Pulse recognition method and device, storage medium, equipment and blood cell analyzer
An identification method and pulse technology, applied in measuring devices, analysis materials, individual particle analysis, etc., can solve the problems of abnormal measured values, increased costs, and high requirements for optical components, and achieve the effects of increasing costs, improving accuracy, and saving resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
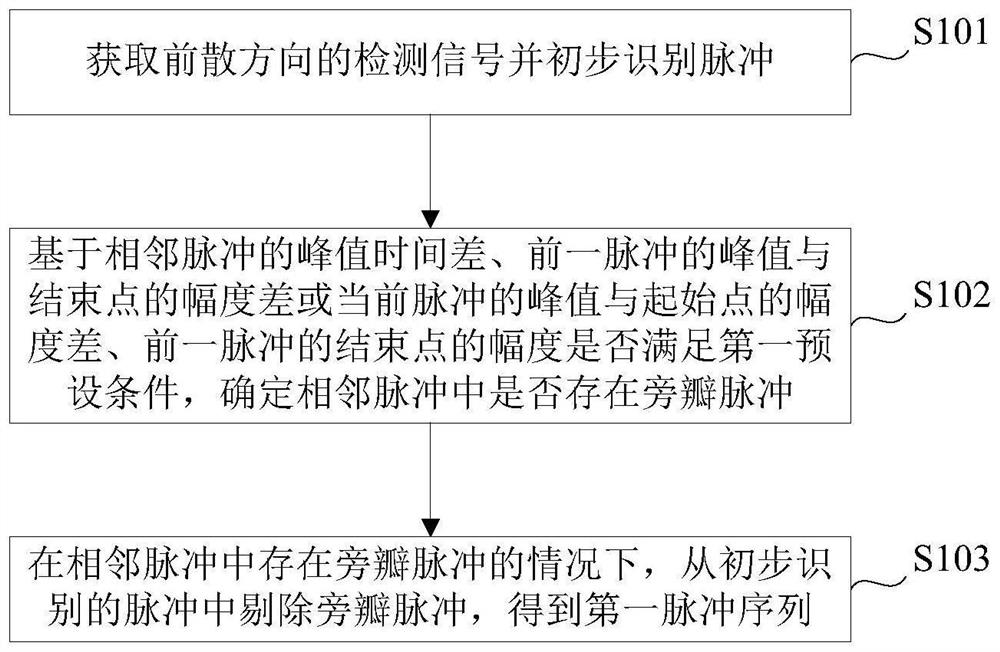
[0057] figure 1 A flow chart of a pulse identification method is shown, such as figure 1 As shown, the pulse identification method provided in this embodiment includes steps S101 to S103:
[0058] Step S101 , acquiring the detection signal of the forward dispersion direction and preliminarily identifying the pulse.
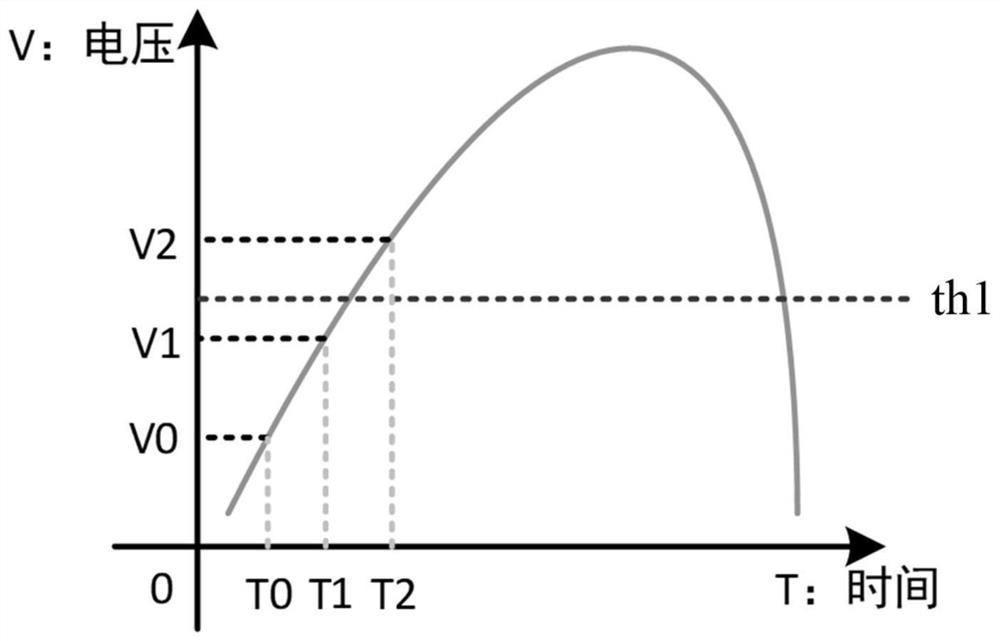
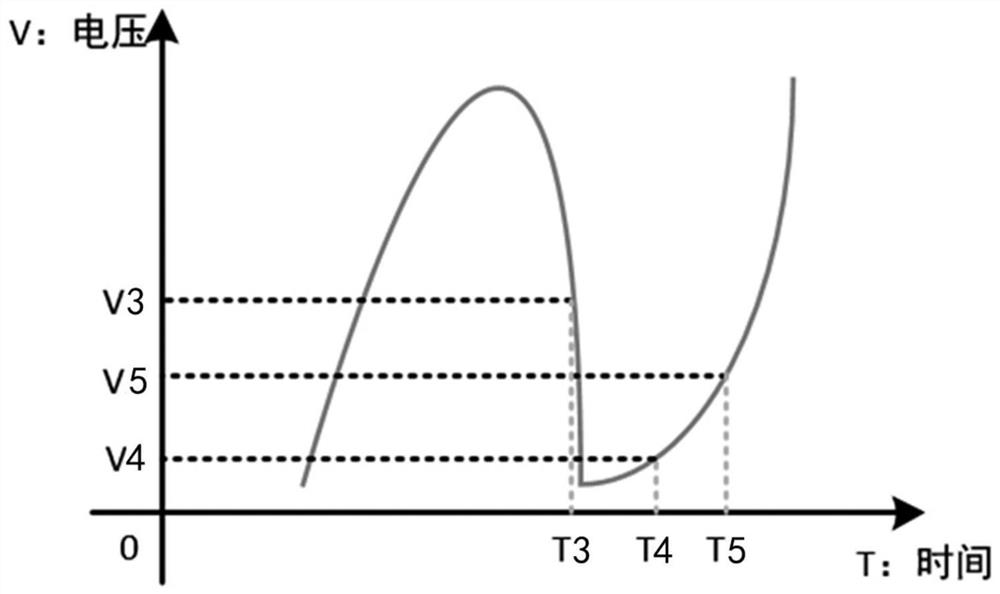
[0059] Step S102, based on whether the peak time difference of adjacent pulses, the amplitude difference between the peak value of the previous pulse and the end point or the amplitude difference between the peak value and the start point of the current pulse, and the amplitude of the end point of the previous pulse meet the first preset condition, Determine whether there are sidelobe pulses in adjacent pulses;
[0060] Step S103 , in the case that there are side lobe pulses in adjacent pulses, remove the side lobe pulses from the preliminarily identified pulses to obtain a first pulse sequence.
[0061] In this embodiment, the detection signal in the forward s...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Figure 12 A block diagram of a pulse identification device is shown, such as Figure 12 As shown, this embodiment provides a pulse identification device, including:
[0108] The pulse identification module 201 is used to acquire the detection signal of the forward dispersion direction and initially identify the pulse;
[0109] The side lobe removal module 202 is used for whether based on the peak time difference of adjacent pulses, the amplitude difference between the peak value of the previous pulse and the ending point or the amplitude difference between the peak value and the starting point of the current pulse, and the amplitude of the ending point of the previous pulse. A preset condition is to determine whether there are side lobe pulses in adjacent pulses; if there are side lobe pulses in adjacent pulses, remove the side lobe pulses from the preliminarily identified pulses to obtain a first pulse sequence.
[0110] In this embodiment, the detection signal in t...
Embodiment 3
[0136] This embodiment provides a computer-readable storage medium. The computer-readable storage medium stores a computer program. When the computer program is executed by one or more processors, the pulse identification method provided in the first embodiment is implemented.
[0137] In this embodiment, the storage medium may be implemented by any type of volatile or nonvolatile storage device or a combination thereof, such as static random access memory (Static Random Access Memory, SRAM for short), electrically erasable programmable Read-Only Memory (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory, EEPROM for short), Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EPROM for short), Programmable Read-Only Memory (PROM for short) ), read-only memory (Read-Only Memory, ROM for short), magnetic memory, flash memory, magnetic disk or optical disk. The content of the method is detailed in Embodiment 1, which will not be repeated this time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com