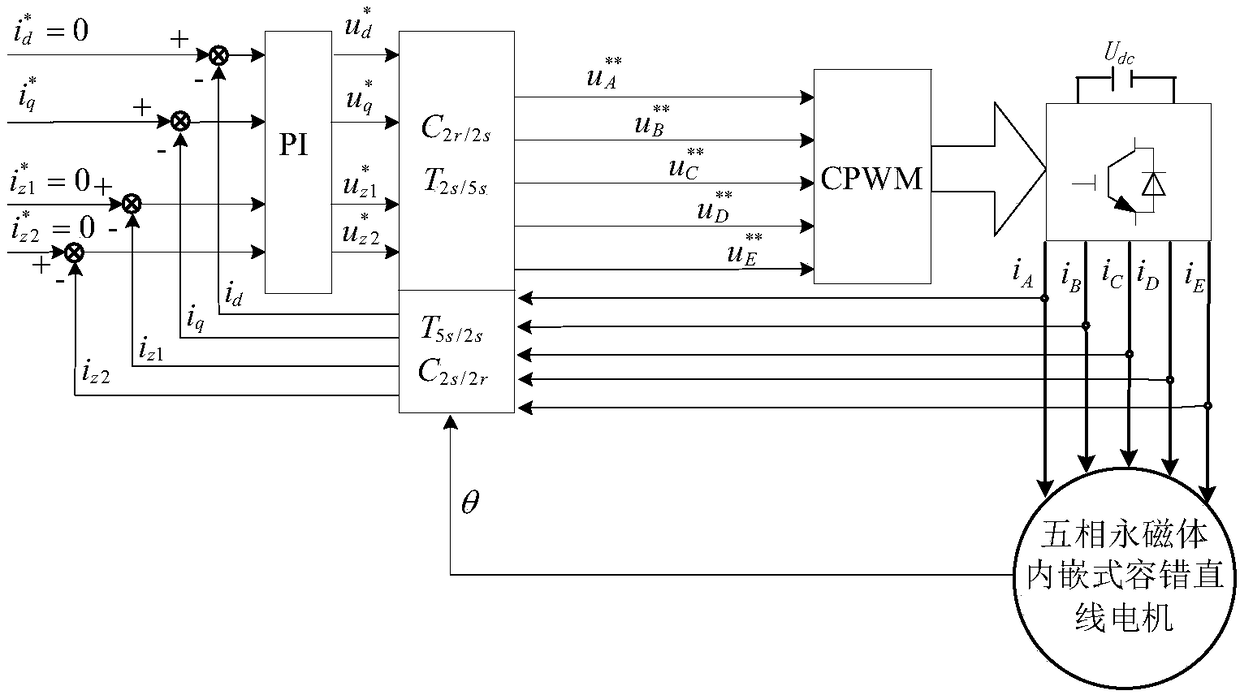
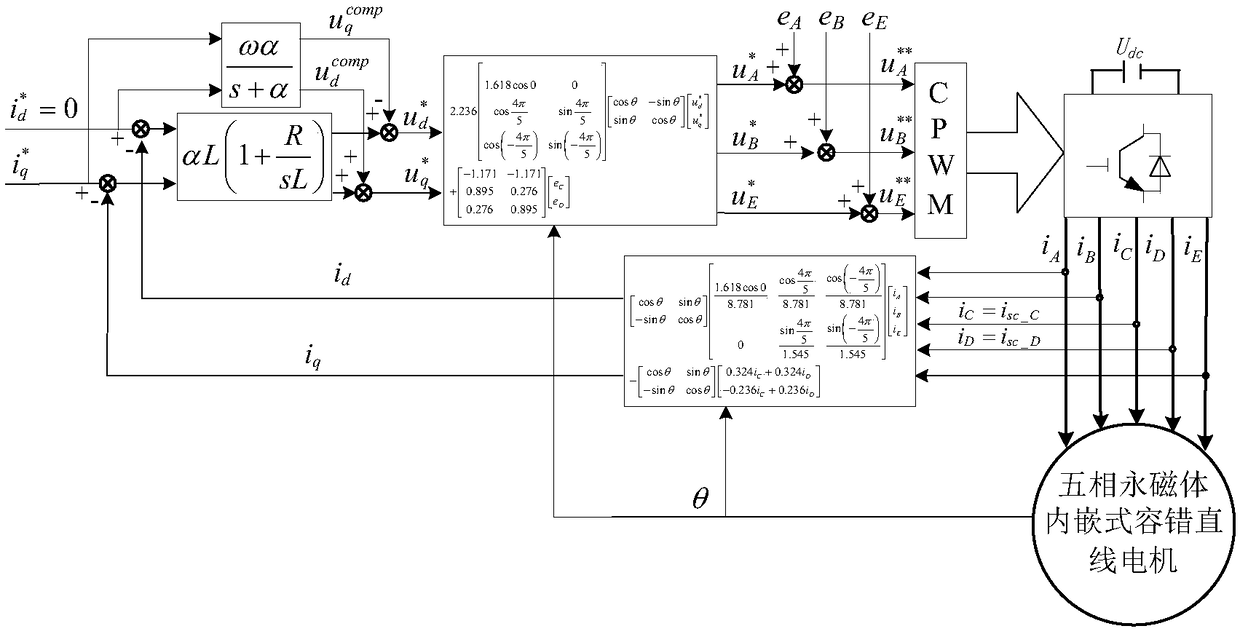
Short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method for embedded hybrid magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor
InactiveCN105245156ASimple structureImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage source inverterCompensation strategy
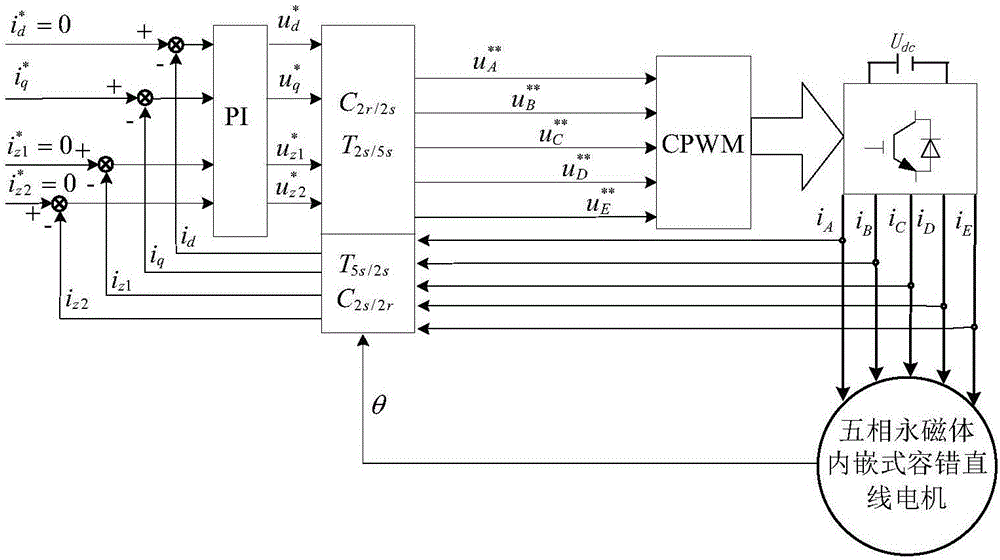
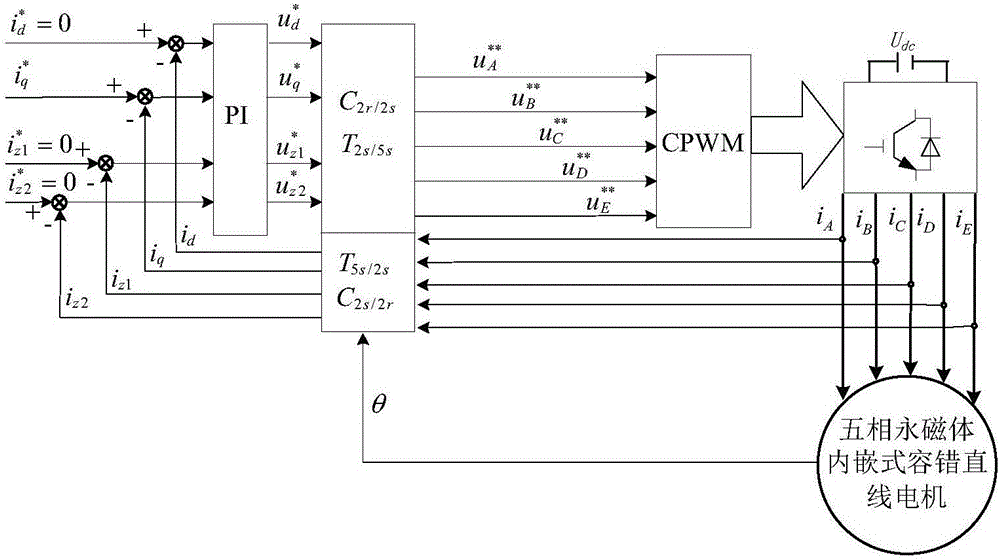
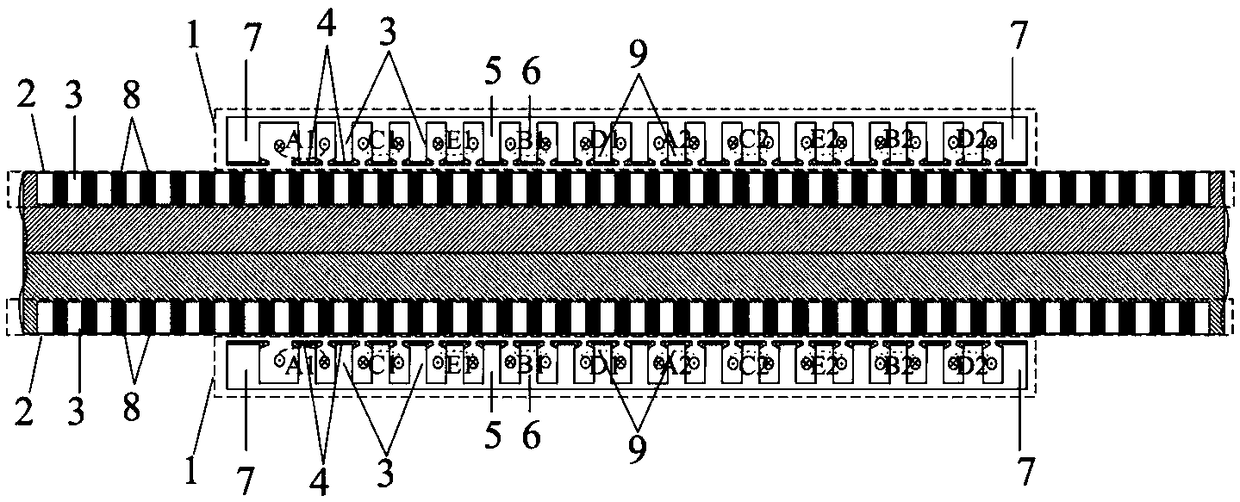
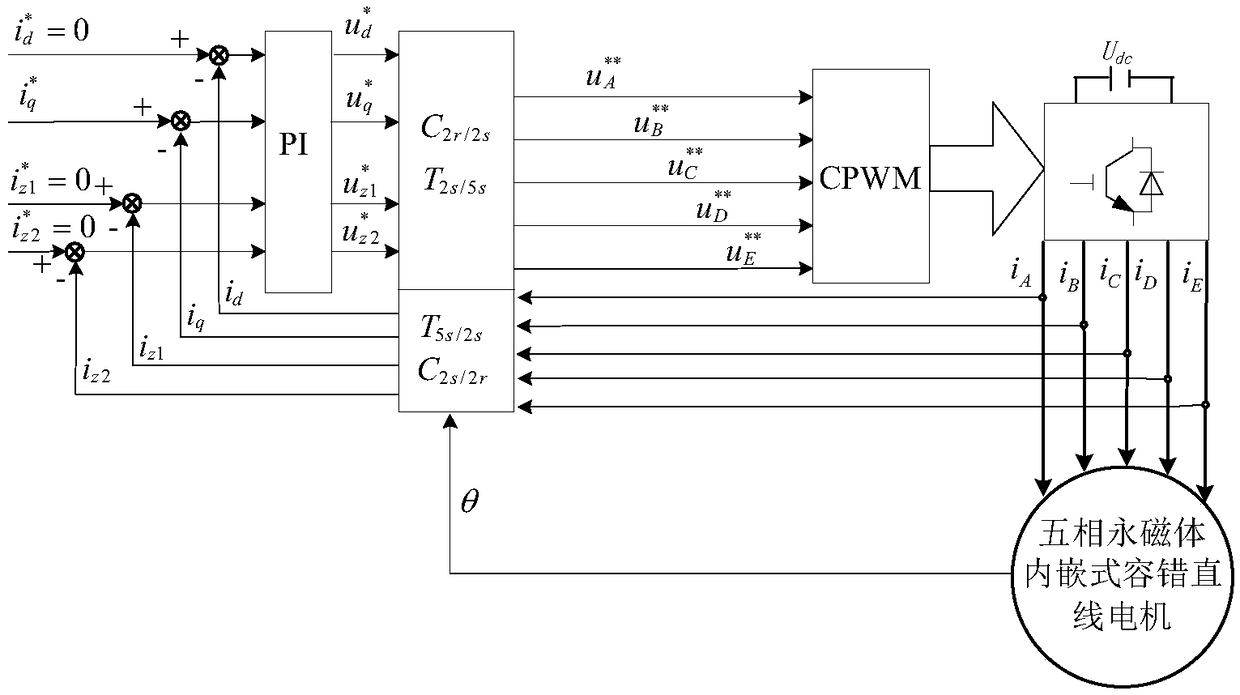
The invention discloses a short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method for an embedded hybrid magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor. The short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method comprises the following steps: building a five-phase embedded hybrid magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor model; compensating normal thrust missing caused by a short-circuit fault phase and suppressing a thrust ripple caused by phase short-circuit current with non-fault phase current of the motor; and obtaining expected phase voltage by adopting a series of coordinate conversion and voltage feed-forward compensation strategies, and achieving a fault-tolerant vector control after the phase short-circuit fault of the motor by a zero-sequence voltage harmonic injection-based CPWM modulation mode. According to the short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method, the motor can suppress the thrust ripple of the motor under the condition of a phase short-circuit fault-tolerant operation; more importantly, the dynamic property, the steady-state performance and the properties in a normal state are consistent; the switching frequency of a voltage source inverter is constant; a CPU is low in overhead; and a natural coordinate system only needs to counterclockwise rotate a certain angle in any phase short-circuit fault, so that the motor fault-tolerant operation can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
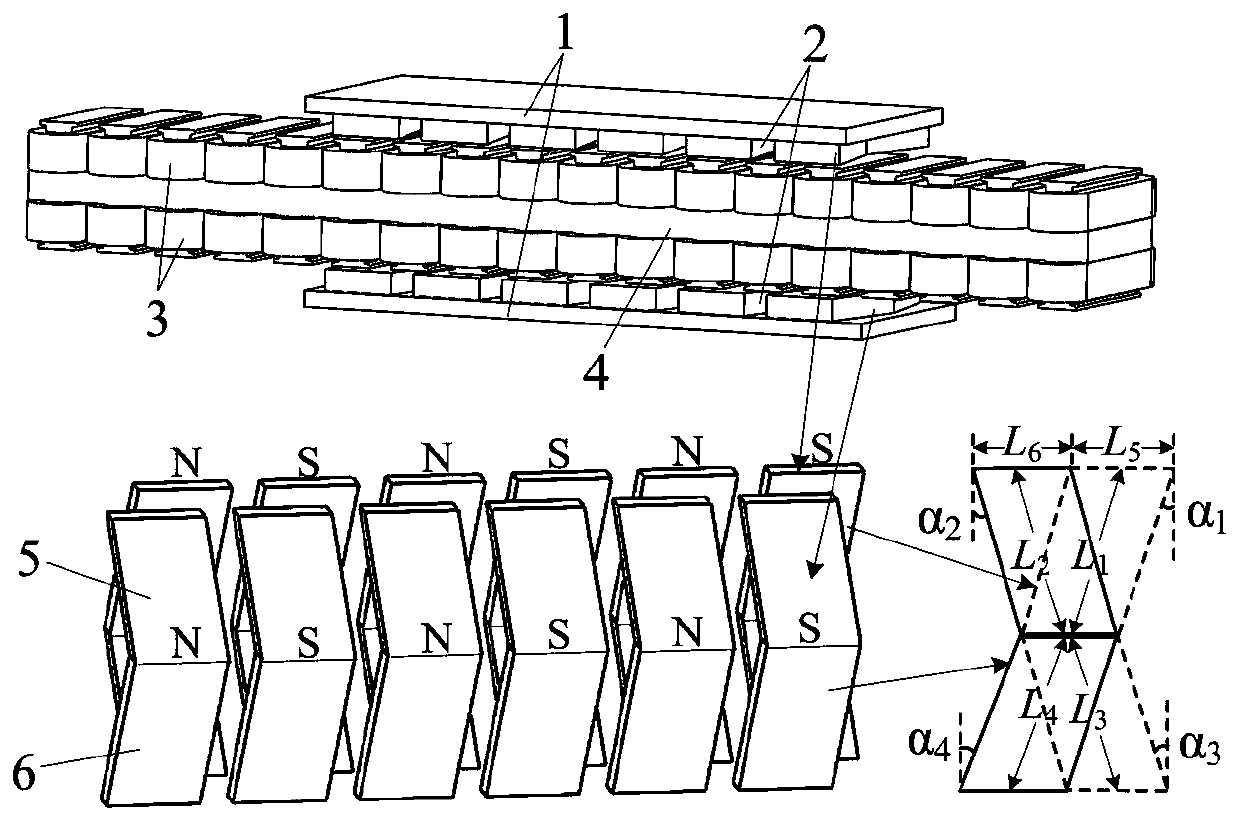
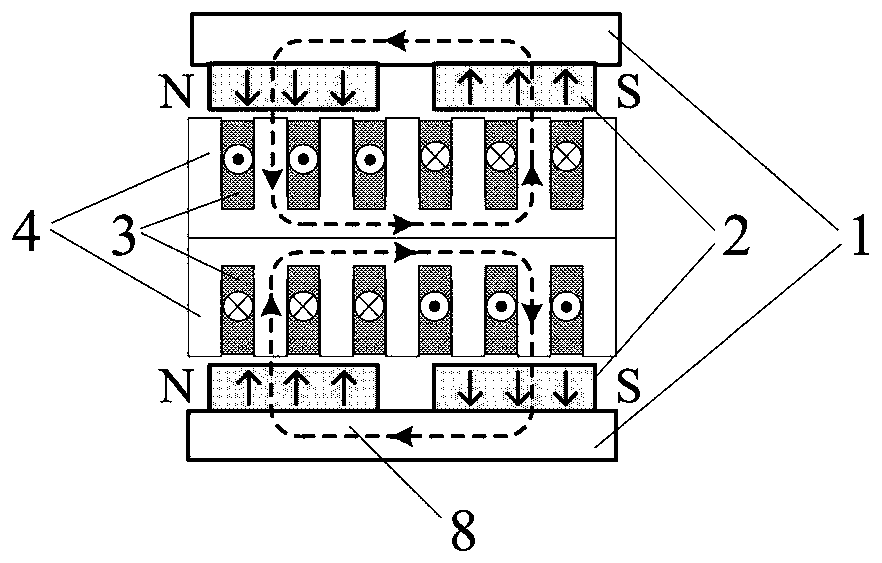
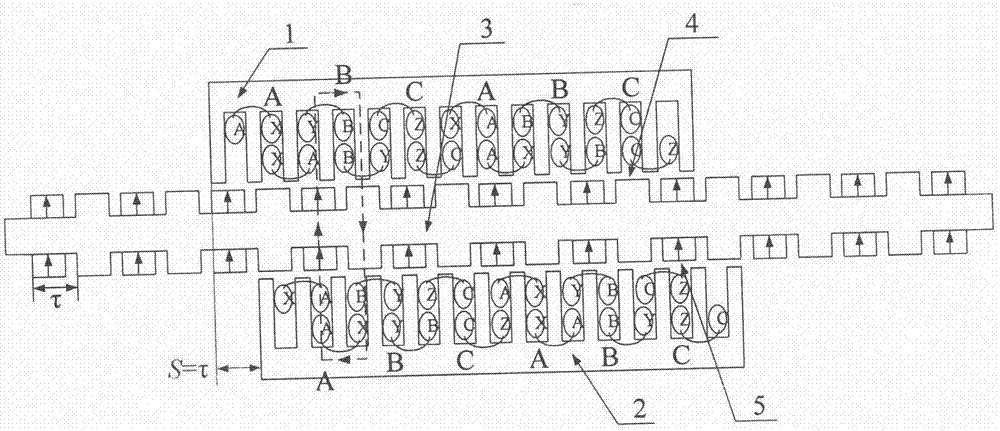
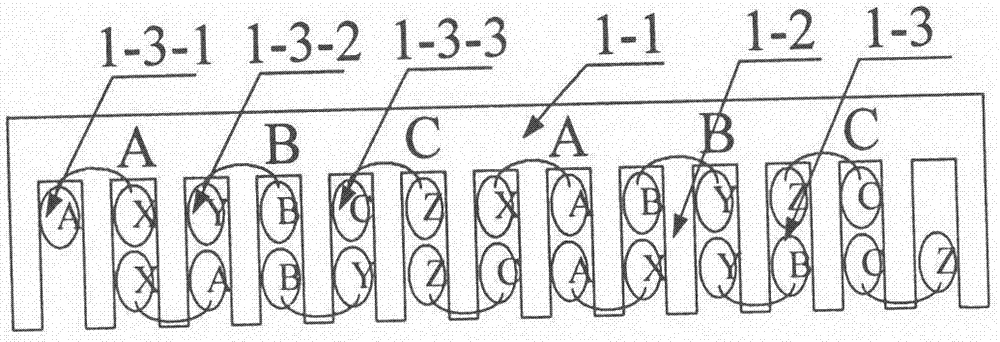
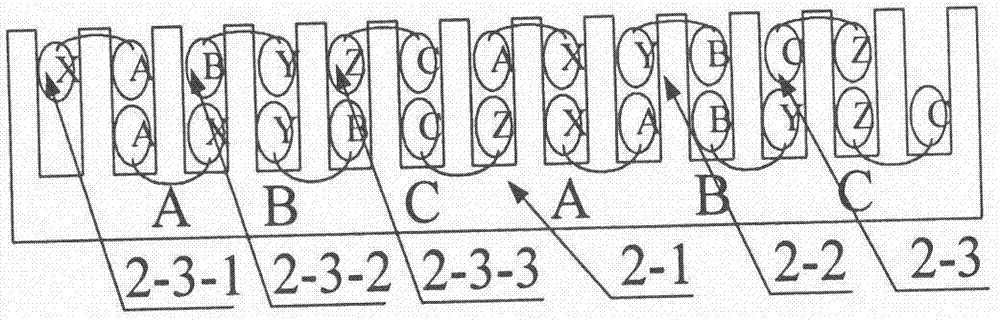
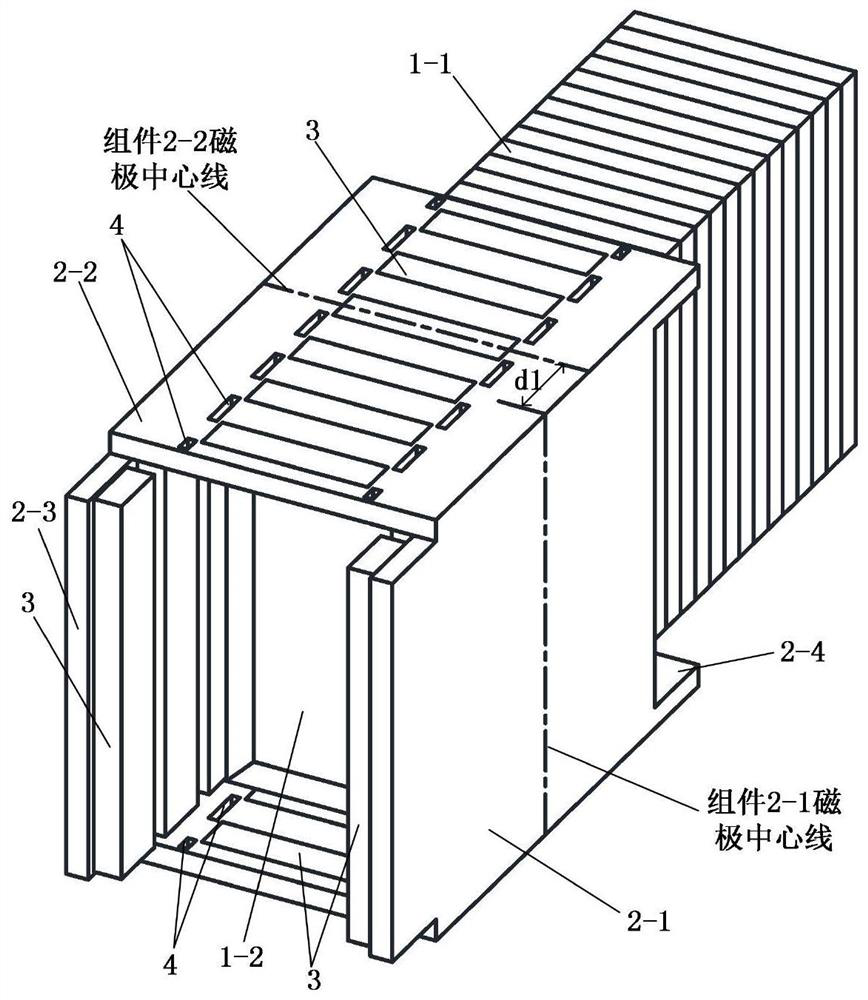
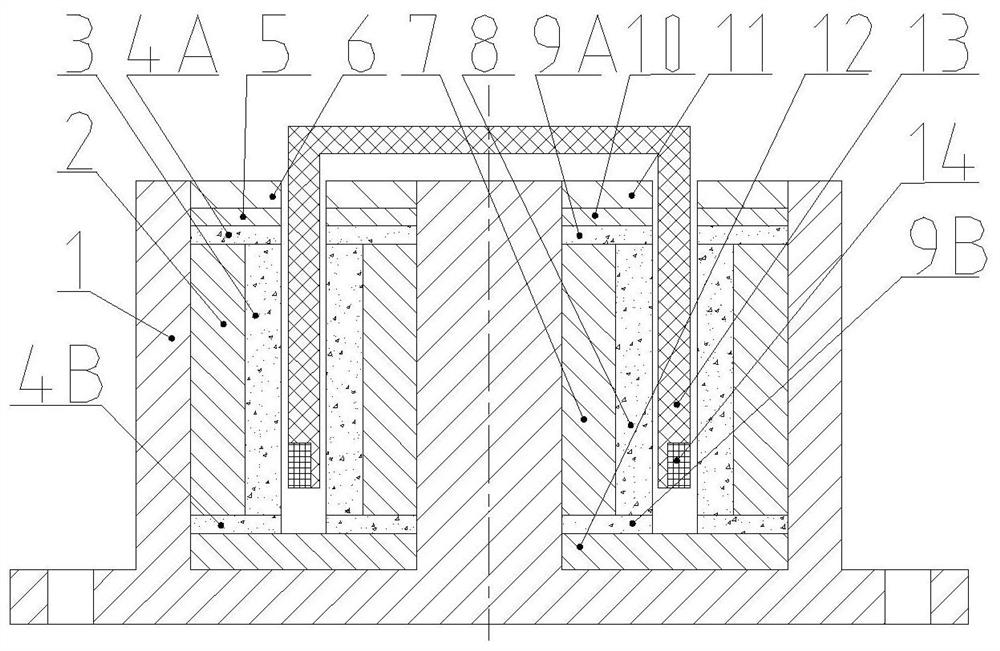
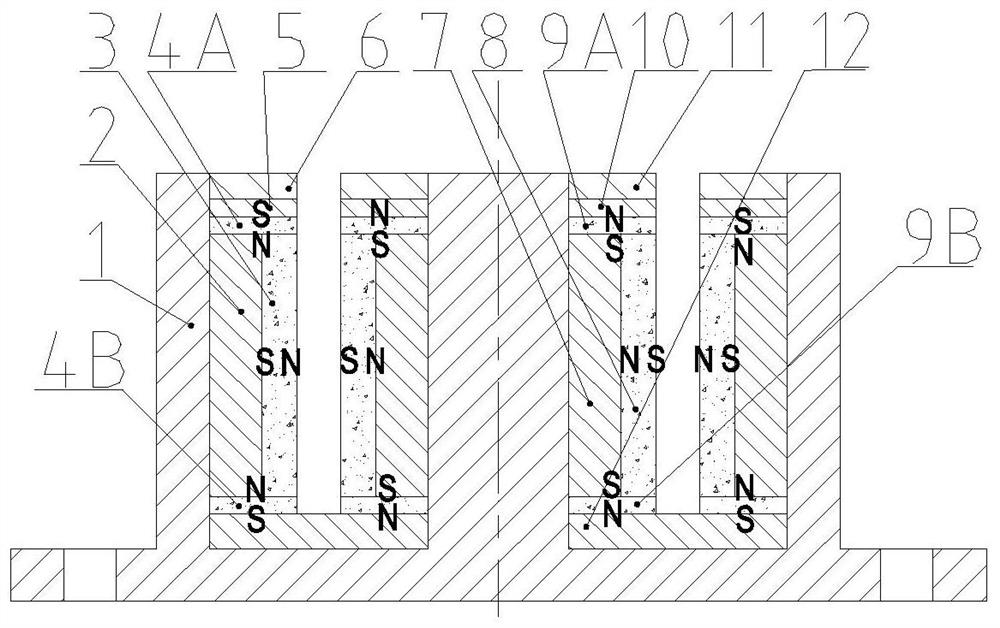
Embedded type mixing magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor
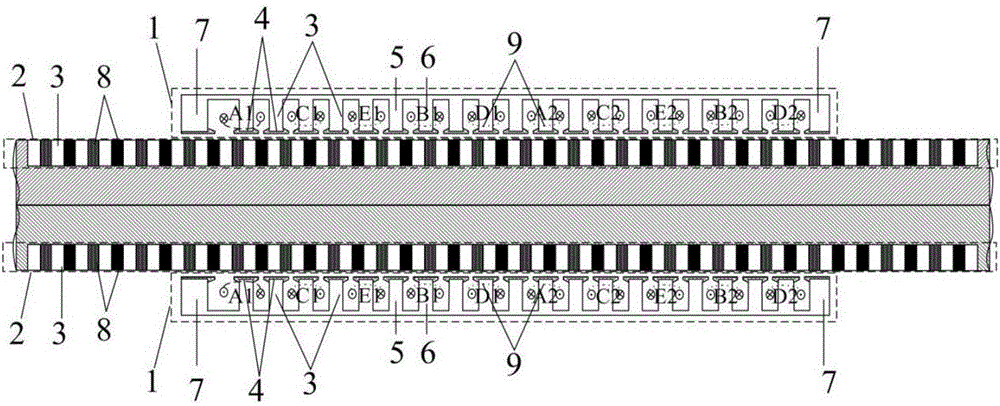
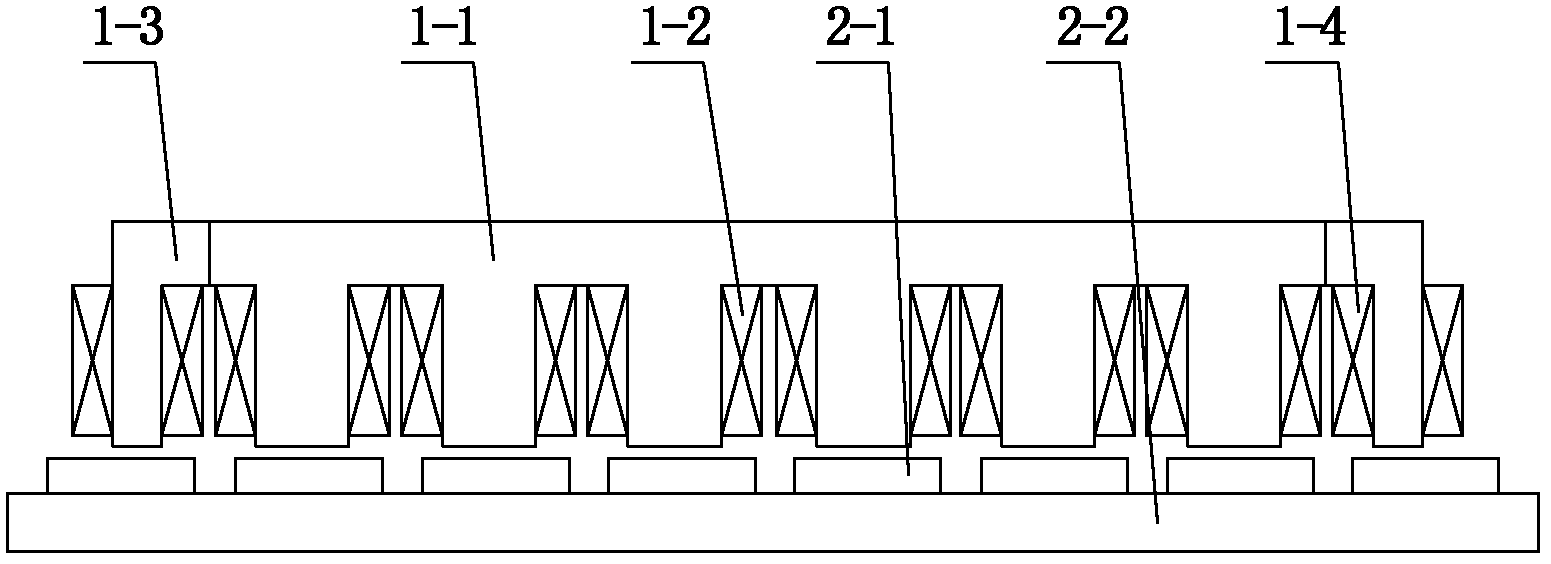
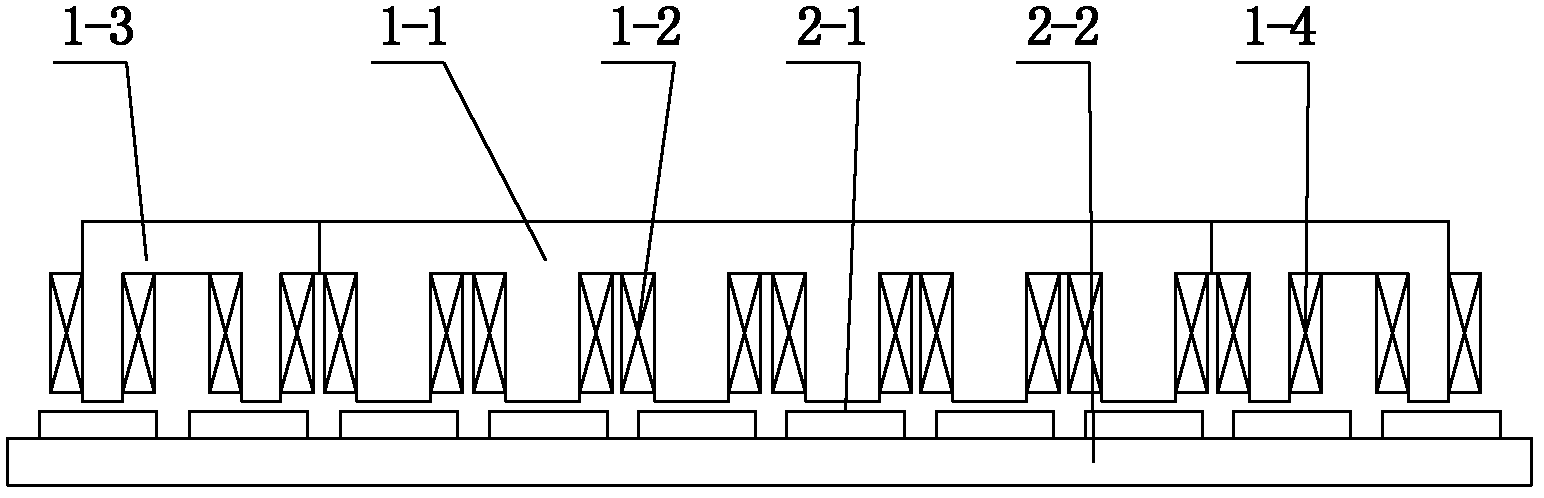
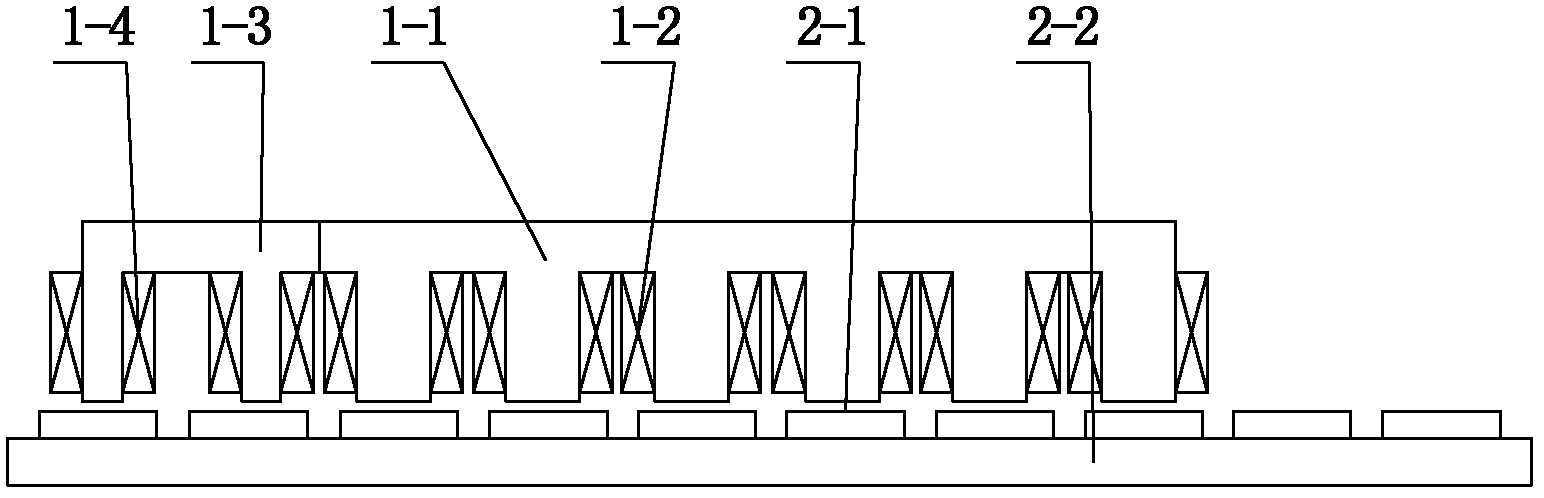
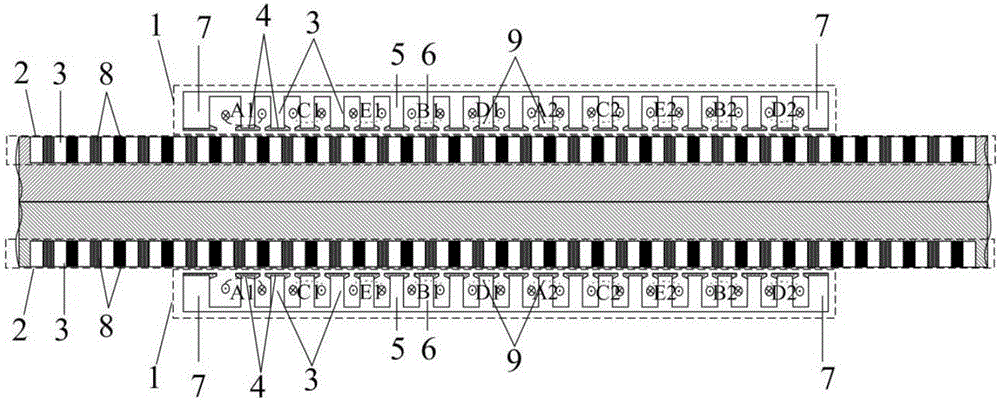
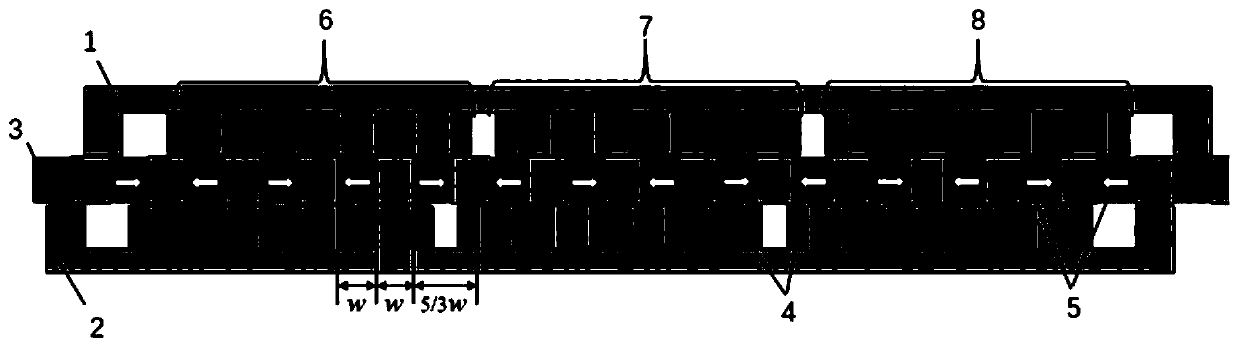
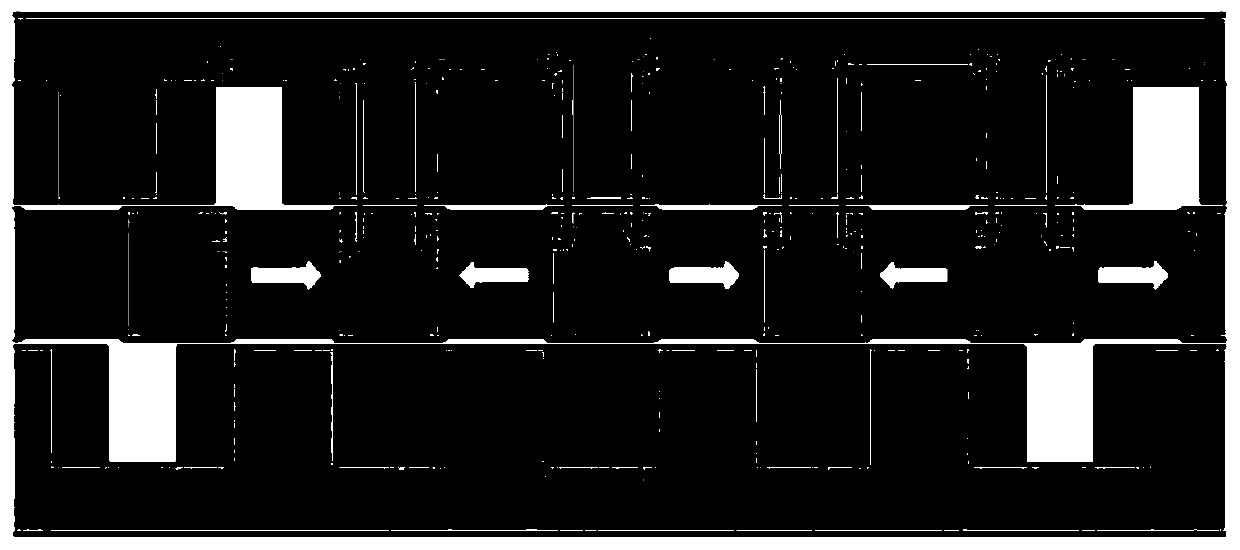
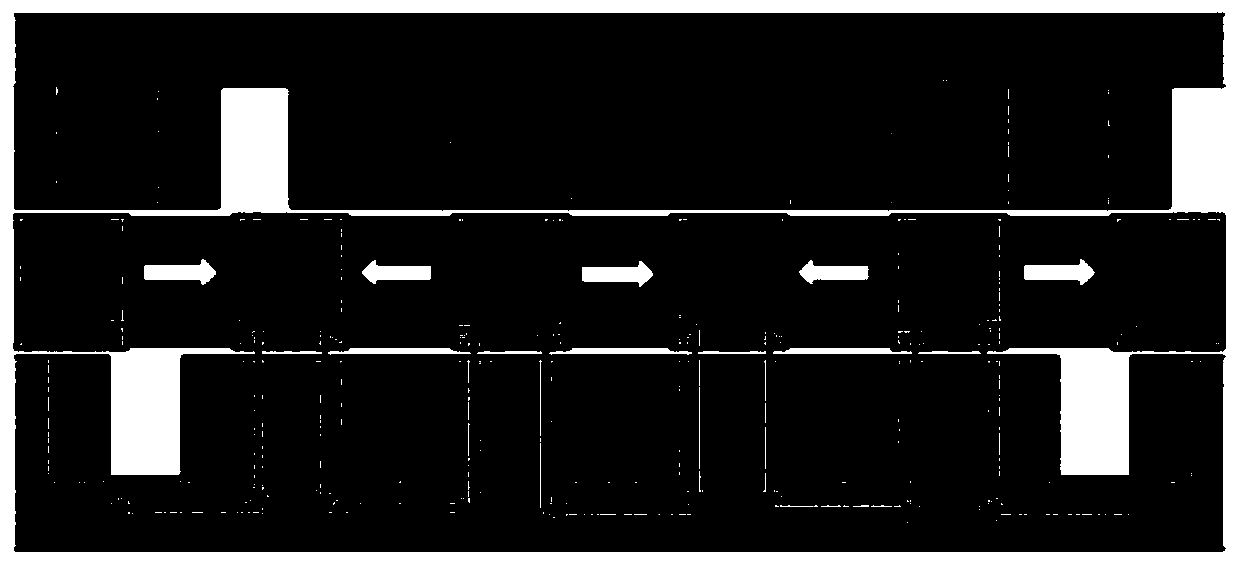
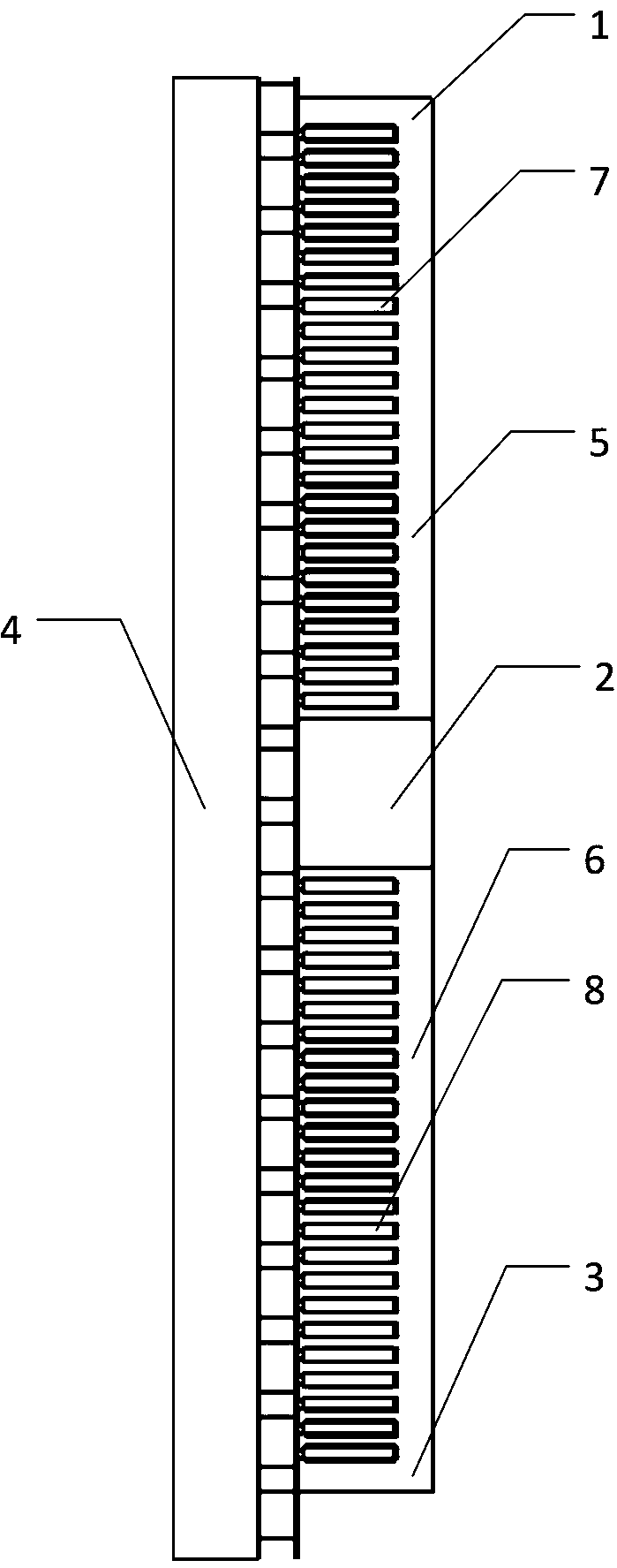
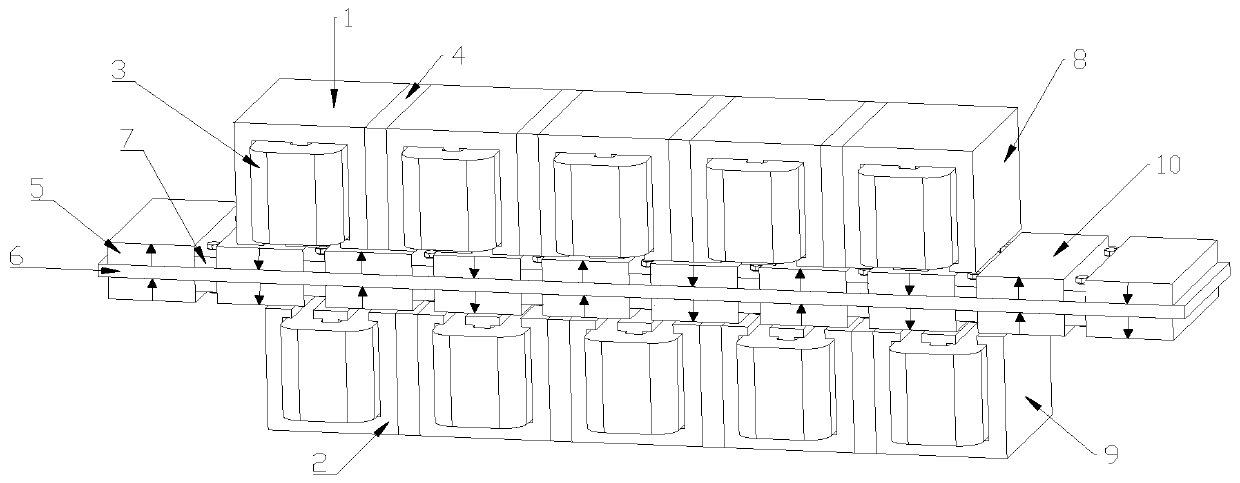
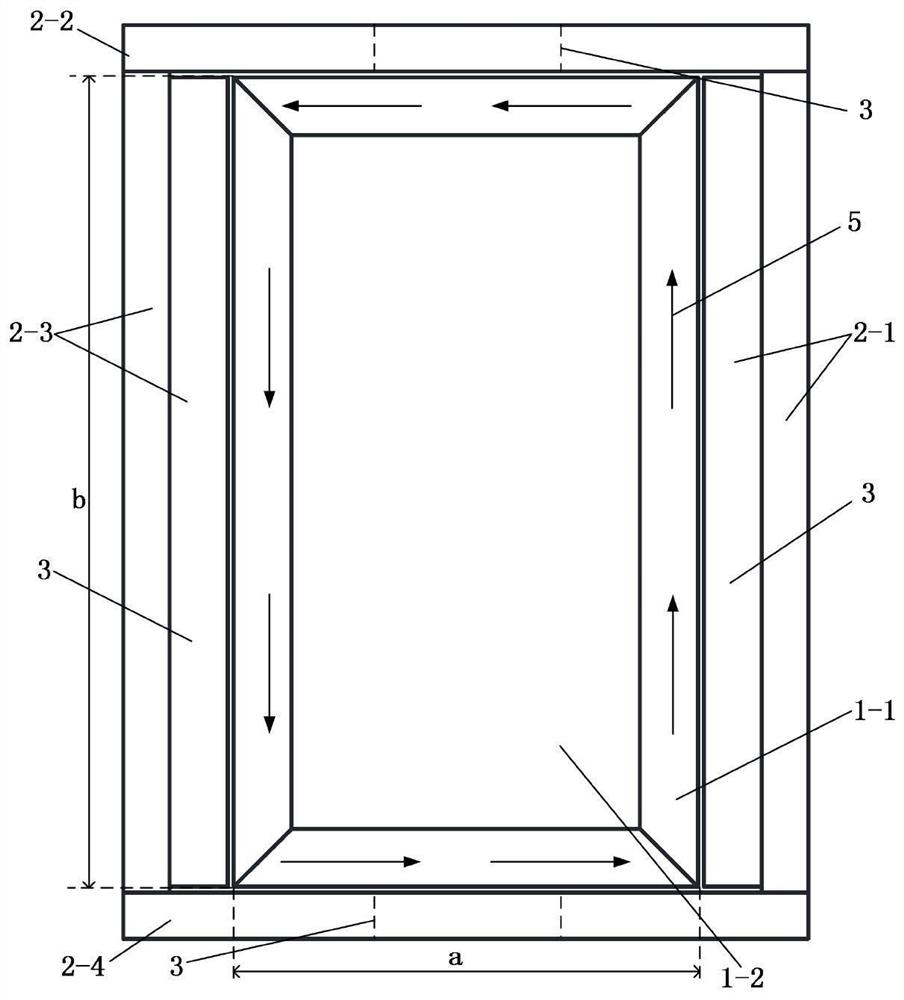
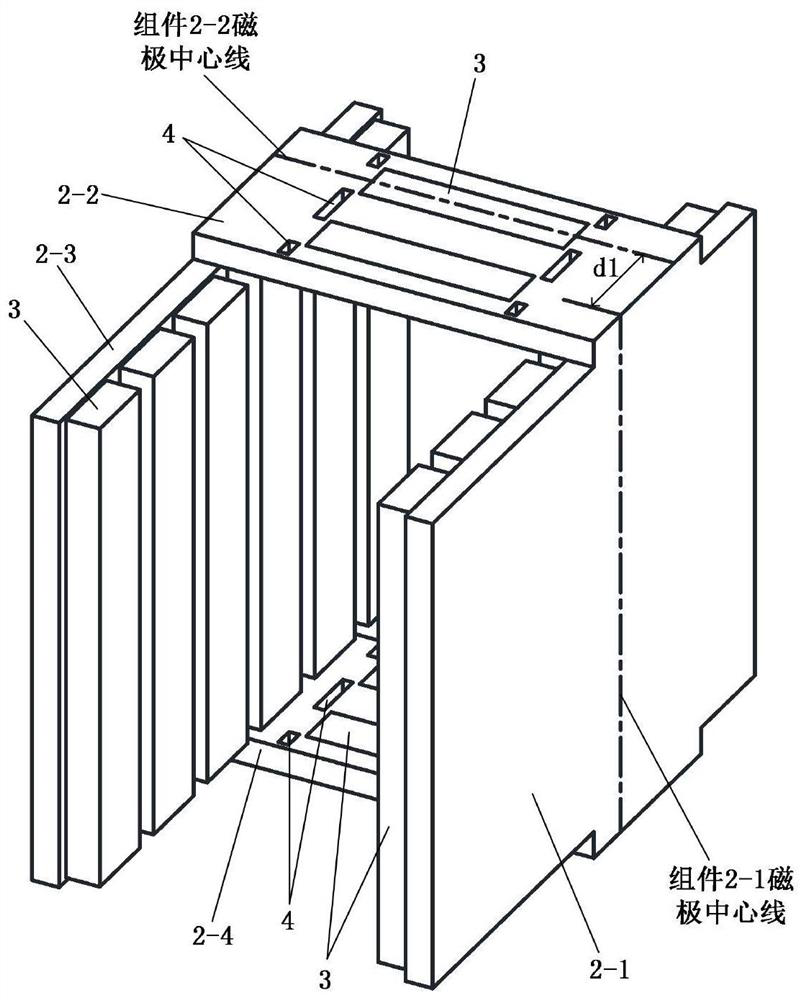
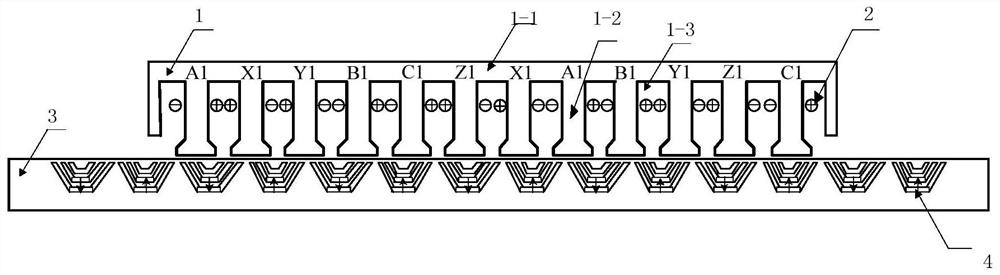
The invention discloses an embedded type mixing magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor which comprises primary bodies and secondary bodies. The length of each primary body is smaller than that of each secondary body. An air gap is reserved between each primary body and the corresponding secondary body. Each primary body comprises armature teeth, fault-tolerant teeth and a coil winding. The 2*m armature teeth and the 2*m fault-tolerant teeth are uniformly distributed on each primary body, wherein m is the phase number of the motor and is larger than or equal to three; the armature teeth and the fault-tolerant teeth are arranged at intervals in a staggered mode. Only one set of disc-shaped coil windings are placed into an armature tooth groove of each primary body. No windings are arranged on the fault-tolerant teeth. The secondary bodies of the motor are made of mixing magnetic materials, a part of ferrite is used for replacing a part of rare earth permanent magnets to form four different mixing magnetic material structures, on one hand, the quantity of the adopted rare earth permanent magnets is greatly reduced, and the cost of the motor is reduced; on the other hand, as the magnetic energy product of the permanent magnets is reduced, the eddy-current loss of the motor is reduced greatly, and efficiency of the motor is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Low-speed high-thrust-density linear motor
