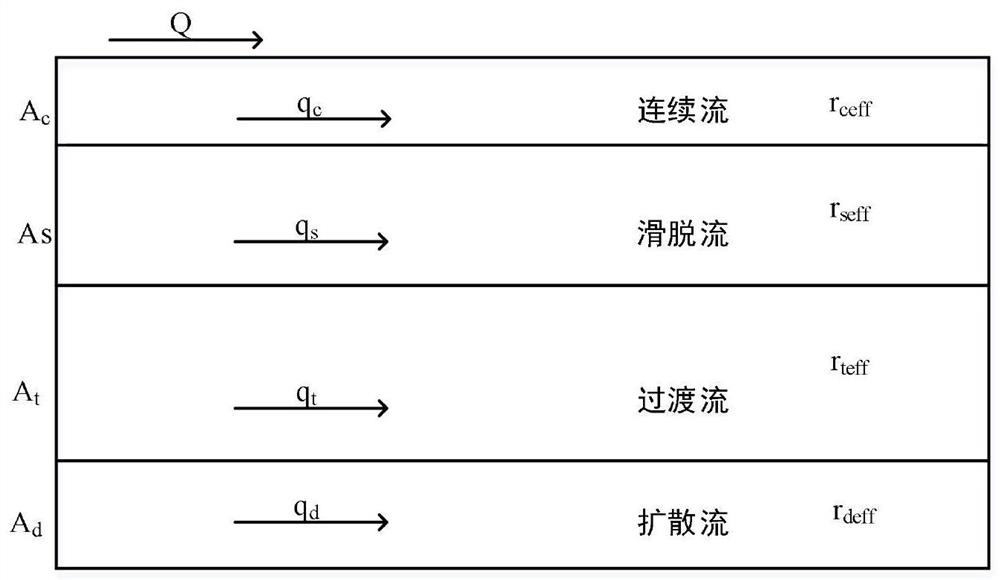
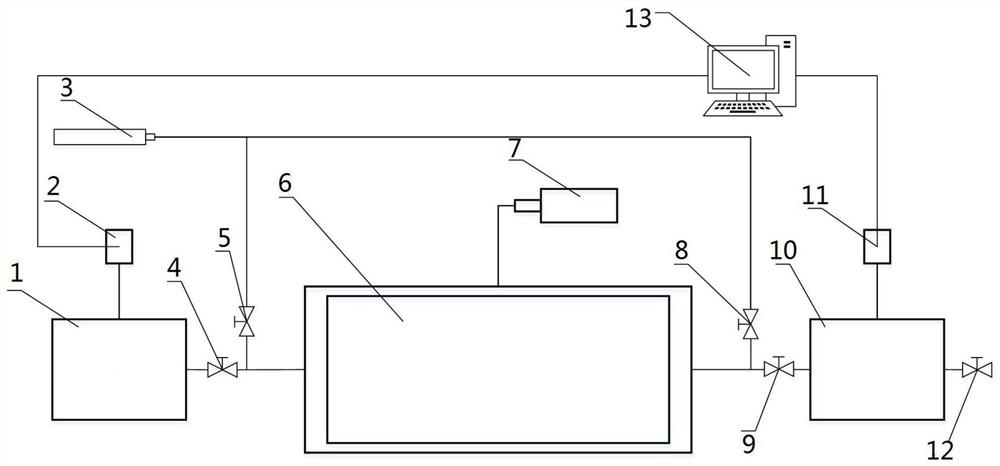
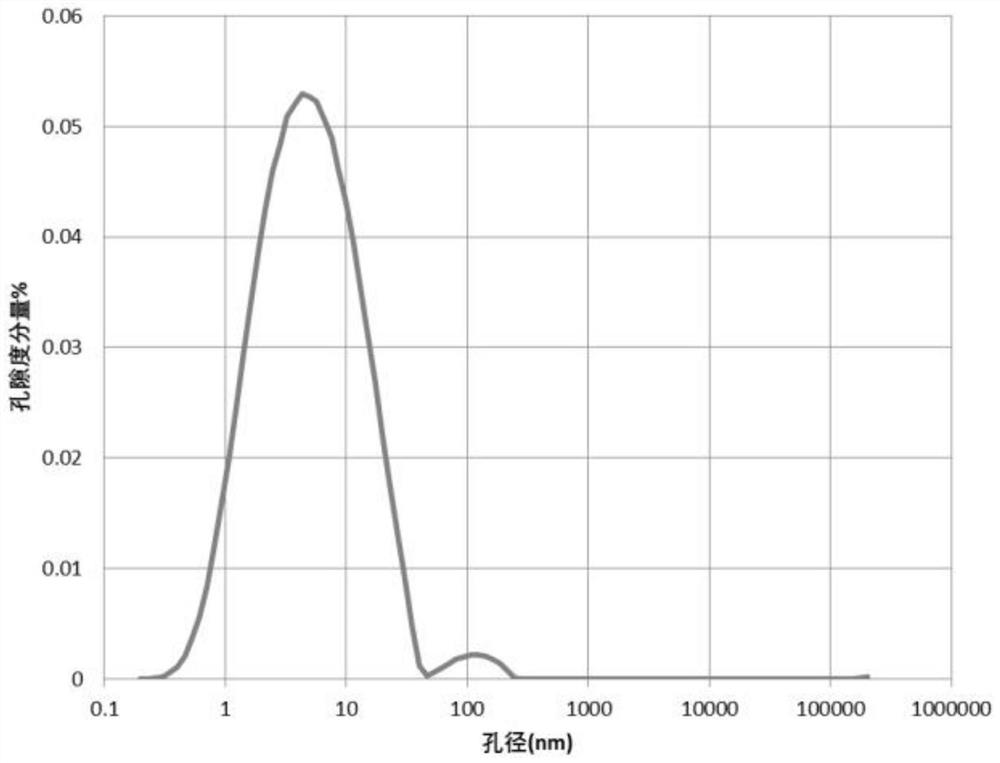
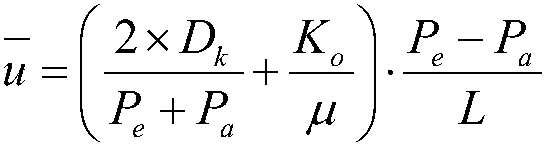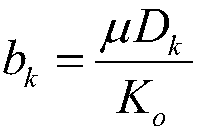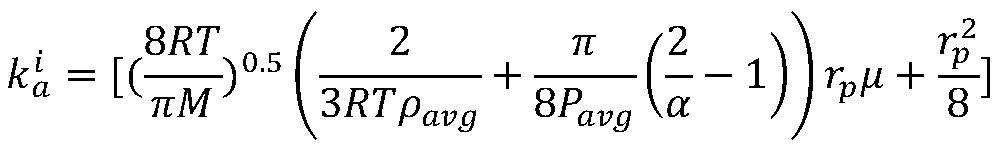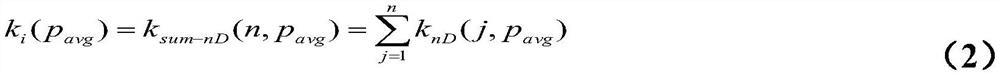Patents
Literature
47 results about "Apparent permeability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
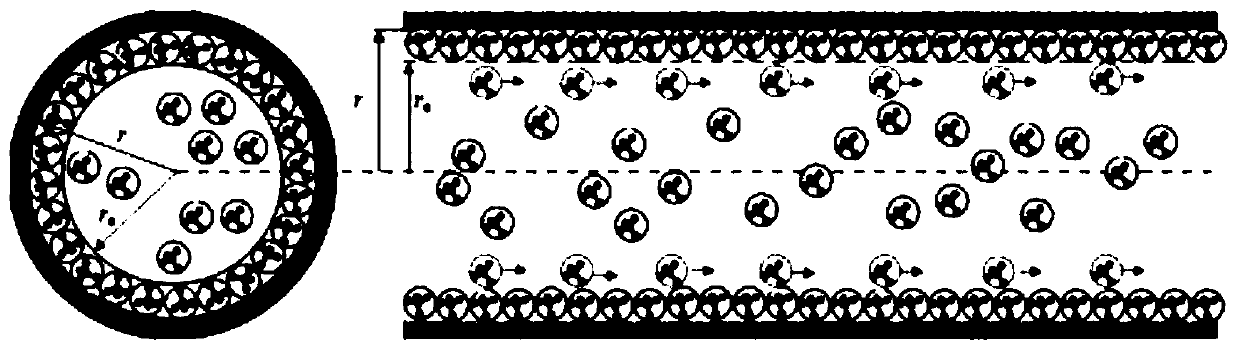
The apparent permeability index is widely used as part of a general screening process to study drug absorption, and is routinely obtained from in vitro or ex vivo experiments.
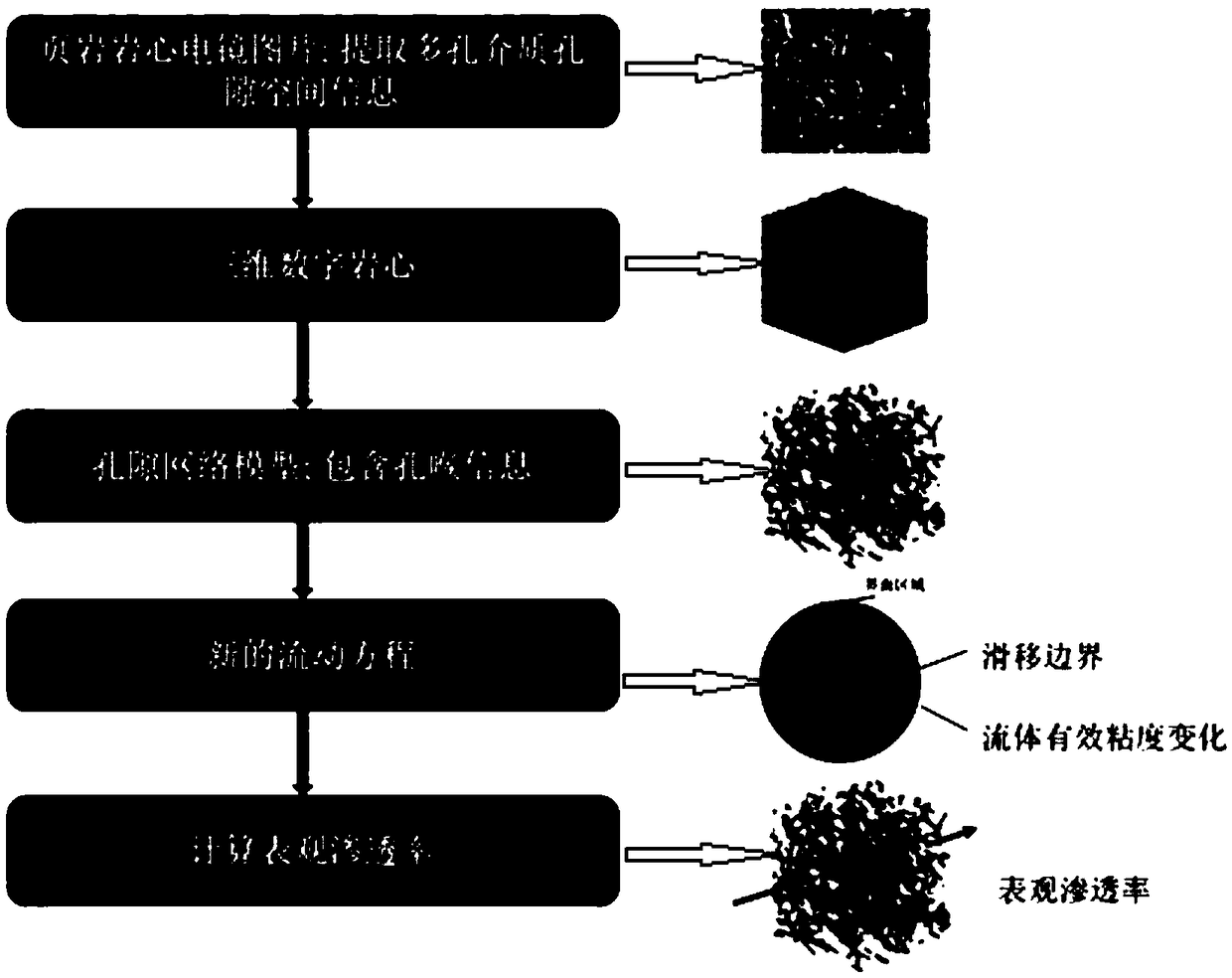
Tight oil flow simulation and permeability prediction method based on pore network model
ActiveCN108729908AThe flow is accurately describedFlow descriptionSurveyDesign optimisation/simulationData fileNetwork model
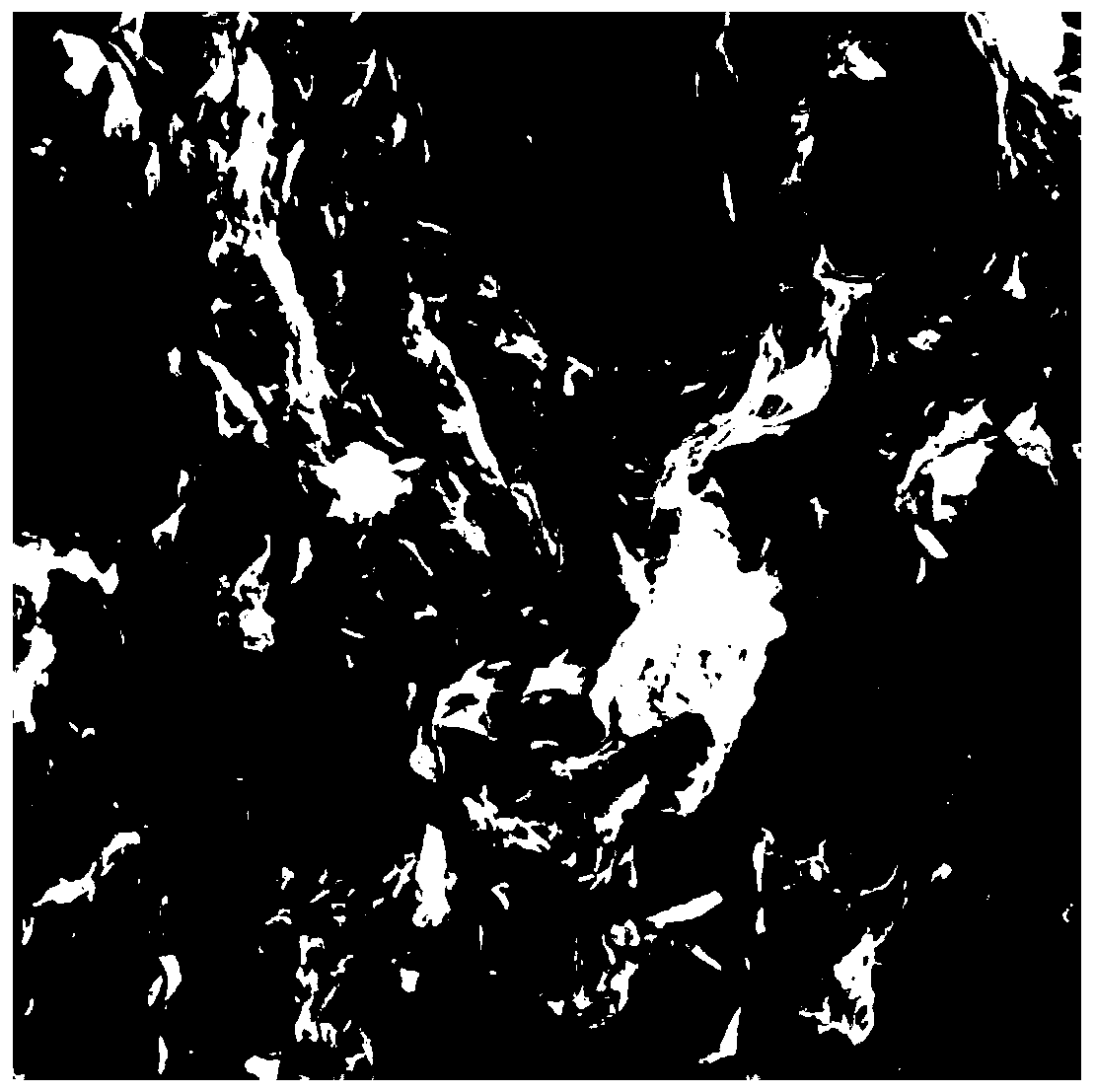
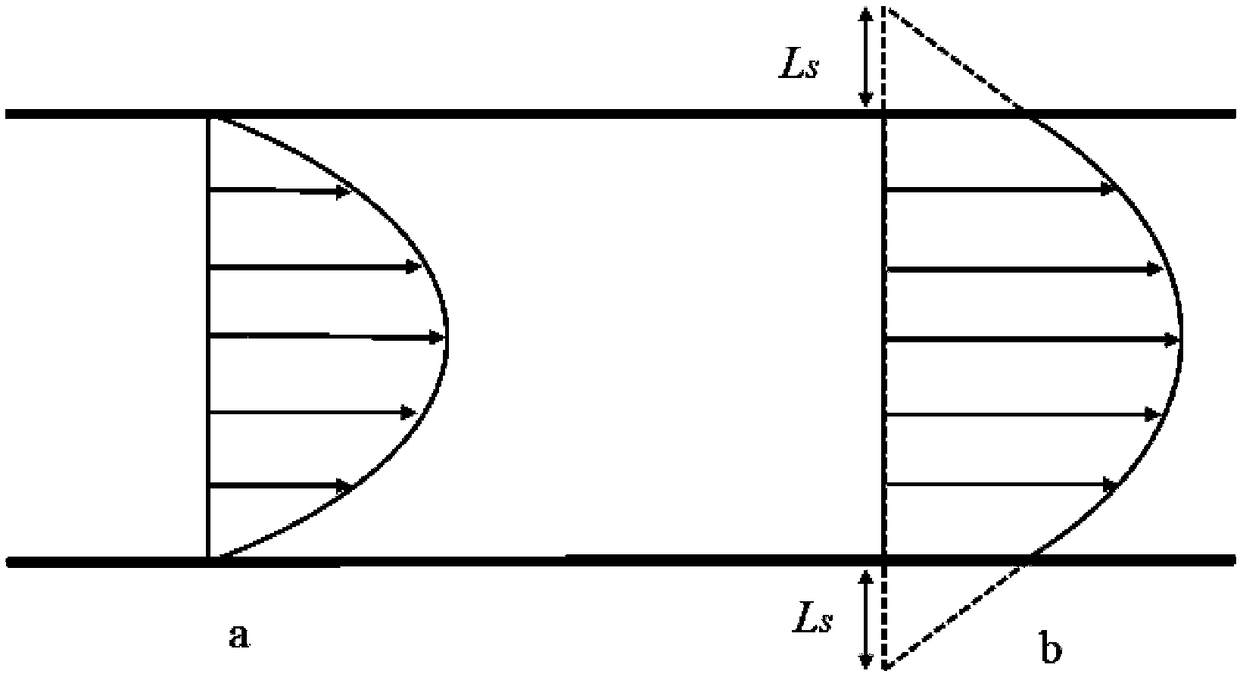
The invention relates to a tight oil flow simulation and permeability prediction method based on a pore network model. The method includes the following steps: (1) scanning a tight core to obtain a two-dimensional electron microscope image and obtain spatial geometric information of porous medium pores; (2) reconstructing a digital core to obtain a geometric data file of the digital core; (3) extracting the pore network model of the digital core to obtain a data file of the pore network model of the tight core; (4) obtaining the pressure at each pore and the volume flow rate at each pore throat position to further obtain the flowing condition of a fluid in the nano-scale pore network model; (5) obtaining the volume flow rate Q of the fluid at the outlet end of the pore network model and calculating the apparent permeability of the pore network model according to the Darcy law. The newly developed pore network model overcomes the shortcoming that the traditional pore network model cannot consider the boundary slip and the change of the effective viscosity of the fluid when the fluid flows in the nanopores.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
