Quantum secret communication identity authentication system and method based on secret sharing and multiple mobile devices
A technology for quantum secure communication and mobile devices, applied in the field of quantum secure communication identity authentication systems, can solve problems such as rights theft, digital signatures with low anti-quantum computing capability, and key fob loss, and achieves the effect of reducing the amount of computation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
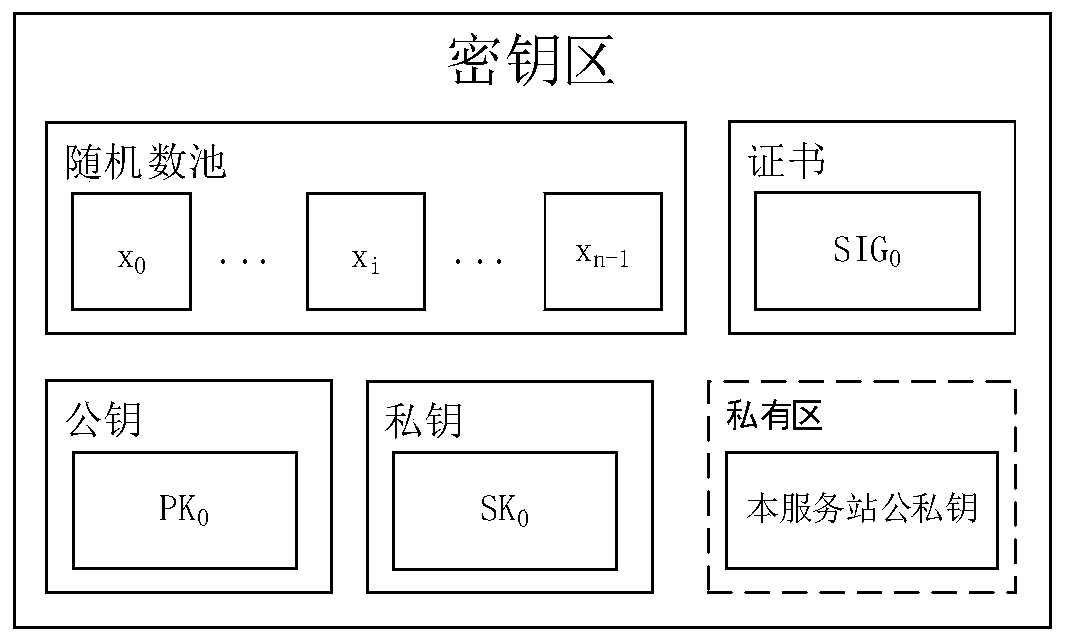
[0100] In this embodiment, R is W's issuing service station.
[0101] Due to the regional limitation of network connection (for example, the wireless connection can only access the local service station, or the operator can only access the local service station), S is W's access service station.
[0102] Step 1: W→S.
[0103] The n-1 mobile devices take a unified time timeR and an authentication request message Request.
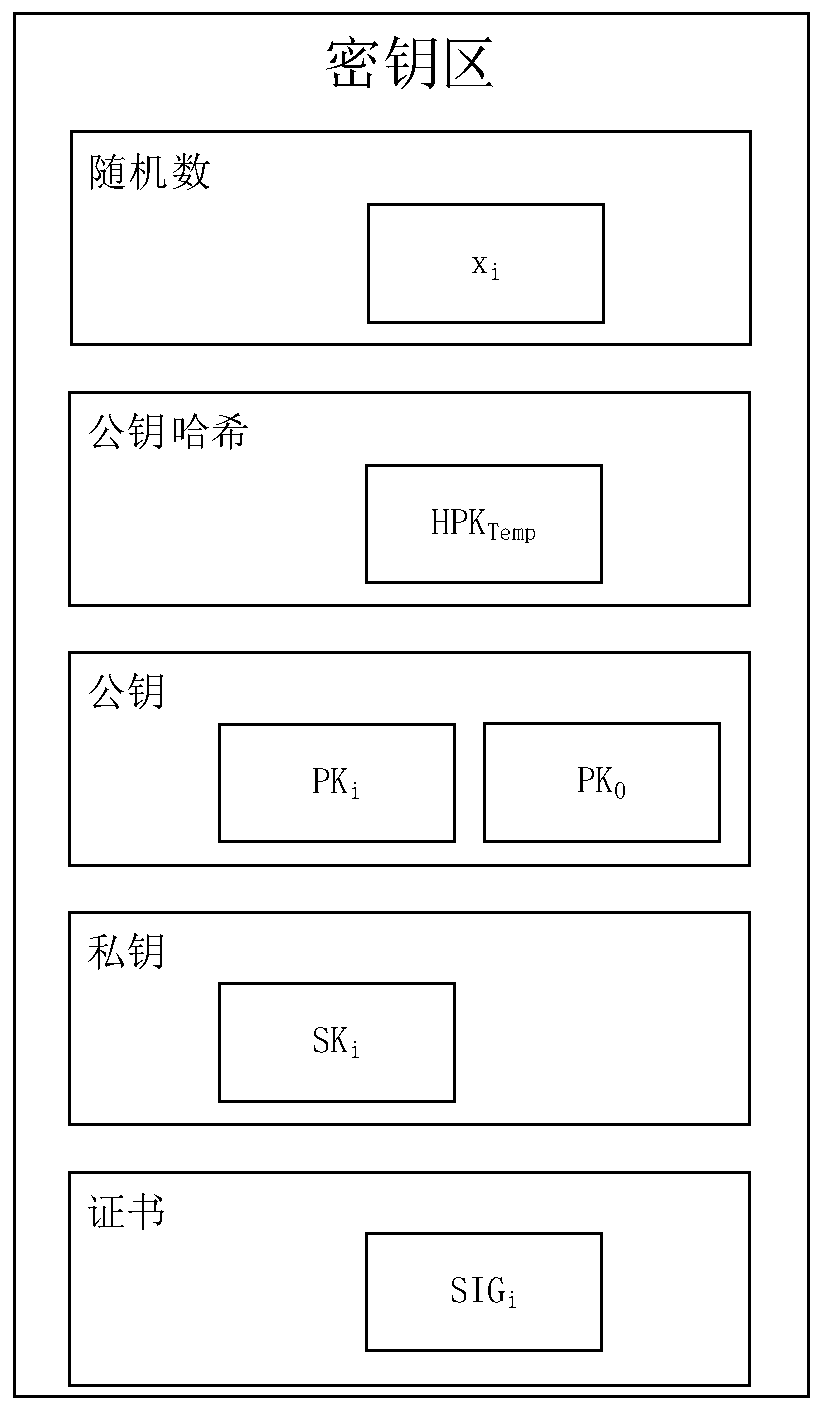
[0104] Each mobile device generates the key PK that can be used for the next round of signatures iTempNew / SK iTempNew , (i∈1,n-1, where SKiTempNew is a random number, PKiTempNew=SKiTempNew*P.
[0105] Each mobile device is calculated using the ECIES algorithm