The invention relates to a low-speed high-thrust-density linear motor which comprises a motor short primary and a motor long secondary arranged opposite to the motor short primary, wherein an air gap (5) is reserved between the motor short primary and the motor long secondary; the motor short primary comprises a stator core (1), stator teeth (3) uniformly distributed at the periphery of the stator core (1), a stator winding (2) and stator permanent magnets (4); the stator core (1) is of an open slot stator structure, i.e., the stator core (1) is provided with a stator slot (8), the stator permanent magnets (4) are uniformly distributed between every two adjacent stator teeth (3), and the stator winding (2) is inserted into the stator slot (8); the motor long secondary comprises an active cell yoke (7) and active cell permanent magnets (6); and the active cell permanent magnets (6) are embedded into the active cell yoke (7) alternately and equidistantly in a horizontal direction. In the low-speed high-thrust-density linear motor provided by the invention, the magnetic modulation rings in a magnetic gear are replaced by the stator teeth, thereby simplifying the machining process, improving the reliability of the device and reducing the system manufacturing cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Thrust ripple suppressing method of primary permanent magnet linear motor
InactiveCN103346721ASuppression of thrust fluctuationsReduce noiseElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsHysteresisFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a thrust ripple suppressing method of a primary permanent magnet linear motor. Positioning force of the primary permanent magnet linear motor is obtained by measuring in practice by a finite element simulation or torque testing instrument. The waveform of the positioning force undergoes harmonic spectral analysis to confirm the component of base waves and main ultraharmonics in the positioning force. The no-load counter emf wave form of a finite element simulation motor is utilized to calculate out the three-phase current component which is used for counteracting the harmonic component of the positioning force so that additional electromagnetic force is equal to the component of the base waves and the main ultraharmonics in the positioning force in terms of amplitude, but opposite in terms of phase. Three-phase harmonic currents are filled into a current hysteresis vector control system to suppress thrust ripple of the permanent magnet linear motor. The body of the motor does not need transforming and a control strategy can be used for achieving suppression. The thrust ripple of the motor can be obviously hindered, noise in operation of the motor is reduced and characteristics of the motor such as no-load magnetic potentials and thrust outputting capability are kept unchanged.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
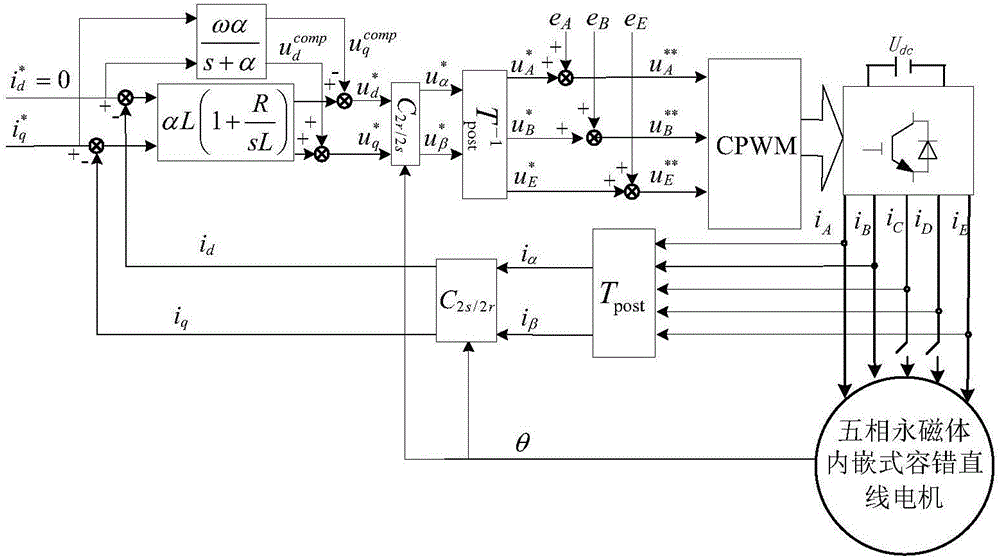
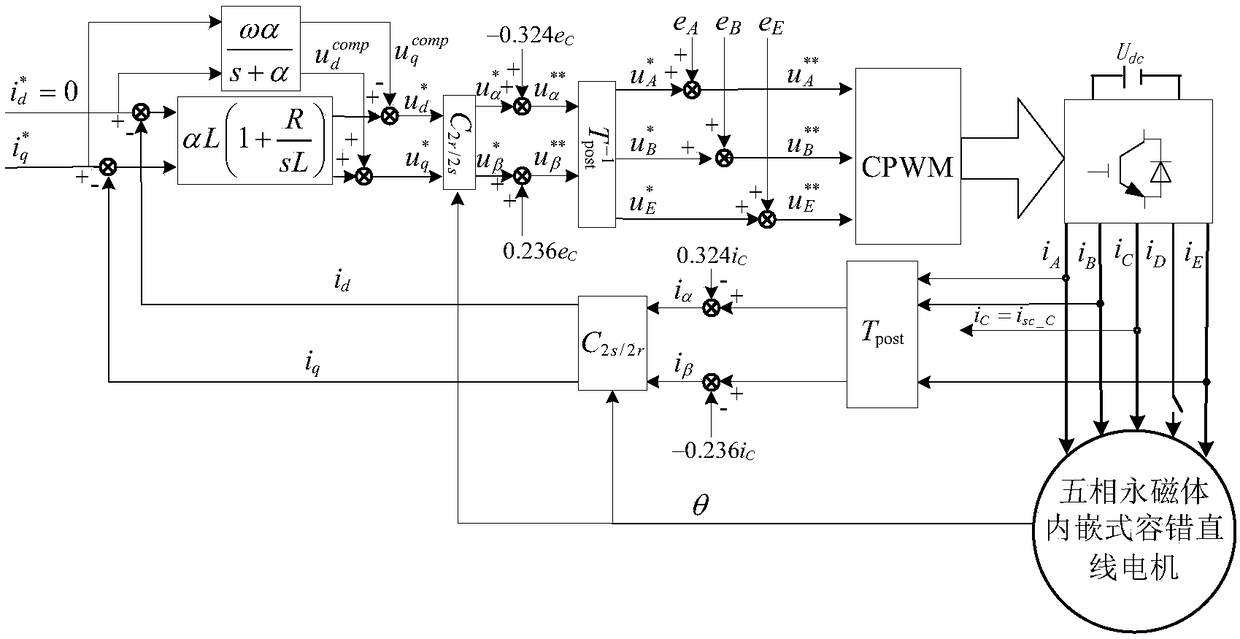
Fault-tolerant field-oriented control method for non-adjacent two-phase short circuits of five-phase permanent magnet-embedded fault-tolerant linear motor
InactiveCN106208891ASuppression of thrust fluctuationsConsistent dynamic performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsSwitching frequency
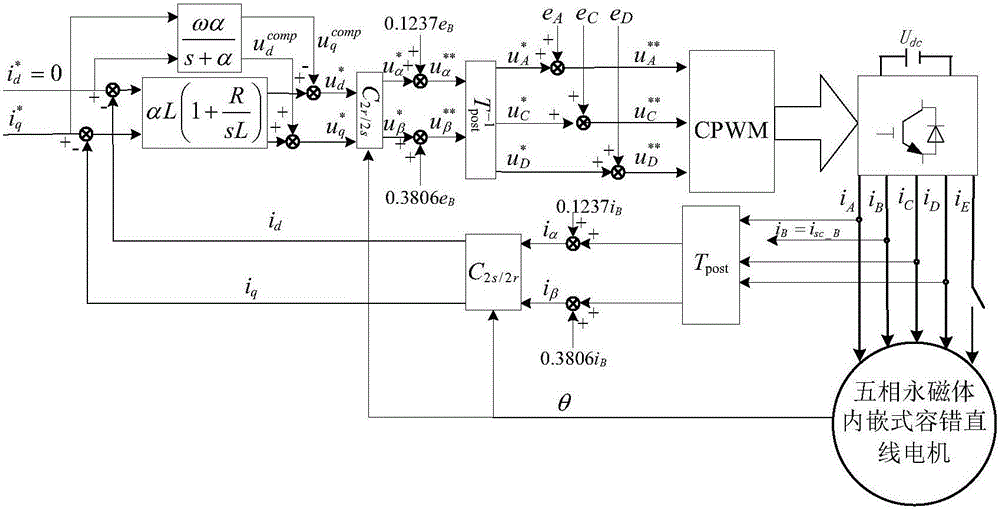
