Method for polymerization and in-vitro culture of embryo without zona pellucida before implantation
A technology of in vitro culture and zona pellucida, which is applied in the field of embryo engineering and developmental biology, can solve problems such as not easy to remove, affect embryo development, and take a long time, so as to reduce adverse side effects of embryo development, increase the efficiency of blastocyst development, and improve The effect of blastocyst development rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
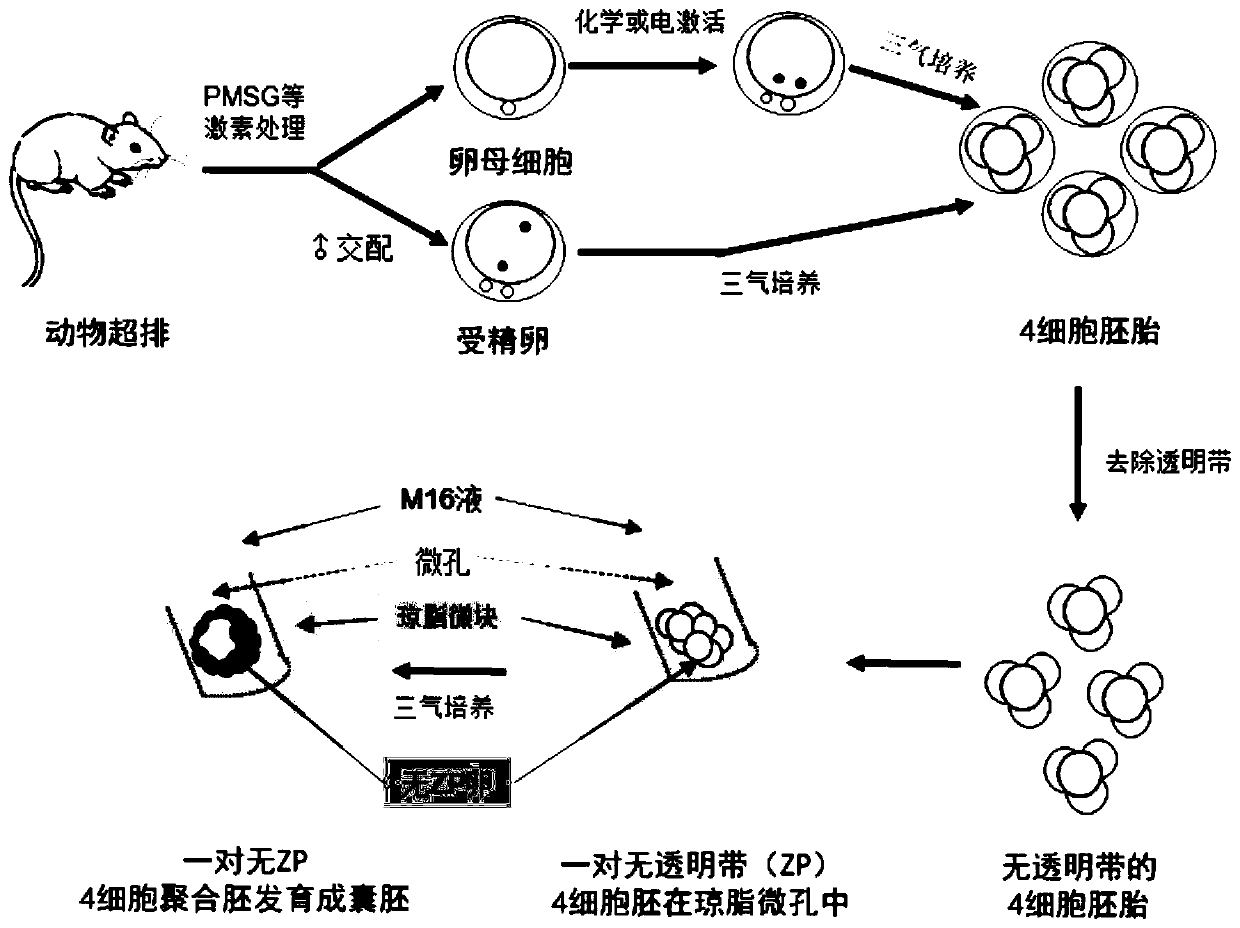
[0027] (2) Preparation of Diploid (2N) Embryos
[0028] 1. Preparation of 2N embryos from parthenogenetic activation
[0029] Parthenogenetic activation of rodent oocytes, the recovered oocytes in the MII stage were placed in activation solution [containing 5μg / mL CB (sigma), 10mM SrCl 2 (sigma) Ca-free 2+ , Mg 2+ M16 (sigma) culture medium], at 37°C, 6% CO 2 , 5%O 2 , 89%N 2 Cultured in a three-gas incubator for 6-10hr; livestock parthenogenetic activation, the recovered oocytes in the MII stage were first treated in M16 solution containing 10μM ionomycin (sigma) for 5 minutes, and then treated in M16 solution containing 2μM 6 -Dimethylaminopurina (6-DMAP, sigma), 5 μg / mL CB in M16 solution, at 37°C, 6% CO 2 , 5%O 2 , 89%N 2 Cultivate in a three-gas incubator for 4-6 hours; double pronuclei can be seen in the activated oocytes. Then place the above-mentioned activated oocytes in M16 or G1 droplets, at 37°C, 6% CO 2 , 5%O 2 , 89%N 2 Cultured in a three-gas incubato...
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 Polymerization and in vitro culture of mouse preimplantation fertilized embryos without zona pellucida
[0042] 1 Materials and methods
[0043] 1.1 Reagents: All reagents used in this experiment are embryo-grade reagents, which are all Sigma products unless otherwise specified.
