Protein engineered extracellular vesicles
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and cells, applied in the field of extracellular vesicles, can solve the problems of lack of loading and bioactive delivery disclosure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
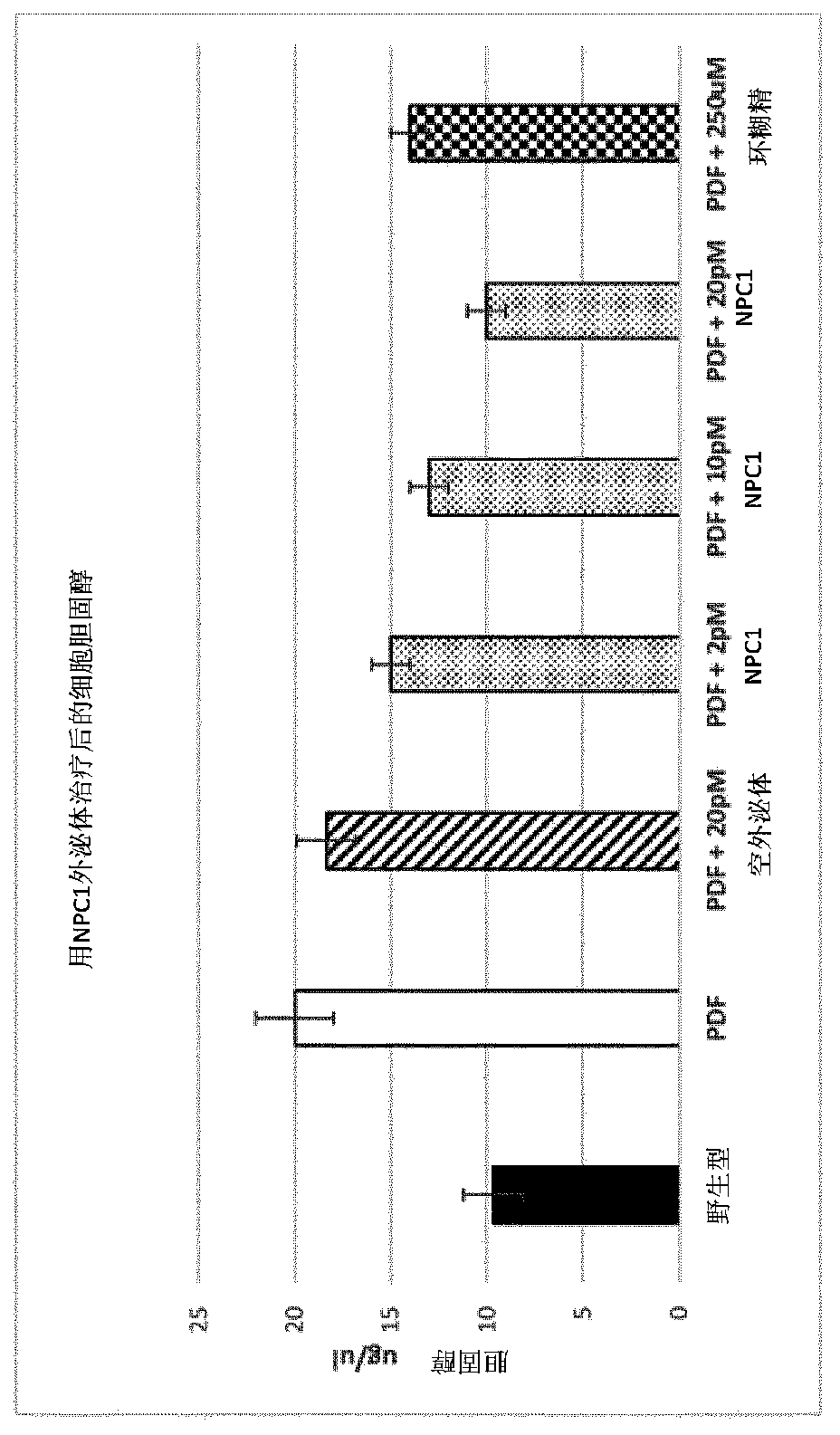
[0073]Example 1. Genetic engineering of amniotic epithelial (AE) cells obtained from postpartum placenta with a polynucleotide construct encoding a polypeptide construct comprising NPC1 protein and EV-enriched protein (using lentiviral transduction) N-terminal portion of inhabitin (PNC1 S) (SEQ ID NO 2). AE-EVs produced from AE cells were harvested, purified, and assessed in vitro for their ability to enhance cholesterol transport in patient-derived fibroblasts. From figure 1 It can be seen that NPC1 AE-EV significantly reduces cholesterol levels in target cells by delivering large amounts of biologically active NPC1 protein to cells. Interestingly, when using only AE-EVs and MSC-EVs (and no other cell sources), it was possible to achieve a dose-dependent reduction in cholesterol accumulation by genetically engineering AE cells to express the NPC1 protein itself, in the absence of Any EV-enriched polypeptides (data not shown). Both EV-producing cells and their corresponding...
