Compass double-leg distance locking method
A compass foot and compass technology, applied in the field of stationery, can solve the problems of changes, the feet of the compass are not easily broken apart, and the operation is inconvenient.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
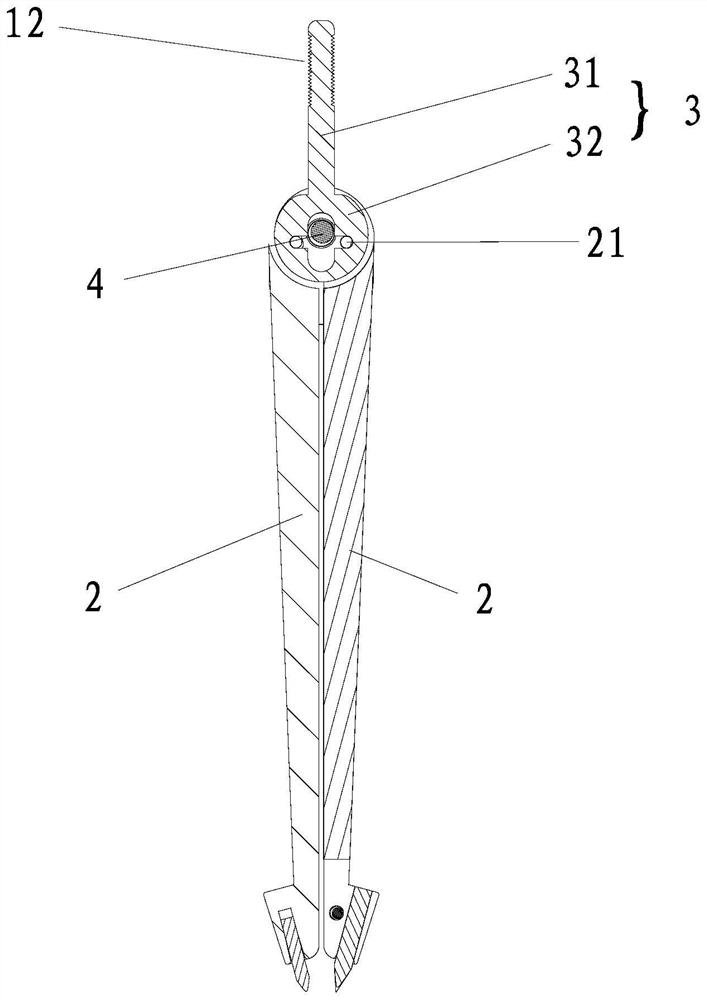
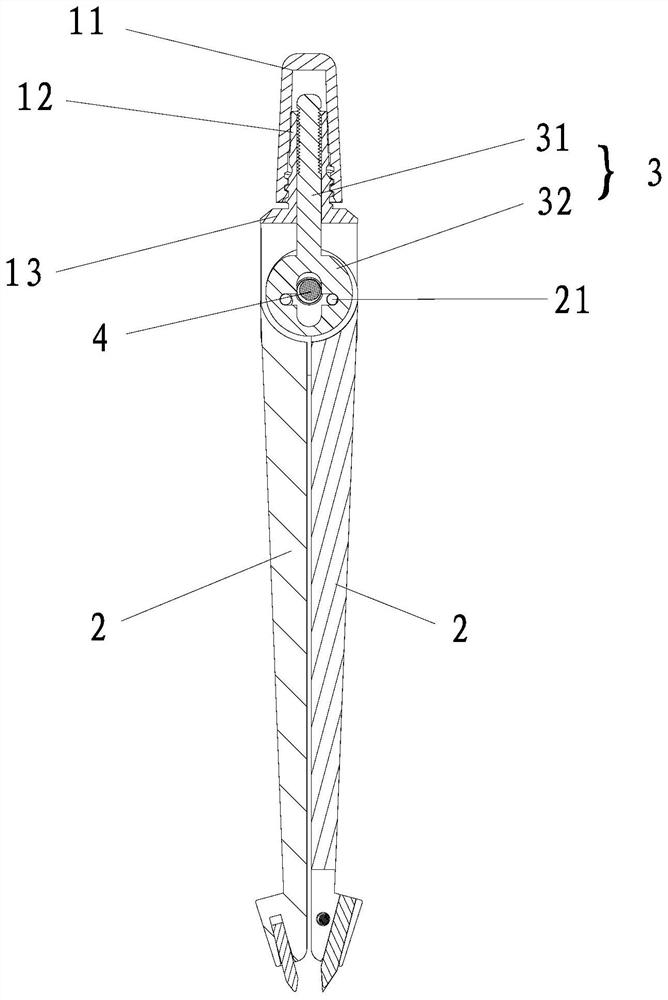
[0031] A method for locking the distance between the feet of a compass, comprising the steps of:
[0032] Step 1. Linearly slide and connect a handle in the compass head of the compass, and connect the handle with the two compass feet of the compass through a mechanism transmission, so that when the distance between the two compass feet changes The handle slides within the compass head.