[0106] EPK i =ENC(PK iMain ||PK iTemp ||PK iTempNew , PK 0Temp )={EPK iR ,EPK ic ,EPK it}. to EPK iR Calculate the offset to get EPK' i ={EPK iR -HG(timeR||x i ||IDW i ),EPK ic ,EPK it}. where HG is a hash function that maps integers to elliptic curve points.
[0107] Each mobile...
Embodiment 2
[0147] In this embodiment, R is W's issuing service station and W's access service station.
[0148] Step 1: W→R.
[0149] The n-1 mobile devices take a unified time timeR and an authentication request message Request.
[0150] Each mobile device generates the key PK that can be used for the next round of signatures iTempNew / SK iTempNew (i∈[1,n-1]). Among them, SK iTempNew is a random number, PK iTempNew =SK iTempNew *P.
[0151] Each mobile device is calculated using the ECIES algorithm
[0152] EPK i =ENC(PK iMain ||PK iTemp ||PK iTempNew , PK 0Temp )={EPK iR ,EPK ic ,EPK it}. to EPK iR Calculate the offset to get EPK' i ={EPK iR -HG(timeR||x i ||IDW i ),EPK ic ,EPK it}. Among them, HPK Temp =H(PK Temp ).
[0153] Each mobile device combines timeR and Request into Tx, let TxsigR=HPK Temp , calculate TxsigE=H(TxsigR||Tx).
[0154] Each mobile device calculates the signature component ReqSig i =SK iTemp +SK iMain *TxsigE(mod q).
[0155] Make ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com