example 2
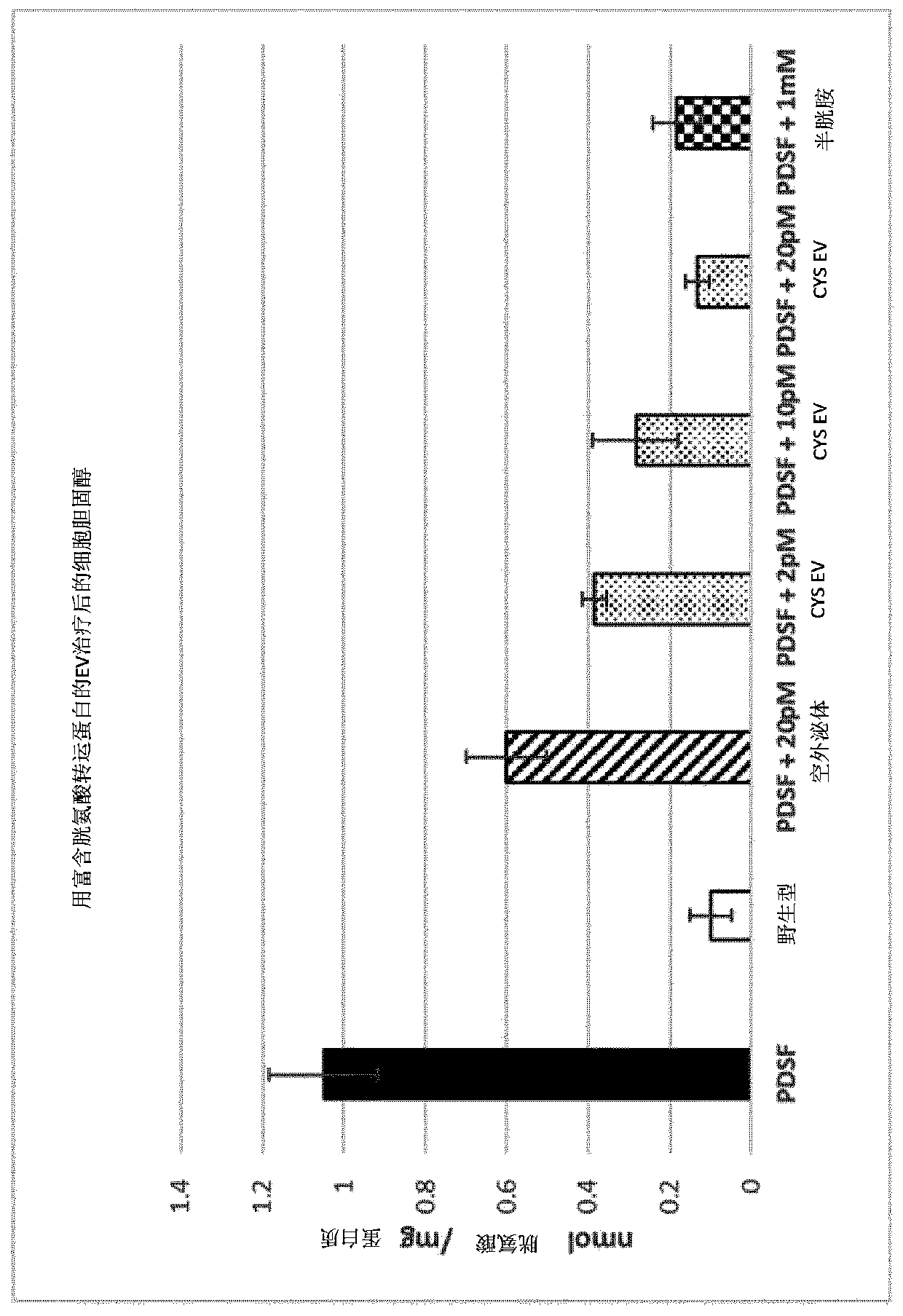
[0074] Example 2. Effect of Wharton's jelly MSC-derived EVs (WJ-MSC-EV, available from Hua obtained from Dun's gum) for genetic engineering. Cystine transporter-containing WJ-MSC-EVs (CYS-EVs) were harvested from hollow-fiber bioreactor cell cultures of WJ-MSCs, purified, and expressed in vitro on patient-derived dermal fibroblasts (PDSF) An assessment was performed to assess the reduction of cystine accumulation in an in vitro model of cystinosis. figure 2 It was shown that a significant reduction in cysteine was seen upon application of WJ MSC EVs comprising a CD63-cystine transporter polypeptide construct. As shown in Example 1, WJ-MSCs and WJ-MSC-EVs were positive for Hsp70 proteins, especially Hsp70-8, and for tetraspanins CD63 and CD81.
