Compositions and methods for targeting anti-TNF-alpha antibodies
An anti-drug antibody, monoclonal antibody technology, applied in the direction of antibody mimics/stents, antibody medical components, introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the dose or frequency of administration, and impairing the clinical response of anti-TNA-α antibodies Adverse events, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0150] Example 1. Expression of CADAR in human primary T cells.
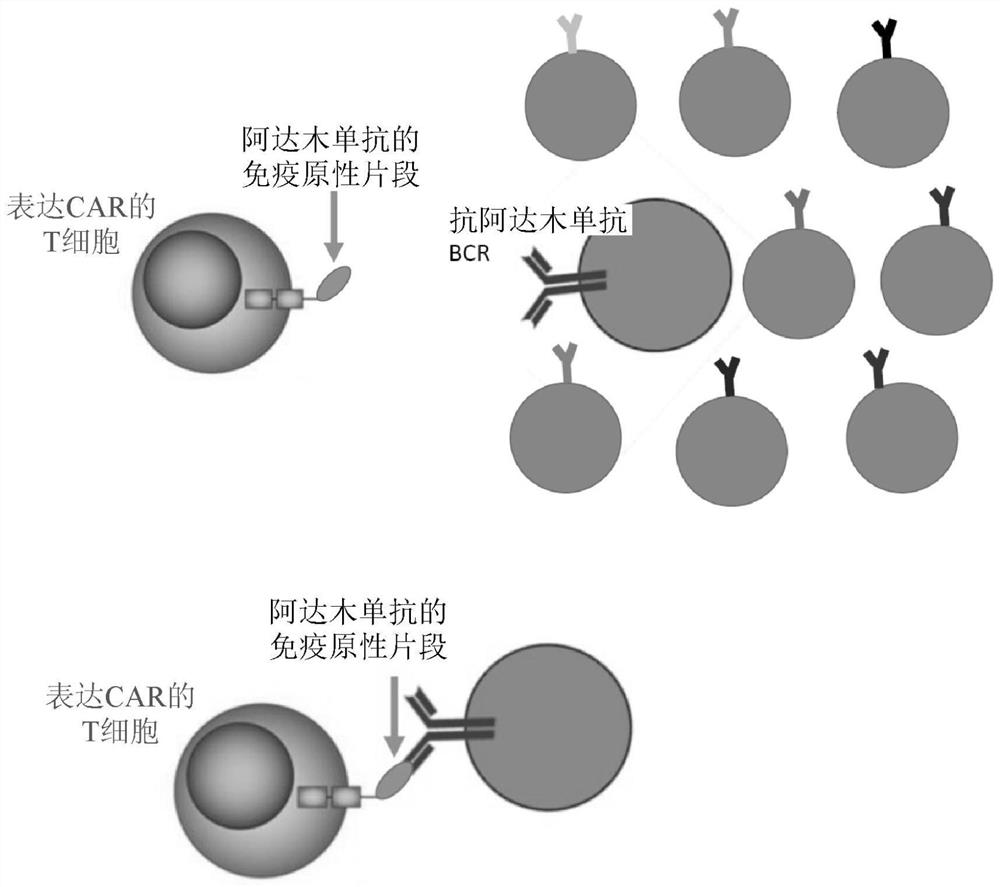
[0151] A transfer plasmid including the DNA sequence encoding CADAR was designed and synthesized (see the schematic diagram of the structure in figure 2 ), which sequence comprises a scFv derived from adalimumab (scFv-ADL) (Genewiz, NJ). The transfer plasmid was then used to generate VSV-G pseudotyped lentiviral particles using a generation 4 packaging system. Briefly, 293T cells were transfected at 80% confluency with a mixture of transfer plasmid, envelope plasmid, packaging plasmid and Lipofectamine 30000 (Life Technologies). The lentivirus-containing supernatant was harvested after 49 h, filtered through a 0.45 μm PES membrane, concentrated at 1500 × g for 45 min at 4°C, and stored at -80°C.
[0152] Human PBMCs from healthy donors were activated with CD3 / CD28 Dynabeads (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at a 1:1 cell / bead ratio for 24 hours. 2E+6 T cells were transduced with lentiviral particles. T cells were ...
Embodiment 2
[0153] Example 2. In vitro efficacy test of CADAR-T cells.
[0154] Anti-adalimumab (ADL) hybridoma cells were generated by immunizing Balb / c mice with purified scFv-ADL protein. B lymphocytes from mouse spleen fused with myeloma cells. Positive hybridoma clones were screened by three rounds of ELISA. One positive (expressing antibodies against ADL) and one negative (not expressing antibodies against ADL) hybridoma cells in XF T supplemented with 50 U / ml IL-2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 10% FBS (Gibco) Cell expansion medium (STEMCELL Technologies) cultured. Change the medium every 1 to 2 days.
[0155] Positive and negative hybridoma cells were first stained with CFSE (CellTrace, Cat# C34554). 1E+4 hybridoma cells / well were stained with CFSE (2.5 μM) for 10 min at 37°C, washed twice and resuspended in a medium supplemented with 50 U / ml IL-2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 10% FBS (Gibco) XF T cell expansion medium (STEMCELL Technologies).
[0156] CADAR-T cells (8 days...
Embodiment 3
[0162] Example 3. In vivo efficacy test of CADAR-T cells
[0163] After pretreating the mice with intravenous immunoglobulin to minimize FcyR-mediated toxicity against BCR-expressing cells, positive or negative hybridoma cells were injected intravenously into NSG mice. A few days later, CADAR-T cells (or mock T cells) were injected intravenously. Bioluminescence and / or serum ADA were quantified to monitor CADAR-T cell efficacy. CADAR-T cells controlled the growth of positive but not negative hybridoma cells, while mock T cells did not control the growth of positive or negative hybridoma cells.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com