High-speed train running gear system fault diagnosis method based on semi-quantitative information fusion
A technology for high-speed trains and system failures, applied to computer parts, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as no analysis, achieve the effects of improving results, realizing fault classification, and realizing fault diagnosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
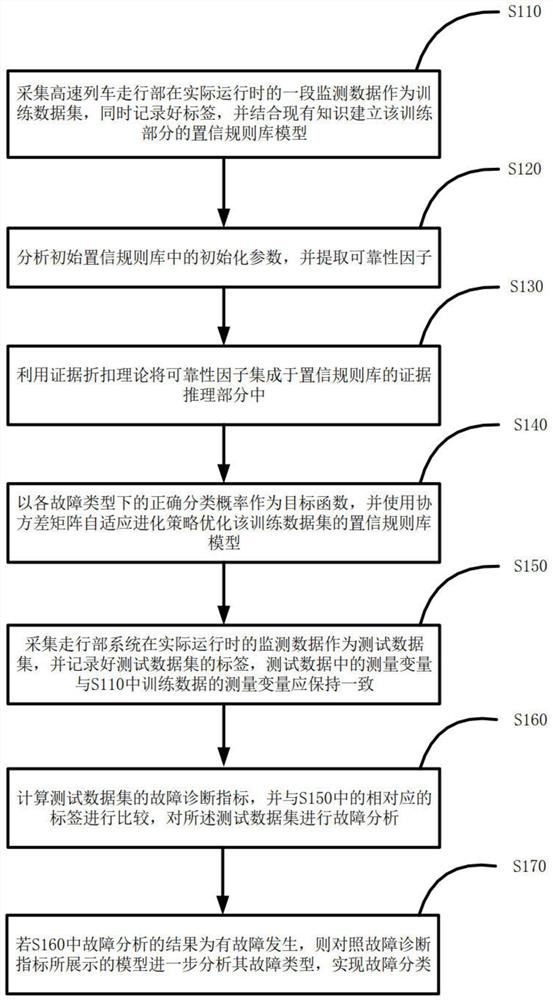
[0020] DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT One, a kind of semi-quantitative information fusion method for fault diagnosis of the high-speed train running part system described in the present embodiment, the method specifically includes the following steps:
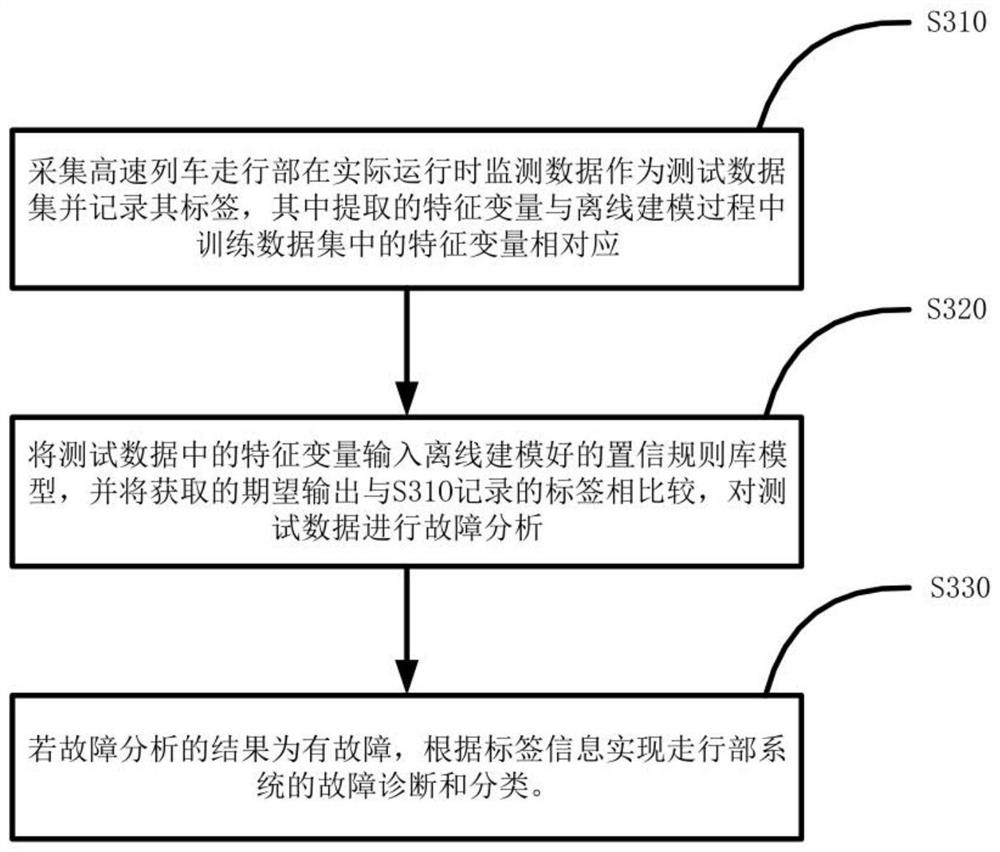
[0021] Step 1. Collect the monitoring data of the running system during actual operation, then use the collected monitoring data to construct a training data set, and record the labels;
[0022] Initialize the parameter vector in the confidence rule base, and establish the confidence rule base model of the training part;
[0023] Step 2, analyze the reliability of the initialization parameters in the confidence rule base model, and obtain the reliability factor of each confidence rule;
[0024] Step 3: Integrate the reliability factor into the evidence reasoning part of the confidence rule base model by using the evidence discount theory to realize the optimization of model reasoning;
[0025] Step 4. The tra...
