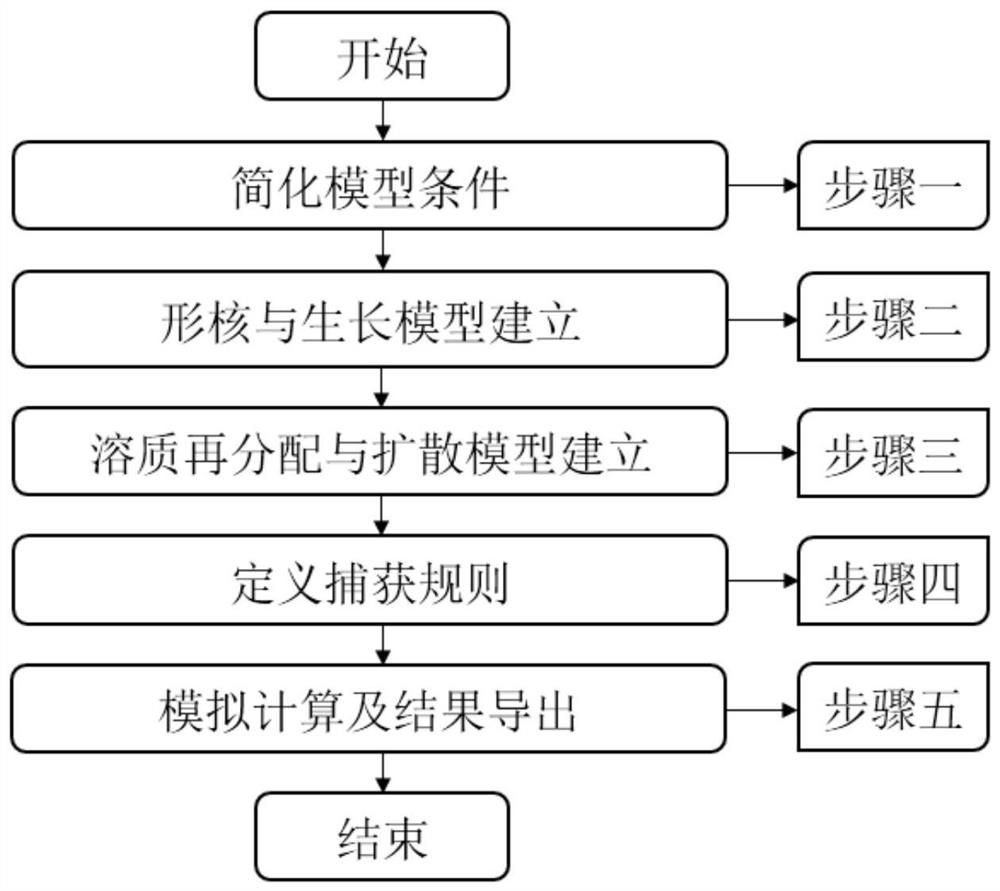
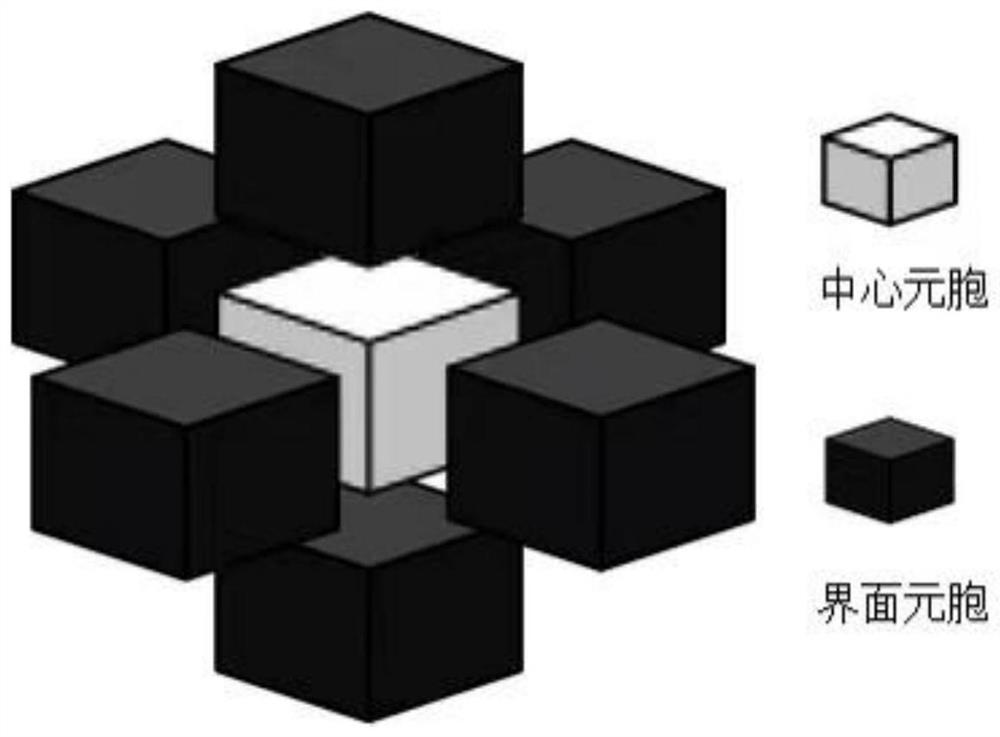
Three-dimensional numerical simulation method for grain growth in directional solidification process of titanium-aluminum alloy
A technology of directional solidification and grain growth, which is applied in the fields of chemical data visualization, instrumentation, computational theoretical chemistry, etc., can solve the problems that the three-dimensional numerical simulation model is not widely used, and achieve the effect of saving manpower and material resources and simplifying the solidification conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Input the various thermophysical parameters of the Ti-45%Al alloy in Table 1 into the programmed model of the present invention, and obtain the dendrite growth morphology of the Ti-45%Al alloy at different times through calculation, and the simulation results are as follows image 3 a, 3b shown. It can be seen that when the grains complete nucleation at the nucleation point, due to the specific temperature gradient, the main dendrites of the grains start to grow upwards, and at the same time some secondary dendrites are generated. The secondary dendrites of the grains form a tendency to hinder each other.
Embodiment 2
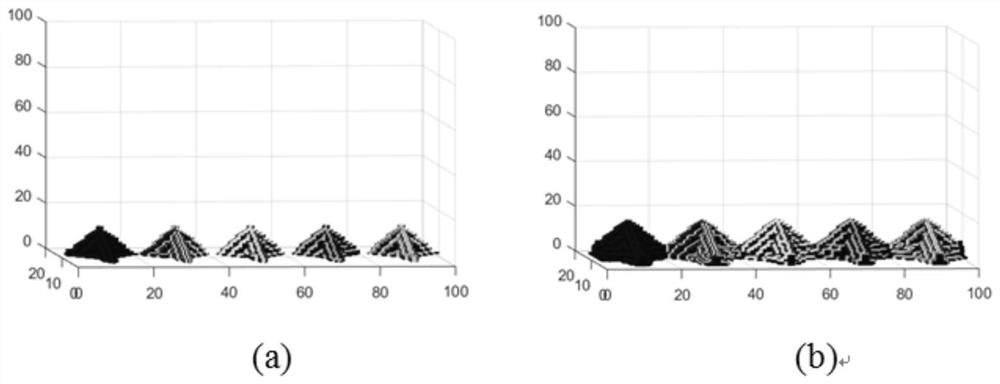
[0099] Input the thermophysical parameters of Table 1Ti-45%Al alloy in the model programmed by the present invention. Under the condition that other conditions are constant, the dendrite growth morphology when the disturbance amplitude is 0.2 and 2 respectively, the simulation results are as follows Figure 4 a, 4b shown. By comparison, it is found that with the increase of the disturbance amplitude when other conditions remain unchanged, the growth amplitude of the secondary dendrites is coarsened and the growth amplitude also decreases, but the growth spacing of the secondary dendrites does not change significantly.
Embodiment 3
[0101] Input the thermophysical parameters of Table 1Ti-45%Al alloy in the model programmed in the present invention, under the situation that other conditions are constant, the degree of supercooling is respectively 2 and 10 when the dendrite growth morphology simulation, the result Such as Figure 5 a, 5b shown. Through comparison, it can be found that when other conditions remain unchanged, as the degree of supercooling increases, the growth rate of dendrites also increases, and the growth rate of primary dendrites is the fastest. Dendrites grow successively, and the growth advantage of primary dendrites gradually disappears until it is replaced by the growth of secondary dendrites.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com