The invention discloses a fault-tolerant field-oriented control method for non-adjacent two-phase short circuits of a five-phase permanent magnet-embedded fault-tolerant linear motor. Non-fault-phase fault-tolerant current is calculated according to the principles that pre- and post-fault traveling wave magnetomotive force is constant and the sum of non-fault-phase current is zero; a nonlinear strong coupling system of the motor in a fault state is converted into a first-order inertia system by employing an internal model controller, a first-order inertia feedforward voltage compensator and a counter electromotive force observer; non-fault-phase voltage commands are calculated on this basis and the voltage commands and counter electromotive force of various phases are added respectively to achieve fault-tolerant field-oriented control on the non-adjacent two-phase short circuits of the motor. Motor output thrust fluctuation caused by the non-adjacent two-phase short circuits of the motor is inhibited; fault-tolerant operation that one of the non-adjacent two phases is in an open-circuit fault and the other one is in a short-circuit fault can be achieved; more importantly, the dynamic property and the steady-state performance of the motor are consistent with those in a normal state; and a voltage source inverter is constant in switching frequency and has certain universality.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Permanent magnet synchronous linear motor with bilateral asymmetric V-shaped magnetic poles
ActiveCN111224530AInhibition localizationSuppression of thrust fluctuationsPropulsion systemsElectric machineMagnetic poles
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous linear motor with bilateral asymmetric V-shaped magnetic poles. A flat-plate-shaped secondary pole of the motor is composed of a yoke plate and bilateral magnetic poles, wherein each magnetic pole is in a V shape formed by a plurality of sections of permanent magnets, the inclination directions of V-shaped magnetic pole sections located at mirror symmetry positions are different, that is, the directions of V openings are different, a bilateral asymmetric state is formed, and the inclination angles and the side lengths of the V-shaped magnetic pole sections located at the mirror symmetry positions are equal; a primary armature is composed of an iron core and windings, wherein the current directions of the bilateral windings at mirror symmetry positions are opposite, and the primary armature and bilateral magnetic poles form a series magnetic circuit and interact to generate same-direction electromagnetic thrust. According to the invention, the asymmetric V-shaped skewed poles have multiple combination forms, so it is guaranteed that electromagnetic thrust does not drop drastically while thrust fluctuation of the motor is reduced, and good thrust characteristics are achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Five-phase permanent magnet embedded fault tolerant linear motor adjacent two-phase open circuit fault tolerant vector control method
InactiveCN106059442ASuppression of thrust fluctuationsConsistent dynamic performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsClose coupling
The invention discloses a five-phase permanent magnet embedded fault tolerant linear motor adjacent two-phase open circuit fault tolerant vector control method. Based on the principles that the magnetic motive force of traveling waves remains unchanged before and after a fault occurs and that the non-fault phase current sum stays at zero and taking the equality of the non-adjacent two-phase current amplitude as a constrained condition, the non-fault phase fault tolerant current is obtained to further deduce the generalized Clark transform matrix from the natural coordinate system of the non-fault phase to the two-phase stationary coordinate system. The non-fault opposite potential is observed by the transpose matrix of the transform matrix. A current internal model controller, a first-order inertial feed-forward voltage compensator and a counter-electromotive force observer are used to convert the nonlinear close coupling system of such motor under the condition of an adjacent two-phase open-circuit fault into a first-order inertial system. According to the invention, not only the thrust fluctuation caused by motor failure is restrained, but also more importantly, the dynamic performance and the steady-state performance are consistent with those under a normal condition to realize the fast response to non-overshoot and the stable switching frequency of a voltage source inverter.