Phase locked loop circuit
A phase-locked loop and circuit technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, automatic power control, etc., can solve problems such as the increase in the number of terminals and the increase in circuit size.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
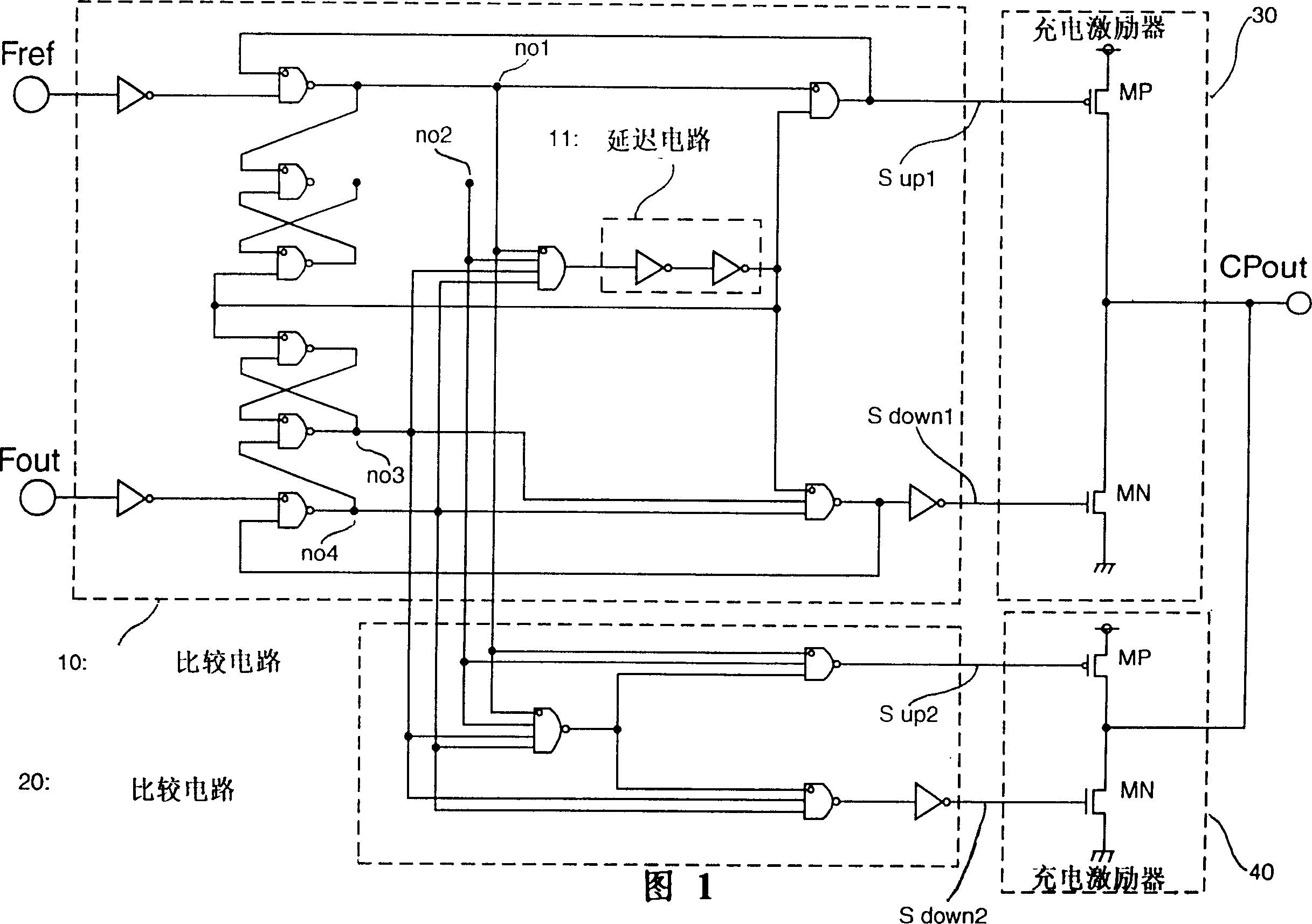
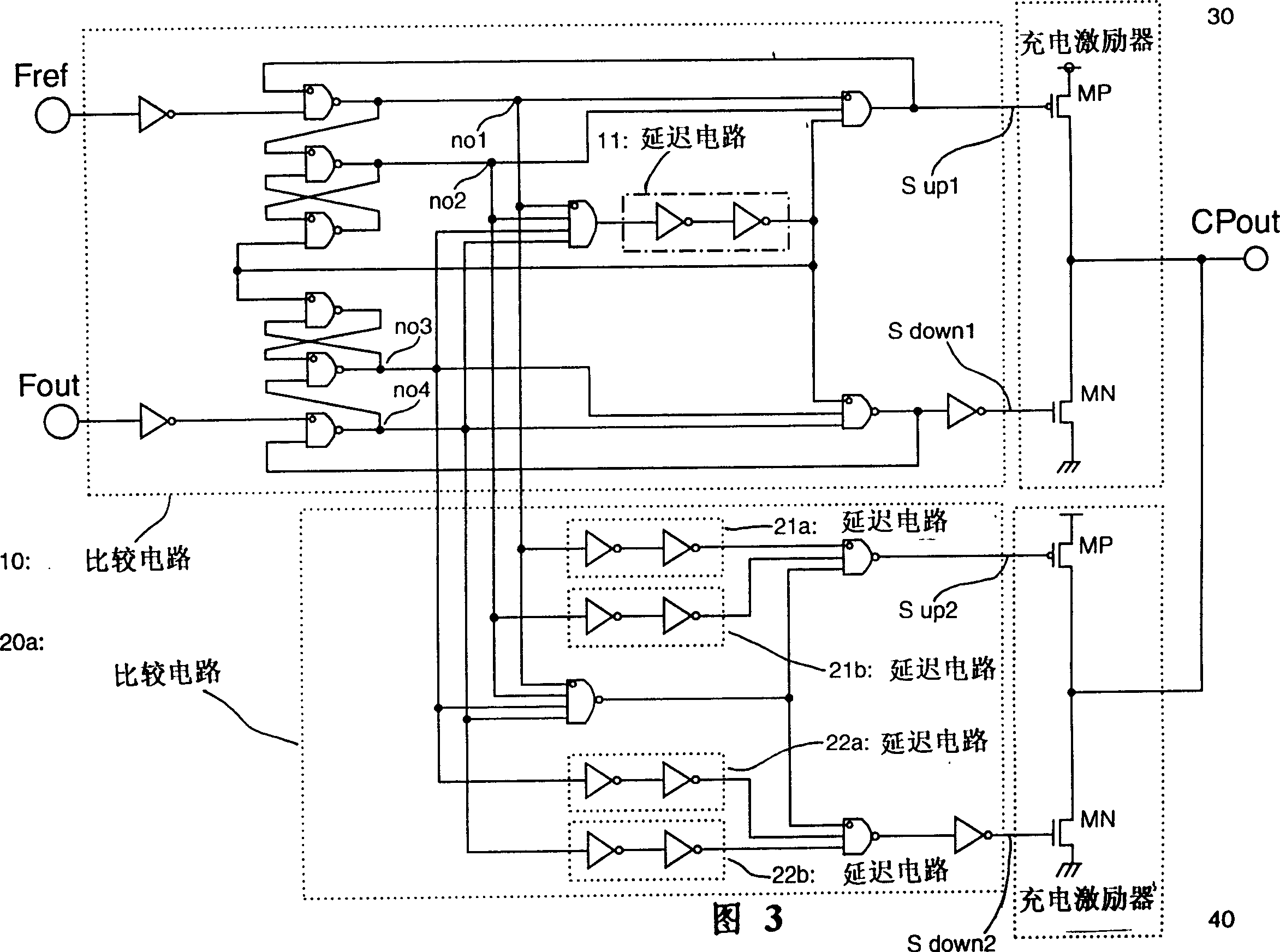
[0052] The present invention will be described below. FIG. 1 is a schematic structural connection diagram of an example of a PLL circuit according to a first embodiment of the present invention. It can be seen that the structure of the feedback circuit of the PLL circuit adopted by the embodiment of the present invention is similar to the conventional one, so the diagram and detailed description of the feedback circuit are omitted.
