Dynamic reasoning network and method for multi-hop questions and answers
A dynamic, networked technology, applied in inference methods, biological neural network models, electrical and digital data processing, etc., to solve the problems that text information cannot be fully utilized, texts are rarely accessed, and paragraph selection is not performed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
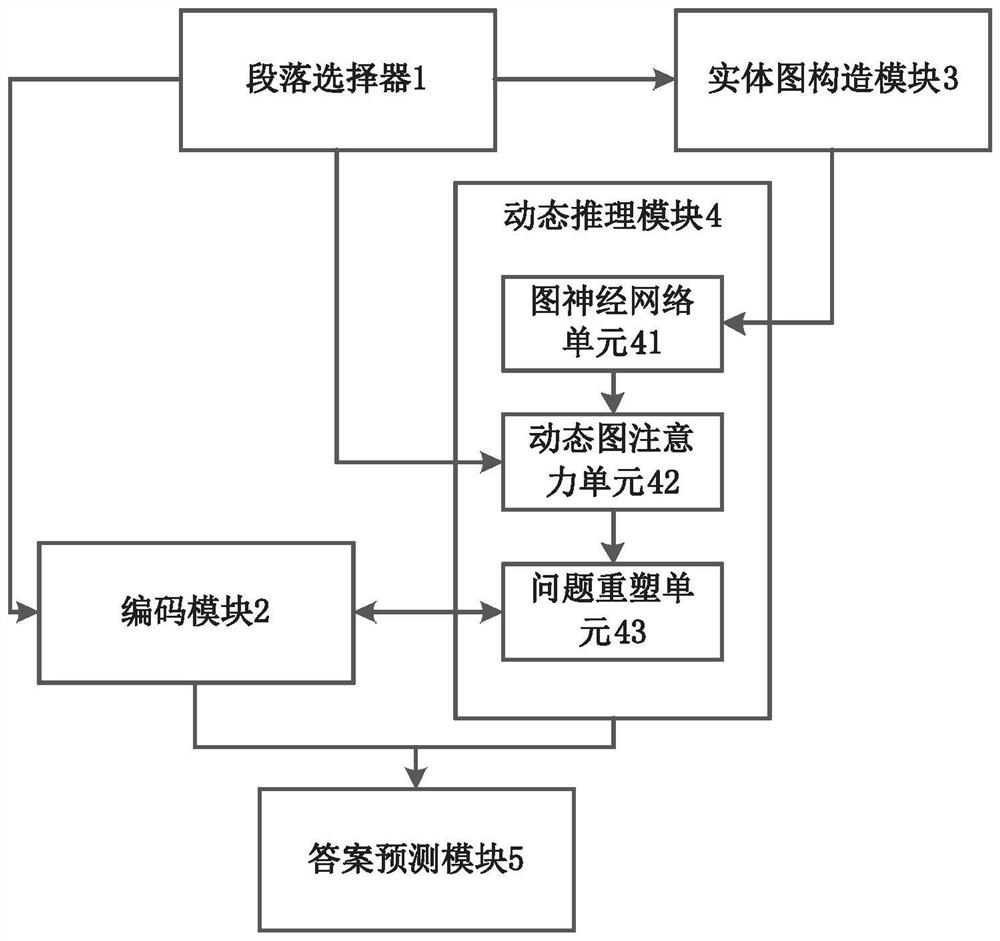
[0066] refer to figure 1 , is a schematic structural diagram of a dynamic reasoning network oriented to multi-hop question answering in the present invention. Specifically, a dynamic reasoning network oriented to multi-hop question answering includes:
[0067] Paragraph selector 1, which receives paragraphs and questions, and selects subparagraphs related to the answers to questions in the paragraphs to eliminate interfering information;
[0068] In this embodiment, the paragraph selector 1 includes a pre-trained BERT model with a sentence classification layer. The pre-trained BERT model is used to predict the similarity between questions and paragraphs. The paragraph selector 1 connects "[CLS]"+question +"[SEP]" + document + "[SEP]" as input for questions and paragraphs, and outputs a matching score between 0 and 1. Paragraph selection follows the following rules: if the paragraph contains an answer, the label is 2; if the paragraph contains at least one supporting statement...