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Thrust fluctuation active compensation type linear permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102361388AEliminate or reduce thrust fluctuationsSuppression of thrust fluctuationsPropulsion systemsCompensation windingPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a thrust fluctuation active compensation type linear permanent magnet synchronous motor and belongs to the technical field of motors. By the thrust fluctuation active compensation type linear permanent magnet synchronous motor, the problems that the thrust fluctuation of a linear motor can be only restrained to a certain extent and an effective thrust of the motor can be reduced by using the conventional method for reducing the thrust fluctuation of the linear motor are solved. An air gap is formed between a primary and a secondary; the primary comprises an armature core and an armature winding; and the armature winding of the primary has a surface mounted structure or the primary has a tooth groove structure. The thrust fluctuation generated by a thrust fluctuation compensation unit arranged at the end of the armature core is counteracted with the thrust fluctuation generated by the linear permanent magnet synchronous motor by controlling current of a compensation winding through a compensation controller or by serially connecting the compensation winding and the armature winding; therefore, an aim of actively eliminating or reducing the thrust fluctuation of the linear motor can be fulfilled. The invention is applicable to linear permanent magnet synchronous motors.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Five-phase permanent-magnet embedded fault-tolerant linear-motor non-adjacent two-phase fault-tolerant vector control method
InactiveCN106100495ASuppression of thrust fluctuationsConstant switching frequencyElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsNormal state
The invention discloses a five-phase permanent-magnet embedded fault-tolerant linear-motor non-adjacent two-phase fault-tolerant vector control method. According to principles that magnetomotive forces before and after a two-phase open-circuit fault are invariant and a non-fault-phase current sum is zero, a condition that adjacent two phase current amplitudes are equal is taken as a constraint condition so as to derive and popularize a Clark transformation matrix; matrix transposition is used to estimate a counter potential; and an inner model controller, a first-order inertia feedforward voltage compensator and a counter potential observer are used to change a nonlinear strong coupling system of the motor under a fault state into a first-order inertia system. According to a principle that a synthesized magnetomotive force of a non-fault-phase short circuit compensation current and a short circuit fault phase current is zero, a short circuit compensation voltage is calculated. The voltage is superposed with an output voltage of a vector control device. By using the method of the invention, a motor thrust fluctuation caused by one phase short circuit and one phase open circuit of non-adjacent two phases of the motor is restrained, and dynamic performance and stable state performance are consistent with the performance under a normal state.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Five-phase permanent-magnet embedded fault-tolerant linear-motor adjacent two-phase fault-tolerant vector control method
InactiveCN106100496ASuppression of thrust fluctuationsConstant switching frequencyElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsVoltage source inverter
