Ground based synthetic aperture radar (GBSAR) with transmitting and receiving multiple antennas (MIMO) and using the processing technique called compressive sensing (CS)
A synthetic aperture radar, transmitting antenna technology, applied in the direction of utilizing re-radiation, radio wave measurement system, reflection/re-radiation of radio waves, etc., can solve problems such as speeding up image acquisition time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
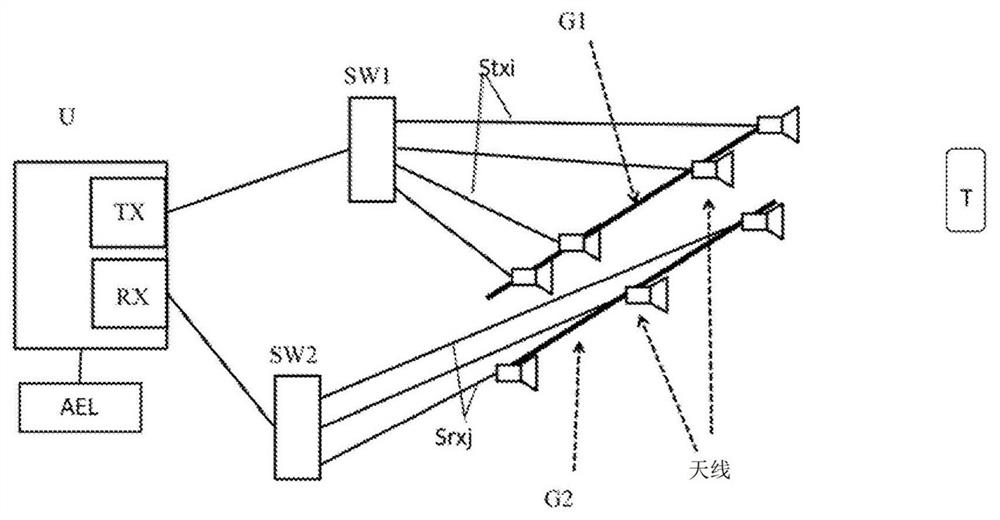
[0022] Referring to the accompanying drawings, the transmitting and receiving unit U is connected to N by means of two switching systems (also called SPNT: Single Pole N-through) SW1 and SW2 respectively. TX transmit antenna and N RX Receive antenna. Similarly, each switching system can be replaced by SPDT pairs (SPNT: Single Pole Double Throw) arranged in a tree.
[0023] Similarly, the receiving switching system can be composed of parallel running N RX receiver instead.
[0024] Similarly, as with many types of MIMO systems, N TX Waveform division transmitters instead of transmit switching systems (see for example J.J.M. De Wit, et al. "Orthogonal Waveforms for FMCW MIMO Radar", Radar Conference (RADAR, 2011IEEE, pp. 686-691, 2011 (J.J.M. De Wit, et al . “Orthogonal waveforms for FMCWMIMO radar.” In Radar Conference (RADAR), 2011 IEEE, pp. 686-691, 2011)).
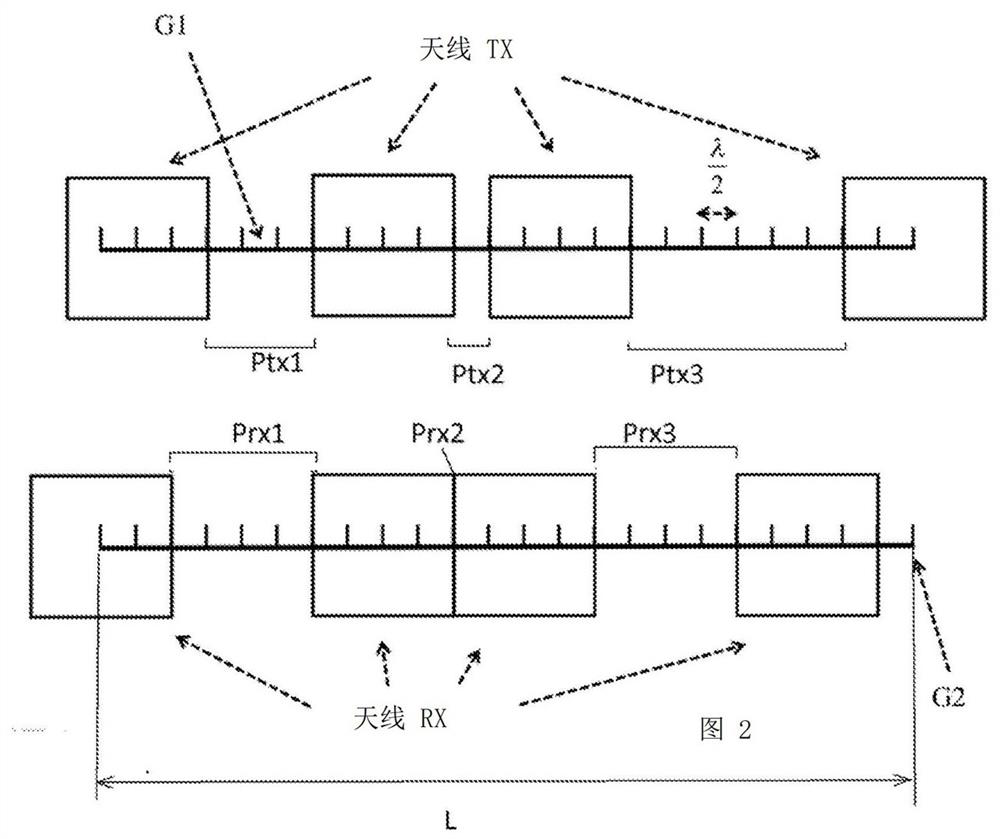
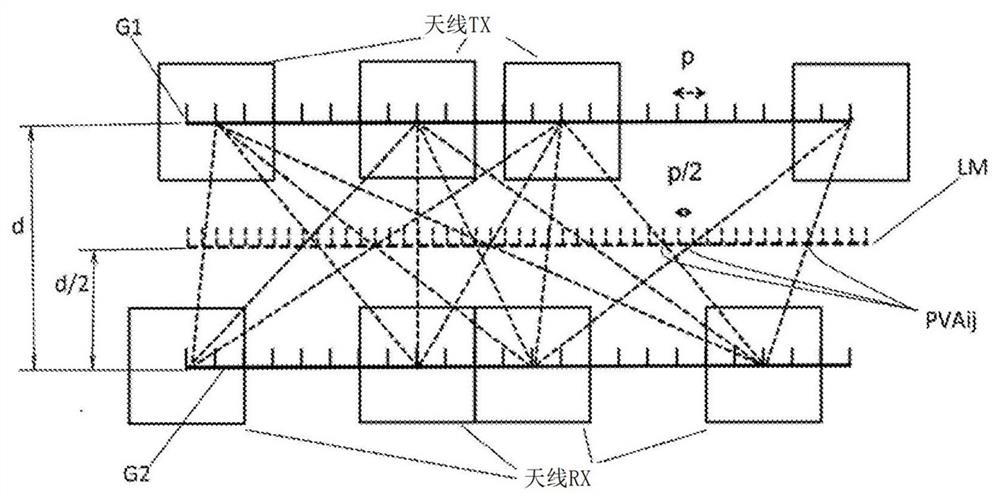
[0025] The radar target of the present invention is based on a specific distribution of transmit (TX) and receive...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com