Embodiment 2
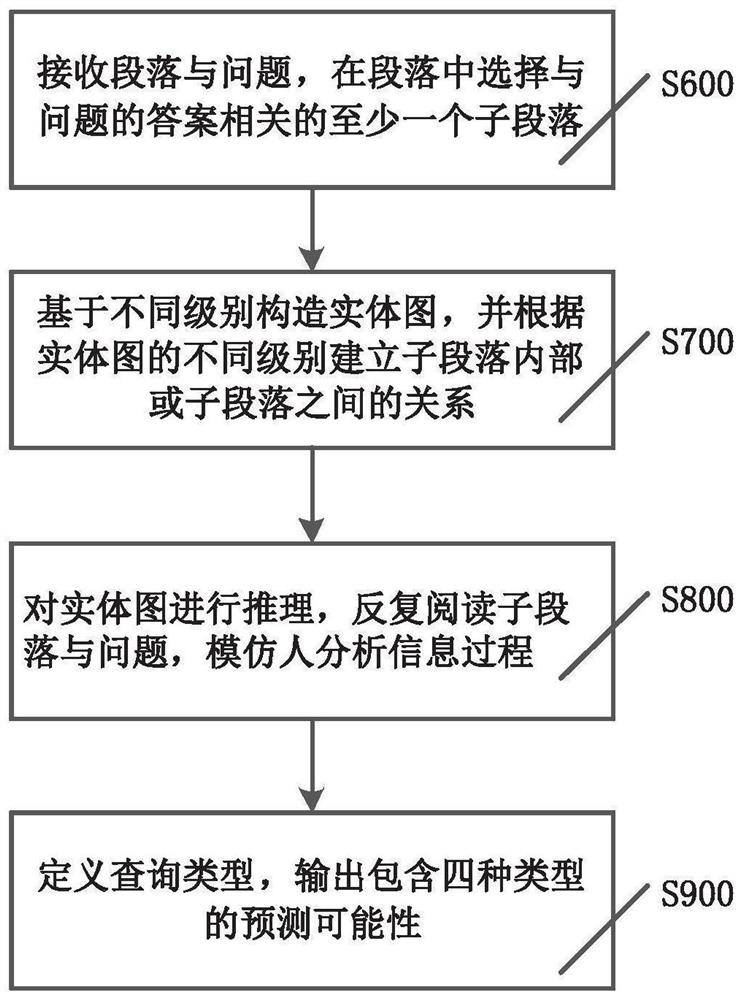
[0086] refer to image 3 It is a flow diagram of a dynamic reasoning method for multi-hop question answering in the present invention, specifically, a dynamic reasoning method for multi-hop question answering, comprising the following steps:
[0087] S600: Receive a paragraph and a question, select at least one sub-paragraph related to the answer to the question in the paragraph; then perform step S700;
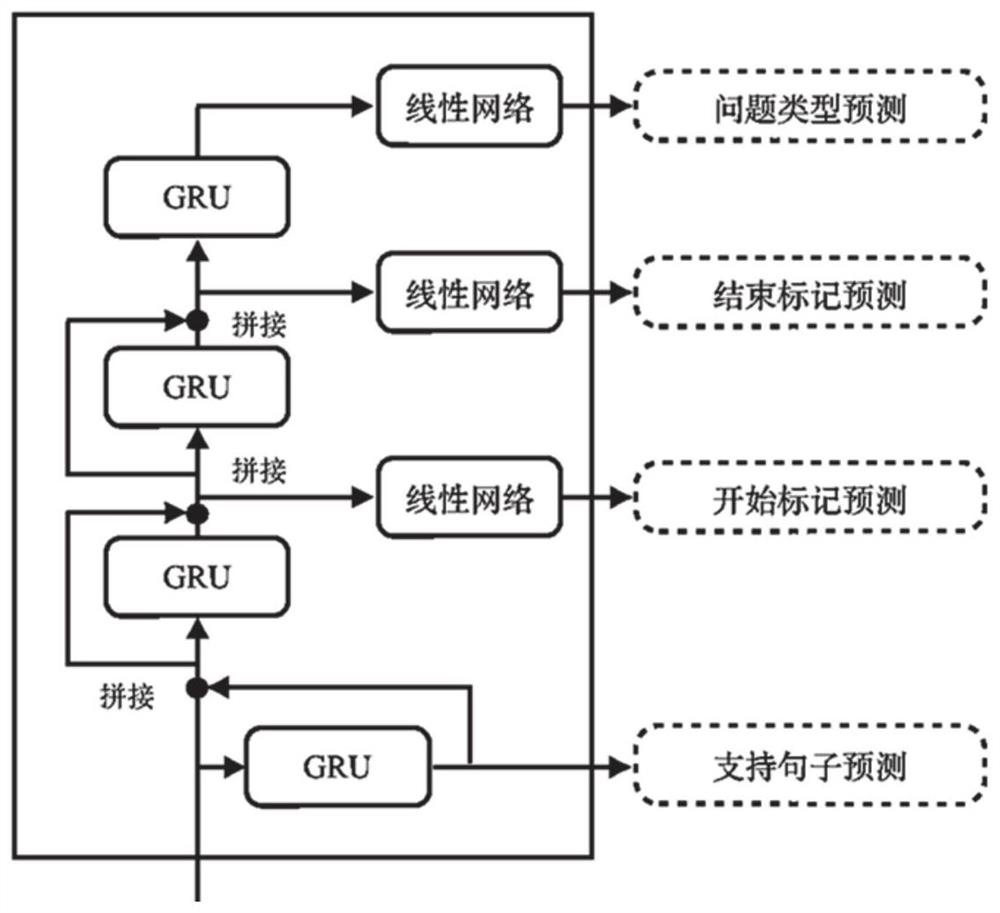
[0088] In this embodiment, after receiving the paragraphs and questions that need to be inferred, the paragraph selector 1 in Embodiment 1 will select the paragraphs in the paragraphs related to the answers to the questions as sub-paragraphs, so as to eliminate the interference information, and Coding the question with the resulting subparagraph, specifically, the question is set to Q=[q 1 ,q 2 ,...,q m ]∈R m×h , the subparagraph is set to P=[p 1 ,p 2 ,...,p n ]∈R n×h , m and n are the lengths of the question and paragraph respectively, h is the size of the hidden sta...
Embodiment 3
[0139] In this embodiment, the validity of the system of embodiment 1 and the method of embodiment 2 is verified, specifically, this embodiment is in the HotpotQA data set (the latest benchmark data set for multi-hop reasoning across multiple paragraphs) Evaluate the inference network of the present invention on the TriviaQA data set (a benchmark data set based on information retrieval (IR) construction), and compare the results of other models with the same parameter data,
[0140] In this example, baseline (the model used when Yang, Zhilin, et al. proposed the hotpot qa dataset in 2018), GRN (a model with a good ranking but unpublished papers on the leaderboard of the Hotpot qa dataset in 2019), QFE (the model proposed by Nishida, Kosuke, et al. in 2019), DFGN (the model proposed by Xiao, Yunxuan, et al. in 2019) are compared with the system of the present invention, and EM and F1 are used as measurement indicators, and EM is the exact match value and F1 is the F1 score.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com