The invention discloses a five-phase permanent-magnet embedded fault-tolerant linear-motor adjacent two-phase fault-tolerant vector control method. According to principles that traveling wave magnetomotive forces before and after a two-phase open-circuit fault are invariant and a non-fault-phase current sum is zero, a condition that non-adjacent two-phase current amplitudes are equal is taken as a constraint condition so as to derive and popularize a Clark transformation matrix; matrix transposition is used to estimate a counter potential; and an inner model controller, a first-order inertia feedforward voltage compensator and a counter potential observer are used to change a nonlinear strong coupling system of the motor under a fault state into a first-order inertia system. According to a principle that a synthesized magnetomotive force of a non-fault-phase short circuit compensation current and a short circuit fault phase current is zero, a short circuit compensation voltage is calculated. The voltage is superposed with an output voltage of a vector control device. By using the method of the invention, a motor thrust fluctuation caused by adjacent two phase faults of the motor is restrained, dynamic performance and stable state performance are consistent with the performance under a normal state, and a switch frequency of a voltage source inverter is constant.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Bilateral 180 DEG-staggered tooth low-thrust ripple continuous pole permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
ActiveCN107332427AImprove performanceDoes not affect the average output thrustPropulsion systemsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionPull forceLinear motor
The invention provides a bilateral 180 DEG-staggered tooth low-thrust ripple continuous pole permanent magnet synchronous linear motor, which belongs to the technical field of motors. The bilateral 180 DEG-staggered tooth low-thrust ripple continuous pole permanent magnet synchronous linear motor comprises a first primary assembly, a second primary assembly and a secondary assembly, wherein both the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly are formed by armature windings and primary iron cores; the secondary assembly is composed of permanent magnets, iron poles and back yokes; the permanent magnets all have the same polarity and are arranged alternatively with the iron poles; the permanent magnets are attached to the upper surface and the lower surface of a yoke plate; the iron poles and the yoke plate are integrally formed; the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly are located at two sides of the secondary assembly, and two air gap structures are formed with the secondary assembly; and the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly are staggered for a 180-DEG electrical angle in a horizontal direction, that is, a distance of displacement S=ktau (k is an uneven number and tau is the pole pitch of the motor) is staggered. A three-phase winding on the first primary assembly is arranged in an iron core slot according to a sequence of A-B-C, a three-phase winding on the second primary assembly is arranged in an iron core slot according to a sequence of A-B-C, and in-phase windings on the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly have opposite winding directions. The structure can reduce the thrust ripple of the motor, and a unilateral magnetic pulling force and the ripple thereof can be reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Dual-stator magnetism-gathering permanent magnet linear motor with concentrated winding of phase windings
ActiveCN110165852AImprove performanceReduce manufacturing costPropulsion systemsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionPermanent magnet linear motorMagnetization
