Rigidity-variable robot flexible joint
A flexible joint and stiffness technology, applied in the field of robots, can solve the problems of small adjustable range of joint stiffness and large volume of robot joints.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
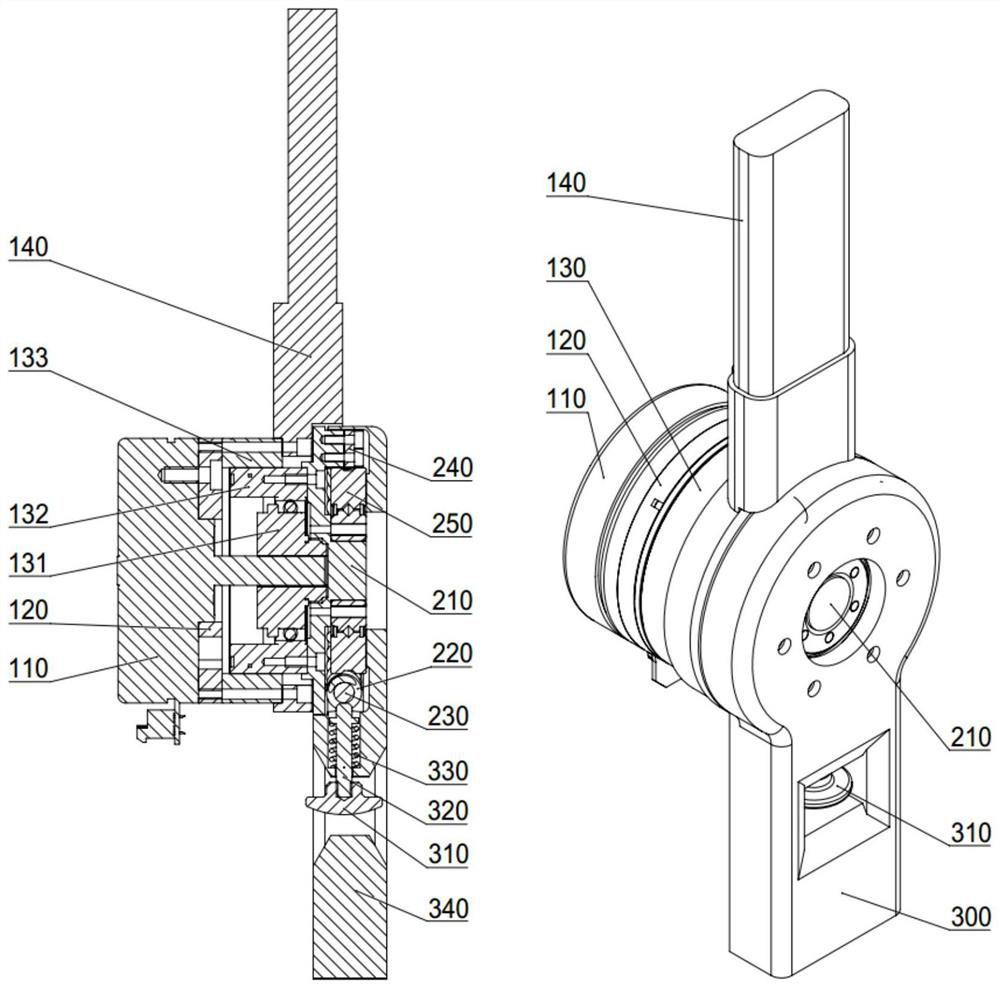
[0023] figure 1 It is a structural diagram of a robot flexible joint with variable stiffness in the present invention.