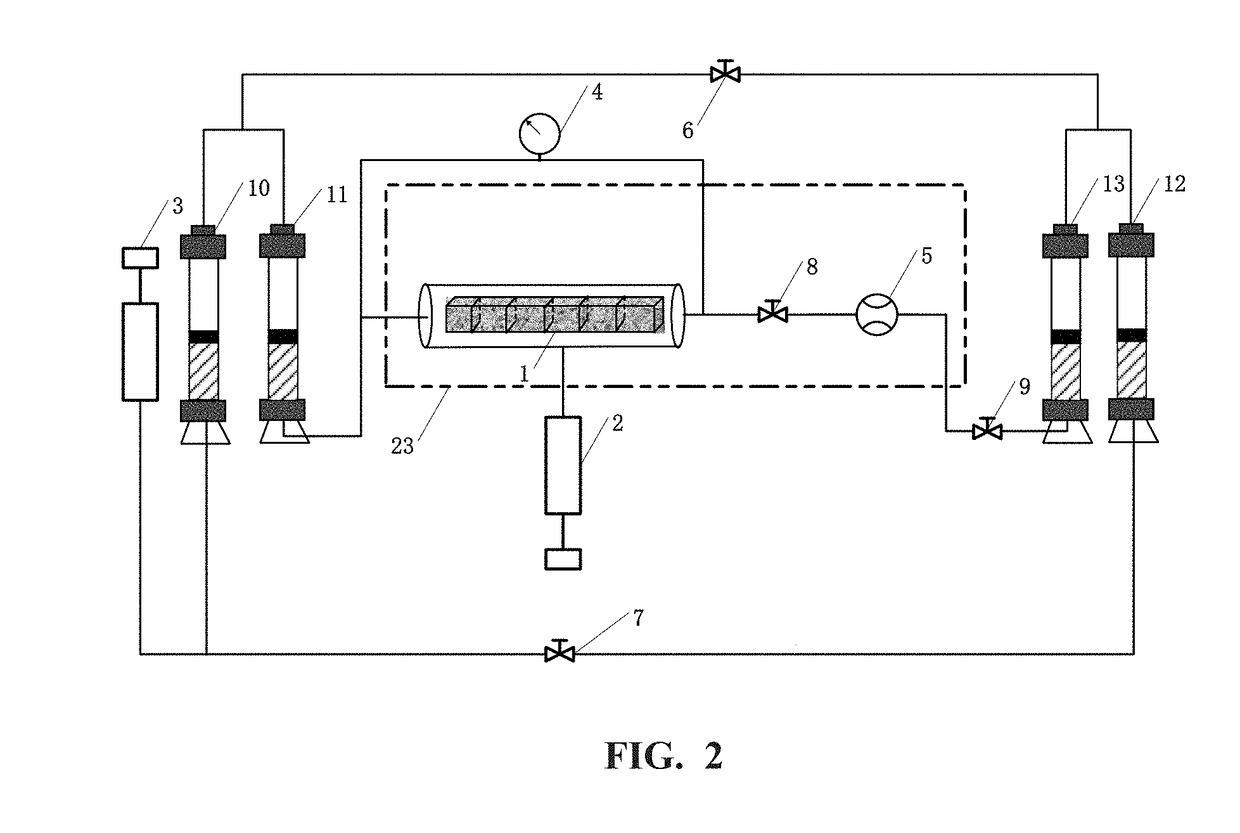
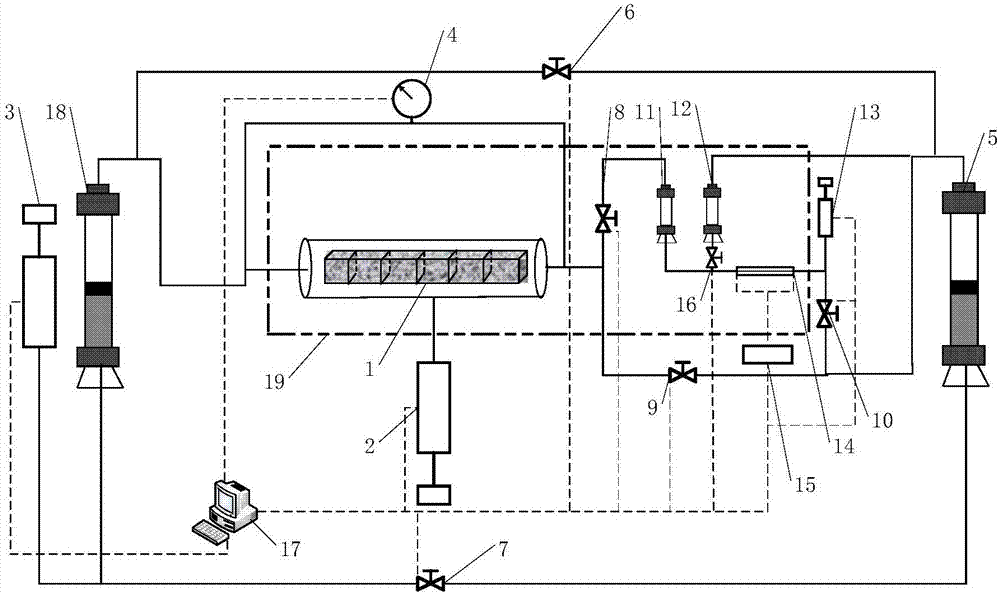
Apparatus and method for measuring apparent permeability of tight rock core
ActiveUS20180372611A1Accurate measurementEasy to operatePermeability/surface area analysisPressure difference measurement between multiple valvesRock coreDifferential pressure
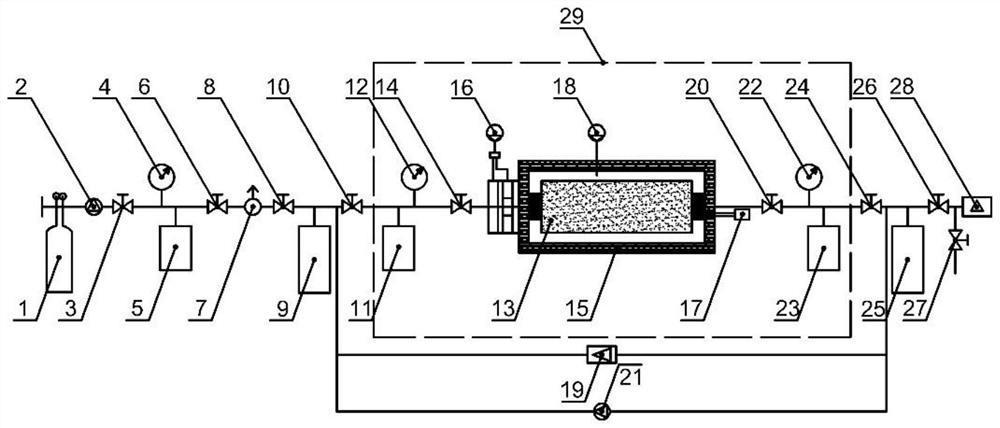
The present application provides an apparatus and a method for measuring apparent permeability of a tight rock core, the apparatus comprises: a rock core holder, a first high-pressure injection pump, a second high-pressure injection pump, a micro-differential pressure meter, a micro-flow meter, a first pressure control unit, a second pressure control unit, a first valve, a second valve, a third valve, and a fourth valve; the first pressure control unit comprises: a first pressure-resistant piston container and a second pressure-resistant piston container, both of which are divided into an upper cavity and a lower cavity by a piston, the upper cavities of the first pressure-resistant piston container and the second pressure-resistant piston container are filled with gases and communicate with each other, and the lower cavity of the first pressure-resistant piston container is filled with pump pressure-transmission liquids, and the lower cavity of the second pressure-resistant piston container is filled with experimental fluids.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
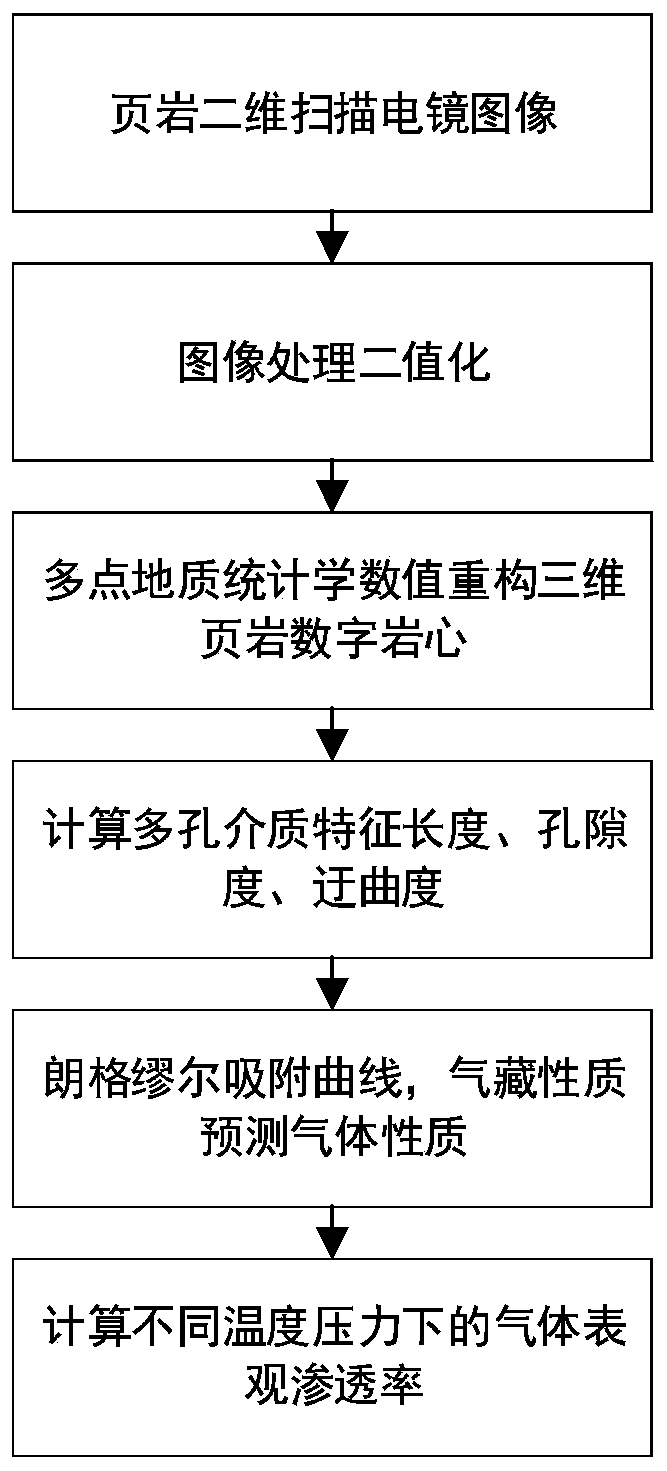
Shale gas apparent permeability calculation method considering influence of multiple factors
PendingCN110210460ASimplify the penetration calculation processReduce computing timeImage analysisBorehole/well accessoriesDesorptionPorous medium
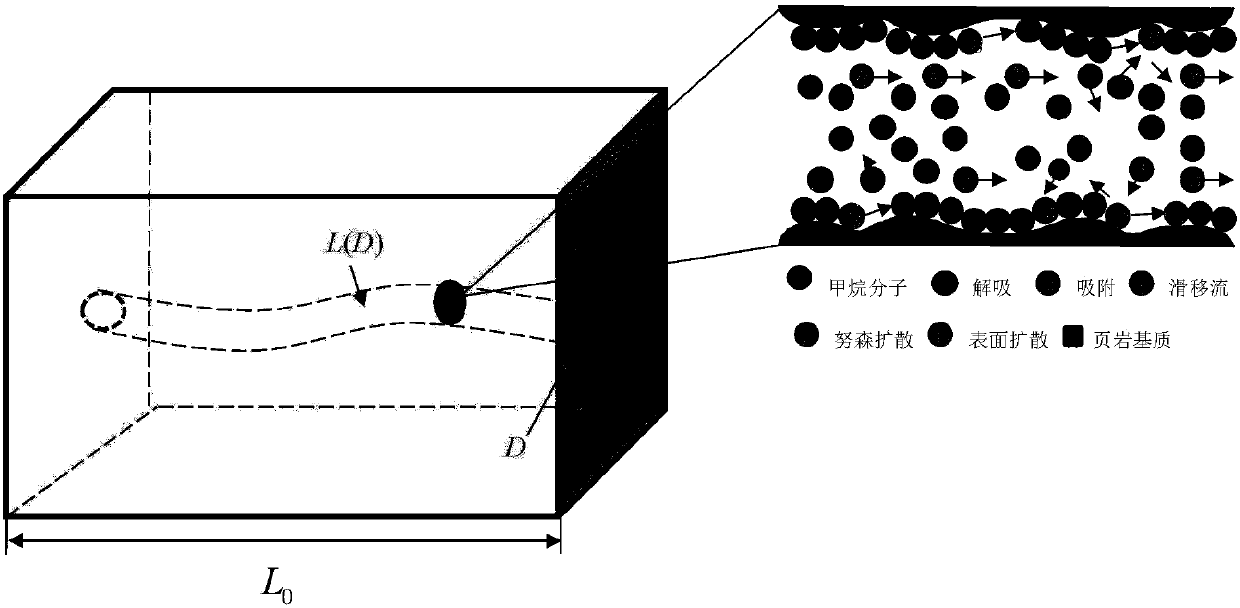