The invention provides a dual-stator magnetism-gathering permanent magnet linear motor with concentrated winding of phase windings, which comprises a mover and two single-sided stators arranged at twosides of the mover face to face, wherein the mover is a magnetism-gathering permanent magnet mover structure, permanent magnets are horizontally magnetized along the movement direction of the mover,and two adjacent permanent magnets are opposite in magnetization direction; at least one of the single-sided stators is provided with windings and has a mode of concentrated winding of the phase windings. Each single-sided stator is a certain air gap distance away from the mover, the two air gap distances are equal, and the two single-sided stators has an offset of one stator tooth width along themovement direction of the mover. The permanent magnet linear motor provided by the invention has high power density and output thrust, and effectively suppresses the magnetic resistance and thrust fluctuation.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Double-side staggered-tooth low thrust fluctuation permanent magnetic synchronous linear motor
InactiveCN107302296AImprove performanceDoes not affect the average output thrustPropulsion systemsPull forceEngineering
The invention provides a double-side staggered-tooth low thrust fluctuation permanent magnetic synchronous linear motor, which belongs to the technical field of motors. The double-side staggered-tooth low thrust fluctuation permanent magnetic synchronous linear motor comprises a primary assembly I, a primary assembly II and a secondary assembly, wherein the primary assembly I and the primary assembly II are respectively formed by an armature winding and a primary iron core. Permanent magnets are adhered onto an upper surface and a lower surface of a yoke plate to form the primary assembly. The primary assembly I and the primary assembly II are disposed at two sides of the secondary assembly and form two air gap structures with the secondary assembly. A staggered displacement of the primary assembly I and the primary assembly II in a transverse direction is: S=(k + / - 1 / 3)tau (k is an integer, and tau is a pole pitch of motor). A groove is formed in the primary iron core, and an armature winding is arranged in the groove. A sequence of a three-phase winding on the primary assembly I is different from the sequence of a three-phase winding on the primary assembly II. By adopting the structure, the thrust fluctuation of a motor can be reduced, and a single-side magnetic pull force and the fluctuation thereof can be reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Low-resistance coreless unilateral permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
ActiveCN110707897ARetention orientationReduce positive pressurePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPropulsion systemsElectric machineStructural engineering
The invention relates to the field of permanent-magnet linear motors, and discloses a low-resistance coreless unilateral permanent magnet synchronous linear motor that includes a linear guide rail, wherein permanent magnets are laid on the linear guide rail at intervals in the axial direction. The motor also comprises a mover seat that is in sliding fit with the linear guide rail; a first rail anda second rail are symmetrically arranged on the linear guide rail in parallel in the axial direction. A first guide groove and a second guide groove of which the groove walls are cavities are correspondingly formed in the mover seat; at least one long steel magnet is arranged on at least one axial side wall of each of the first rail and the second rail in the vertical direction; the groove bottoms of the first guide groove, the second guide groove and the long steel magnets on the same side are connected with piezoelectric ceramics; coils are arranged in adjacent groove wall cavities, and thecoils are connected with the piezoelectric ceramics through wires. The guide effect of the guide rail is reserved; when the mover seat bears load and is pressed, the positive voltage effect of piezoelectric ceramic is used for providing current for the coil, so upward lifting force is generated on the mover seat under cutting of a symmetric magnetic field of the long steel magnets, thrust fluctuation is restrained, and the robustness of an advancing system is improved.
