Digital halftoning with clustered microdots
A halftone and tone technology, which is applied in the field of digital halftone processing, can solve problems such as inability to implement a wide range of installation bases, complexity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
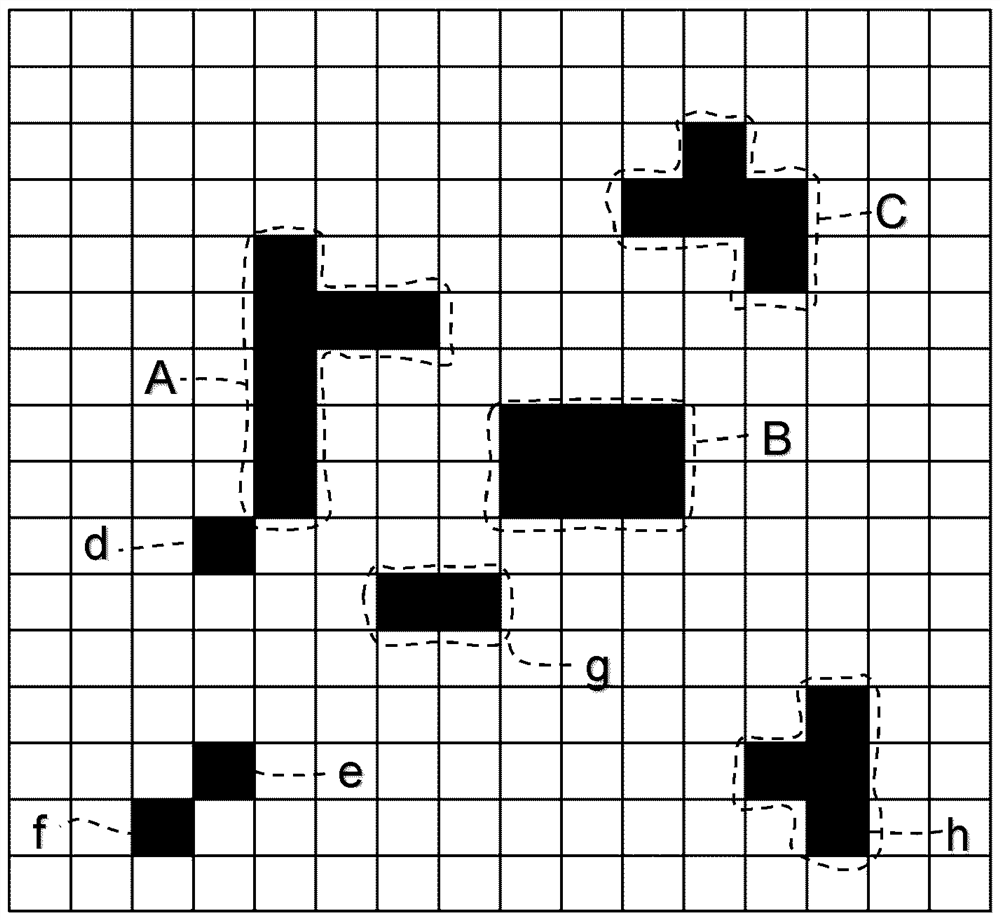
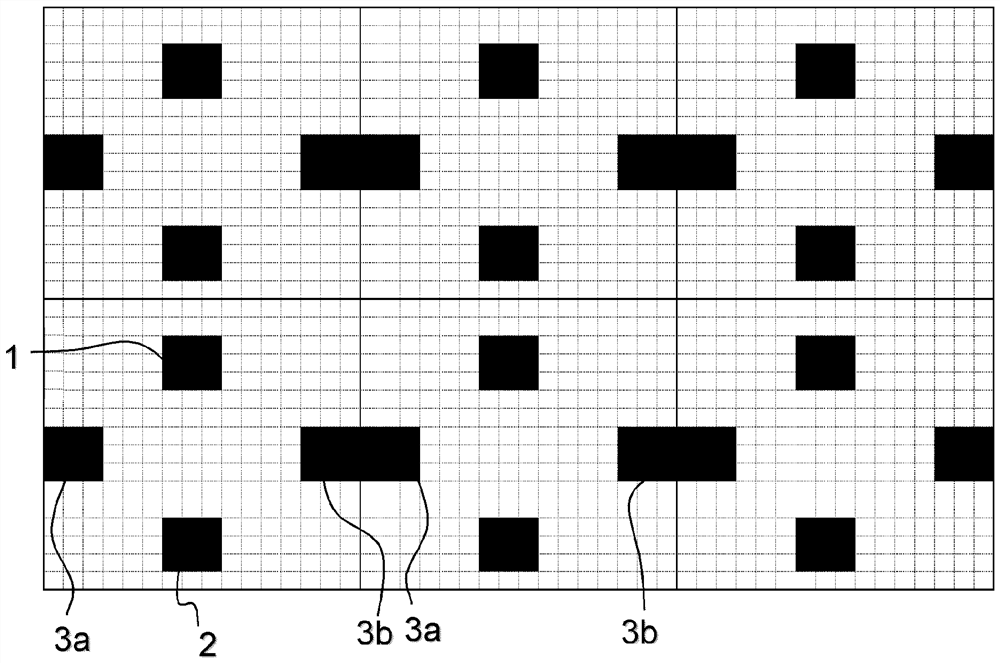
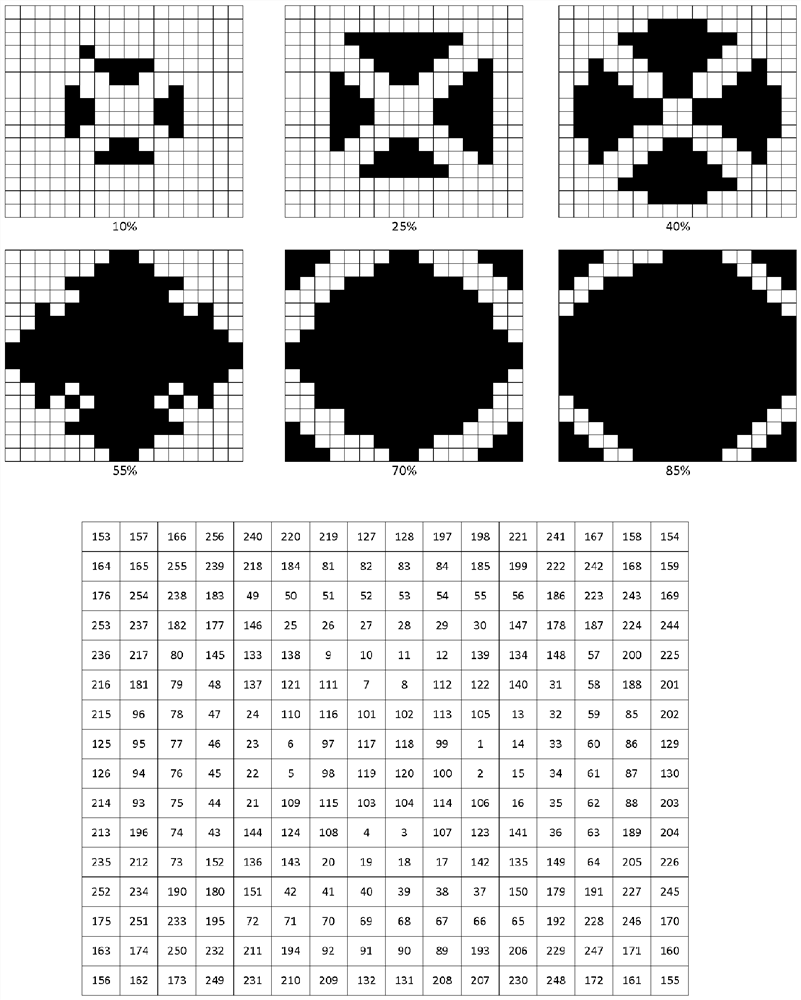
[0022] raster image
[0023] The raster image produced in the method of the invention is suitable for rendering a continuous tone image (CT), ie it creates the illusion of a continuous tone image (CT) on a printed copy. This requirement implies that the screen frequency (i.e. the number of halftone elements placed next to each other per length unit in the direction producing the maximum value) is above 40 lines per inch (LPI; 15.7 lines / cm), more preferably 60 LPI (23.6 lines / cm) or more, most preferably 100 LPI (39.4 lines / cm) or more. If the screen frequency is below 40 LPI, halftone dots become visible at a viewing distance (approximately 20 cm) also known as the read distance. Such low screen frequencies are commonly used in artistic screening, which is used for decorative purposes, such as patterned illustrations, where it is desired that the individual dots be visible to the naked eye. Therefore, raster images in which halftone dots are clearly visible at viewing dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com