The invention relates to a shale gas apparent permeability calculation method considering multi-factor influence, which comprises the following steps: (1) reconstructing a shale three-dimensional digital core based on a shale two-dimensional profile scanning electron microscope image by adopting a multi-point geostatistics method; (2) calculating the porosity, tortuosity and porous medium characteristic length of the shale three-dimensional digital rock core; and (3) calculating the gas permeability in the organic matter and inorganic matter of the shale. According to the method, the influenceof the pore structure, different pore types (organic matter pores and inorganic matter pores), adsorption and desorption, surface diffusion, gas slippage, stress sensitivity and critical property change in the shale gas reservoir on the gas flow capacity is fully considered, and the shale gas flow capacity under the conditions of different pore structures and gas reservoirs can be accurately predicted.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Segmentation multi-cluster fractured horizontal well yield prediction method for shale gas reservoir
InactiveCN107622328AImprove forecast accuracyAccurately reflect the actual seepageForecastingFluid removalPhysical modelOperability
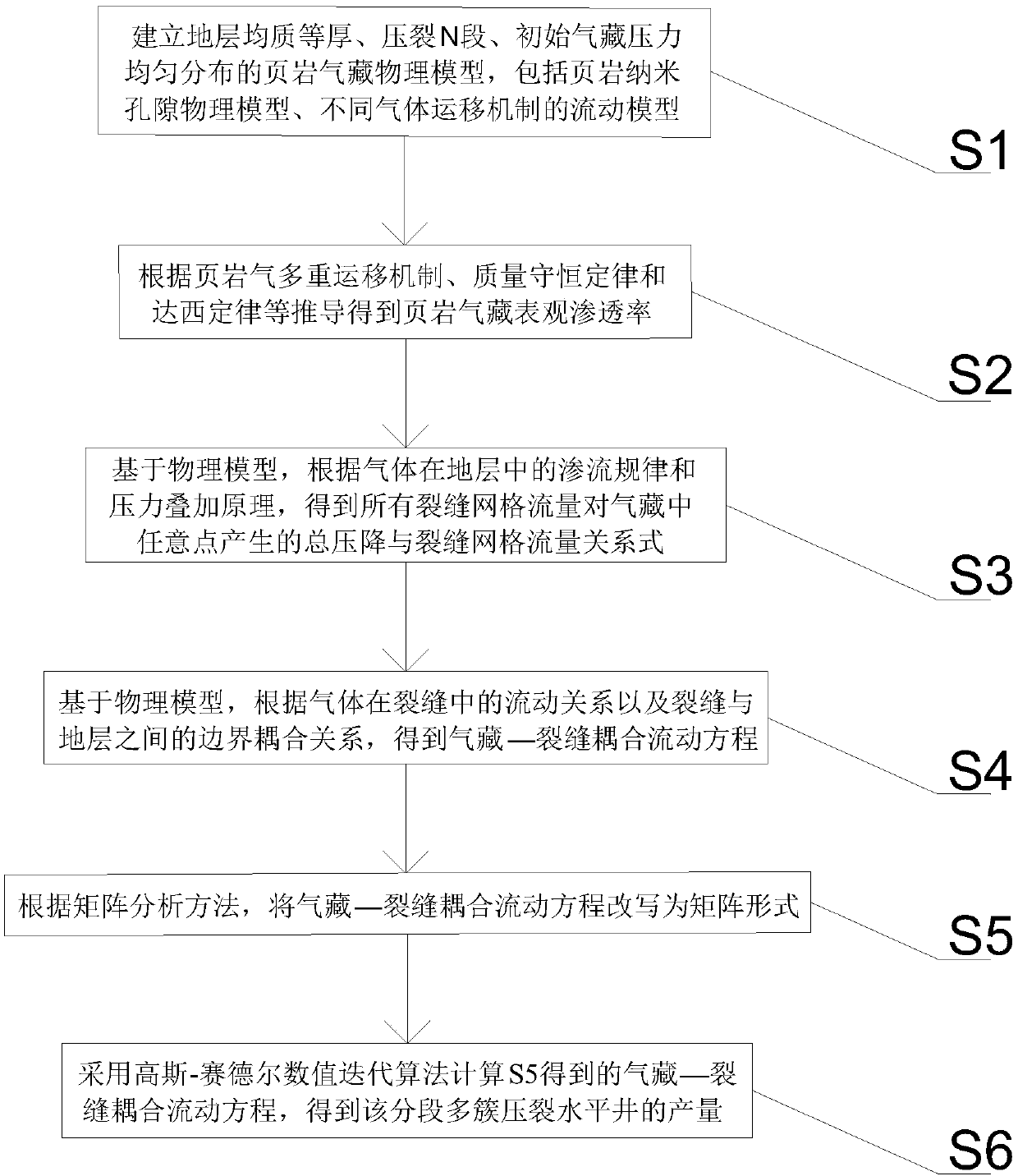
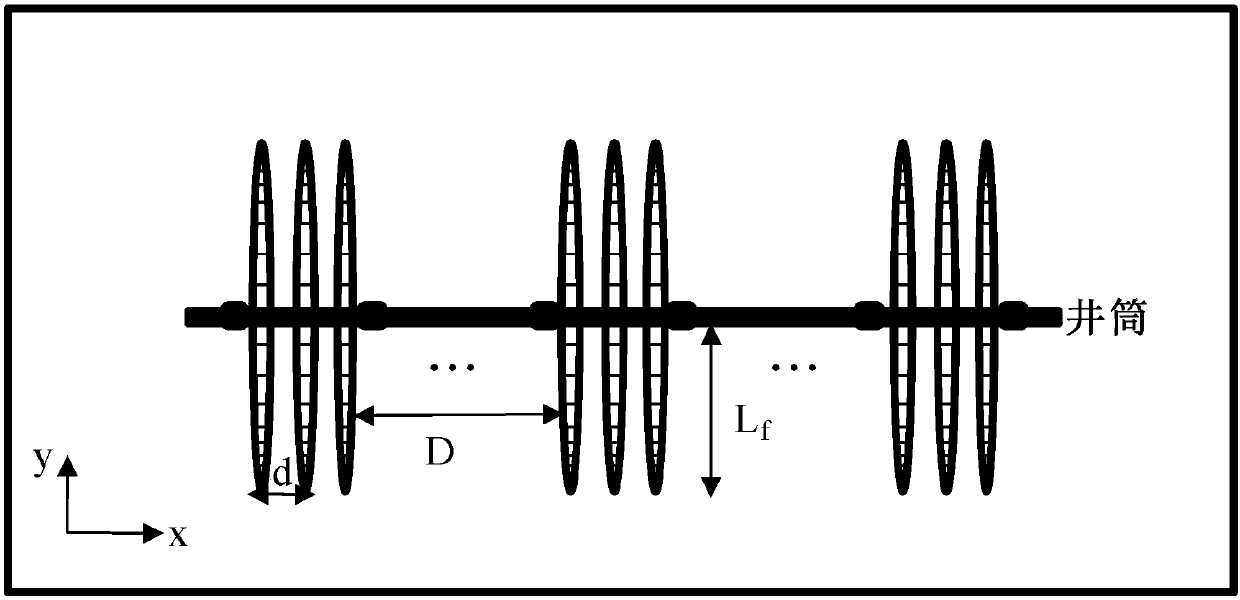
The invention belongs to the technical field of shale gas development, and particularly relates to a segmentation multi-cluster fractured horizontal well yield prediction method for a shale gas reservoir. The method comprises the following steps that: establishing a physical model; obtaining an apparent permeability rate calculation method; according to the permeability rule and the pressure superposition principle of gas in a stratum, obtaining the overall pressure drop and crack grid traffic relational expression of all crack grid traffics for any point in a gas reservoir; according to the flowing relationship of gas in a crack and a boundary coupling relationship between the crack and the strum, obtaining a gas reservoir-crack coupling flowing equation; and adopting a matrix analysis method and a numerical iteration algorithm to obtain the horizontal well yield. By use of the method which is put forward by the invention, a blank of a segmentation multi-cluster fractured horizontal well yield prediction