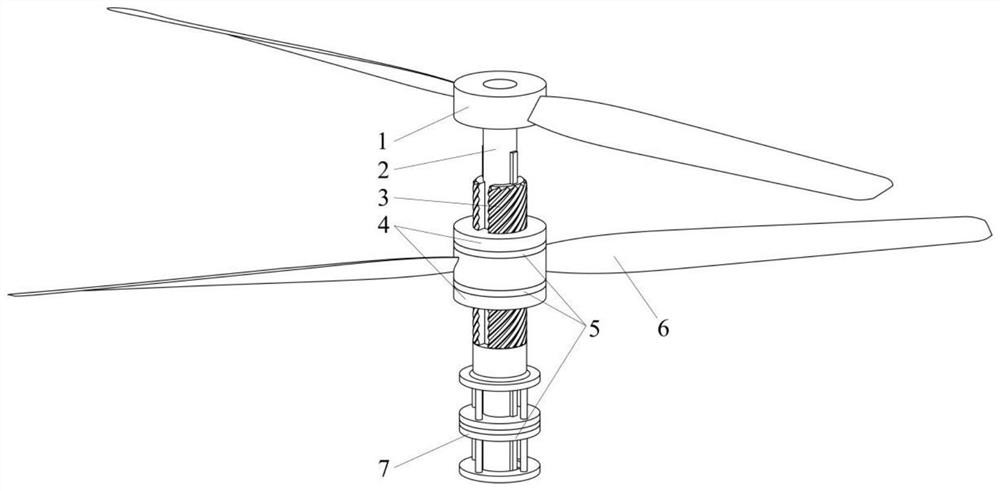
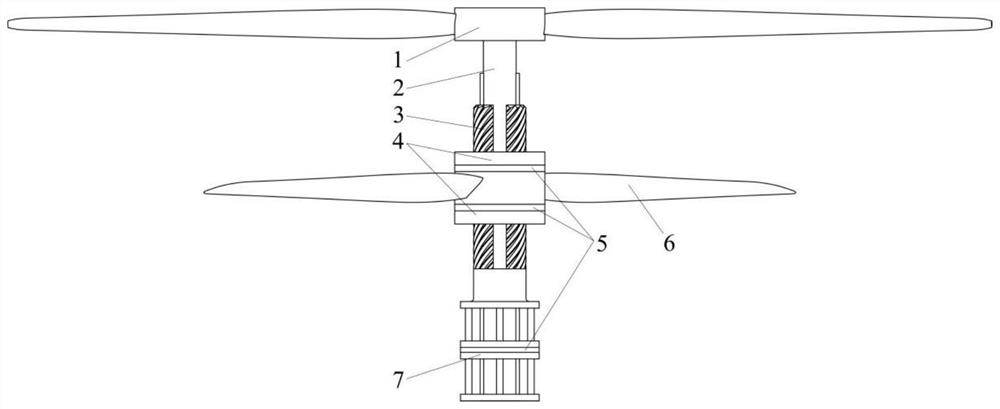
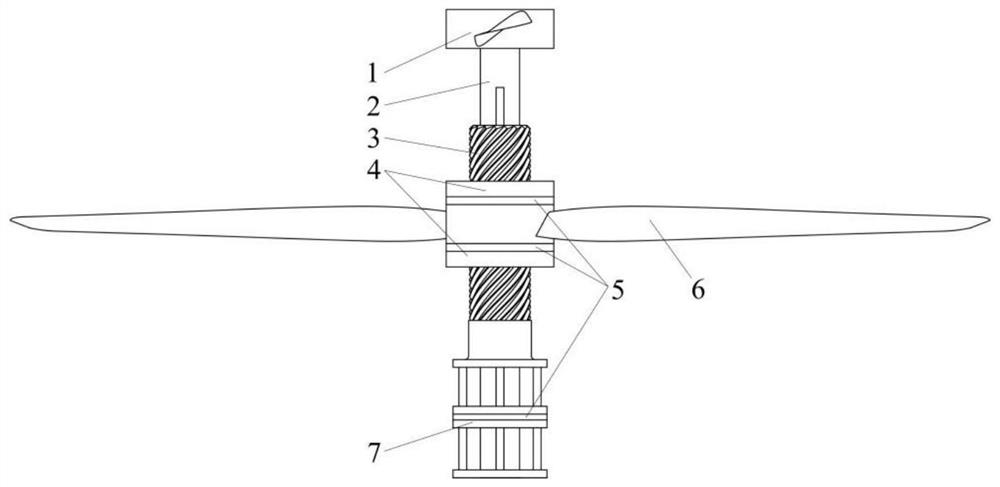
Coaxial homodromous propeller with variable phase difference
A technology of propeller and phase difference, which is applied in the direction of propeller, transportation and packaging, aircraft parts, etc., can solve the problems of propeller aerodynamic efficiency reduction, unfavorable dynamics, shortening the range of propeller aircraft, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] In order to understand the above-mentioned purpose, features and advantages of the present invention more clearly, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments of the present invention and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other.
[0035] In the following description, many specific details are set forth in order to fully understand the present invention. However, the present invention can also be implemented in other ways different from those described here. Therefore, the protection scope of the present invention is not limited by the specific details disclosed below. EXAMPLE LIMITATIONS.
[0036] The present invention proposes a propeller that uses coaxial rotation in the same direction, that is, two propellers with coincident rotating axes are arranged front and rear along the thrust di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com