Shutdown purging method and device for fuel cell stack
A technology of fuel cell stacks and fuel cells, which is applied in the direction of fuel cells, circuits, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as failure to effectively eliminate modal water in proton exchange membranes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
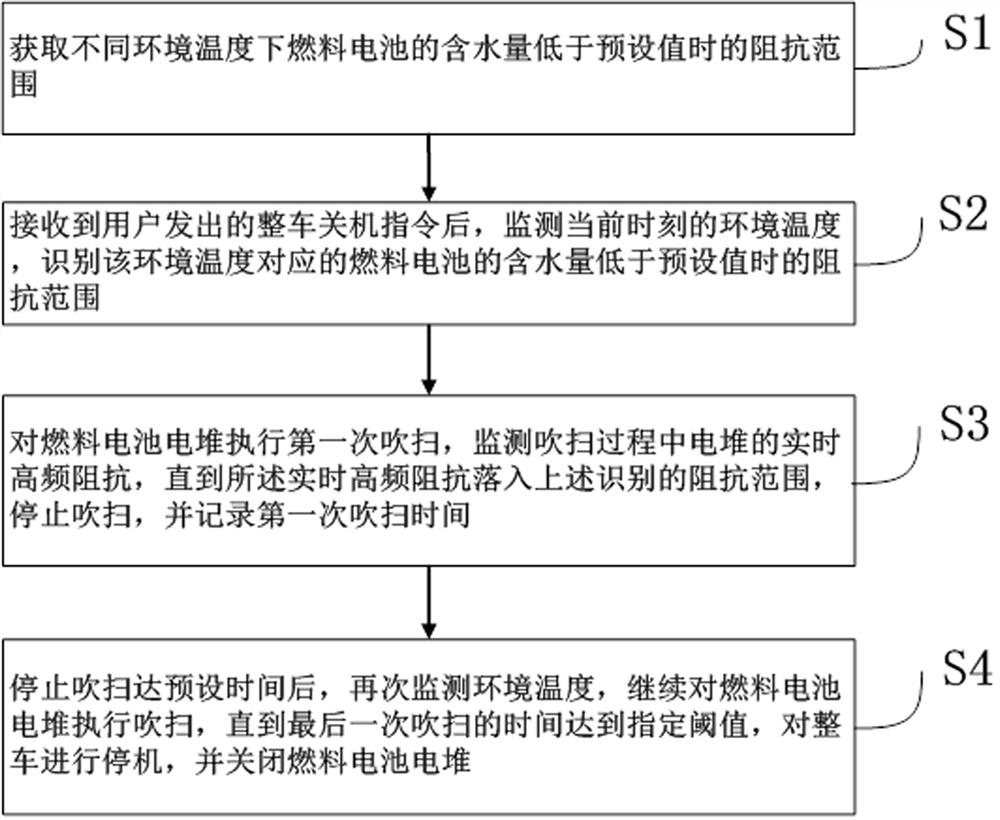
[0064] One embodiment of the present invention discloses a method for shutting down and purging a vehicle-mounted fuel cell, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0065] S1. Obtain the impedance range when the water content of the fuel cell is lower than the preset value at different ambient temperatures;
[0066] S2. After receiving the vehicle shutdown command from the user, monitor the ambient temperature at the current moment, and identify the impedance range when the water content of the fuel cell corresponding to the ambient temperature is lower than the preset value;
[0067] S3. Perform the first purging of the fuel cell stack, monitor the real-time high-frequency impedance of the stack during the purging process, until the real-time high-frequency impedance falls into the above-identified impedance range, stop purging, and record the first Second purge time;
[0068] S4. After stopping the purge for the preset time, monitor the ambient temperature...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Optimizing on the basis of Example 1, the step S1 further includes:
[0073] S11. Obtain data samples of fuel cell stacks including different ambient temperatures, impedances, and battery life;
[0074] S12. Fit the above data samples, and determine the function curve of ambient temperature-impedance-battery life by the best approximation method;
[0075] S13. Through the above function curve, determine the impedance range corresponding to the rated life to the maximum life of the fuel cell at each ambient temperature, as the impedance range when the water content is lower than the preset value.