specific Embodiment approach 2
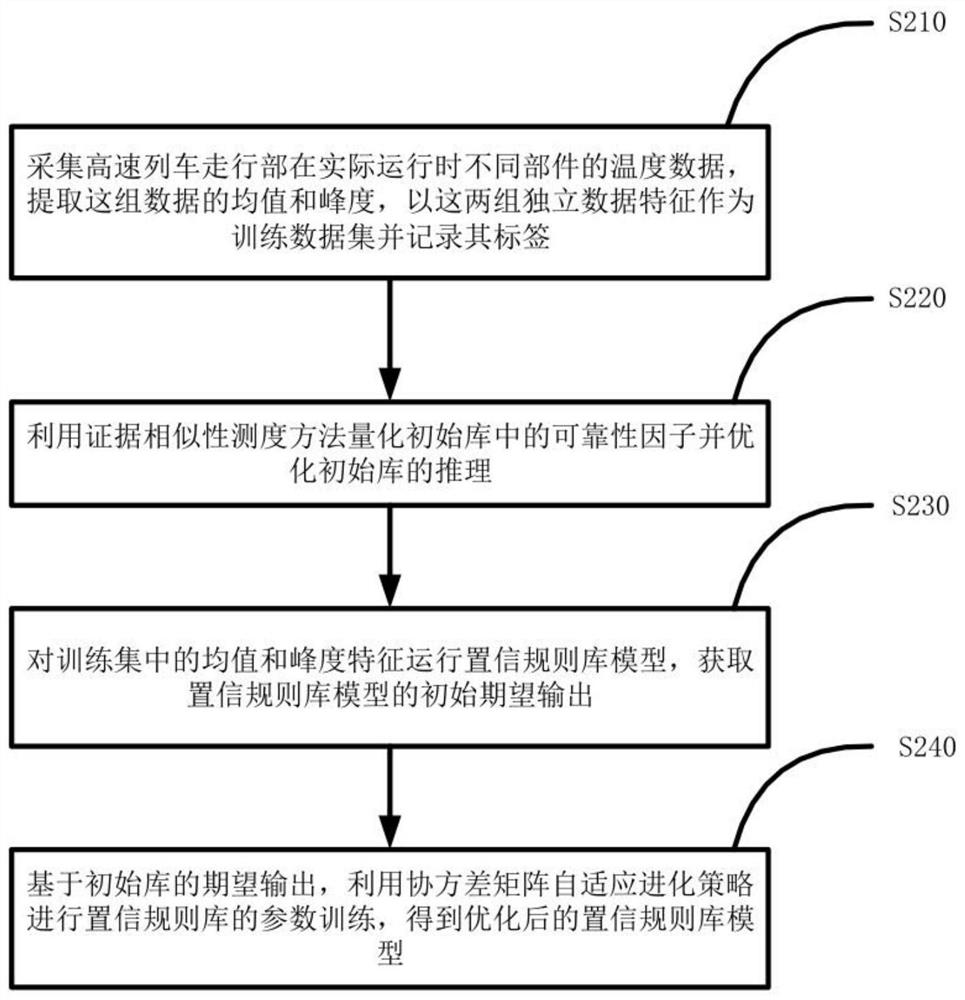
[0029] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in the first step, the monitoring data of the running part system is collected during actual operation, and then the collected monitoring data is used to construct a training data set. The specific process is :
[0030] Collect the N of the running part system of the high-speed train during actual operation 1 The monitoring data of each moment, wherein, the monitoring data of each moment is the temperature data of different components in the running system; then N 1 Time information, collected monitoring data and corresponding labels are stored as a two-dimensional data matrix X 1 , two-dimensional data matrix X 1 The first column is N 1 Time information, the second column is the temperature data collected at each time, and the third column is the label corresponding to each time (marked as whether there is a failure and what type of failure);
[0031] For a two-dimension...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is that in the first step, the parameter vector in the confidence rule base is initialized, and the confidence rule base model is established. The specific process is:
[0034] Initialize the parameter vector in the confidence rule base, select the kth confidence rule R shown in formula (1) k As the knowledge representation of the established initial belief rule base model:
[0035]
[0036] where x mIndicates the mth numeric observation value of the input, Indicates the mth input reference value under the kth confidence rule, m=1,2,...,M, M is the total number of input numerical observation values, is relative to the nth fault type D under the kth confidence rule n Confidence degree of , n=1,2,...,N, N is the total number of fault types, θ k is the rule weight of the kth confidence rule, δ m is the weight of the mth input reference value, r k is the reliability fact...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com