model which considers the complex and multiple migration mechanism is filled. The method has the characteristics of being convenient in calculation, high in operability, effectiveand practical, and a basis can be provided for optimizing the horizontal well segmentation multi-cluster fractured parameters of the shale gas.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
A shale apparent permeability calculation method considering stress sensitive effect
ActiveCN108959789AApparent permeability complies withDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOrganic matterShale gas
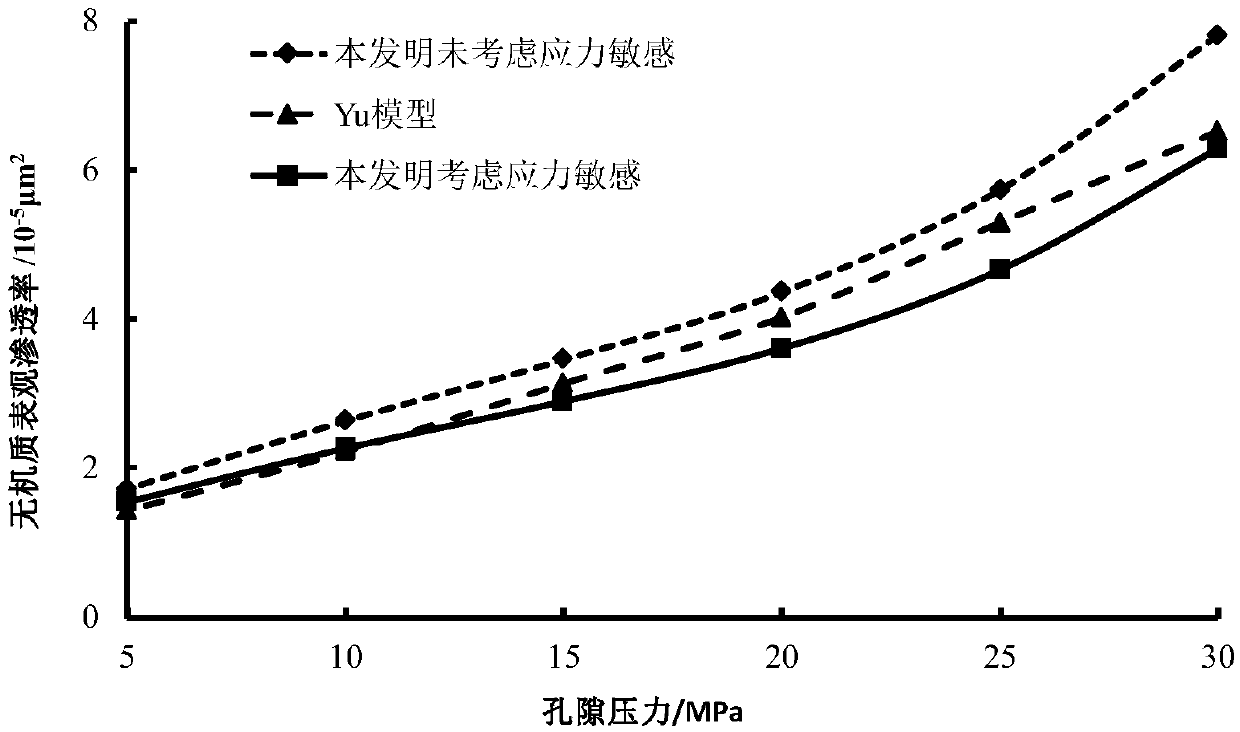
The invention discloses a shale apparent permeability calculation method considering a stress sensitive effect. The method includes the steps of dividing a shale gas flow channel into an inorganic capillary tube and an organic capillary tube, and establishing inorganic pore and organic pore calculation models; considering the different flow mechanism of shale gas in capillary tubes of inorganic matter and organic matter, establishing the apparent permeability calculation models of inorganic matter and organic matter by a fractal theory. Furthermore, the area weighted method is used to calculate the apparent permeability considering the influence of water saturation and stress sensitive effect in shale mining, and the calculation method of apparent permeability is established. Through the improvement, the method establishes a calculation model which is more consistent with the apparent permeability of shale, and provides theoretical support for shale gas production.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method for calculating apparent permeability of porous media of shale reservoir
ActiveCN108710723AApparent permeability is accurateAccurate calculation of apparent permeabilityDesign optimisation/simulationPermeability/surface area analysisPorous mediumUnconventional oil
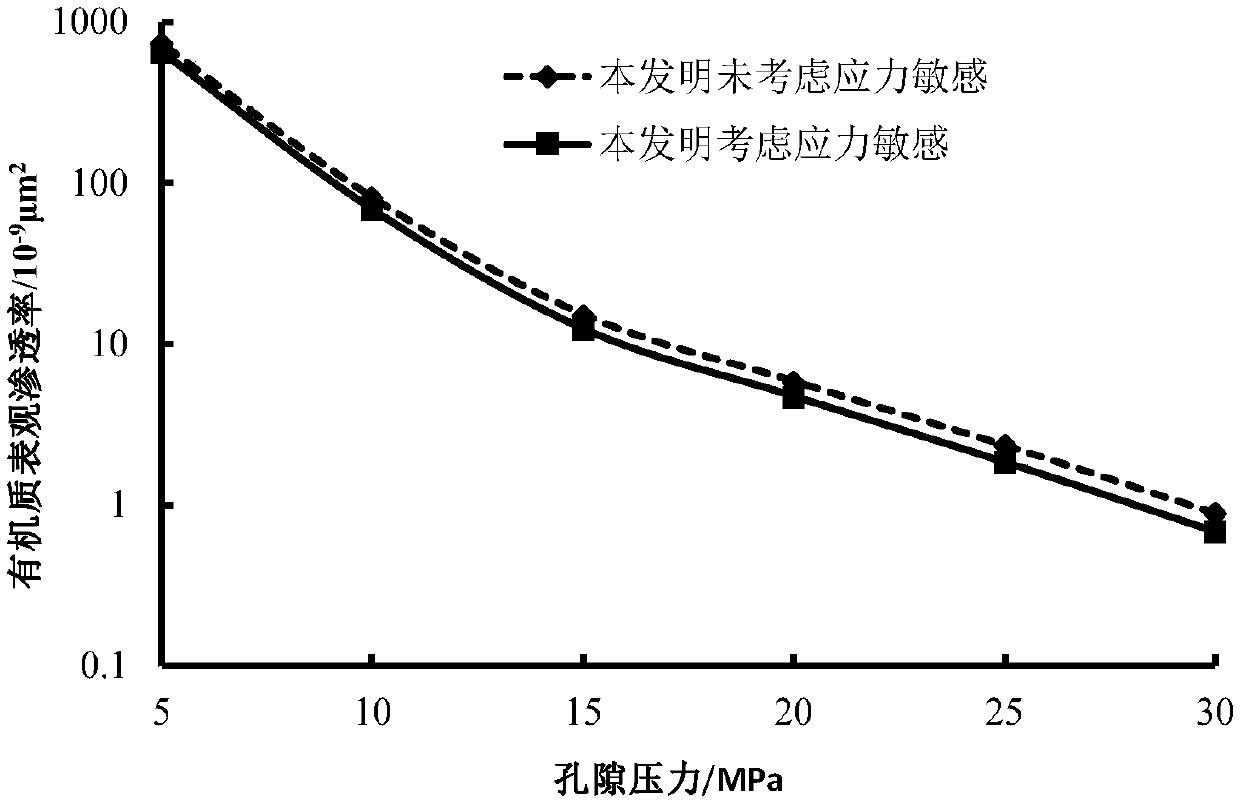
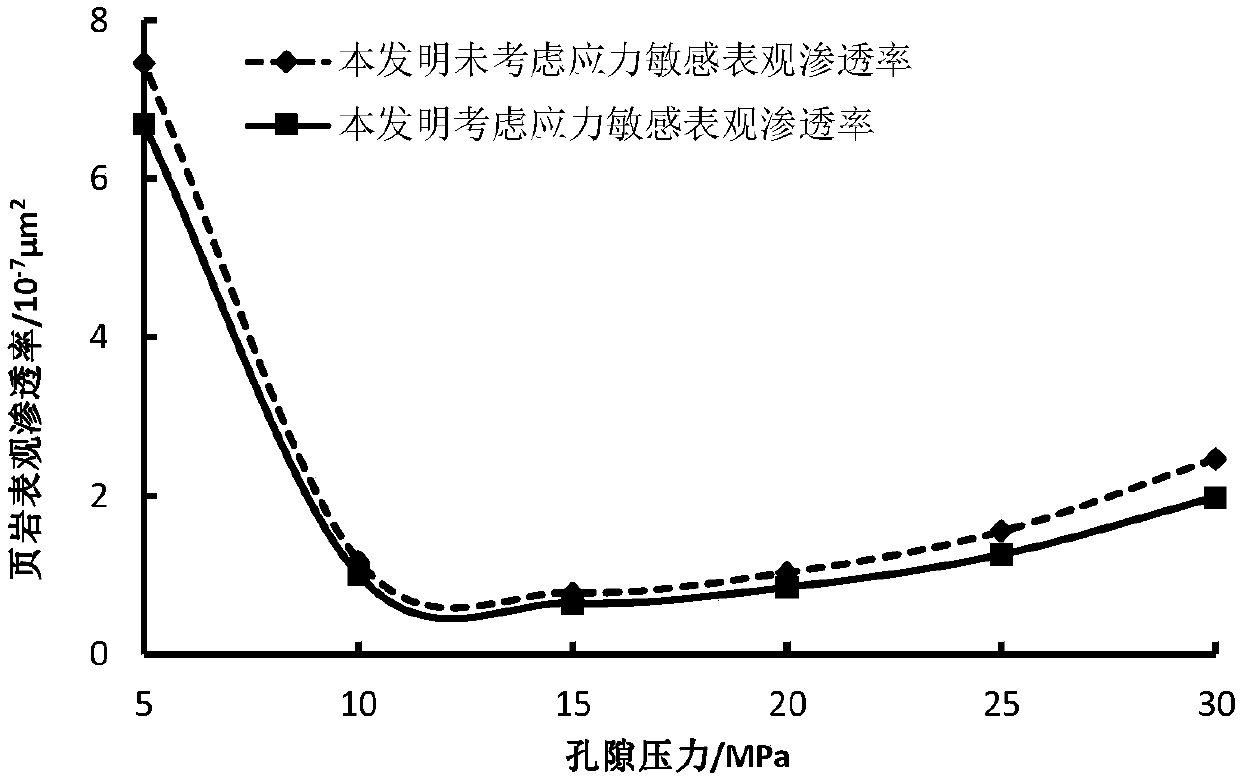
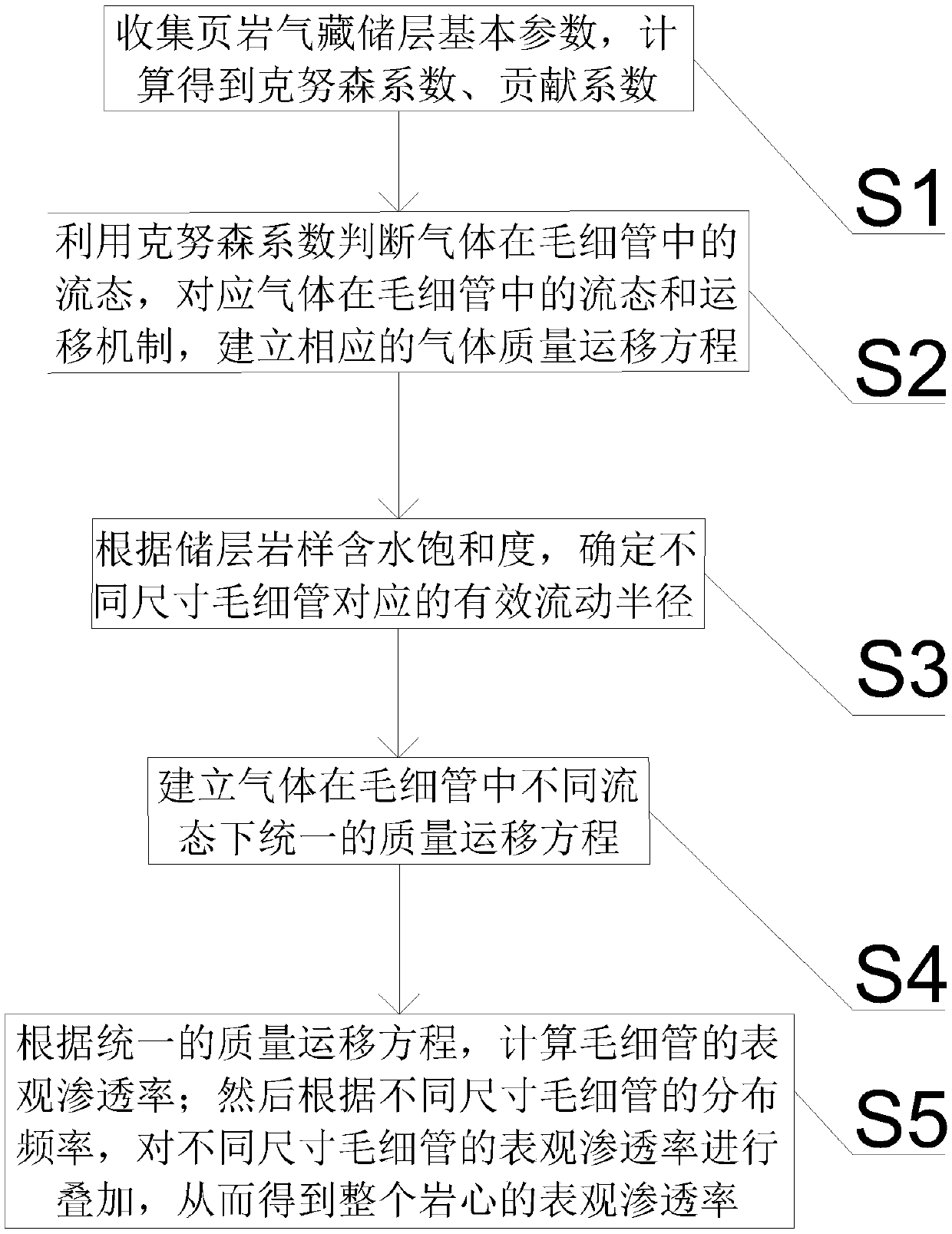
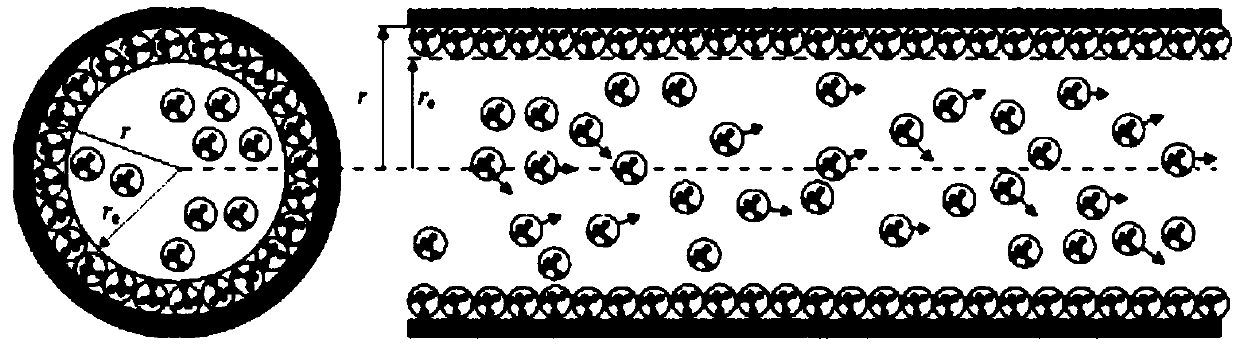