Owner:安徽同兴科技发展有限责任公司 +1
Method for inhibiting velocity fluctuation of electric vehicle driving system
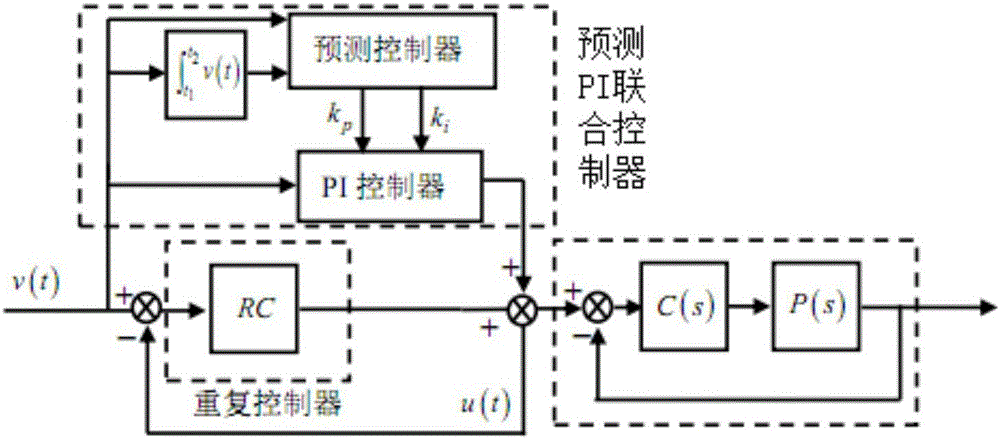
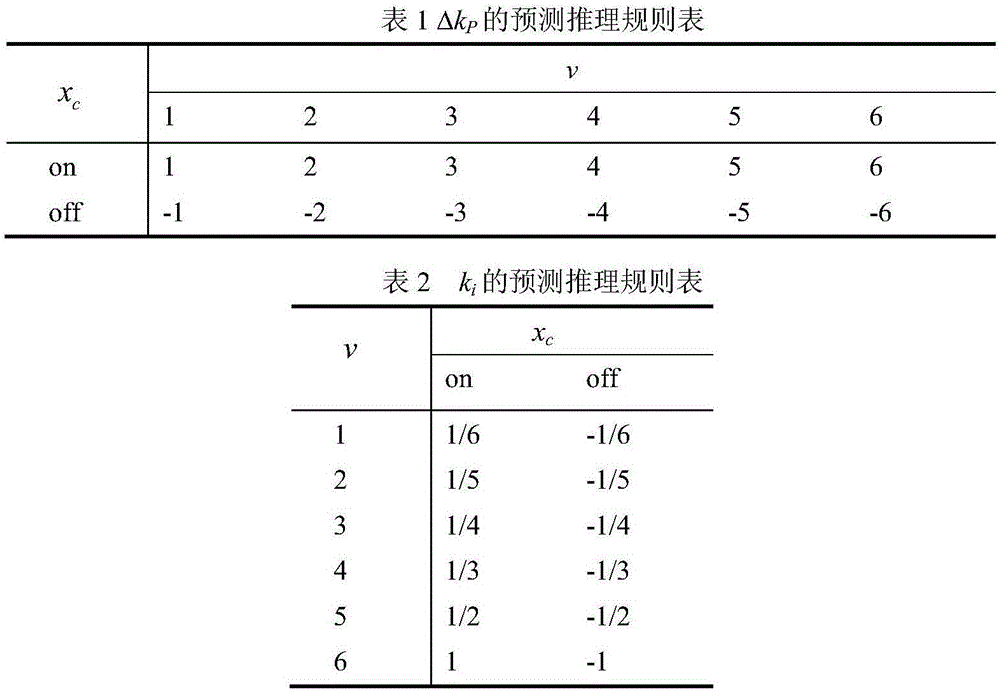
ActiveCN106788089AGuaranteed global asymptotic stabilityOvercoming control performance degradationMotor control for motor oscillations dampingControl vectorOperation mode
The invention provides a method for inhibiting the velocity fluctuation of an electric vehicle driving system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a rotor position by adopting an encoder, and transmitting the rotor position to a velocity control ring; and adopting a parallel mode combining a prediction PI joint controller, a repetitive controller and a nonlinear adaptive feedback observer by the velocity control ring, adopting the parallel mode of the prediction PI joint controller and the repetitive controller during electric start, substituting two continuous sampling values into a prediction domain of the prediction PI joint controller by the encoder, switching to the parallel mode of the repetitive controller and the nonlinear adaptive feedback observer when an electric vehicle enters a stable operation mode, and then transmitting an output signal of the velocity control ring. According to the method provided by the invention, the prediction PI joint control, the nonlinear adaptive feedback observation control, the repetitive control and the vector control are combined together to improve the stability, the accuracy and the dynamic response ability of the electric vehicle driving system and inhibit the velocity fluctuation in an electric vehicle running process.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Double-side staggered-tooth tau/2 low-thrust-ripple permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
ActiveCN108667261AImprove performanceDoes not affect the average output thrustPropulsion systemsPull forcePermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a double-side staggered-tooth tau / 2 low-thrust-ripple permanent magnet synchronous linear motor. A first primary assembly and a second primary assembly are both composed of anarmature winding and a primary iron core, each primary iron core is of a tooth groove structure, and the armature windings are wound on teeth; the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly are located on the two sides of a secondary assembly and form air gaps with the secondary assembly respectively; the secondary assembly comprises a yoke plate and a plurality of permanent magnets, each pair of poles comprises four permanent magnets, the first permanent magnet and the second permanent magnet of each pair of poles are located on the same side of the yoke plate, the third permanentmagnet and the fourth permanent magnet of each pair of poles are located on the same side of the yoke plate, the positions of the first permanent magnets and the third permanent magnets are opposite,the positions of the second permanent magnets and the fourth permanent magnets are opposite, the magnetizing directions of the first permanent magnets and the third permanent magnets are the same, the magnetizing directions of the second permanent magnets and the fourth permanent magnets are the same, and the magnetizing directions of the first permanent magnets and the second permanent magnets are opposite; the displacement of the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly in the transverse direction is S which is equal to tau / 2, and tau is the polar distance of the motor. By means of the structure, the thrust ripple of the motor can be reduced, and meanwhile unilateral magnetic tension and fluctuation of the unilateral magnetic tension are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Bilateral permanent magnet staggered type modularized continuous pole permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
ActiveCN112953158ASuppression of thrust fluctuationsElimination of Positioning Force HarmonicsPropulsion systemsElectric machineControl system
The invention discloses a bilateral permanent magnet staggered type modular continuous pole permanent magnet synchronous linear motor. Bilateral permanent magnets are arranged in a staggered manner, the end force waveform and fluctuation rule of a continuous pole motor are adjusted, and a positioning force period is adjusted to take an electrical angle of 180 degrees as a period due to the arrangement manner that the permanent magnets are arranged in a staggered manner; meanwhile, positioning force harmonic waves generated by the end effect are basically eliminated, and the positioning force generated on the unit motor is counteracted due to reverse phases due to the arrangement of the length of the magnetic isolation structure, so the thrust fluctuation of the continuous pole motor is inhibited. By adjusting the phase sequence of the three-phase windings among the unit motors, on one hand, the electrical angles of the same-phase windings on different unit motors are basically the same, so that the average value of output thrust is not influenced; on the other hand, the magnetic field distribution of the end parts of the unit motors is adjusted, so that the relative positions of each phase winding on each unit motor and the end parts are different, the influence of the end part effect on the asymmetry of the three-phase windings is adjusted, the thrust fluctuation is finally inhibited, and the performance of a control system is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Phase-shifting and shifting unit combined permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
InactiveCN108712054ASuppression of thrust fluctuationsSimple processPropulsion systemsPermanent magnet synchronous motorStator coil
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
A dual mover modular permanent magnet linear motor capable of differential operation
ActiveCN109004805BStable thrustStable outputPropulsion systemsElectric machinePermanent magnet linear motor
The invention discloses a dual-mover modular permanent magnet linear motor capable of differential operation. The motor comprises an upper-layer rotor module, a lower-layer rotor module and a stator module; the stator module is arranged between the upper-layer rotor module and the lower-layer rotor module; the upper-layer rotor module includes a plurality of first E-shaped iron cores, and the opening direction of the first E-shaped iron cores faces the stator module; a magnetic isolation block is arranged between two adjacent first E-shaped iron cores; the lower-layer rotor module comprises aplurality of second E-shaped iron cores, the second E-shaped iron cores have the same structure as the first E-shaped iron cores, the opening direction of the second E-shaped iron cores faces the stator module, and a magnetic isolation block is arranged between two adjacent second E-shaped iron cores; the first E-shaped iron cores and the second E-shaped iron cores are both provided with windings;and the stator module comprises a permanent magnet group and a stator core. The modular structure of the invention facilitates expansion of the thrust range of the motor, weakens the thrust fluctuation of the motor, simplifies the maintenance difficulty of the motor and shortens the maintenance period.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Bilateral staggered teeth 180° low thrust fluctuation continuous pole permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
ActiveCN107332427BImprove performanceDoes not affect the average output thrustPropulsion systemsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionPull forceEngineering
The invention provides a bilateral 180 DEG-staggered tooth low-thrust ripple continuous pole permanent magnet synchronous linear motor, which belongs to the technical field of motors. The bilateral 180 DEG-staggered tooth low-thrust ripple continuous pole permanent magnet synchronous linear motor comprises a first primary assembly, a second primary assembly and a secondary assembly, wherein both the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly are formed by armature windings and primary iron cores; the secondary assembly is composed of permanent magnets, iron poles and back yokes; the permanent magnets all have the same polarity and are arranged alternatively with the iron poles; the permanent magnets are attached to the upper surface and the lower surface of a yoke plate; the iron poles and the yoke plate are integrally formed; the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly are located at two sides of the secondary assembly, and two air gap structures are formed with the secondary assembly; and the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly are staggered for a 180-DEG electrical angle in a horizontal direction, that is, a distance of displacement S=ktau (k is an uneven number and tau is the pole pitch of the motor) is staggered. A three-phase winding on the first primary assembly is arranged in an iron core slot according to a sequence of A-B-C, a three-phase winding on the second primary assembly is arranged in an iron core slot according to a sequence of A-B-C, and in-phase windings on the first primary assembly and the second primary assembly have opposite winding directions. The structure can reduce the thrust ripple of the motor, and a unilateral magnetic pulling force and the ripple thereof can be reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Linear motor and optimization and verification method for improving operation efficiency of the same
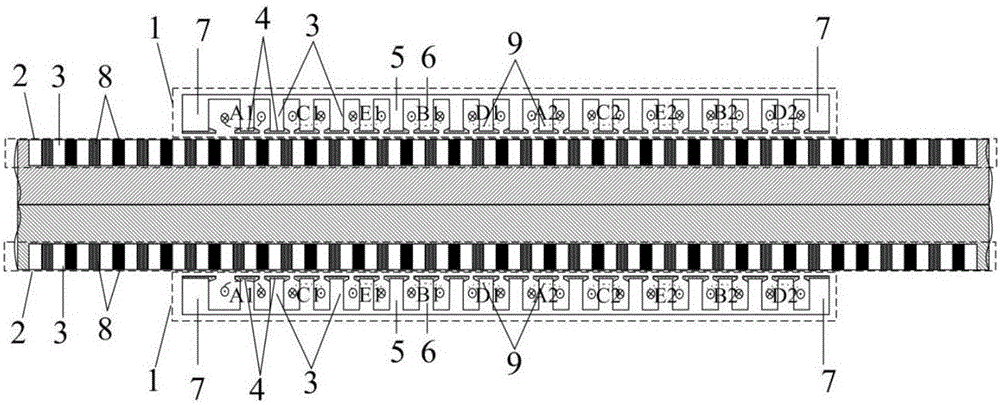
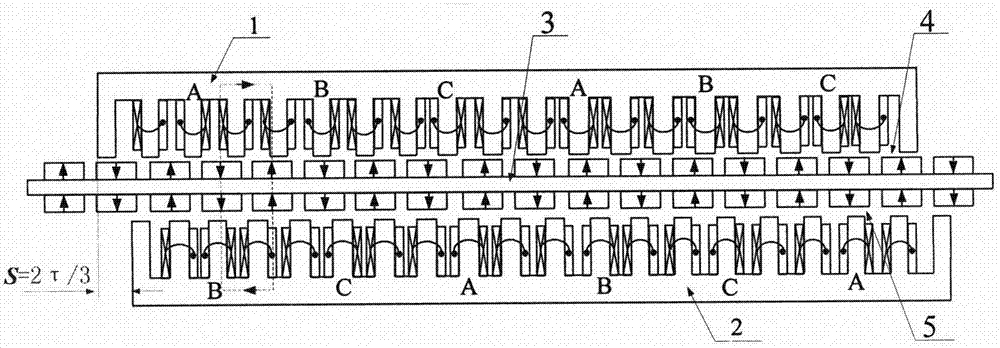
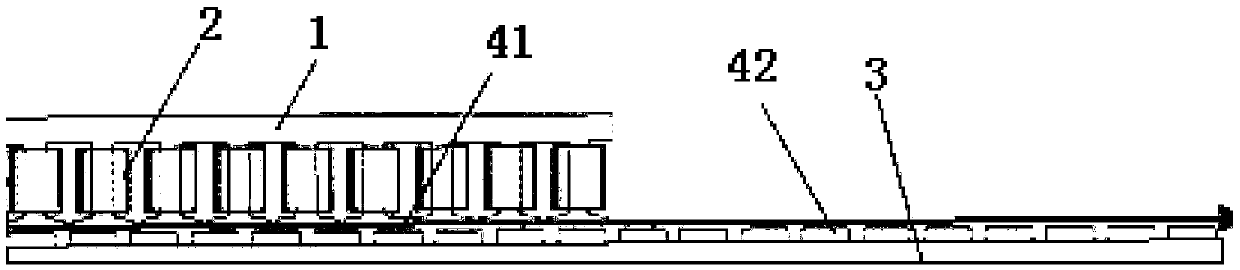
InactiveCN105515333ASimple structureGuaranteed uptimeAC motor controlPropulsion systemsLinear motorMagnet
