Portable electroencephalography devices
A technology of EEG, portable equipment, applied in the direction of medical science, diagnosis, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., which can solve the problem of lack of thorough consideration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
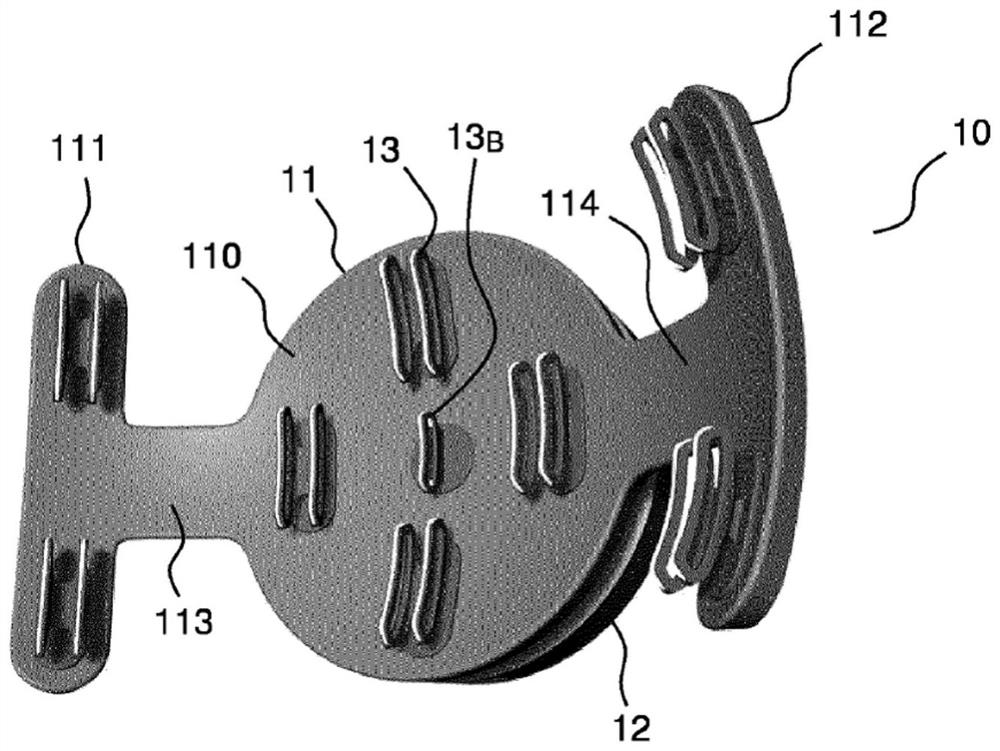
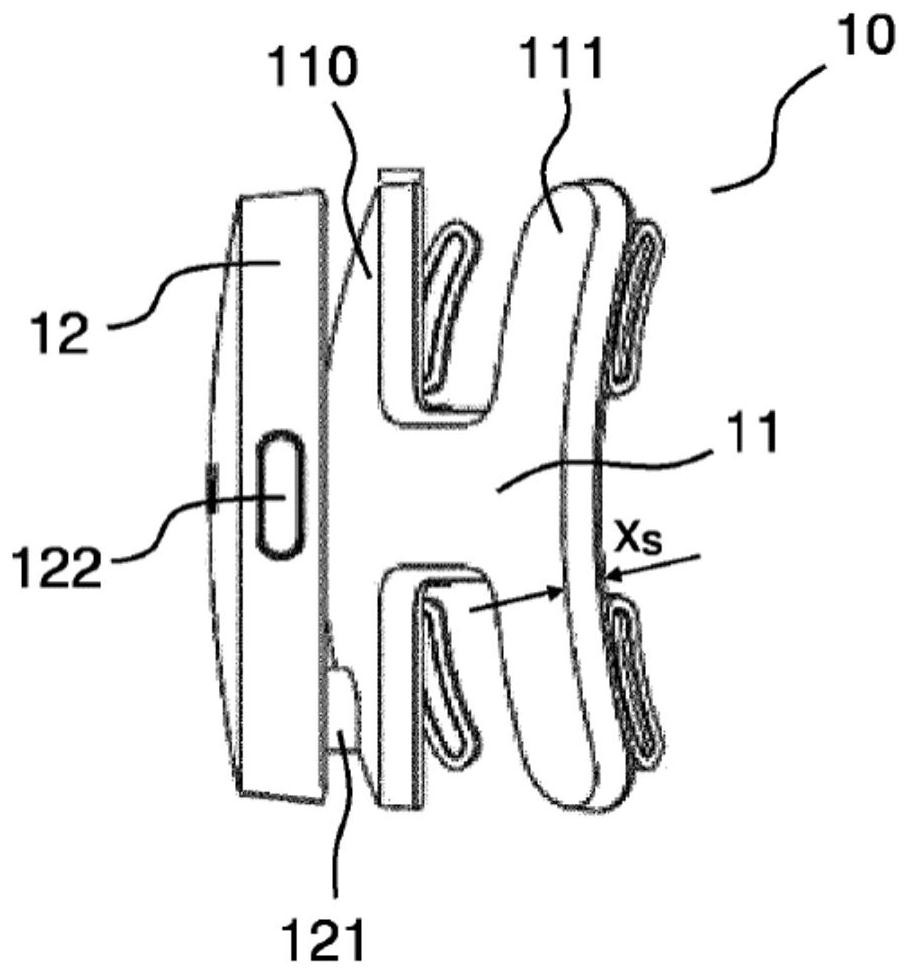
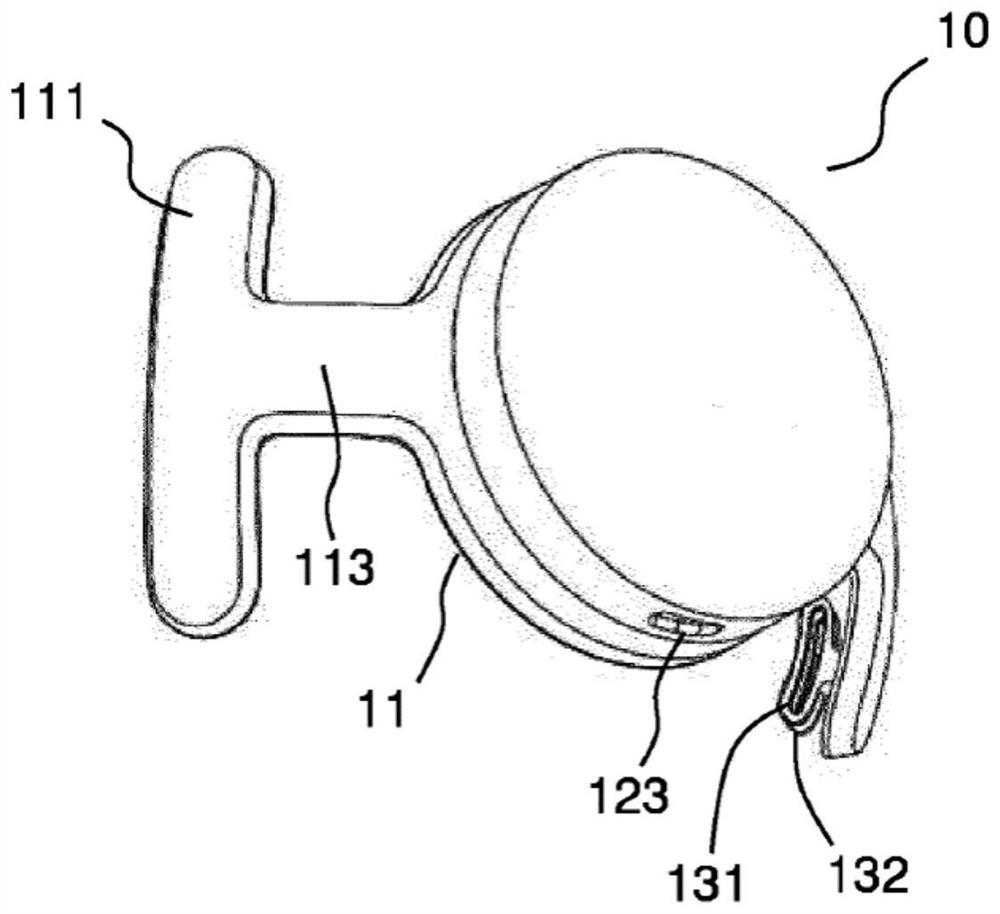
[0059] Figure 1A to Figure 1D respectively represent a front view, a first side view, a rear view and a second side view of a first example of a portable device 10 for acquiring EEG signals according to the present specification, while Figure 1E A view of a device worn by a user is shown.
[0060] Such as Figure 1A to Figure 1D The illustrated portable device includes: a flexible support 11 intended to fit a localized area of the user's skull (e.g., in the occipital region at the back of the skull); and a housing 12 mechanically and electronically ground coupled to the flexible support 11. On said support is arranged a set of sensors 13 for detecting electrical signals generated by the user's neuronal activity. An additional (so-called ground or "bias") electrode 13 is provided B to remove common mode from signals measured by other sensors. As will be described in more detail below, each sensor may include, for example, a plurality of conductive sheets (in this examp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com