Design method of rope-driven micro-instrument external force indirect detection model
A rope-driven, detection model technology, applied in surgical manipulators, surgical robots, computer-aided surgery, etc., can solve problems such as errors, low external force detection accuracy, and hysteresis effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0064] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
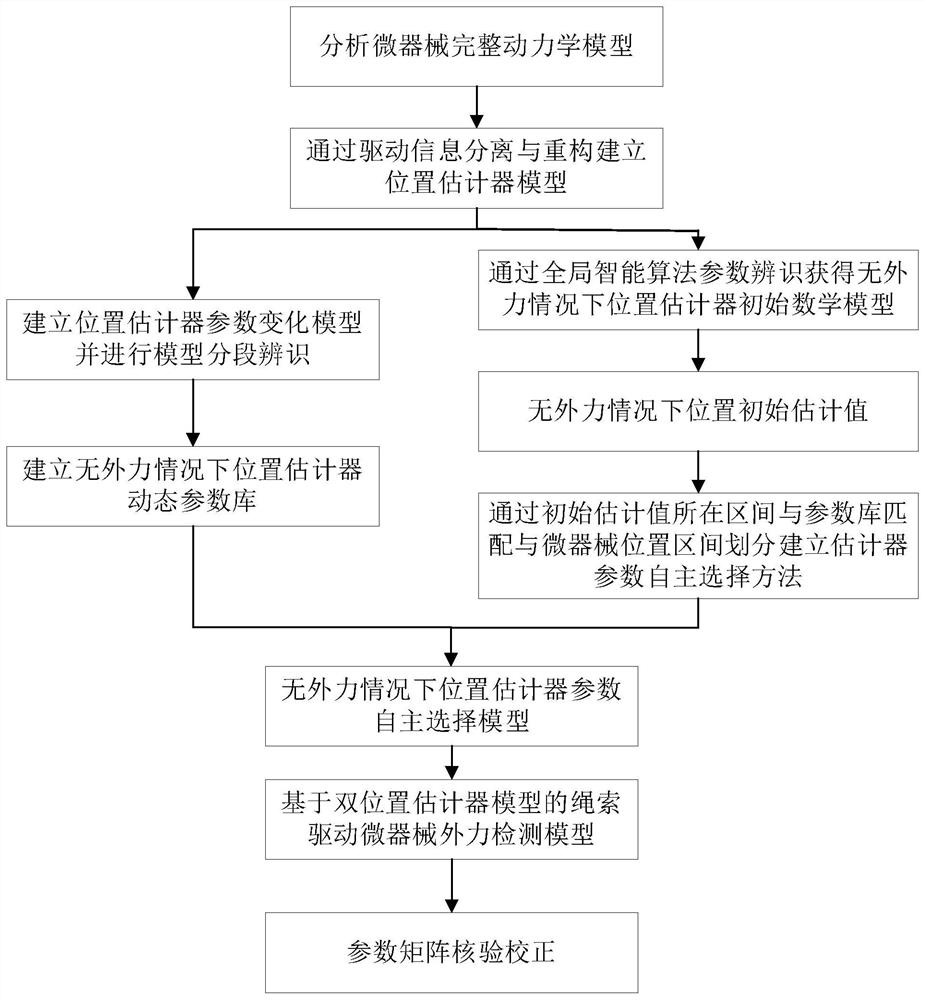
[0065] The invention provides a design method for the indirect detection model of the external force of the rope-driven micro-device, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
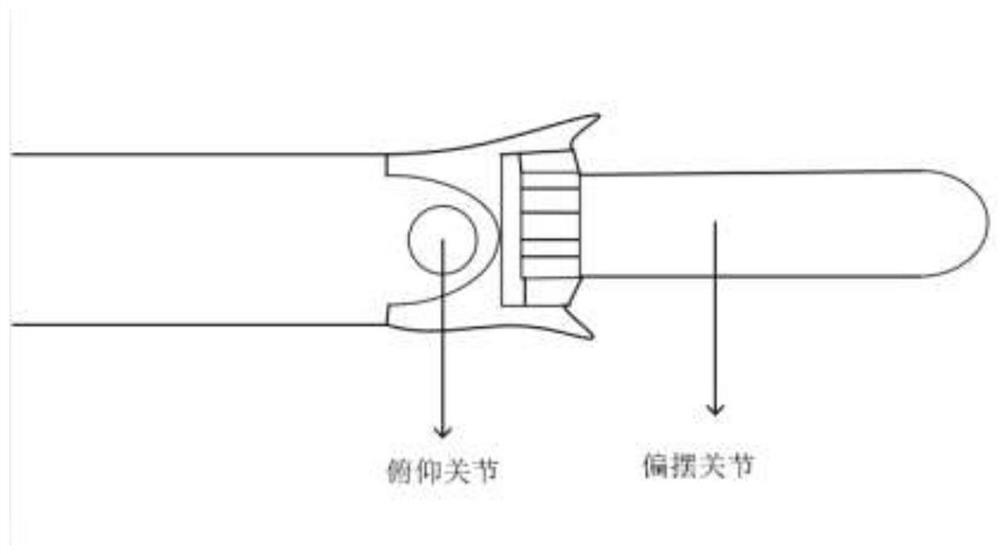
