Peronospora resistance in spinacia oleracea
A technology of spinach and resistance, which is applied in the field of spinach plants to produce spinach plants carrying the gene, and can solve the problems of poor knowledge of the R gene
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Testing Spinach Plants for Resistance to Downy mildew spinach specific
[0090] Resistance to downy mildew infection was determined using differential sets as described by Irish et al. (2008; Phytopathol. 98:894-900). Spinach plants of the present invention were sown together with spinach plants from various other genotypes (see Table 3) in trays containing Scotts Redi-Earth medium and fertilized with Osmocote Peter's (13-13-13) fertilizer after emergence of seedlings ( Scotts) fertilized twice a week. The plants were inoculated with the sporangia suspension (2.5×10 5 / ml). In this way, 4 officially recognized pathogenic races were tested.
[0091] The inoculated plants were placed in a dew room at 18°C with 100% relative humidity for 24 hours and then moved to a growth chamber at 18°C with a 12 hour photoperiod for 6 days. After 6 days, plants were returned to the open room for 24 h to induce sporulation and scored for disease response.
[0092] Plants used for...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Amplification of LRR domain coding regions
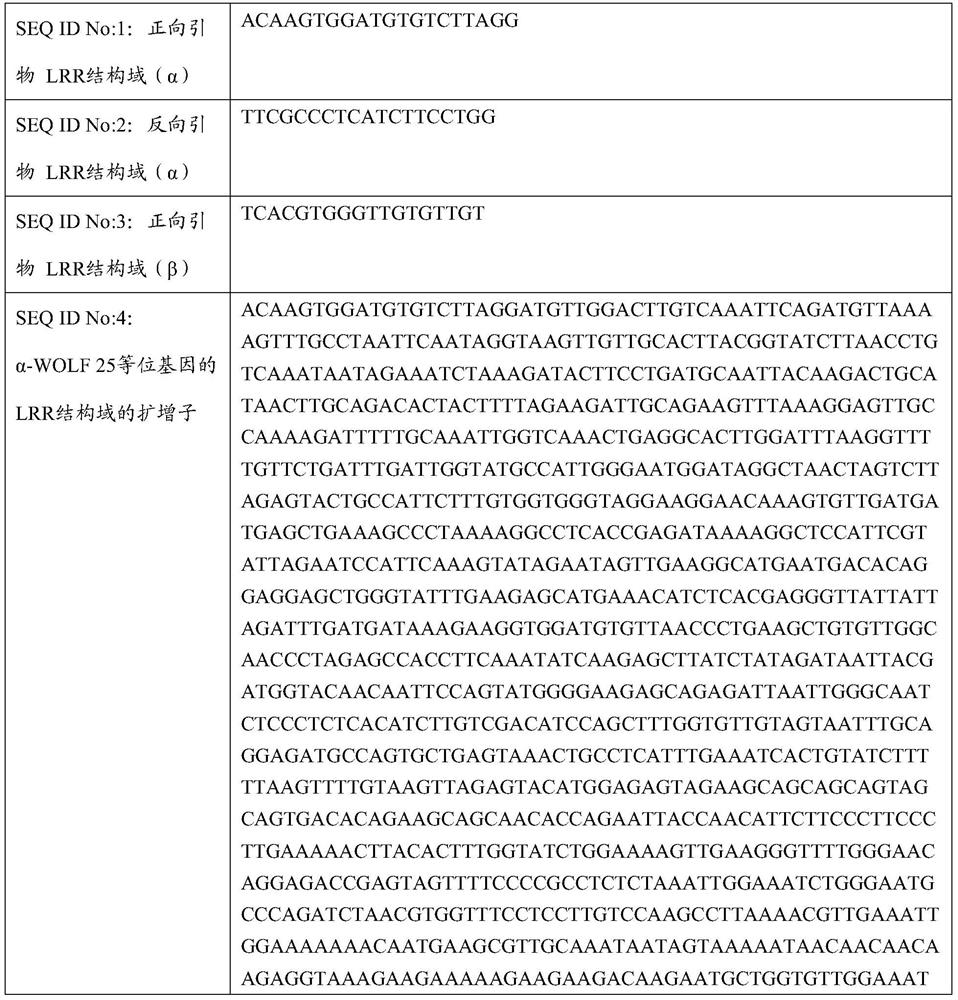
[0099] Using the forward primer ACAAGTGGATGTGTCTTAGG (SEQ ID No: 1) and the reverse primer TTCGCCCTCATCTTCCTGG (SEQ ID No: 2), isolated genomic DNA of spinach plants containing the α-WOLF 25 allele (representative samples of their seeds are given in NCIMB Accession No. 43495 (deposited at NCIMB) for polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The primer pair amplifies the LRR domain coding region of the α-WOLF gene and was designed to selectively amplify portions of the WOLF gene but not other CC-NBS-LRR protein-coding genes.
[0100] The PCR conditions for amplifying the LRR domain coding region of the α-WOLF gene using primers having SEQ ID No: 1 and SEQ ID No: 2 are as follows, using Platinum Taq enzyme (Thermo Fisher Scientific):
[0101] - 3 minutes at 95°C (initial denaturation step)
[0102] - 40 amplification cycles, each consisting of: denaturation at 95°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 60°C for 30 seconds, and extension at 72°...
Embodiment 3
[0117] Introduction of the α-WOLF 25 allele in plants that do not carry the allele
[0118] Spinach plants containing the α-WOLF 25 allele (a representative seed sample of which was deposited with NCIMB under NCIMB accession number 43495) were crossed with plants of the variety Viroflay carrying the β-WOLF 0 allele to obtain the F1 generation. Subsequently, F1 plants were selfed to obtain F2 populations.
[0119] Plants of the F2 population were assayed for resistance to Peronola farinae Pfs:16 as described in Example 1. In the assay, approximately 75% of the plants scored as fully resistant. This segregation pattern is consistent with that of dominant inheritance.
[0120] Genomic DNA from each plant of the same F2 population was isolated and used in two different polymerase chain reactions (PCR). The first PCR reaction was performed using primers for amplifying the LRR domain of the α-WOLF allele, and the second PCR reaction was performed using primers for amplifying the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com