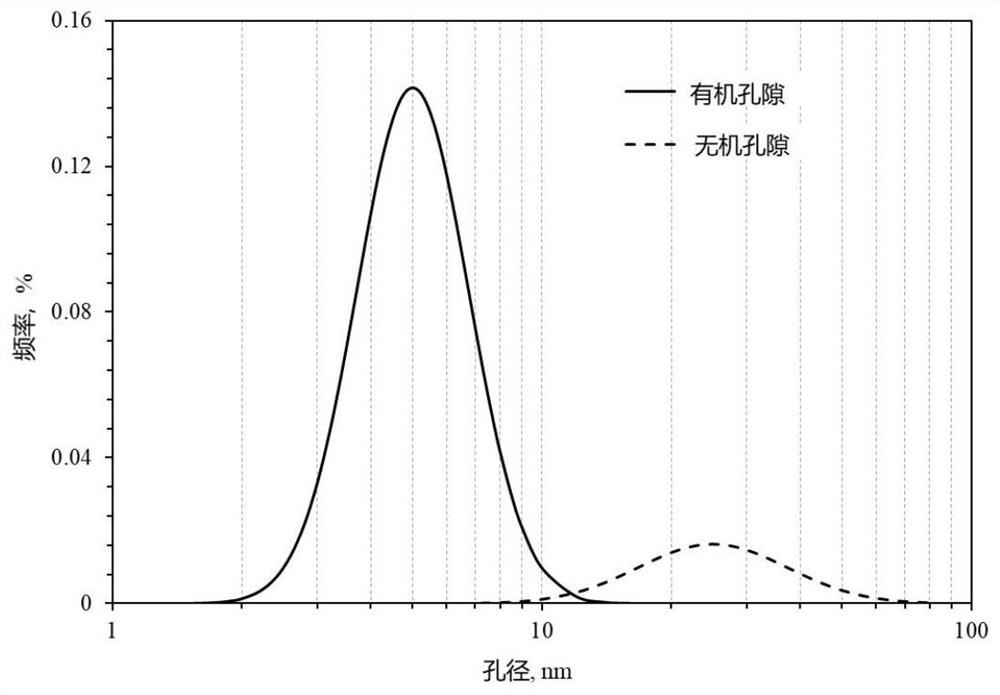
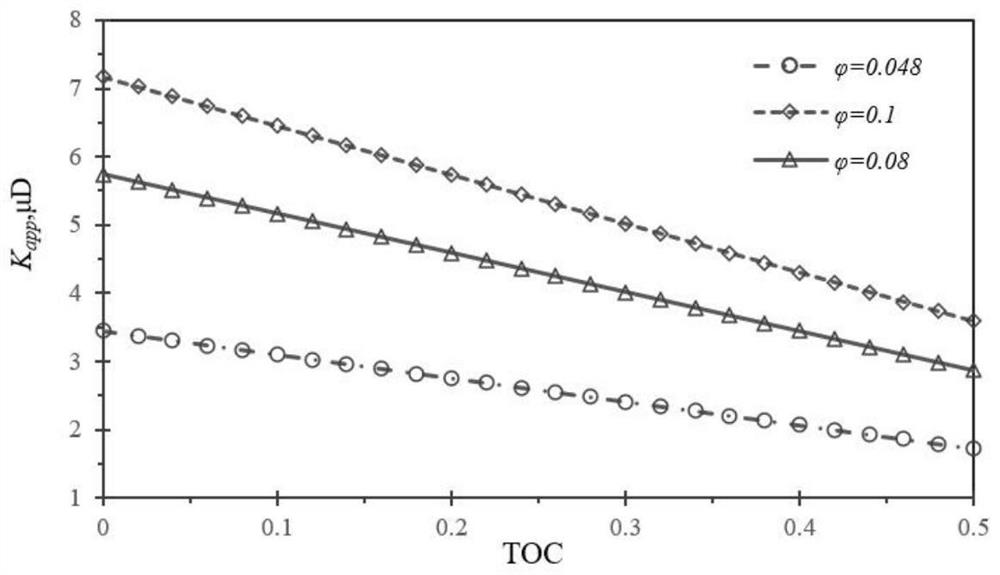
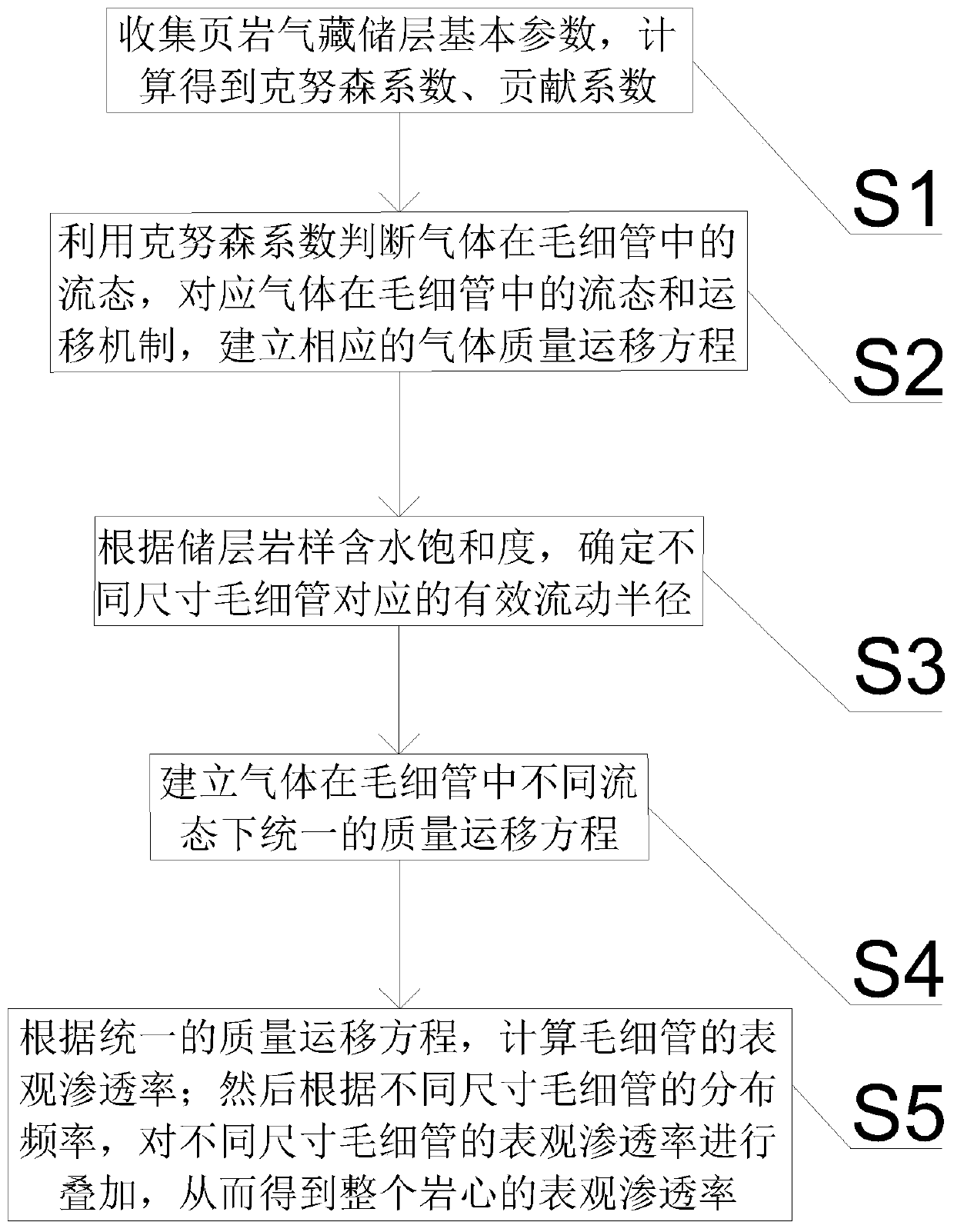
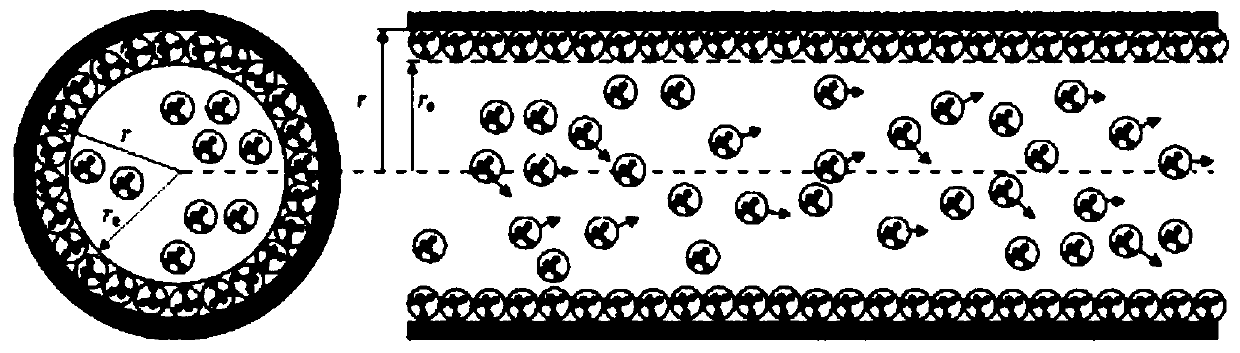
The present invention belongs to the technical field of unconventional oil and gas development, and relates to a method for calculating apparent permeability of porous media of shale reservoir. The method includes the steps of: S1, collecting basic parameters of shale gas reservoir, calculating to obtain a Knudsen coefficient and a contribution coefficient; S2, utilizing the Knudsen coefficient tojudge the flow state of the gas in the capillary tube, and establishing the corresponding gas mass transport equation; S3, according to the water saturation of the reservoir rock sample, determiningthe effective flow radius corresponding to the capillaries of different sizes; S4, establishing unified mass transport equation of gas in different flow states in capillary tubes; S5. according to theunified mass transport equation, calculating the apparent permeability of the capillary tube, and superposing the apparent permeabilities of the capillary tubes with different sizes to obtain the apparent permeability of the whole shale core. The method of the invention takes into account the influence of different capillary sizes, distribution frequencies and water saturation of shale, and the method provided by the invention is closer to the real situation of the reservoir and obtains more accurate data.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
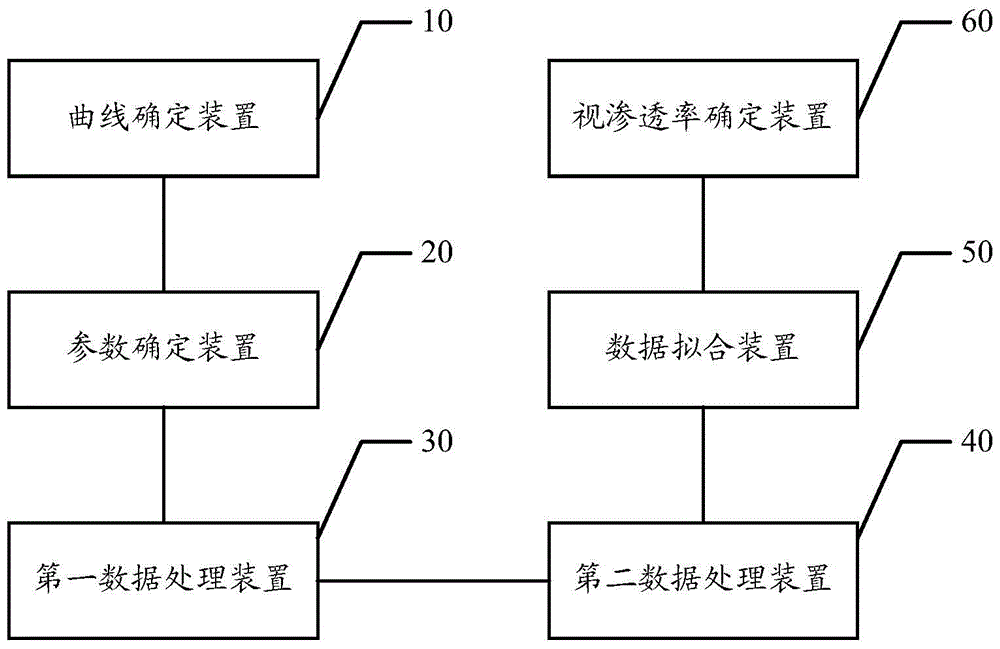
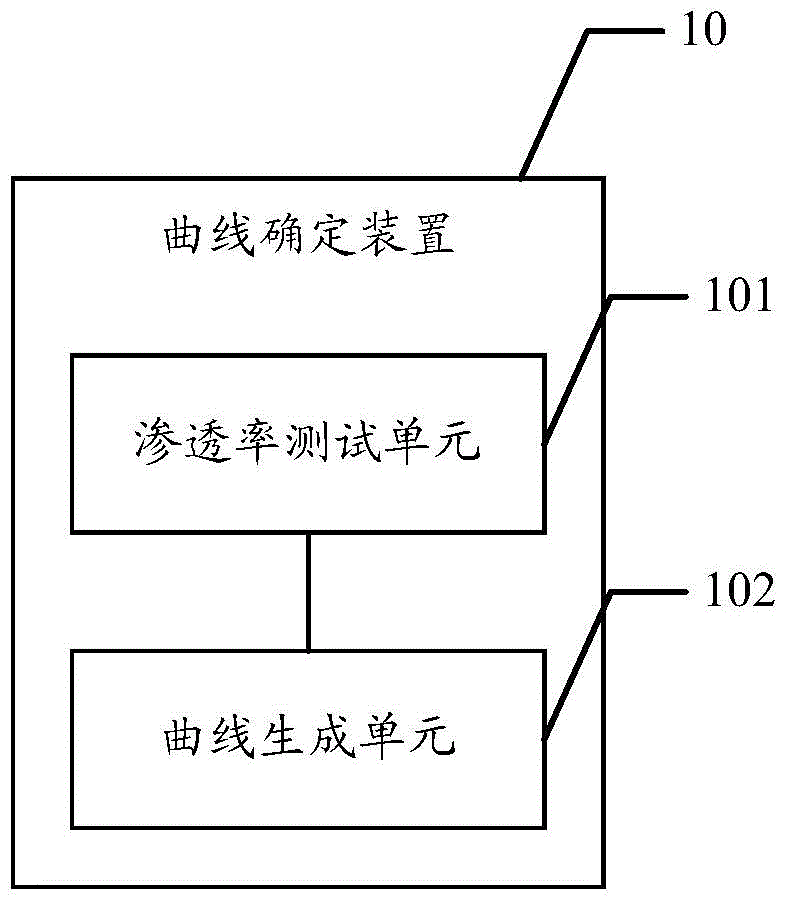
Method and system for interpreting apparent permeability of low-permeability reservoir in formation
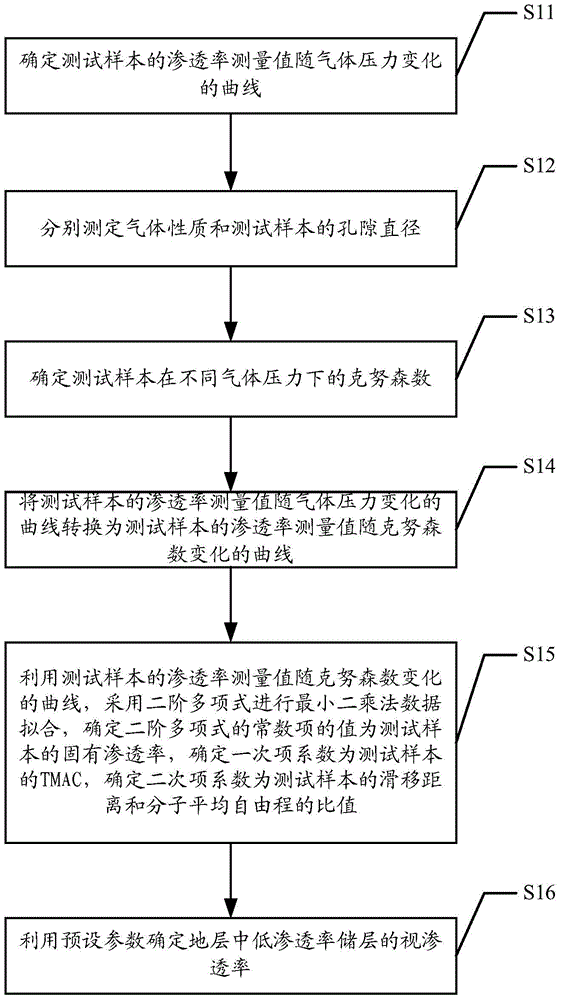
ActiveCN104237107AAccurate explanationPermeability/surface area analysisTest samplePermeability measurements
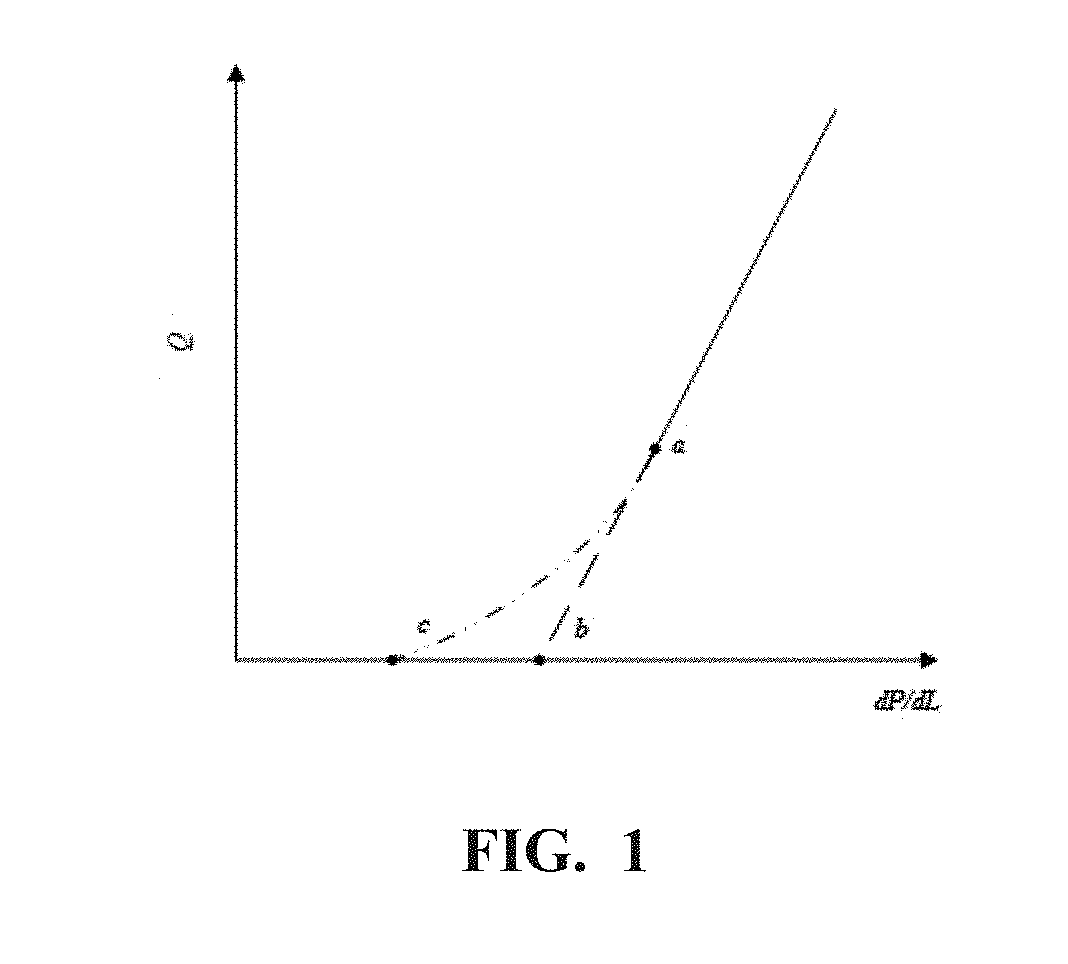
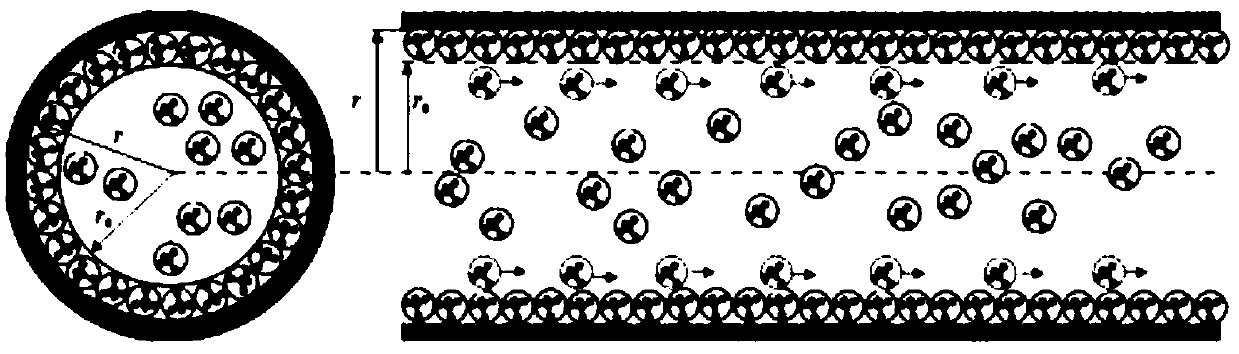
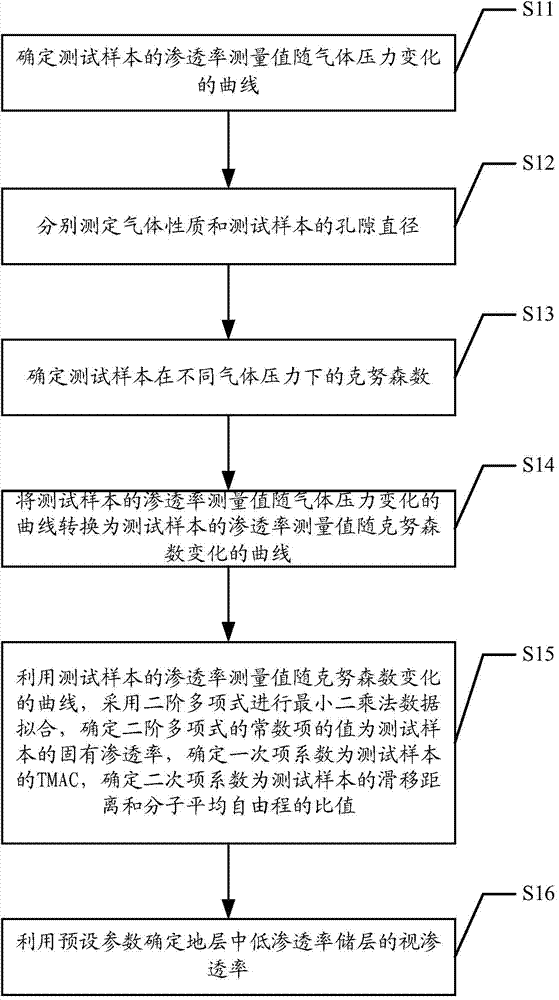
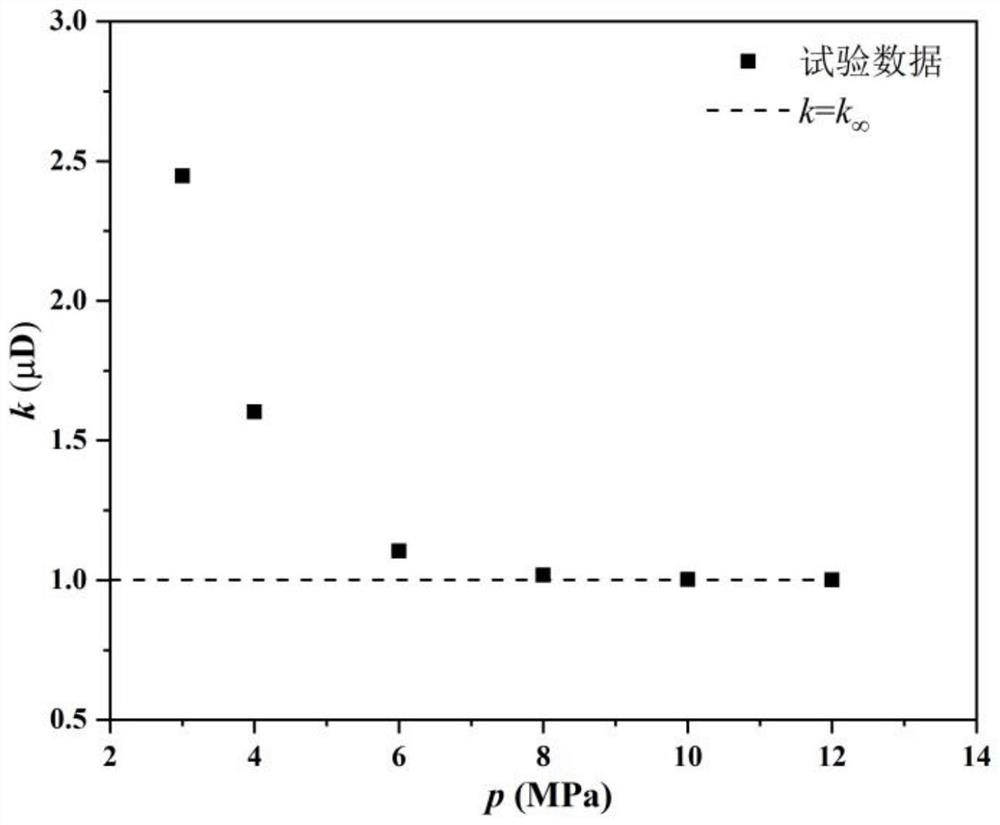
The invention discloses a method and a system for interpreting apparent permeability of a low-permeability reservoir in a formation. The method comprises the steps of firstly, determining a curve that the permeability measured value of a test sample changes along with gas pressure, secondly, determining the Knudsen numbers of the test sample under different pressures, converting the curve that the permeability measured value of the test sample changes along with the gas pressure into a curve that the permeability measured value of the test sample changes along with the Knudsen numbers, determining the intrinsic permeability of the test sample, the wall influence parameter of the test sample and the ratio of the slippage distance of the test sample to the molecular average free path by performing least square method data fitting on the curve that the permeability measured value of the test sample changes along with the Knudsen numbers, and finally, for determining the apparent permeability of the low-permeability reservoir in the formation, correcting the wall slippage effect by use of the wall influence parameter of the test sample and the ratio of the slippage distance of the test sample to the molecular average free path so as to interpret the apparent permeability of the low-permeability reservoir in the formation more accurately.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Intrinsic permeability interpretation method and system for low-permeability reservoir
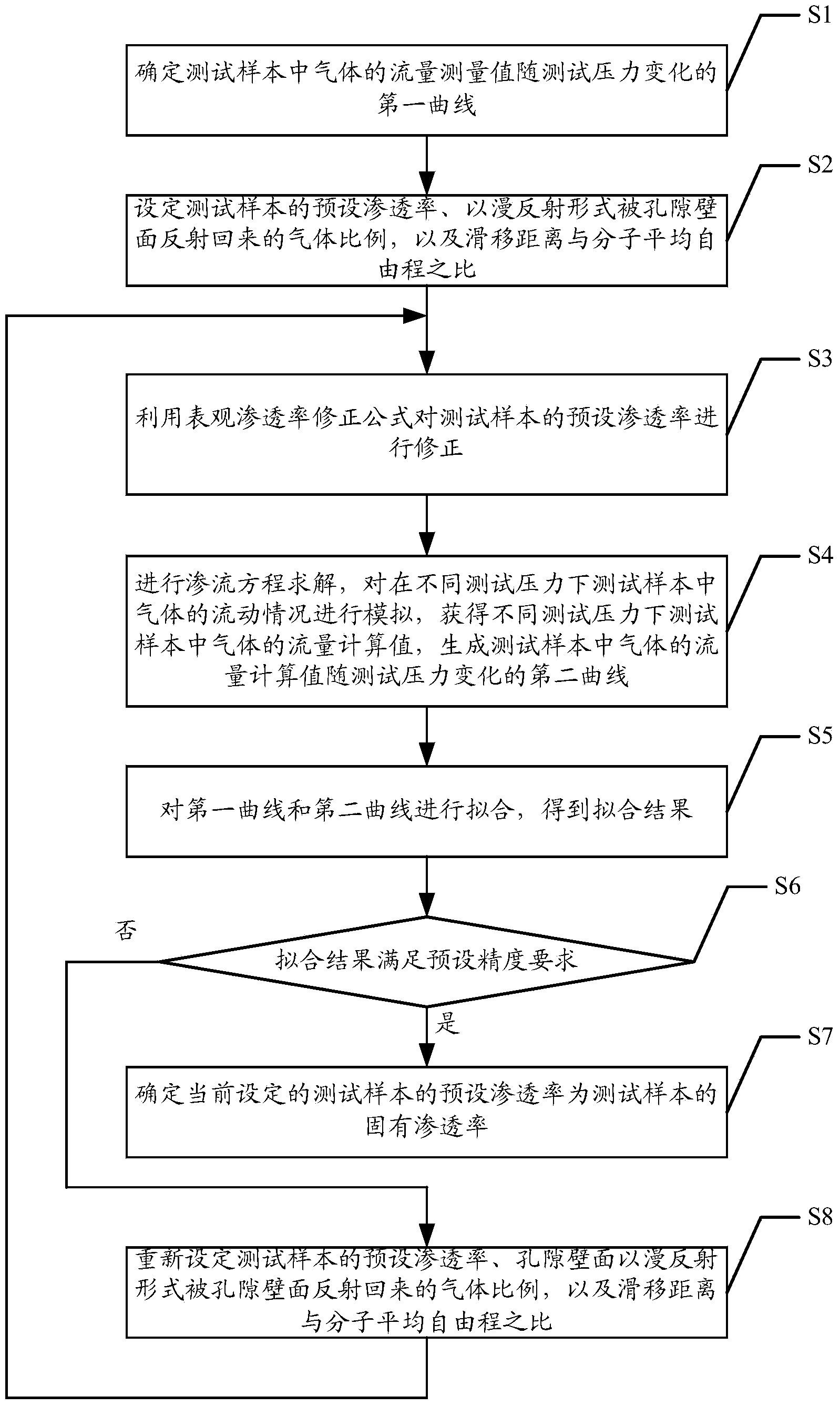
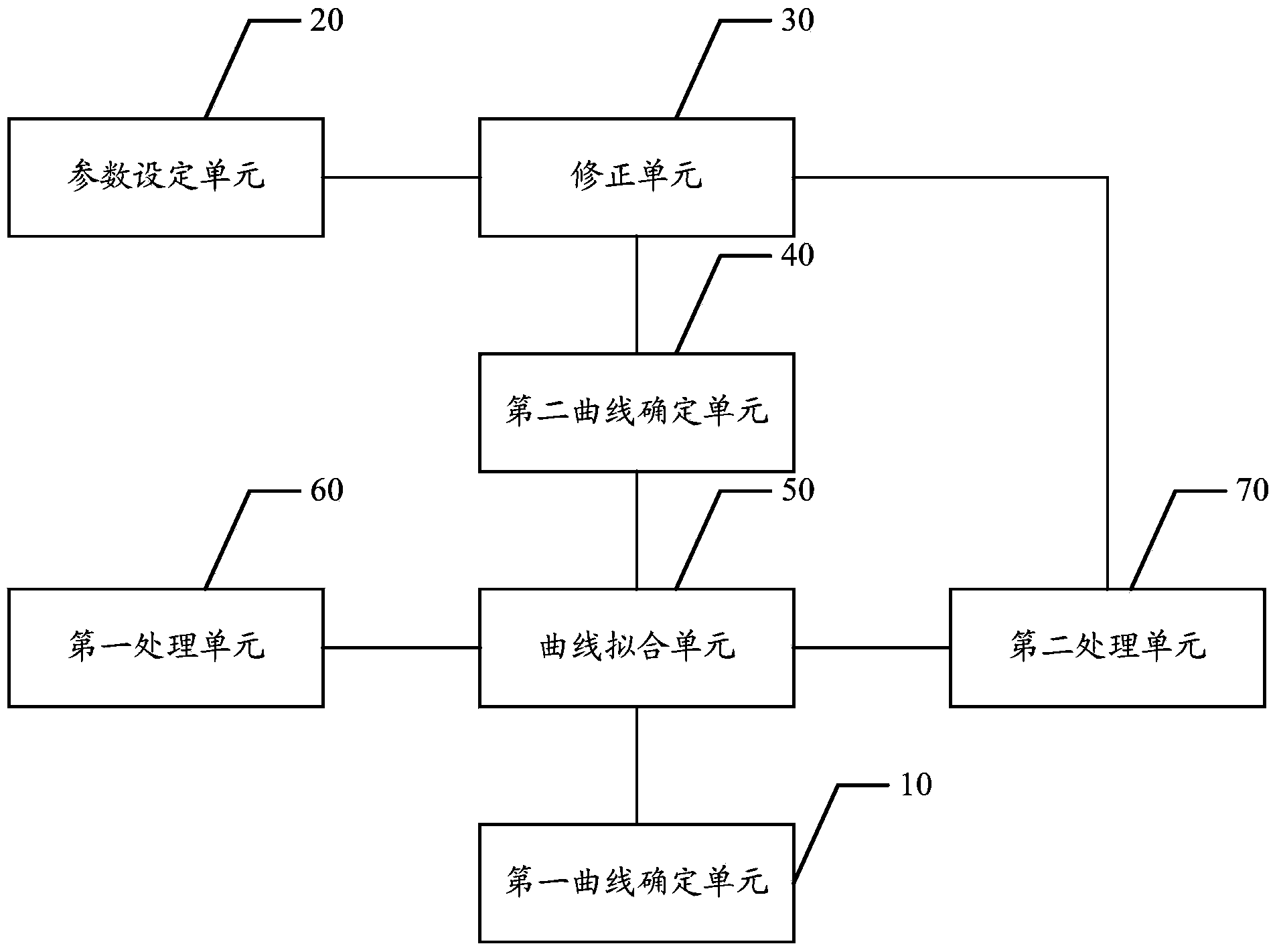
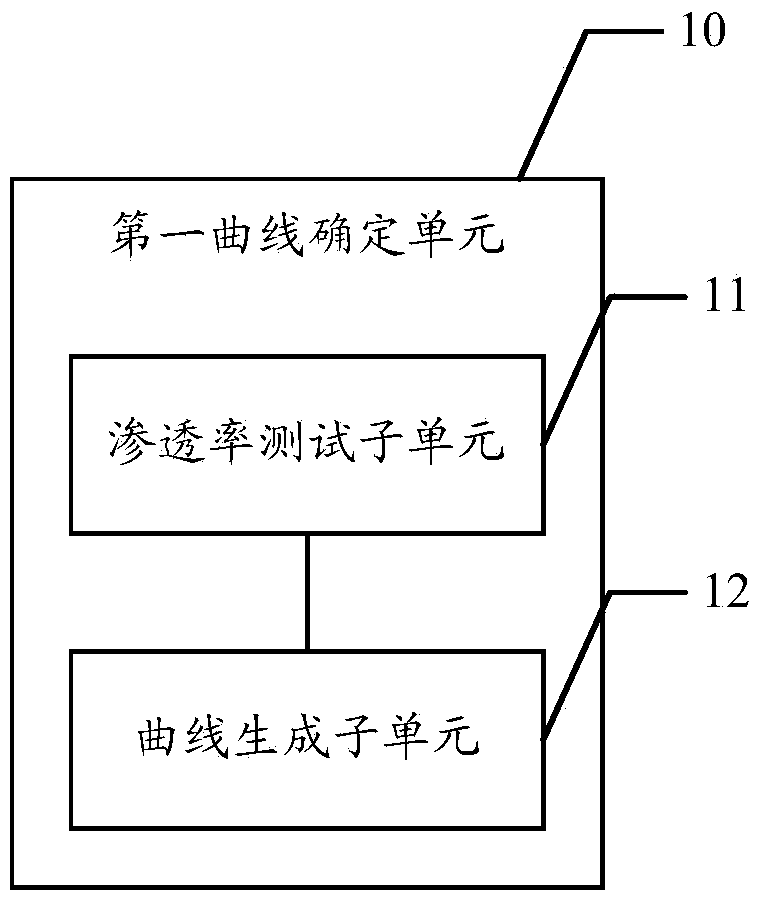
The invention discloses an intrinsic permeability interpretation method and system for a low-permeability reservoir. The intrinsic permeability interpretation method and system for the low-permeability reservoir comprises the following steps: first of all, a first curve in which a gas flow measurement value in a test sample changes with testing pressure is determined; secondly, a preset permeability of the test sample, a gas proportion which is reflected by the pore wall surface in a diffuse reflection manner and a ratio of the sliding distance and a molecular mean free path are set; an apparent permeability correction formula is utilized to correct the preset permeability; on the basis of the corrected permeability and other related parameters, the seepage equation is solved and the gas flow calculated value in the test sample under various testing pressure is obtained; thirdly, a second curve in which gas flow calculated value changes with the testing pressure is generated; when the fitting result of the first curve and the second curve meets the requirement of preset precision, the currently set preset permeability is used as the intrinsic permeability of the test sample. The intrinsic permeability interpretation method and system for the low-permeability reservoir can more accurately interpret the intrinsic permeability of the low-permeability reservoir.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
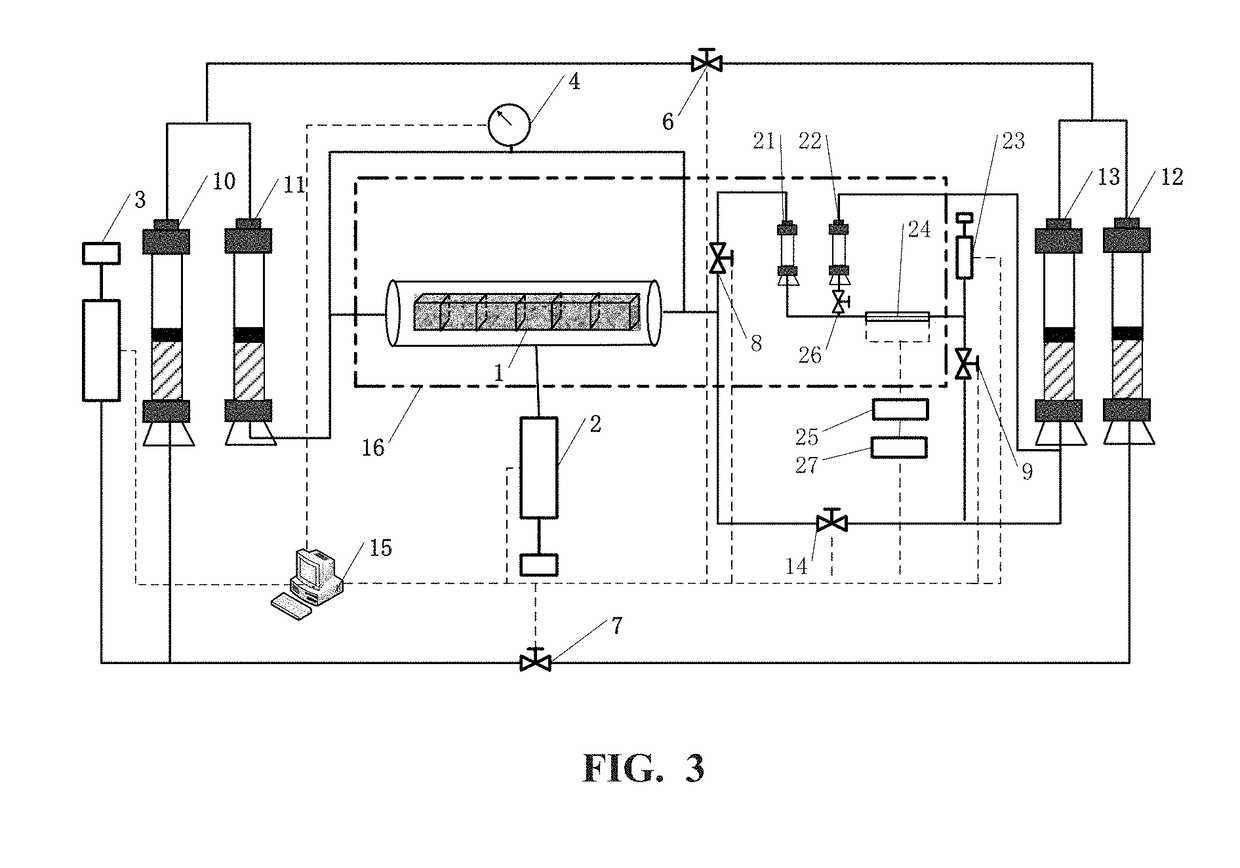
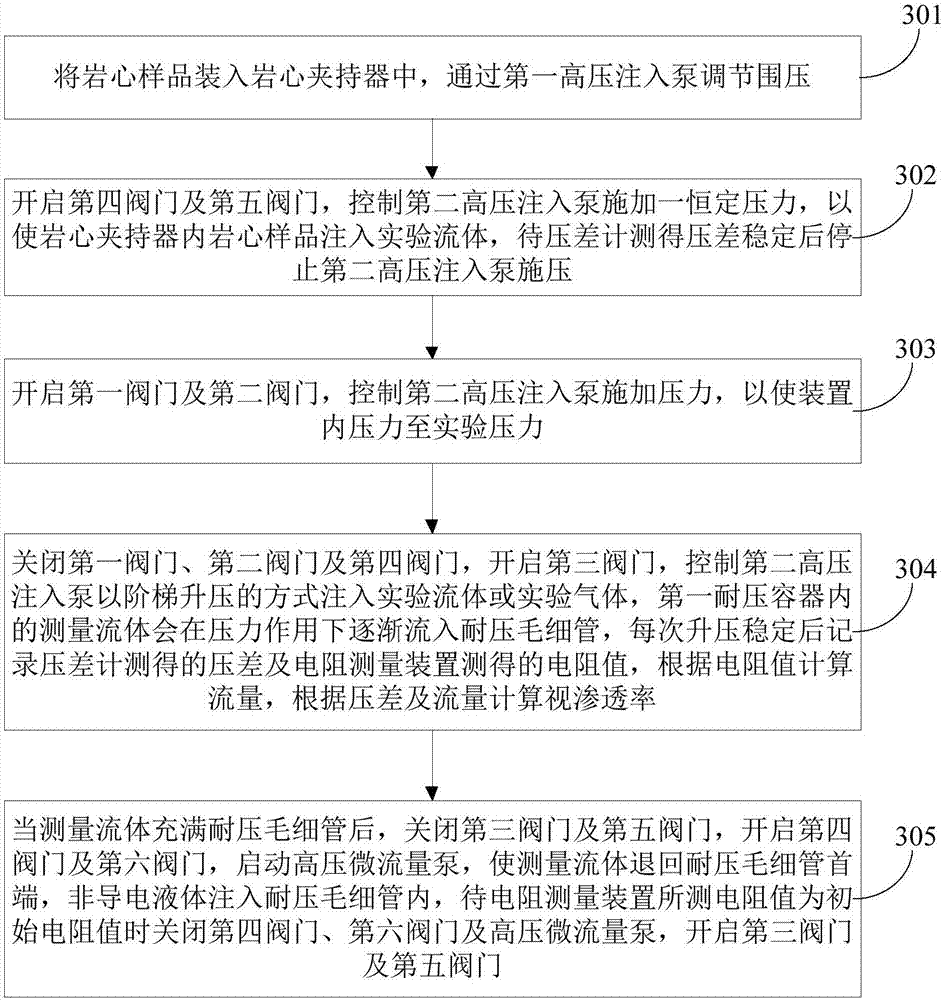
Apparatus and method for measuring apparent permeability of tight rock core
ActiveCN107167413ARealize curve measurementRealize continuous real-time measurementPermeability/surface area analysisContinuous measurementElectrical resistance and conductance
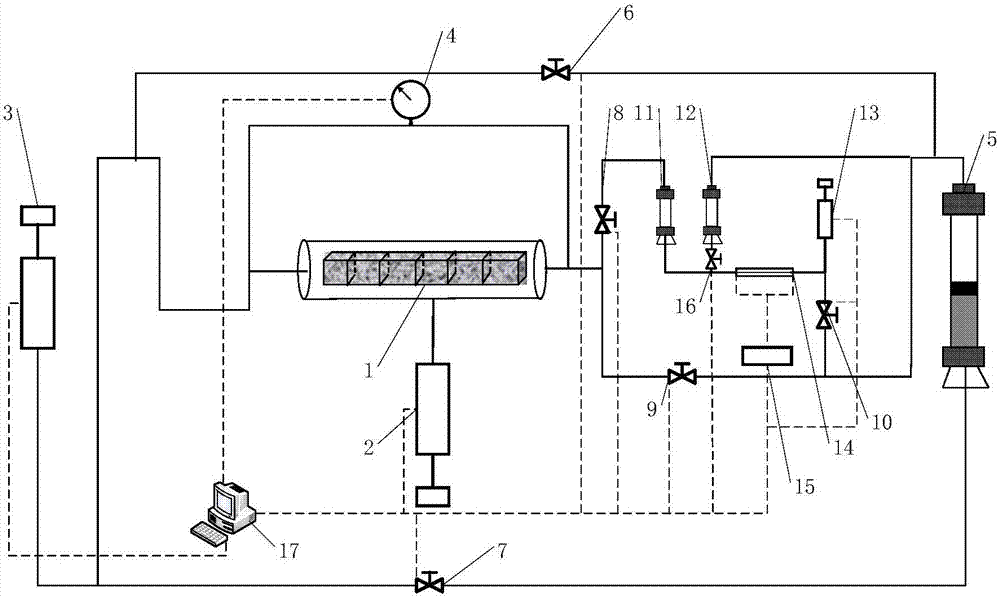
The invention provides an apparatus and a method for measuring the apparent permeability of a tight rock core. The apparatus comprises a rock core holder, a first high pressure injection pump, a second high pressure injection pump, a micro-differential pressure meter, a first pressure-resistant piston container, a micro-flow meter, a first valve, a second valve, a third valve, a fourth valve and a fifth valve, wherein the micro-flow meter comprises a first pressure-resistant container, a second pressure-resistant container, a high pressure micro-flow pump, a pressure-resistant capillary tube, a resistance measuring device and a sixth valve. After the pressure-resistant capillary tube is filled with a measured fluid, the third valve and the fifth valve are closed, the fourth valve and the sixth valve are opened, and the high pressure micro-flow