[0076] Preferably, step S2 further includes:
[0077] S21. After receiving the vehicle shutdown command from the user, monitor the current ambient temperature through the temperature sensor arranged in the vehicle compartment;
[0078] S22. Identify the impedance range corresponding to the above ambient temperature when the water content is lower than the preset value, and o...
Embodiment 3
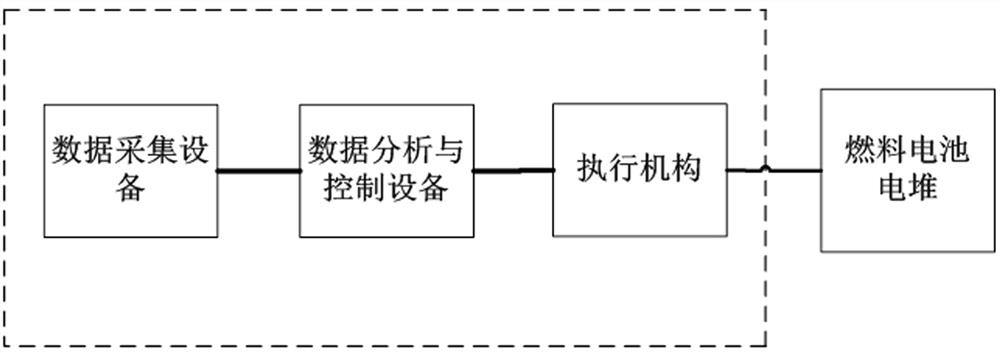
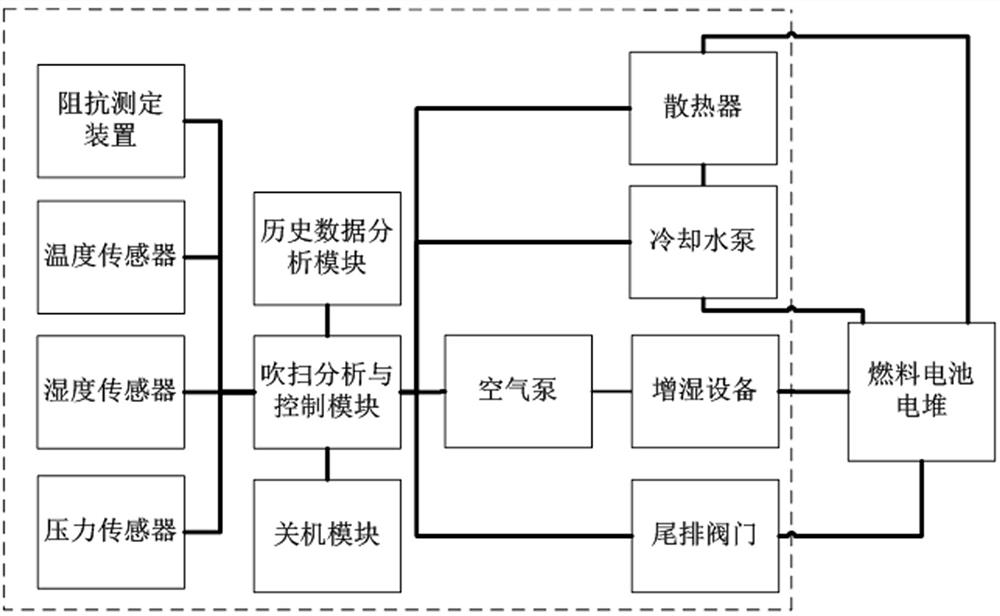
[0089] The present invention also discloses a vehicle-mounted fuel cell shutdown purging device corresponding to Embodiment 1, including data acquisition equipment, data analysis and control equipment, and actuators that are sequentially connected or wirelessly transmitted, such as figure 2 shown.
[0090] The data acquisition device is used to collect the real-time high-frequency impedance of the fuel cell stack and the ambient temperature in the vehicle compartment, and send them to the data analysis and control equipment.
[0091] The data analysis and control equipment is used to obtain the impedance range when the water content of the fuel cell is lower than the preset value under different ambient temperatures; The impedance range when the water content of the battery is lower than the preset value; the control actuator performs the first purge of the fuel cell stack, and monitors the real-time high-frequency impedance of the stack during the purge until the real-time h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com