Composition for 3D printing
A 3D printing and composition technology, which is applied in the field of manufacturing three-dimensional objects, forming green or forming blanks, and can solve problems such as volume flow errors and damage to the quality of printed products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
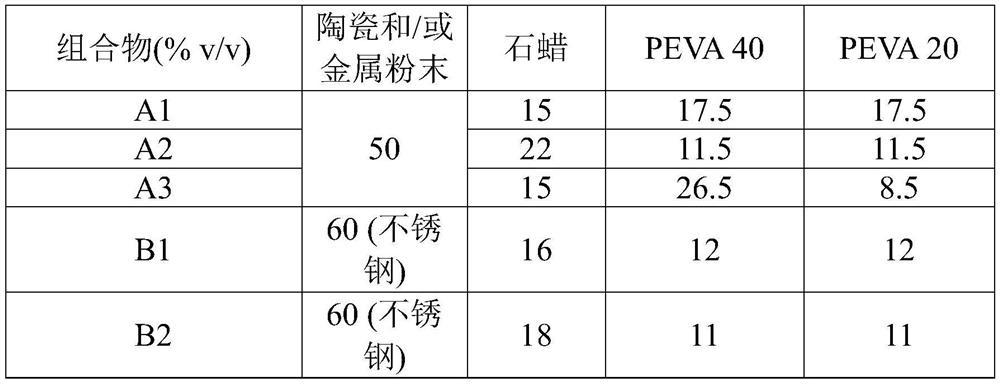
[0056] According to one embodiment, the metal powder comprises or consists of one or more components selected from the group consisting of alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, lanthanides, actinides, transition Metals, metal-poor metals, metalloids, metal oxides, metal carbides, metal borides, and metal nitrides.
[0057] According to one embodiment, the metal powder can be any material suitable for participating in metal injection molding (MIM), preferably an alloy, more preferably an alloy selected from cobalt chromium, stainless steel, titanium alloy and tungsten carbide.
[0058] According to one embodiment, the metal powder is selected from the group consisting of yttrium, yttrium oxide, copper, tantalum (tan), aluminum, cerium, cerium oxide, uranium, uranium oxide, iron, iron oxide, steel, tungsten, tungsten carbide, strontium titanate, Silicon carbide, silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide, zirconium dioxide, titanium dioxide, transition metal oxides such as cobalt dioxide o...
no. 1 approach
[0154] According to a first embodiment, the method includes a debinding step in order to remove the binder from the green body. In one embodiment, the degreasing step is performed by immersing the green body in a solvent selected from the group consisting of acetone, hexane, heptane, gasoline, ethyl acetate, ethanol, methanol, propanol and water. In one embodiment, the solvent is acetone. In one embodiment, the solvent is an alkane selected from pentane, hexane, heptane or a mixture of alkanes such as eg gasoline.
[0155] In one embodiment, the green embryo is defatted by immersing the green body in a solvent for 12h to 72h, preferably at room temperature.
[0156] The sintering step (d) is a heat treatment at a temperature ranging from about 800°C to about 1700°C.
[0157] In one embodiment, the green body comprising metal powder is sintered at a temperature of from about 800°C to about 1300°C, preferably under vacuum.
[0158] In one embodiment, the green body comprising...
no. 2 approach
[0159] According to a second embodiment, the method does not comprise a degreasing step. According to such an embodiment, the binder is removed during the sintering step. In order to avoid vaporization of the binder during sintering and / or bubble formation during calcination; heating is performed with a slow heating gradient.
[0160] In one embodiment, the heating gradient in step (d) is 2°C / h to 10°C / h.
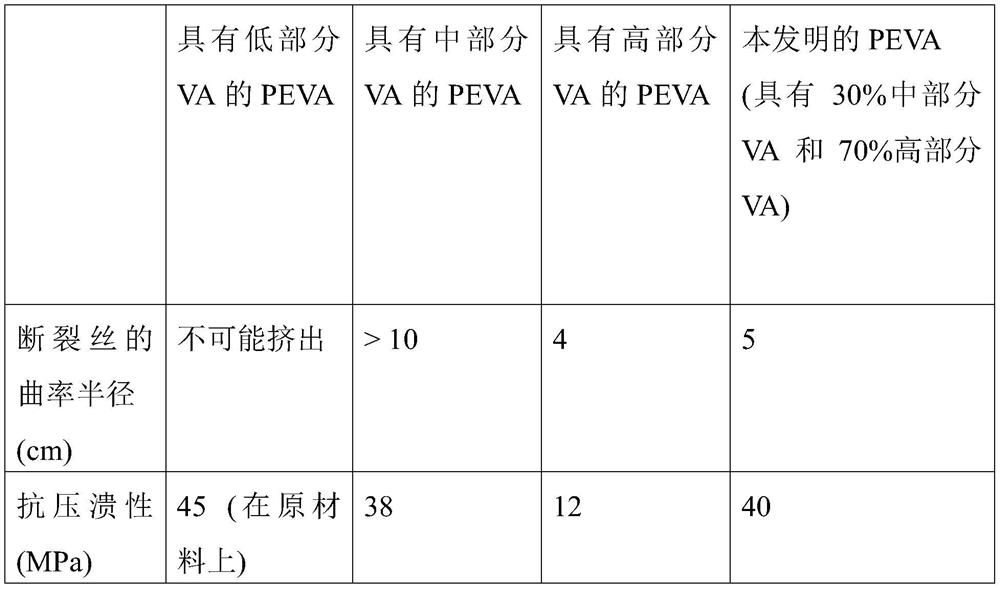
[0161] During 3D printing, ie during FDM printing, the part is printed layer by layer, with typical layer thicknesses of 50 μm to 300 μm. This results in a rather rough surface condition that requires post-processing (such as reworking or polishing) after sintering, which can significantly increase the price of the part and, more importantly, sometimes where polished parts are not available (such as internal channels) may be a serious problem.
[0162] The method may further comprise at least one smoothing step. In one embodiment, the smoothing step is carried out on th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap