Self-adaptive scene marking high-precision geographic information calculation method
A technology of geographic information and calculation methods, applied in calculation, image data processing, 3D image processing, etc., can solve problems such as increased target calculation errors, inapplicable pictures taken at daily angles, and high requirements for two-dimensional directional map pictures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
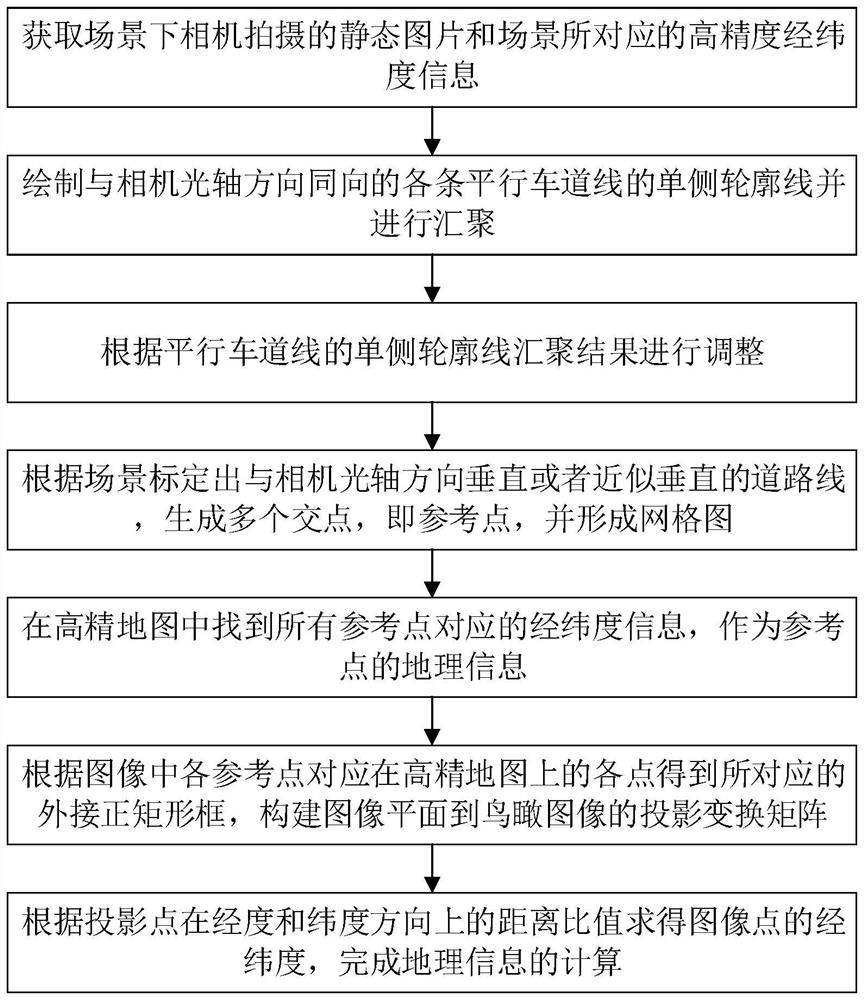
[0043] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described in detail below through embodiments and in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Embodiment: a high-precision geographic information calculation method for adaptive scene marking of this embodiment, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