The invention discloses a linear motor and an optimization and verification method for improving operation efficiency of the same, wherein the linear motor comprises a primary iron core (1), a primary coil (2), a secondary iron core (3) and a permanent magnet (4), the primary iron core (1) comprises a plurality of tooth grooves, the primary coil (2) winds the tooth among the adjacent tooth grooves, the secondary iron core (3) is arranged below the primary iron core to be a substrate of a given length, the permanent magnet (4) is fixedly arranged on the secondary iron core (3), and the ratio between the polar distance of the permanent magnet (4) and the tooth distance of the tooth groove is a fraction. The linear motor has a simple structure and can be stably and conveniently operated, and the thrust ripple can be reduced to a certain extent.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
A short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method for a fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor with embedded hybrid magnetic materials
InactiveCN105245156BSimple structureImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsVoltage source inverter
The invention discloses a short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method of an embedded mixed magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor, which includes establishing a five-phase embedded mixed magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor model; using the non-faulty phase current of the motor to compensate the short-circuit fault phase It leads to the lack of normal thrust of this phase and suppresses the thrust fluctuation caused by the short-circuit current of this phase; the expected phase voltage is obtained by adopting a series of coordinate transformation and voltage feedforward compensation strategies, and the CPWM modulation method based on zero-sequence voltage harmonic injection is used to realize the motor Fault-tolerant vector control after phase short-circuit fault. The invention can not only suppress the thrust fluctuation of the motor under the condition of phase short-circuit fault-tolerant operation, but more importantly, its dynamic performance, steady-state performance and normal performance are consistent, the switching frequency of the voltage source inverter is constant, and the CPU The overhead is small; when any one-phase short-circuit fault occurs, the natural coordinate system only needs to rotate a certain angle counterclockwise to realize fault-tolerant operation of the motor.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Low-thrust fluctuation permanent magnet synchronous linear motor with double-sided staggered teeth τ/2
ActiveCN108667261BImprove performanceDoes not affect the average output thrustPropulsion systemsElectric machineEngineering
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Double-side staggered-tooth tau/2 short primary permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
InactiveCN108667260AImprove performanceDoes not affect the average output thrustPropulsion systemsPrimary permanentSecondary component
The invention discloses a Double-side staggered-tooth tau / 2 short primary permanent magnet synchronous linear motor. The motor comprises a primary assembly, a first secondary assembly and a second secondary assembly, wherein the primary assembly is composed of an upper armature winding, a lower armature winding and a primary iron core, the upper part and the lower part of the primary iron core areboth provided with a groove, and the armature windings are arranged in the grooves respectively; the first secondary assembly and the second secondary assembly are both composed of a permanent magnetand a yoke plate, and the permanent magnets are pasted on the lower surface of the yoke plate of the first secondary assembly and the upper surface of the yoke plate of the second secondary assemblyrespectively; the primary assembly is located between the first secondary assembly and the second secondary assembly and form air gap structures with the first secondary component and the second secondary component respectively; the displacement of the upper armature winding and the lower armature winding of the primary assembly in the transverse direction is S which is equal to tau / 2, and tau isthe polar distance of the motor; in the upper armature winding and the lower armature winding on the primary assembly, the space electric angle difference theta of the same-phase windings is smaller than or equal to 60 degrees and smaller than or equal to 120 degrees or theta is larger than or equal to -120 degrees and smaller than or equal to -60 degrees. By means of the structure, the thrust ripple of the motor is reduced, and meanwhile unilateral magnetic tension and fluctuation of the unilateral magnetic tension are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
A fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor with embedded hybrid magnetic material
InactiveCN105207446BSimple structureImprove reliabilityPropulsion systemsCircular discElectric machine
The invention discloses an embedded type mixing magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor which comprises primary bodies and secondary bodies. The length of each primary body is smaller than that of each secondary body. An air gap is reserved between each primary body and the corresponding secondary body. Each primary body comprises armature teeth, fault-tolerant teeth and a coil winding. The 2*m armature teeth and the 2*m fault-tolerant teeth are uniformly distributed on each primary body, wherein m is the phase number of the motor and is larger than or equal to three; the armature teeth and the fault-tolerant teeth are arranged at intervals in a staggered mode. Only one set of disc-shaped coil windings are placed into an armature tooth groove of each primary body. No windings are arranged on the fault-tolerant teeth. The secondary bodies of the motor are made of mixing magnetic materials, a part of ferrite is used for replacing a part of rare earth permanent magnets to form four different mixing magnetic material structures, on one hand, the quantity of the adopted rare earth permanent magnets is greatly reduced, and the cost of the motor is reduced; on the other hand, as the magnetic energy product of the permanent magnets is reduced, the eddy-current loss of the motor is reduced greatly, and efficiency of the motor is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Fault-tolerant vector control method for adjacent two-phase faults of five-phase permanent magnet embedded fault-tolerant linear motor
InactiveCN106100496BSuppression of thrust fluctuationsConstant switching frequencyElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsEngineering
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
A Thrust Fluctuation Compensated Secondary of Ring Winding Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor
ActiveCN113572338BIncrease thrust densityIncrease flexibilityMagnetic circuit rotating partsPropulsion systemsEngineeringElectric current flow
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Fault-tolerant Field Oriented Control Method for Five-phase Permanent Magnet Linear Motor
InactiveCN106026841BSuppression of thrust fluctuationsConsistent dynamic performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsSwitching frequency
The invention discloses an adjacent two phase short-circuit fault-tolerant filed-oriented control method for a five-phase permanent magnet embedded fault-tolerant linear motor. The method comprises the steps of solving fault-tolerant current of healthy phases according to principles that traveling waves are constant in magnetomotive force before and after a fault and the sum of healthy-phase current is zero; transforming a nonlinear strong-coupling system of the type of motor at a fault state into a one-order inertia system by adopting an internal model controller, a one-order inertia feedforward voltage compensator and a counter potential observer; solving a healthy-phase voltage command on the basis, adding the voltage command to the counter potential of each phase so as to realize fault-tolerant field-oriented control after an adjacent two phase short-circuit fault of the motor. The method disclosed by the invention not only suppresses motor output thrust ripples caused by the adjacent two phase short-circuit fault of the motor, but also can realize fault-tolerant running of a fault that one of the two adjacent phases is open-circuit and the other phase is short-circuit. More importantly, the dynamic performance and the steady-state performance are consistent with the performance at a normal state, the switching frequency of a voltage source inverter is constant, and certain universality is provided.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
A high thrust density electromagnetic actuator for nanosatellite deployer
ActiveCN113452230BReduce magnetic saturationReduce thicknessDynamo-electric machinesMagnetic polesMagnetic flux
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Asymmetric magnetic barrier permanent magnet assisted reluctance synchronous linear motor
ActiveCN112600384BCost controlHigh reluctance thrustMagnetic circuit rotating partsPropulsion systemsMagnetic barrierElectric machine
The invention provides an asymmetric magnetic barrier permanent magnet assisted reluctance synchronous linear motor, which belongs to the technical field of motors. It includes a primary component and a secondary component; the primary component includes a primary core and an armature winding; the primary core is slotted to form a primary core yoke, a primary core tooth and a slot; the armature winding is arranged in the slot, and the winding adopts a concentrated winding structure. The secondary component includes a secondary core and a permanent magnet; there is an air gap structure between the primary component and the secondary component, the secondary core has km+1 slots, k is a positive integer greater than or equal to 2, m is the number of phases, including km ‑One middle slot and two end slots, of which the two end slots are half slots; this structure uses the reluctance thrust to partially replace the permanent magnet thrust, which is beneficial to reduce costs, and the asymmetric magnetic barrier structure is beneficial to reduce the cogging of the motor force to increase the thrust density.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com