example 3
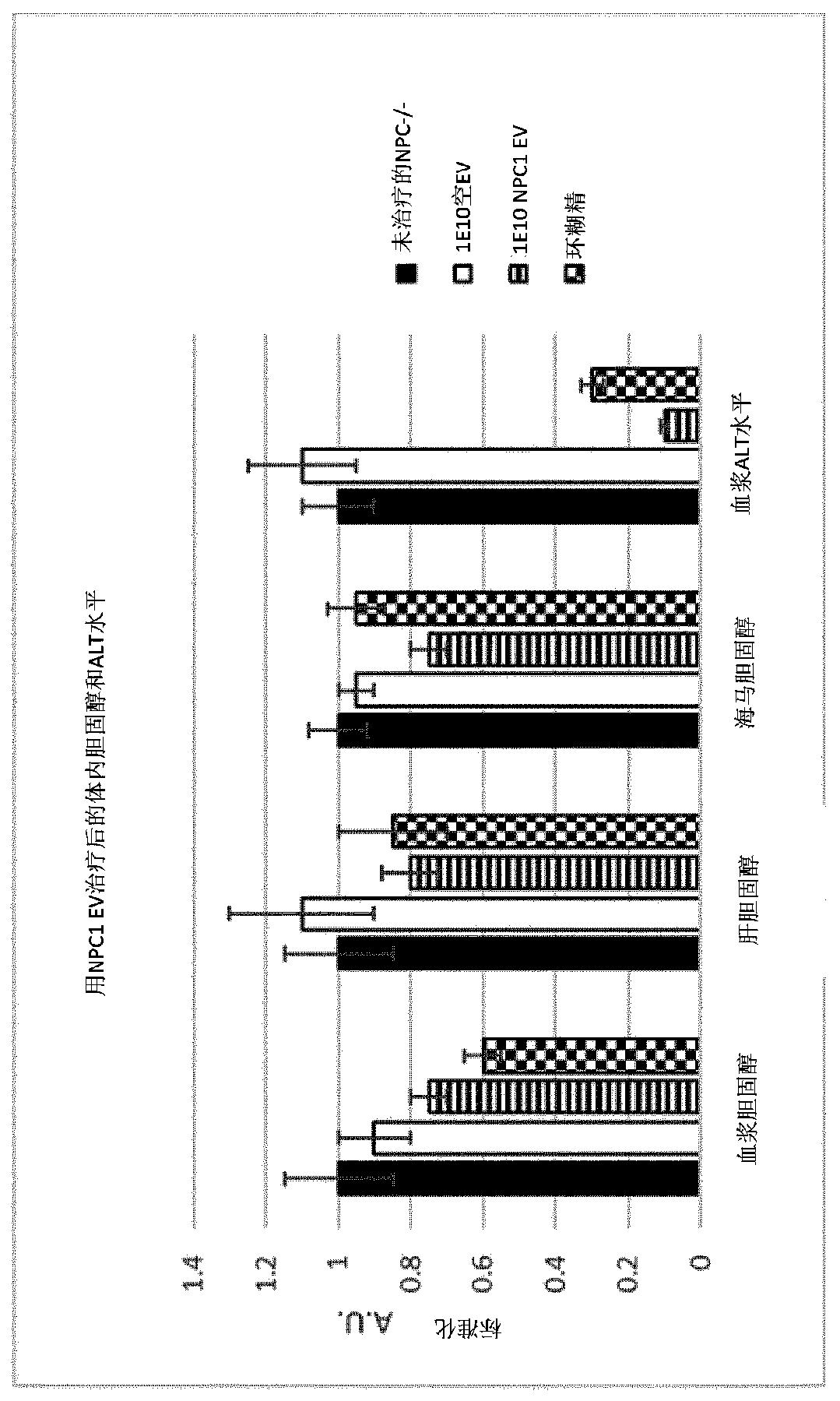
[0075] Example 3. In vivo assessment of AEs positive for CD44, SSEA4, CD133, CD24, and Hsp70-8 and engineered to comprise multiple NPC1-inhabitin polypeptide constructs in a double knockout mouse model of Niemann-Pick disease -EV. The engineered AE-EVs showed significant therapeutic effects on both liver and CNS lesions ( image 3 ). Non-engineered AE-EVs also showed therapeutic efficacy, as inferred from the high content of various heat shock proteins in AE-EVs.
[0076]
[0077]
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap