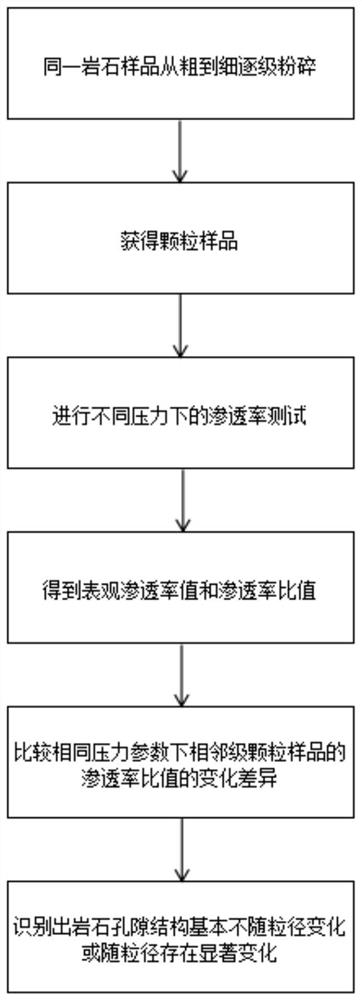
Method for judging whether rock pore structure changes along with particle size
A pore structure and particle size technology, applied in the field of petroleum scientific research, can solve the problems of no one-to-one correspondence, non-reusable, difficult to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the characteristics of rock pore structure with size and its representative scale
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] The following describes the procedure and results of our use of this method on two shale samples. The apparent densities measured for the two rock samples are shown in Table 1.
[0059] Table 1 Basic parameters of rock samples
[0060]
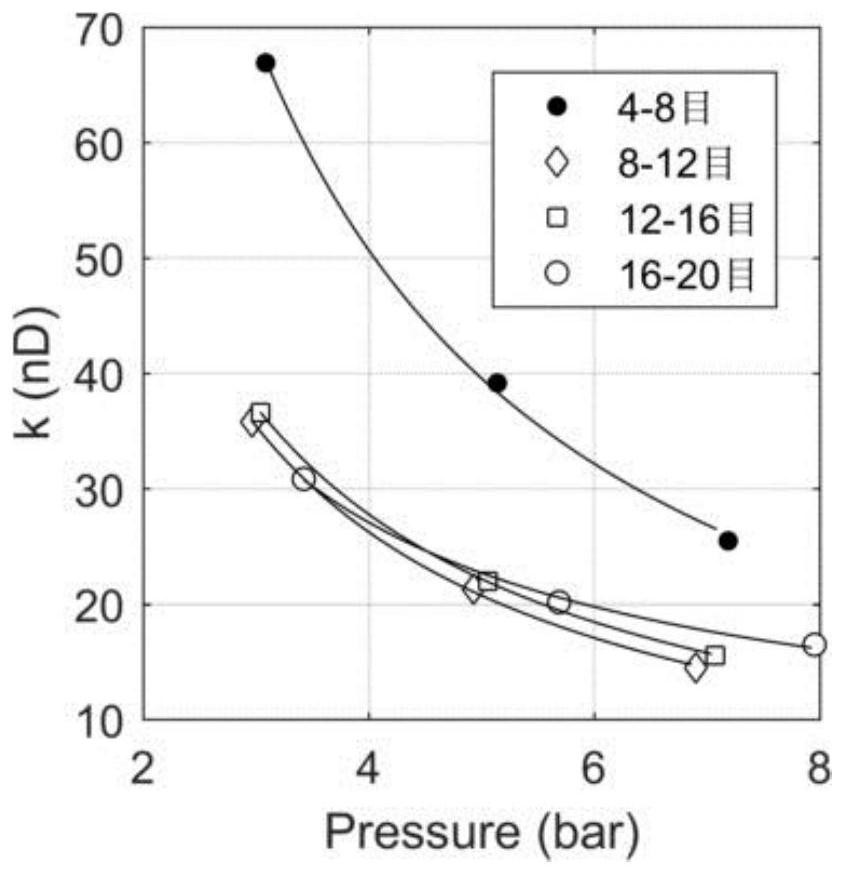
[0061] Among them, the apparent permeability values measured by rock sample 1 under 3 pressure values of particles with different particle sizes and the equation The fitted curve see image 3 , the apparent permeability value kn_3 under the 3bar condition calculated based on the equation and fitting parameters, the permeability ratio of the 5bar apparent permeability value to the 3bar apparent permeability value Rn_53, the 7bar apparent permeability value and the 3bar permeability value Rate ratio Rn_73 see Table 2 and Figure 4 . It can be seen that for this sample, from 8 to 16 mesh, the permeability ratios (non-Darcy characteristics, Rn_53, Rn_73) are very close, and it is judged that the pore structure has not changed si...
Embodiment 2
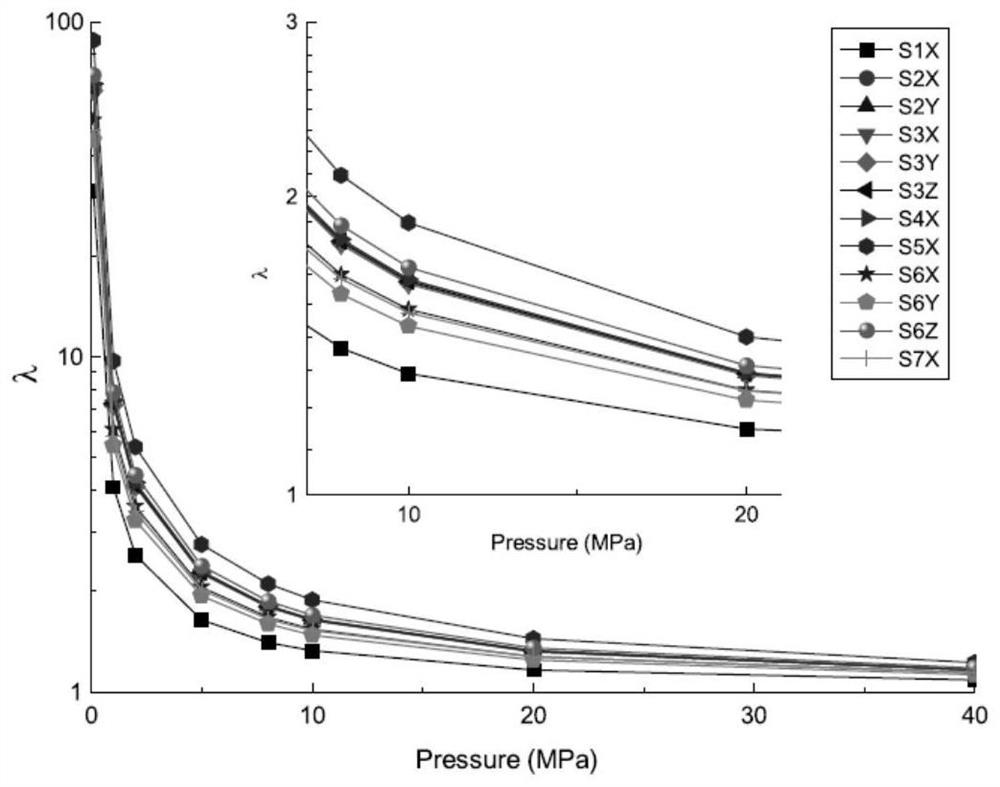
[0065] For sample 2, the measured apparent permeability values under 3 pressures of particles with different particle sizes and the equation The fitted curve see Figure 5 , based on the equation and fitting parameters, the apparent permeability value kn_3 under the condition of 3bar, the permeability ratio of the apparent permeability value of 5bar to the apparent permeability value of 3bar Rn_53, the apparent permeability value of 7bar and the apparent permeability value of 3bar The permeability ratio Rn_73 of the permeability value is shown in Table 3 and Image 6 . It can be seen that for this sample, from 8 to 20 mesh, its permeability ratio (non-Darcy characteristics, Rn_53, Rn_73) continues to decrease significantly, and it can be judged that its pore structure has undergone a relatively obvious change, and its apparent The permeability values are also in continuous variation with particle size.
[0066] Table 3 Apparent permeability value and different pressure...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com