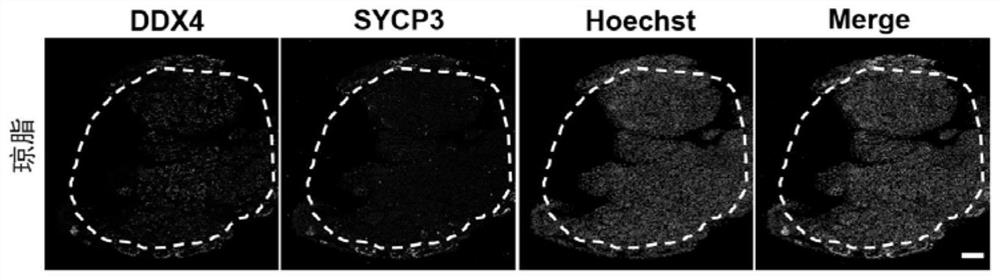
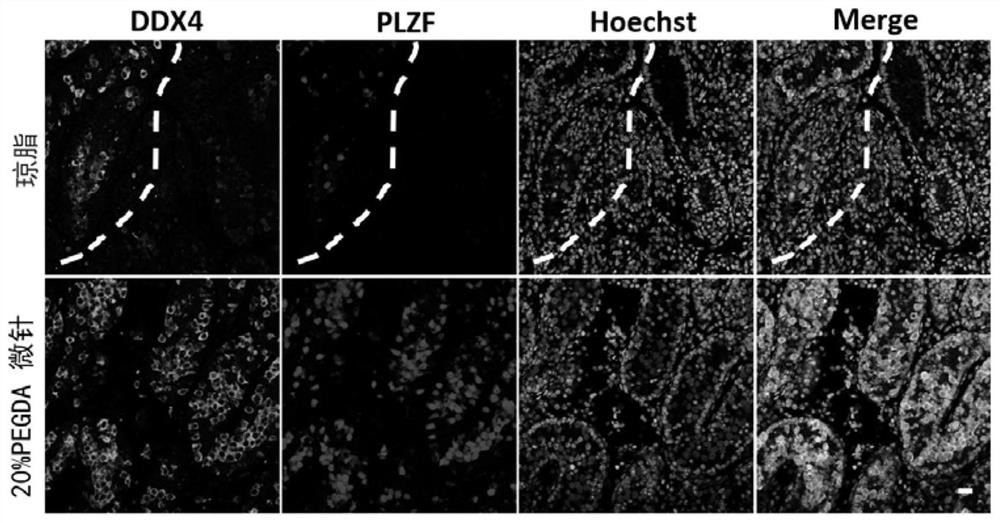
In vitro culture method and application of testicular tissue based on microneedles
A technology of in vitro culture and tissue culture, applied in the direction of tissue culture, culture process, cell culture active agent, etc., can solve the problem of inability to provide, and achieve the effect of promoting proliferation, improving tissue center death, and maintaining physiological structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1: A method for culturing testicular tissue in vitro to promote the proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells
[0063] This embodiment provides a method for cultivating testicular tissue in vitro to promote the proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells. The method is not a therapeutic method, comprising the following steps:
[0064] Establishment of the culture system: soak the PEGDA microneedles in the culture medium for replacement to obtain a culture system containing the replaced PEGDA microneedles and the culture medium;
[0065] Culture of testicular tissue: add the isolated testicular tissue after removing the capsule to the culture system for cultivation, so that the spermatogonial stem cells in the isolated testicular tissue proliferate;
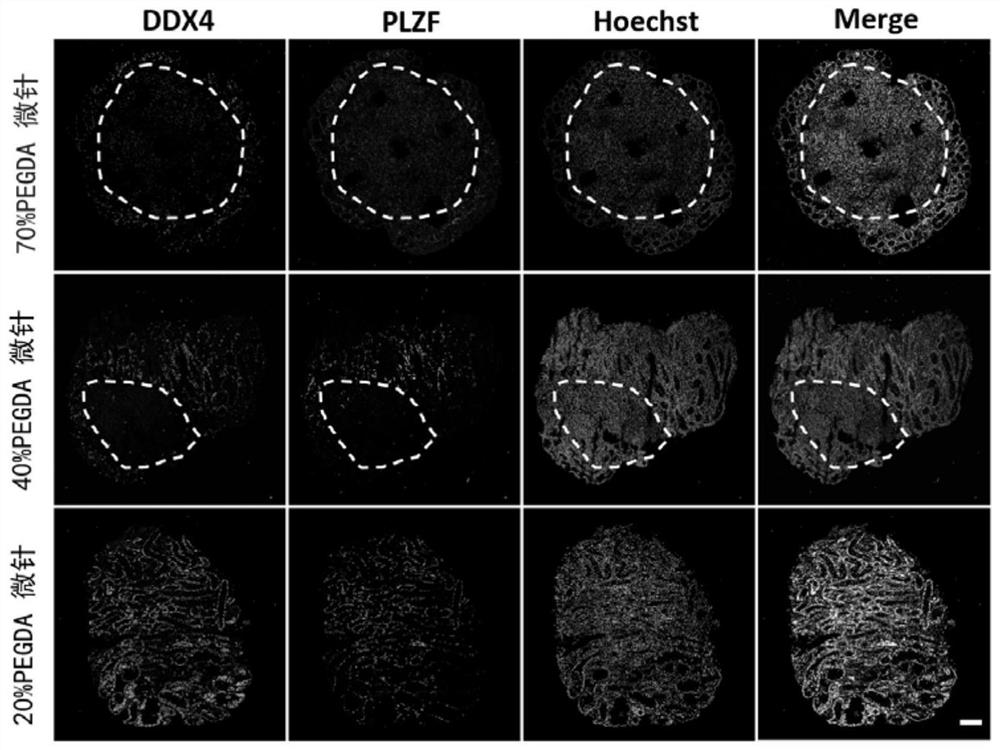
[0066] The PEGDA microneedle is a PEGDA microneedle prepared by using PEGDA with a volume fraction of 20%;
[0067] The soaking is: soaking at a temperature of 34°C for 24 hours;
[0068] The culture medium is a c...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2: A method for culturing testicular tissue in vitro to promote the proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells
[0074] This embodiment provides a method for cultivating testicular tissue in vitro to promote the proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells. The method is not a therapeutic method, comprising the following steps:
[0075] Establishment of the culture system: soak the PEGDA microneedles in the culture medium for replacement to obtain a culture system containing the replaced PEGDA microneedles and the culture medium;
[0076] Culture of testicular tissue: add the isolated testicular tissue after removing the capsule to the culture system for cultivation, so that the spermatogonial stem cells in the isolated testicular tissue proliferate;
[0077] The PEGDA microneedle is a PEGDA microneedle prepared by using PEGDA with a volume fraction of 40%;
[0078] The soaking is: soaking for 12 hours at a temperature of 37°C;
[0079] The medium is SSC medium;...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3: A method for culturing testicular tissue in vitro to promote the proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells
[0085] This embodiment provides a method for cultivating testicular tissue in vitro to promote the proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells. The method is not a therapeutic method, comprising the following steps:
[0086] Establishment of the culture system: soak the PEGDA microneedles in the culture medium for replacement to obtain a culture system containing the replaced PEGDA microneedles and the culture medium;
[0087] Culture of testicular tissue: add the isolated testicular tissue after removing the capsule to the culture system for cultivation, so that the spermatogonial stem cells in the isolated testicular tissue proliferate;
[0088] The PEGDA microneedle is a PEGDA microneedle prepared by using PEGDA with a volume fraction of 70%;
[0089] The soaking is: soaking at a temperature of 32°C for 20 hours;
[0090] The culture medium is a c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com