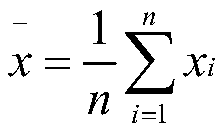Target grouping method based on SA-PFCM + + algorithm
A target and algorithm technology, applied in computing, computer parts, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in setting initial parameter values, too many parameters, and reduced decision-making efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The following describes in detail the embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings, wherein the same or similar reference numerals refer to the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The embodiments described below with reference to the accompanying drawings are exemplary, and are intended to explain the present invention and should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
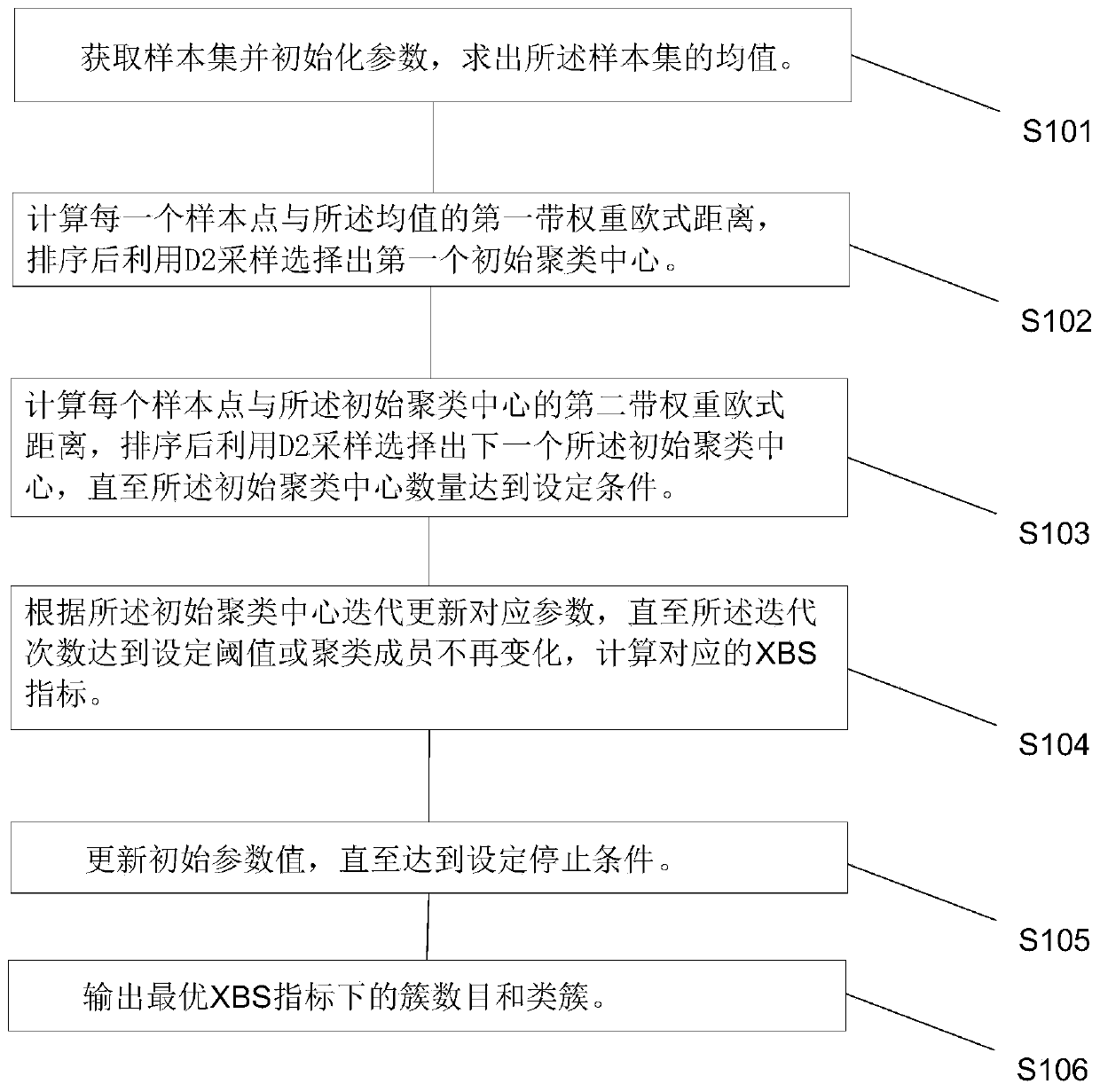
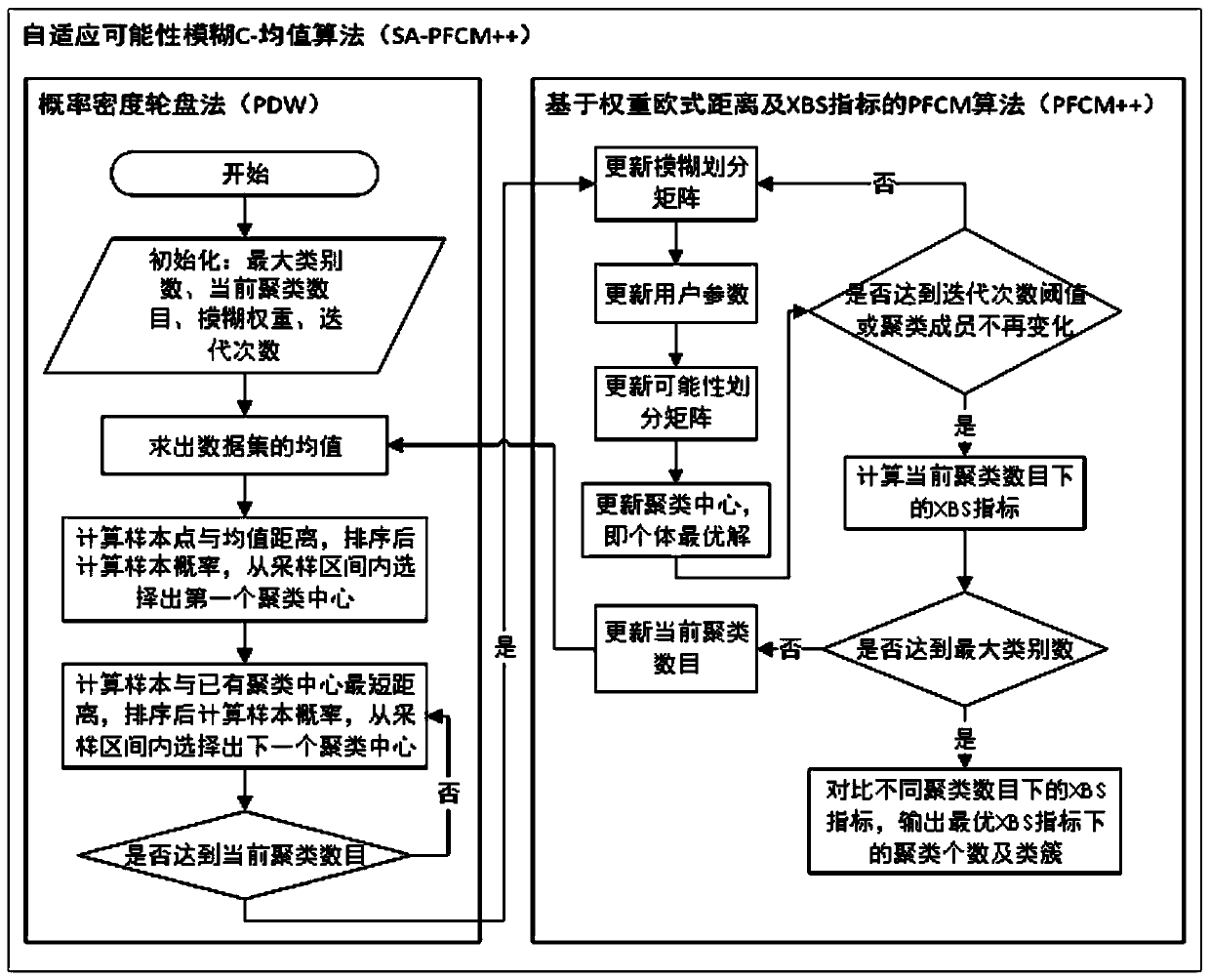
[0028] see figure 1 and figure 2 , the present invention provides a kind of target grouping method based on SA-PFCM++ algorithm, including:
[0029] S101. Obtain a sample set and initialize parameters, and obtain an average value of the sample set.
[0030] Specifically, input a dataset x={x containing n data objects 1 ,x 2 ,...,x n}, initialize the maximum number of categories k max , the current number of clusters k, the fuzzy weight u, the number of iterations iter, and calcula...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com