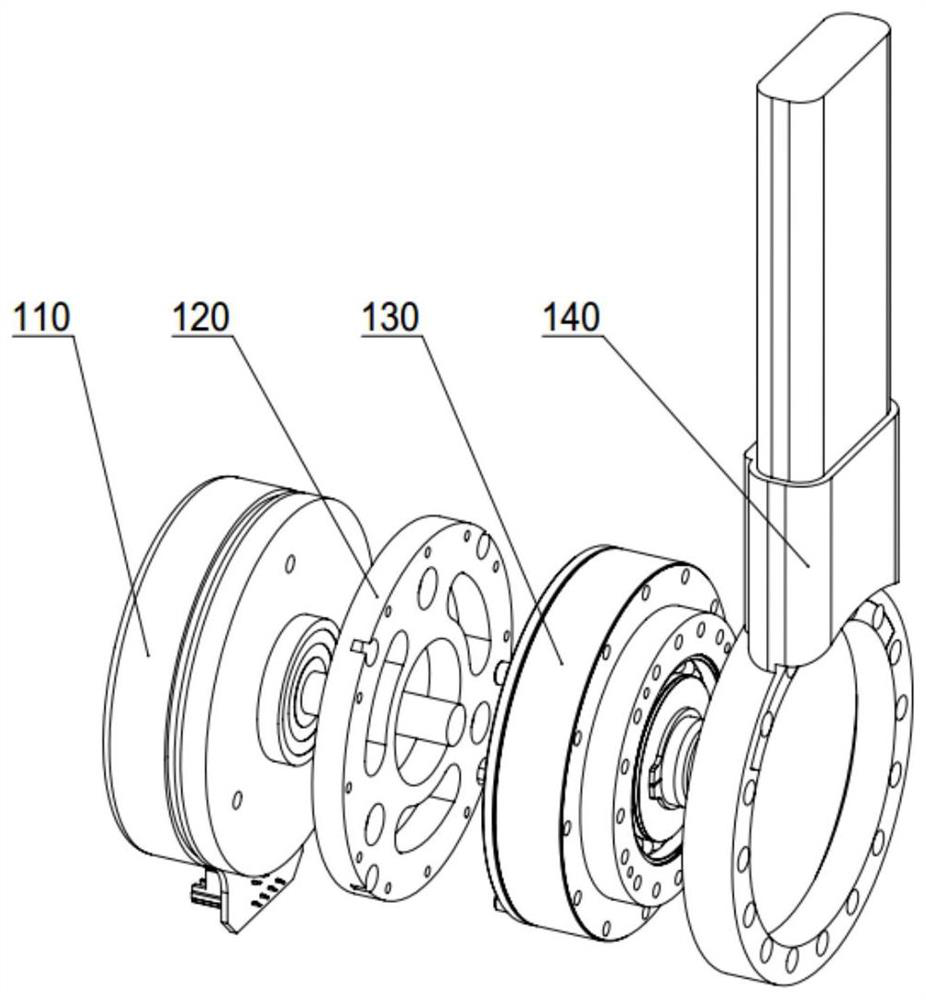
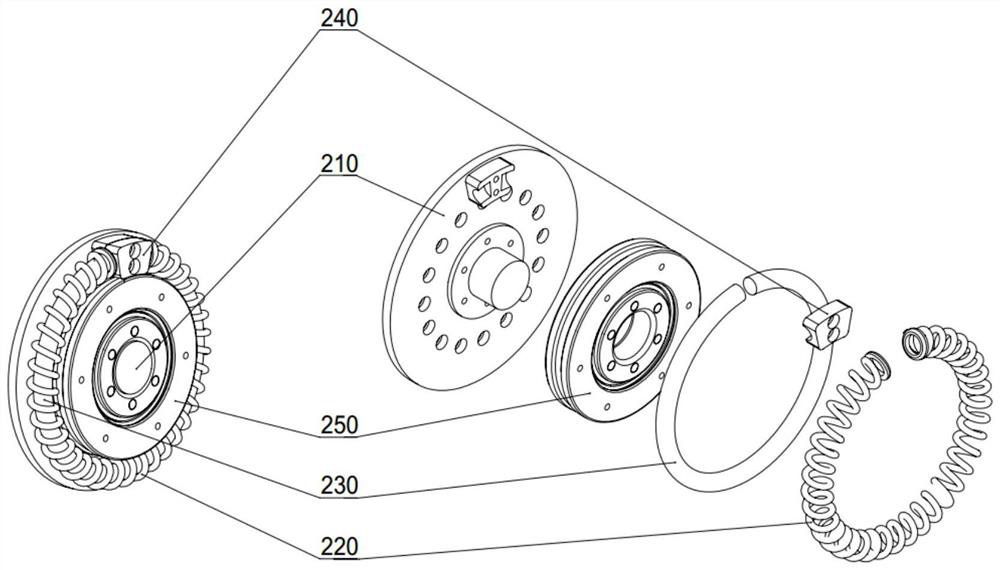
[0024] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, a robot flexible joint with variable stiffness in the present invention includes: a driving input group 100, a flexible module group 200, a stiffness adjustment and an output group 300; in this embodiment, the flexible module group 200 and the driving input group can be 100 is highly integrated, so that the volume of the flexible joint of the robot is small, and there is no complicated transmission mechanism between the two, which ensures the reliability and high transmission accuracy of the flexible joint of the robot;
[0025] Wherein, the output terminal of the driving input group 100 is connected with the input terminal of the flexible module group 200, such as figure 2 As shown, the drive input group 100 specifically includes a drive motor 110, a flange 120, a harmonic reducer 130 and an upper link 140; w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com