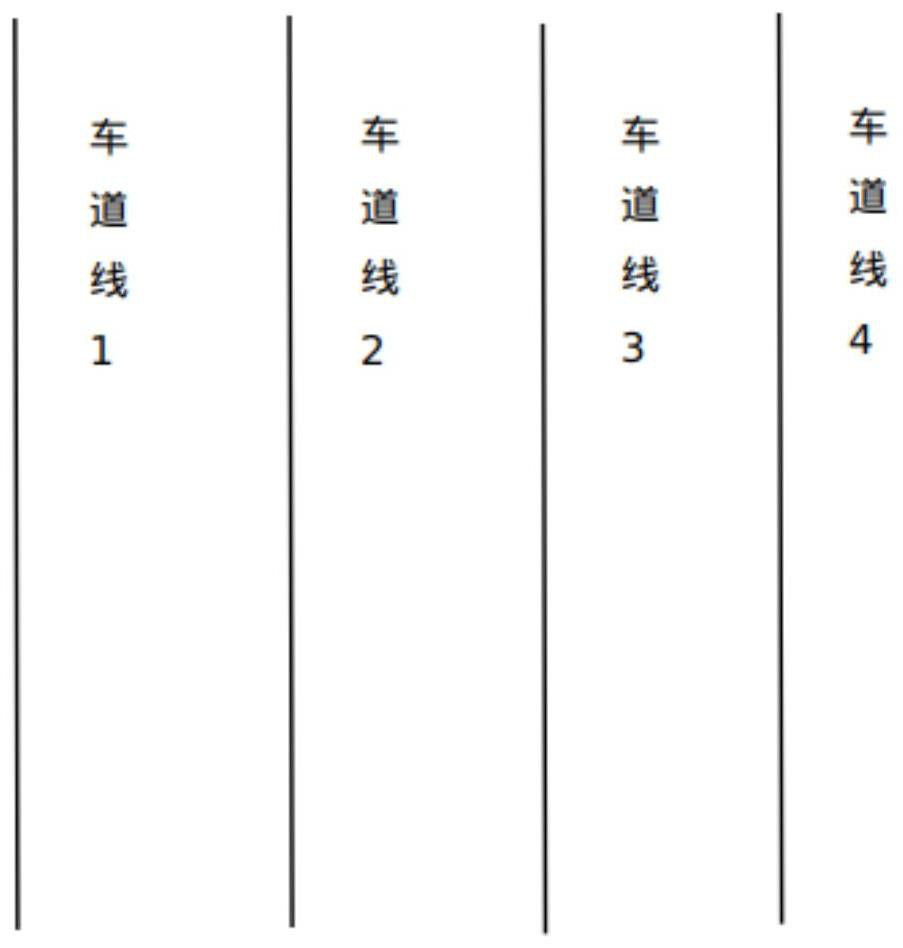
[0044] S1 acquires a still picture captured by a camera in a scene and high-precision latitude and longitude information corresponding to the scene. Step S1 obtains the static picture taken by the camera in the scene, and marks three or more parallel lane lines or at least two points on the unilateral contour of the line parallel to the lane line, and at least two points on the unilateral contour of the line parallel to the lane line, and the non-parallel to the lane line by manual method or detection algorithm detection method. , but conveniently marked straight lines in the image, such as figure 2 shown.
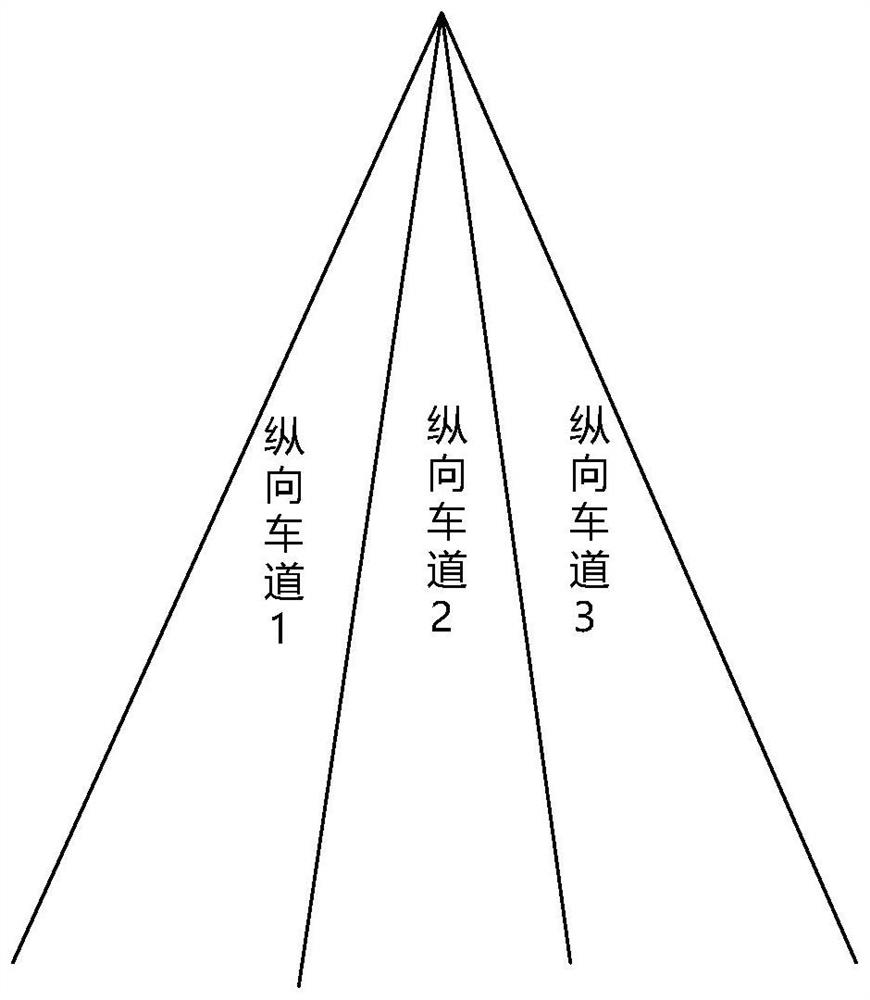
[0045] S2 draws the unilate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com