Automobile driver brain visual load evaluation method and system based on subtask
A visual load and evaluation system technology, applied in medical science, psychological devices, sensors, etc., can solve problems such as inability to perform real-time, high requirements for instruments, and insufficient objectivity, and achieve the effect of objective evaluation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
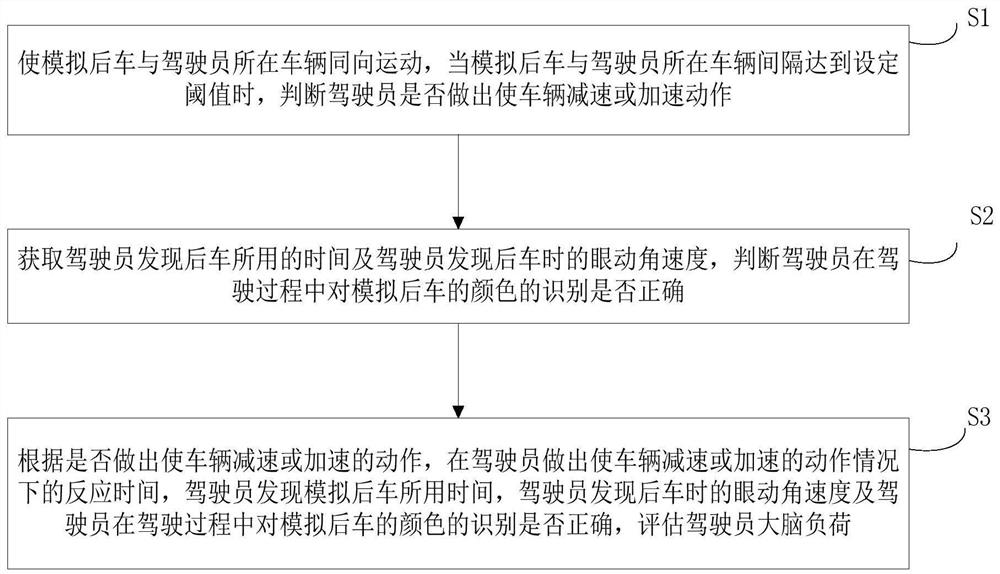
[0034] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for assessing the visual load of the car driver's brain based on sub-tasks, the schematic flow chart of which is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0035] Step S1. Make the simulated rear vehicle and the driver's vehicle move in the same direction, and when the distance between the simulated rear vehicle and the driver's vehicle reaches a set threshold, determine whether the driver decelerates or accelerates the vehicle;
[0036] Step S2, obtain the time taken by the driver to find the rear car and the eye movement angular velocity when the driver finds the rear car, and determine whether the driver's recognition of the color of the simulated rear car during driving is correct;
[0037] Step S3, according to whether to make the action of decelerating or accelerating the vehicle, the reaction time when the driver makes the action of decelerating or accelerating the vehicle, the time it tak...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The embodiment of the present invention provides a car driver's brain load evaluation system based on secondary tasks, including a rearview mirror simulation module, an eye tracker, a motion sensing module, a motion sensing device, and a brain load evaluation module;
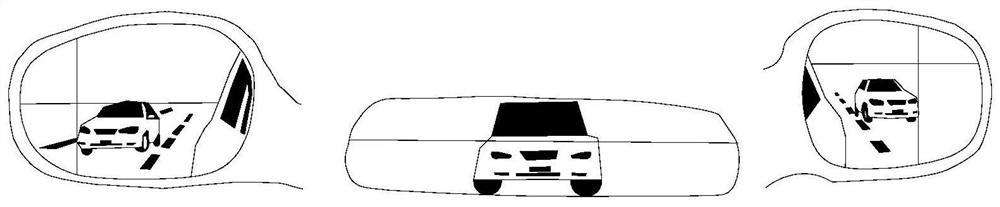
[0050] The rearview mirror simulation module is used to make the simulated rear vehicle and the driver's vehicle move in the same direction;
[0051] The motion sensing module is used to determine whether the driver makes an action to slow down or accelerate the vehicle when the distance between the simulated vehicle behind and the vehicle where the driver is located reaches a set threshold;
[0052] The eye tracker is used to obtain the time the driver finds the car behind and the eye movement angular velocity when the driver finds the car behind;
[0053] The voice sensor module is used to judge whether the recognition of the color of the simulated rear car by the driver during driving is correct throug...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com