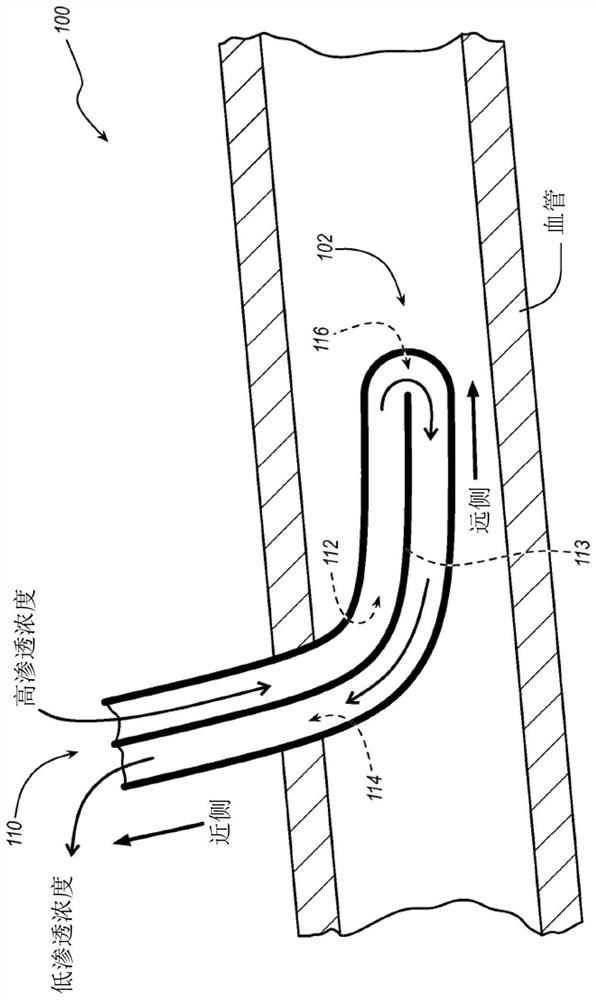
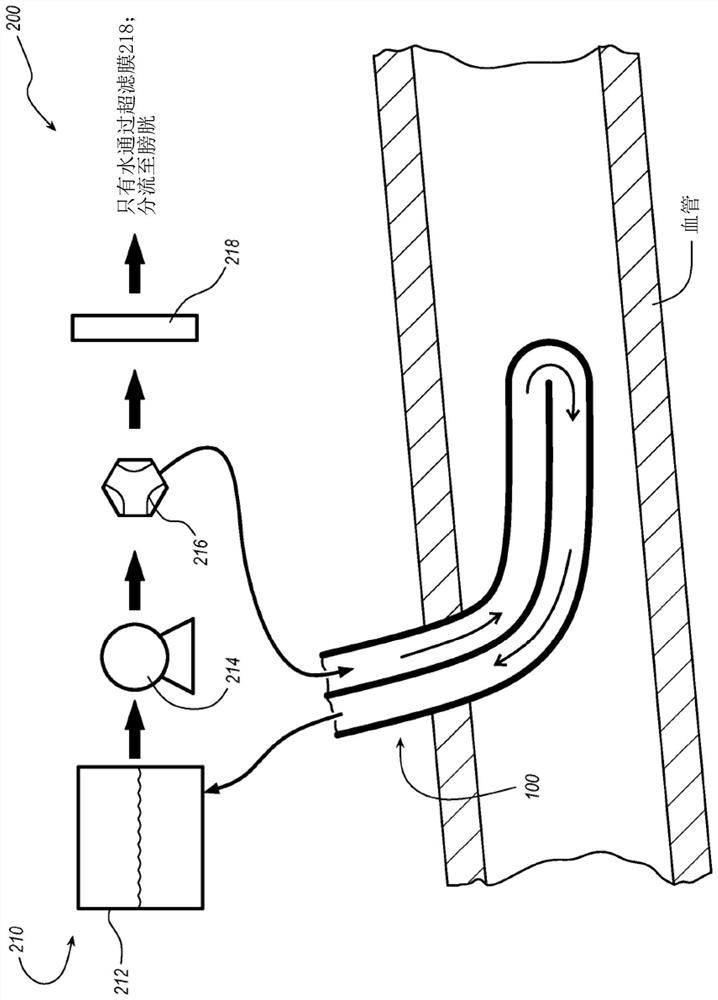
Catheters, catheter-based systems, and methods thereof for treating hypervolemia
A blood volume and catheter technology, applied in catheters, dialysis systems, blood filtration, etc., can solve problems such as death, lower quality of life, and disease progression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037]Before certain specific embodiments are disclosed in greater detail, it should be understood that the specific embodiments disclosed herein do not limit the scope of the concepts presented herein. It should also be understood that a particular embodiment disclosed herein may be characterized as being readily separable from a particular embodiment and optionally combined with or substituted for any one of the many other embodiments disclosed herein.
[0038] With respect to the terminology used herein, it should also be understood that these terms are for the purpose of describing some particular embodiments and that these terms do not limit the scope of the concepts presented herein. Ordinal numbers (eg, first, second, third, etc.) are generally used to distinguish or identify different features or steps within a group of features or steps, and do not provide a series or numerical limitation. For example, "first", "second" and "third" features or steps do not have to app...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com