[0066] Step 1. Complete dynamic modeling of the rope-driven micro-device system;
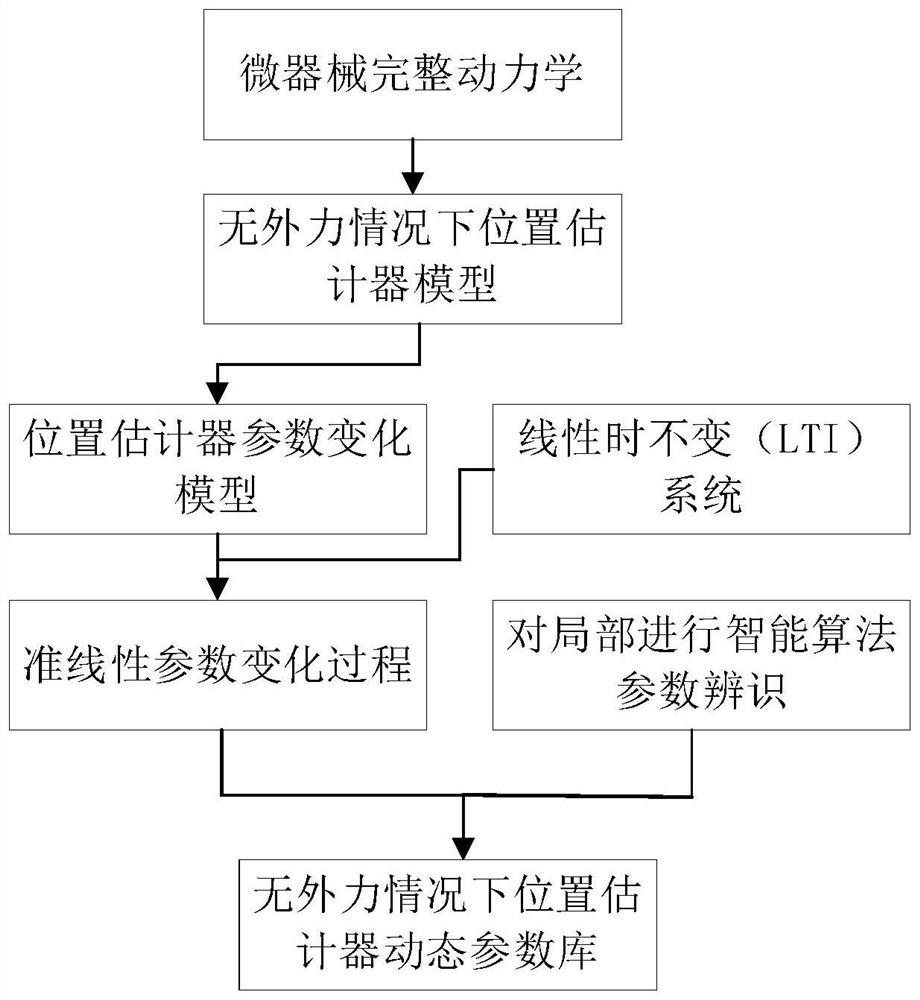
[0067] Step 2. Based on the complete dynamic model of the micro-device, establish a position estimator model and a position estimator parameter change model under the condition of no external force;
[0068] Step 3. Segmentally identify the model of the micro-device position estimator without external force, and establish a dynamic parameter library of the micro-device position estimator without external force;
[0069] Step 4, establishing a parameter autonomous selection model of the micro-device position estimator under the condition of no external force;
[0070] St...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com