[0033] Step 2: After adjusting the included angle between the two compass feet to a desired angle, fix the handle and the compass head together, and keep the handle and the compass head relative to each other.
[0034] Further, the compass head has a clamping device, and in the second step, the clamping device clamps the handle so as to keep the handle and the compass head relative to each other.
[0035] The above-mentioned mechanism can adopt the crank-slider mechanism and can also adopt the center piece mechanism adopted by the existing partial compasses. Specifically, in this embodiment,...
Embodiment approach 2
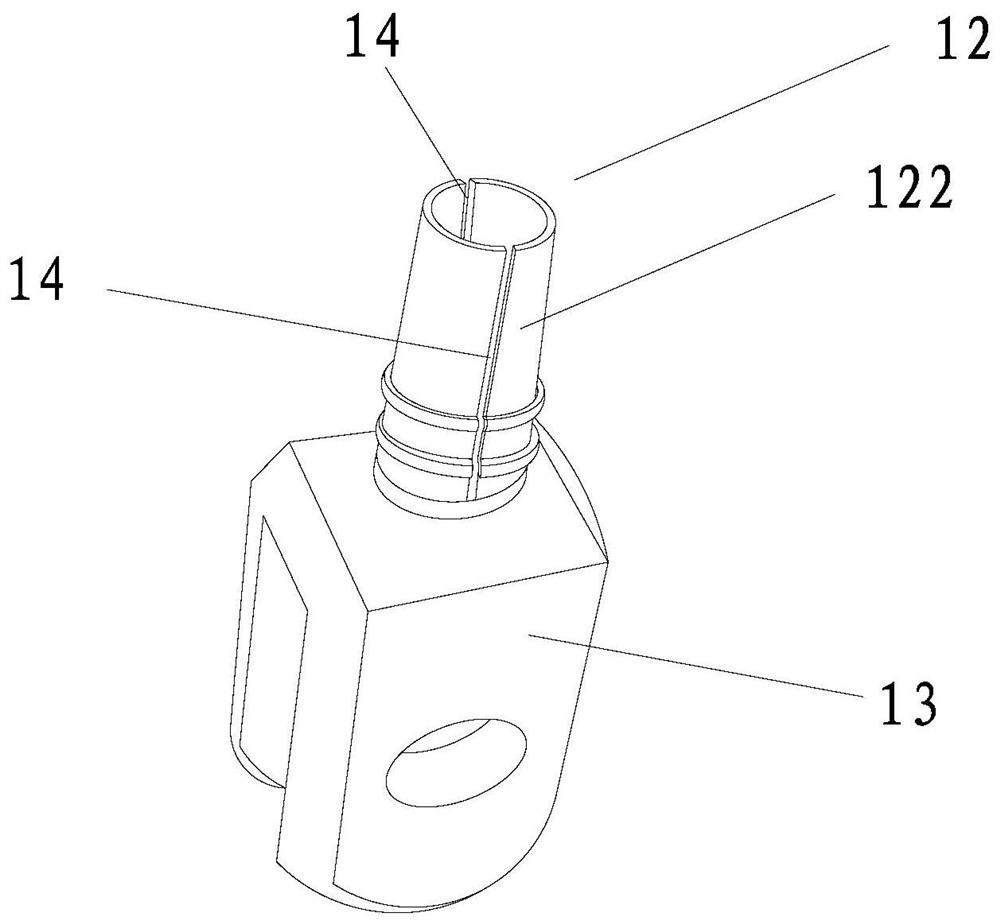
[0055] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, the handle and the compass head are not fixed together by clamping the handle, but by clamping the handle from one side in the width direction of the handle Or place the handle on the compass head on one side in the thickness direction so as to keep the handle and the compass head relative to each other.
[0056] Specifically, in this embodiment, a locking device can be used to realize that the handle is on the compass head so as to keep the handle and the compass head relative to each other.
[0057] Such as Figure 12 As shown, the locking device includes a locking bolt 6 and a locking threaded hole 116 provided on the compass head. The compass head only includes the compass cap 11 and the compass head main body 13 connected together. The compass cap 116 is a cylinder Body, the locking threaded hole 116 runs through the compass cap 11 in the radial direction, the locking bolt 6 cooper...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com