A linear flexible variable stiffness adaptive artificial joint transmission device
A technology of artificial joints and transmission devices, which is applied to engine components, elastic couplings, sliding contact bearings, etc., can solve the problems of mismatching human knee joints, mismatching centers of rotation, complex geometric structures of human joints, etc. Adaptive features, effects that avoid rigid drive damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, but the scope of implementation of the present invention is not limited thereto.
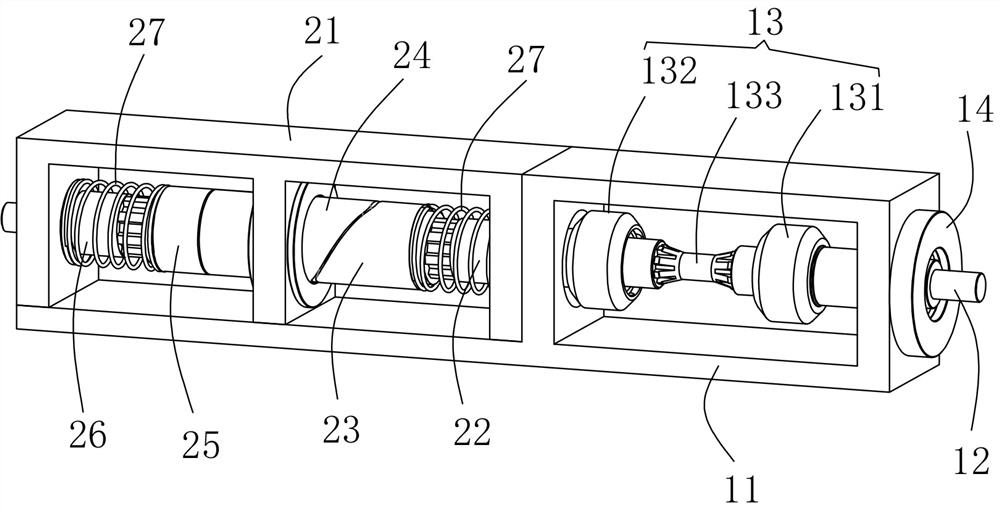
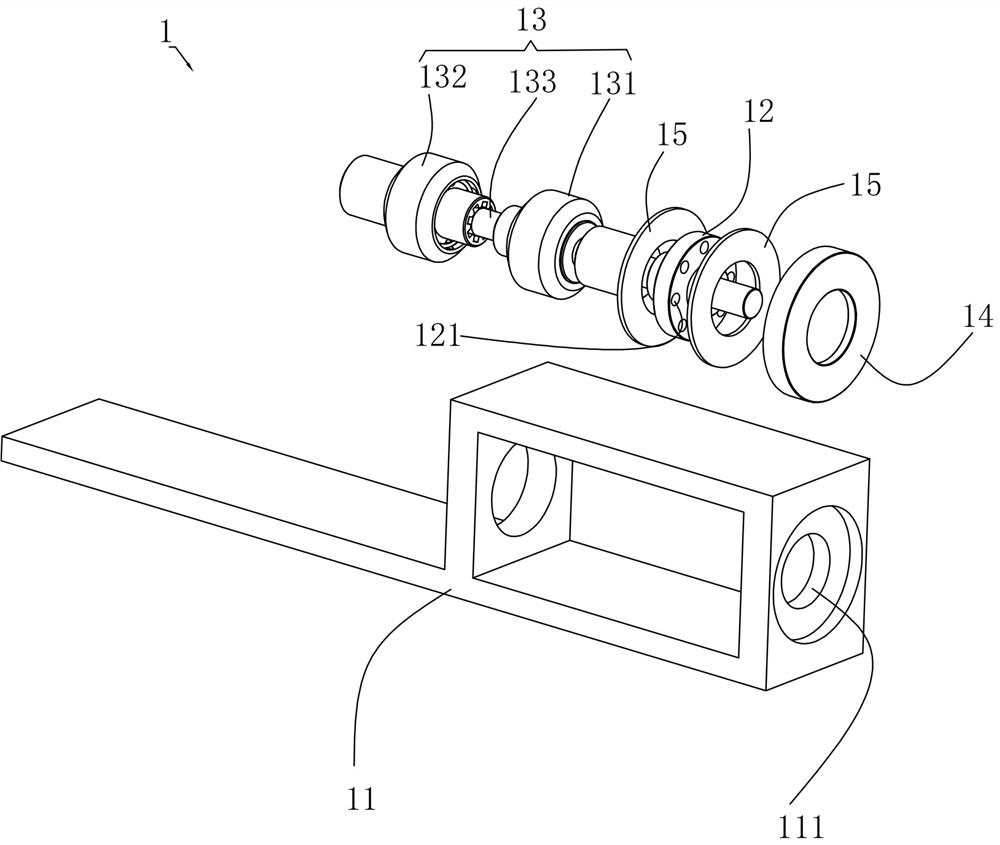
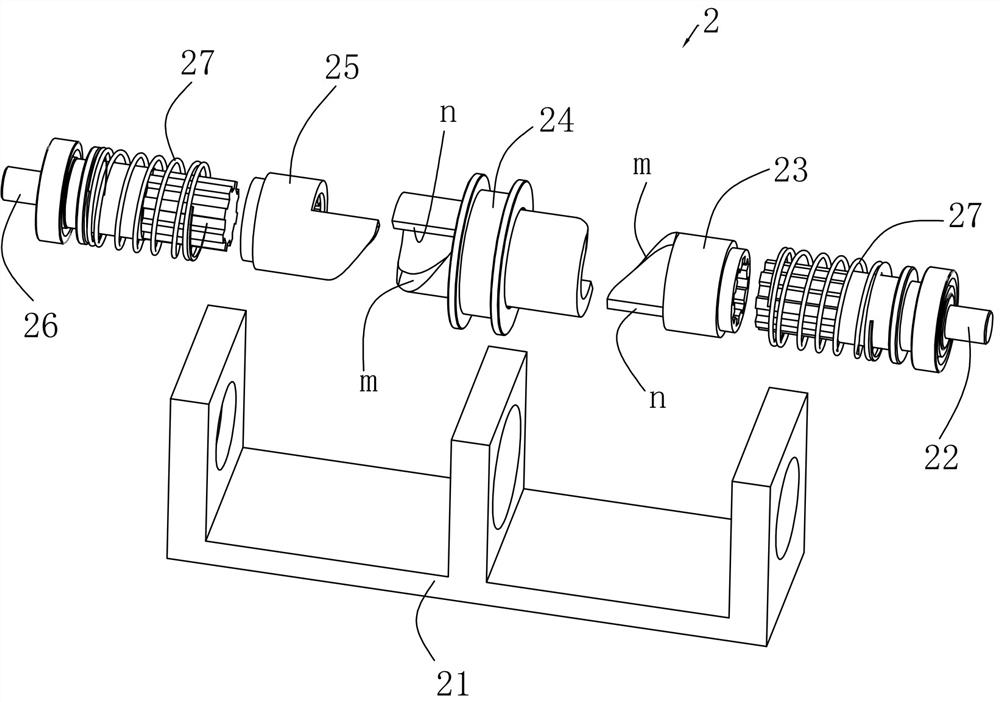
[0021] like Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, a linear flexible variable stiffness adaptive artificial joint transmission device described in this embodiment includes an input part 1 and an output part 2;
[0022] The input component 1 includes a drive shaft bracket 11, a disc-shaped input shaft 12 and a ball cage universal joint 13. One end of the drive shaft support 11 is provided with a slot 111 for installing the input shaft 12. The input shaft 12 is installed in the slot 111 through a shaft end cover 14 and two plane lubricating bearings 15, and it can move in the radial direction relative to the plane lubricating bearings 15. One end of the ball cage universal joint 13 passes through the first coupling It is drivingly connected with one end of the inpu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com