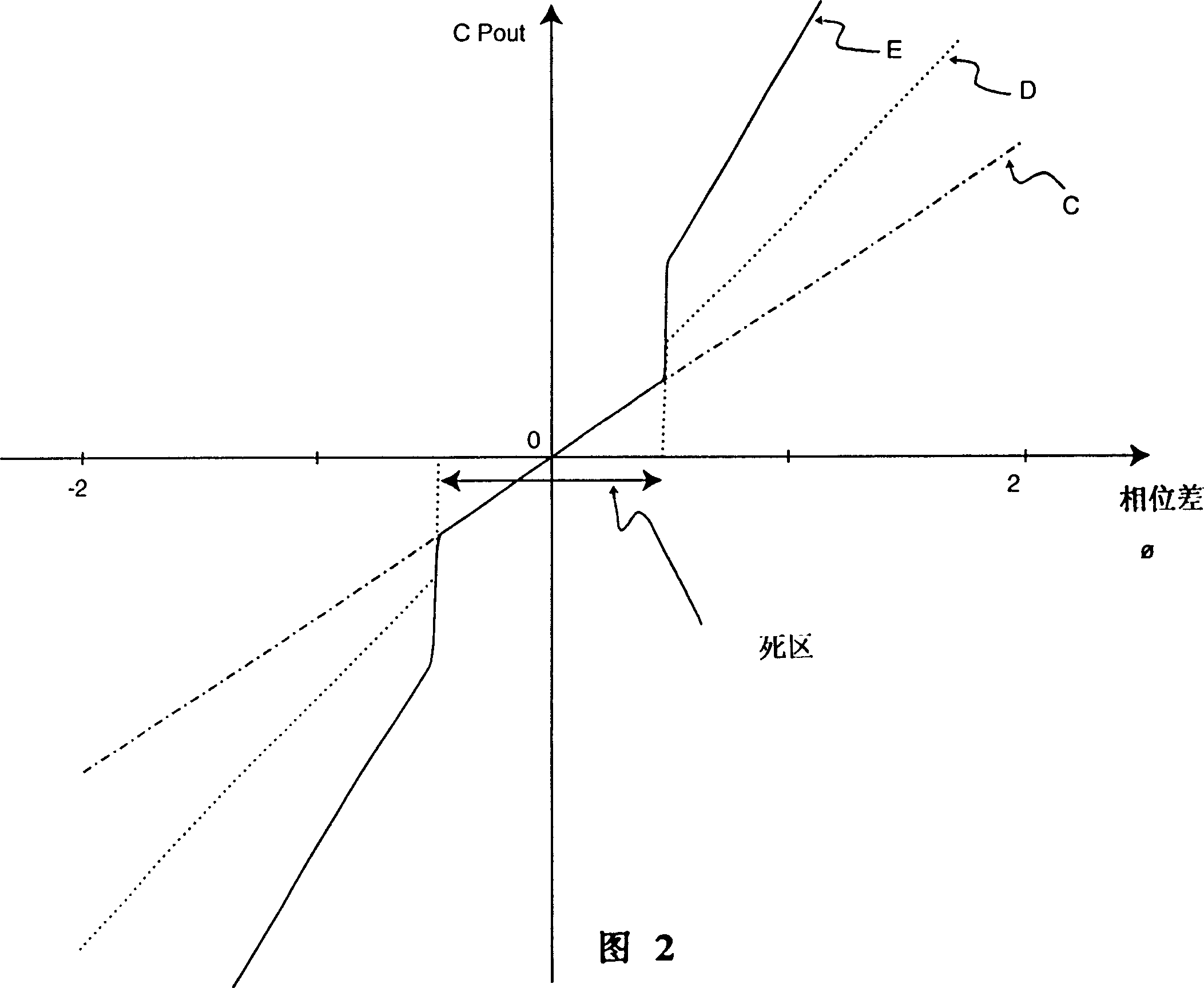
[0053] In FIG. 1, reference numerals 10 and 20 denote comparison circuits. Among these comparison circuits, the comparison circuit 10 has the characteristic of having no dead zone, and the oscillation signal F output from a voltage-controlled oscillator (not shown) out is input to the compare circuit.
[0054] These comparison circuits, comparison circuits 10 and 20 are circuits using logic gates and FF (flip-flop) circuits and similar circuits, as in US Patent 4,281,259 and IEEE Document, Volume CE-27, No. 3, pp. As shown in the August edition...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com