Method and device for classifying protein-ligand complexes
A classification method and protein technology, applied in bioinformatics, instruments, character and pattern recognition, etc., can solve the problems of lack of negative information, lack of non-binding protein-ligand complexes, lack of ineffectiveness, etc., and meet the requirements of computing resources Low, the effect of retaining key physical and chemical information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the specific implementation manners of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Examples of these preferred embodiments are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. The embodiments of the invention shown in and described with reference to the drawings are merely exemplary, and the invention is not limited to these embodiments.
[0027] Here, it should also be noted that, in order to avoid obscuring the present invention due to unnecessary details, only the structures and / or processing steps that are closely related to the solution according to the present invention are shown in the drawings, and the relationship between them is omitted. Little other details.
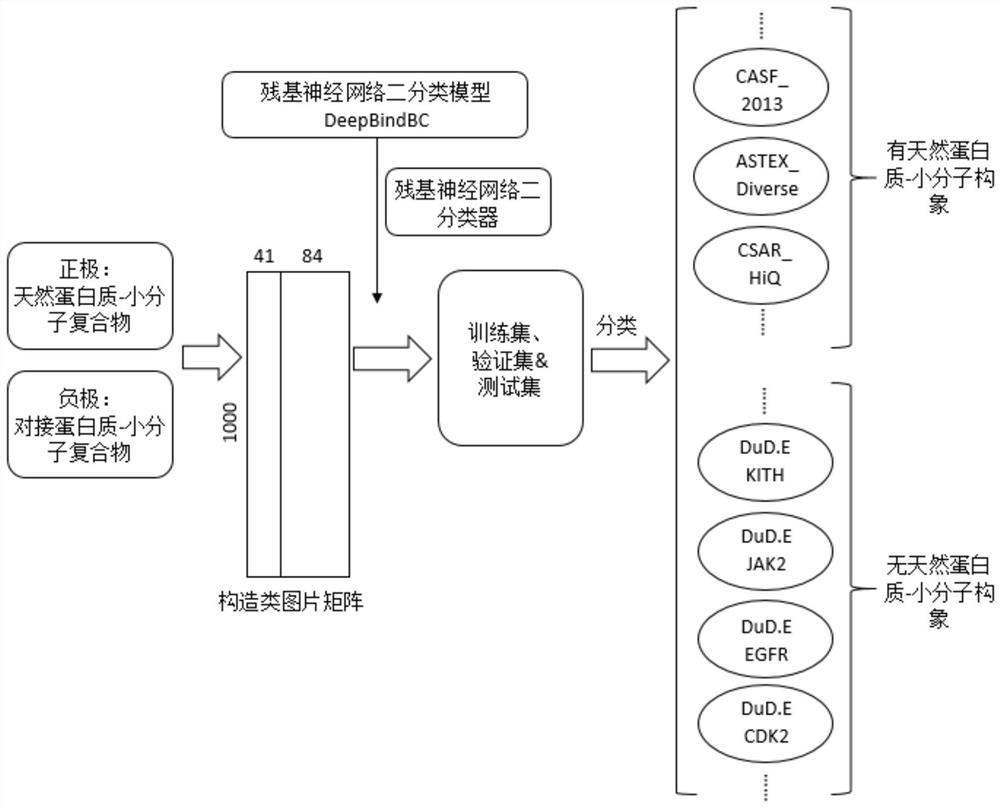
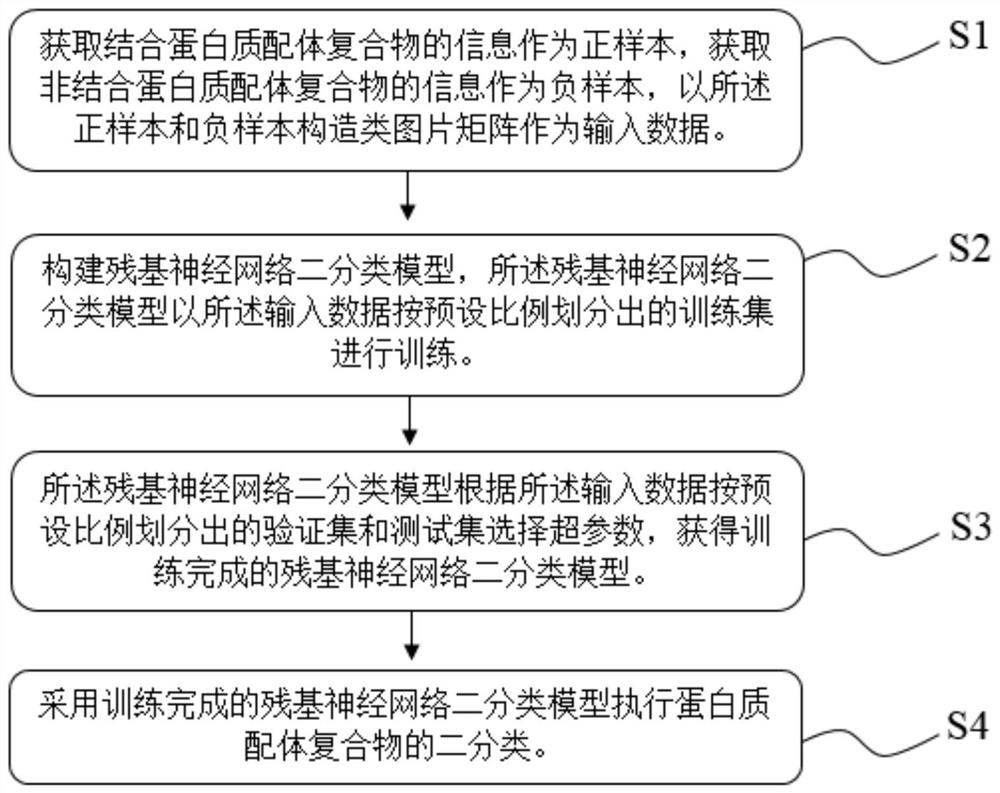
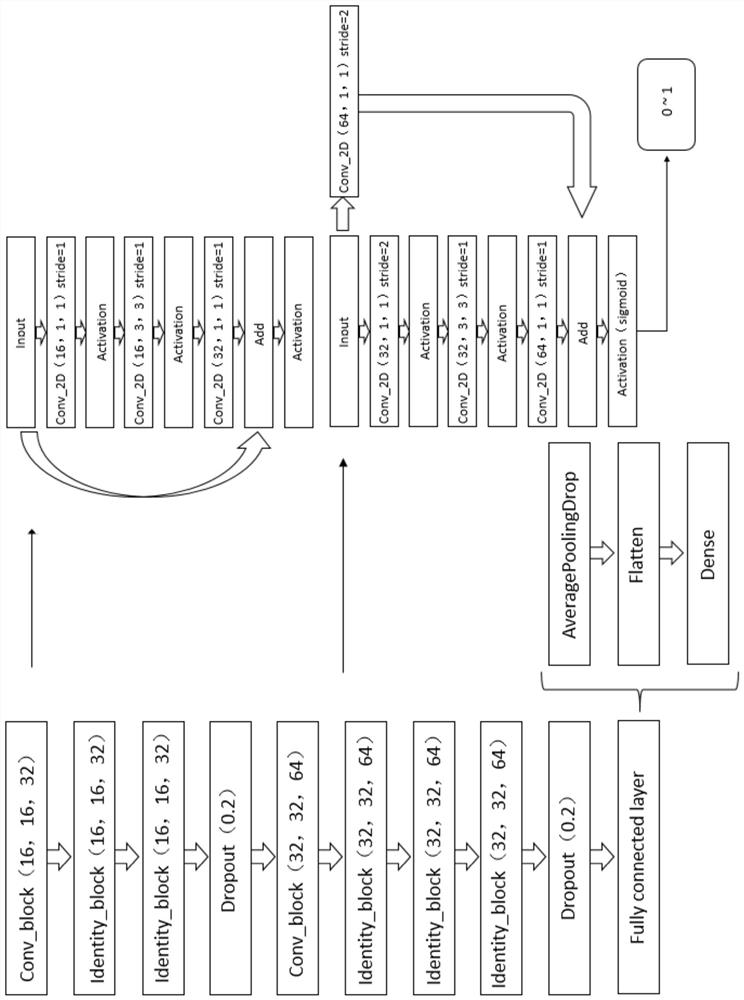
[0028] The invention provides a method for classifying protein-ligand complexes, referring to figure 1 and figure 2 Shown, the classification method of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com