[0044]1.2 Method
[0045] 1.2.1 Experimental grouping:
[0046] The experiment was divided into experimental group and control group, respectively:
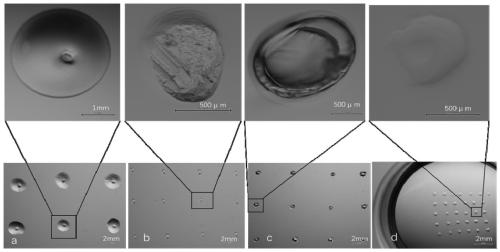
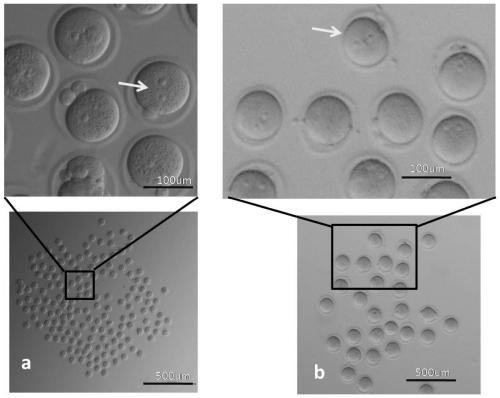
[0047] Experimental group: cultured by the gel microdrop hole method, i.e. the method of the present invention, after adopting 1% low-melting point agarose gel to heat and melt, to make 1-3 μ L agarose micro-droplets, and the tiny blocks after solidification Make small holes on ( figure 2 a), the detailed method is shown in the following "1.2.4 Preparation of gel droplet holes".
[0048] Control group Ⅰ: cultivated by the indentation method, that is, using a sharp instrument (ophthalmological tweezers) to press small depressions o...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2 Polymerization and in vitro culture of mouse preimplantation parthenogenetic embryos without zona pellucida
[0070] 1 Materials and methods
[0071] 1.1 Reagents All reagents used in this experiment are embryo grade reagents, unless otherwise stated, are all Sigma products.
[0072] 1.2 Method
[0073] 1.2.1 Experimental grouping, same as Example 1.
[0074] The experiment was divided into experimental group and control group, respectively:
[0075] Experimental group: cultured by the gel microdrop hole method, i.e. the method of the present invention, after adopting 1% low-melting point agarose gel to heat and melt, to make 1-3 μ L agarose micro-droplets, and the tiny blocks after solidification Make small holes on ( figure 2 a), the detailed method is shown in the following "1.2.4 Preparation of gel droplet holes".
[0076] Control group Ⅰ: cultivated by the indentation method, that is, using a sharp instrument (ophthalmological tweezers) to press sma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com