pump is started to make the measured fluid return to the head end of the pressure-resistant capillary tube; and when the resistance measured by the resistance measuring device is an initial resistance, the fourth valve, the sixth valve and the high pressure micro-flow pump are closed, and the third valve and the fifth valve are opened. The apparatus and the method can realize continuous real-time measurement of unstable micro-flow under a high pressure in order to realize the continuous measurement of the apparent permeability of the tight rock core.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
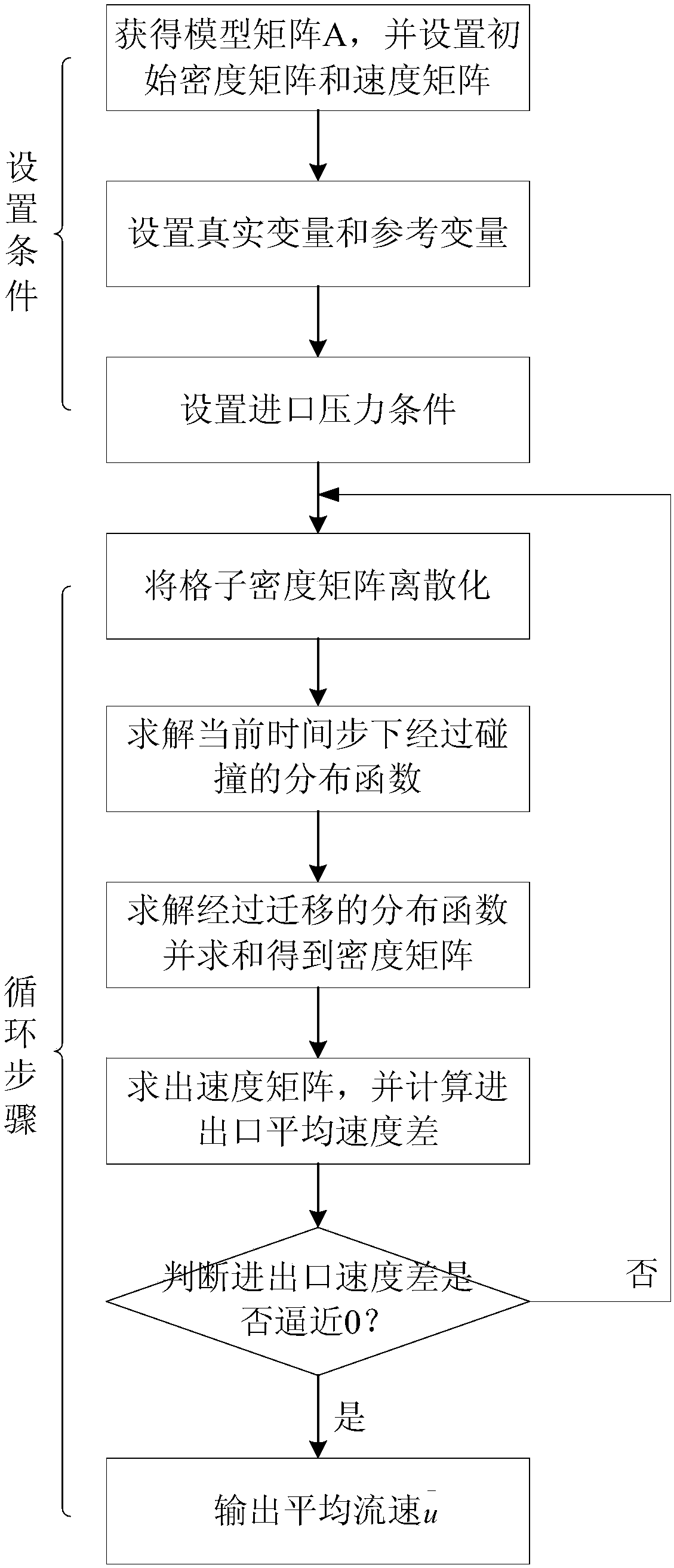
Gas permeability determination method of nano-pore-containing reservoir
The invention relates to a gas permeability determination method of a nano-pore-containing reservoir. The method includes the steps: simulating and calculating gas flow in a digital model matrix of arock by a lattice Boltzmann method (LBM), and counting average fluid velocity under different inlet pressure conditions mu (m / s); performing least square fitting on average fluid velocities corresponding to different inlet-outlet pressure differences by the aid of fitting target functions to obtain unknown intrinsic permeability Ko (m<2>) and a diffusion coefficient Dk (m<2> / s) of the rock; calculating a slip factor bk (Pa), and calculating gas permeability of the rock, namely, apparent permeability Ka (m<2>). The method solves the problem that the permeability of an excessively compact reservoir cannot be measured.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
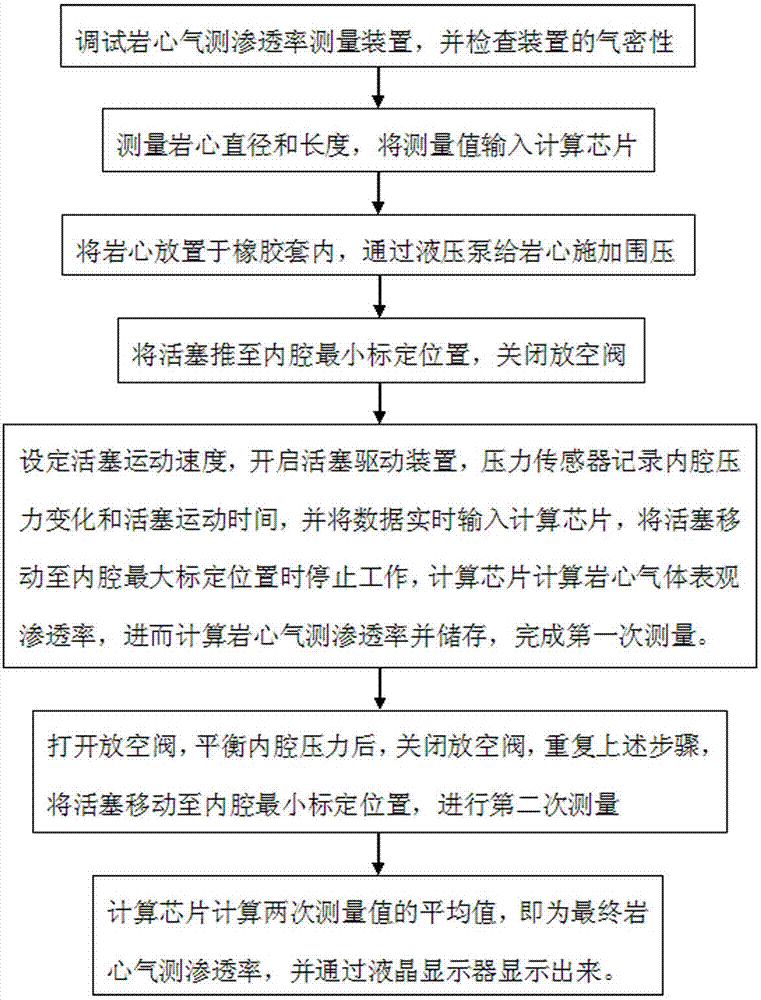
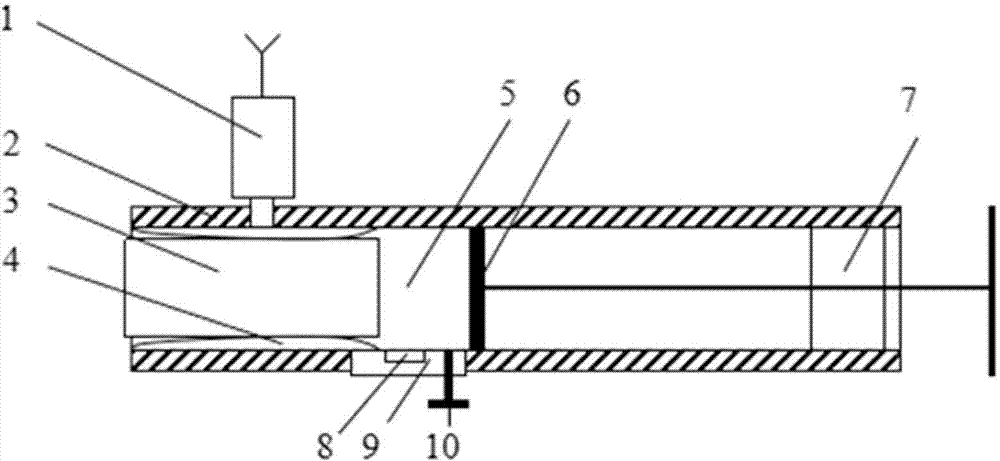
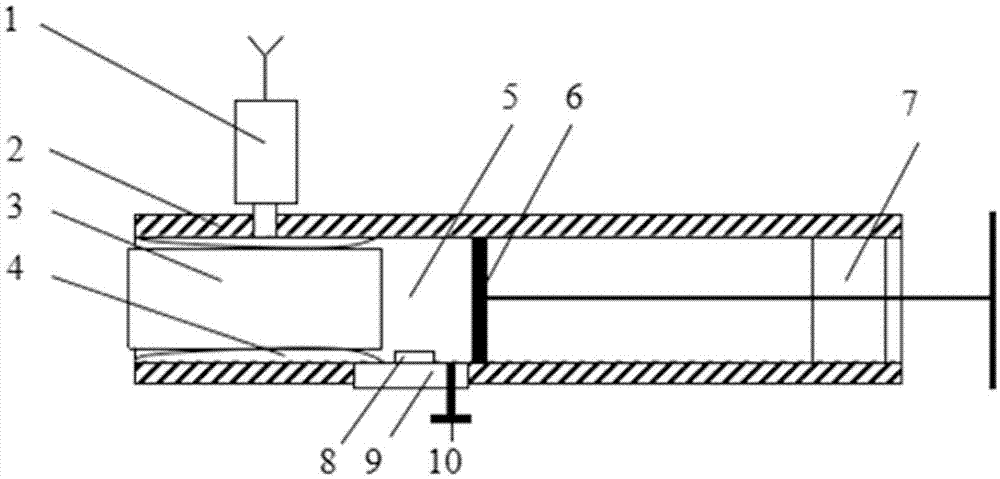
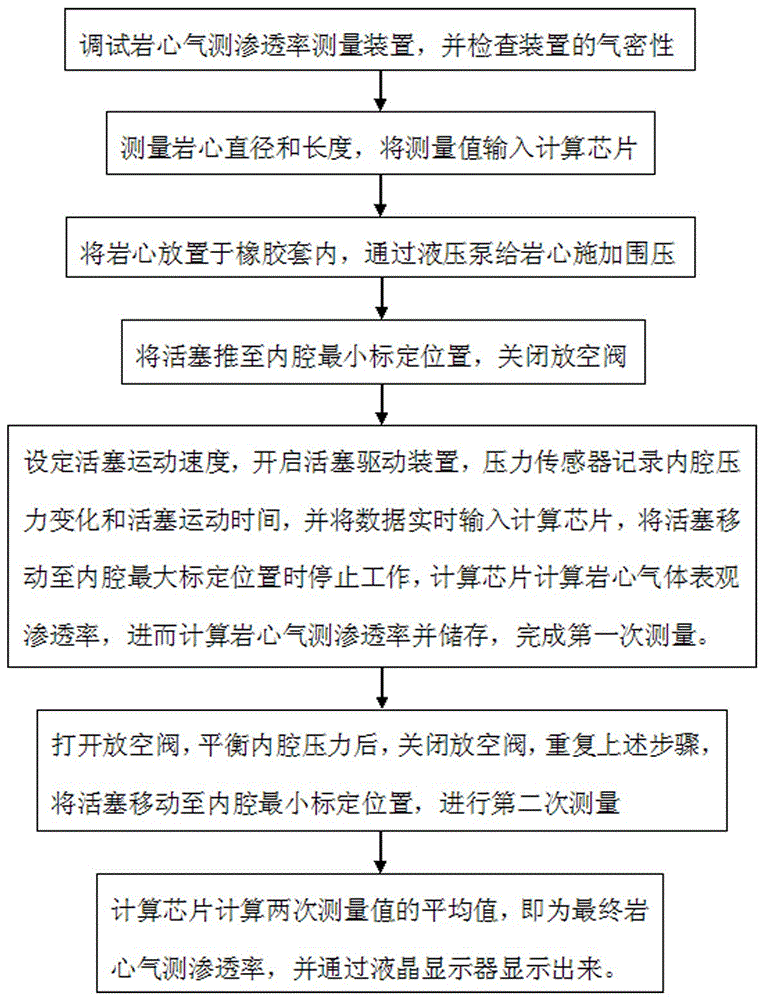
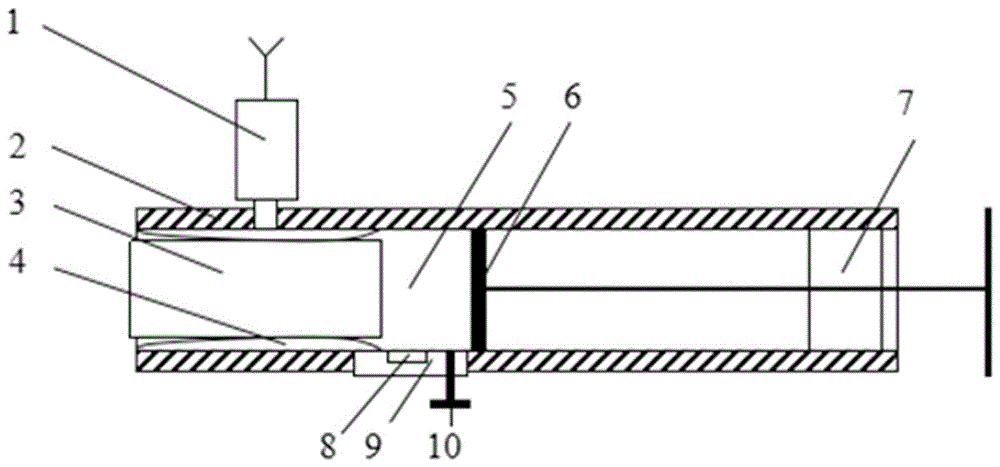
Measurement method of rock core gas logging permeability
ActiveCN104266949ADerivation is simpleReliable resultsPermeability/surface area analysisStopped workRock core
The invention discloses a measurement method of rock core gas logging permeability. The method comprises the following steps of inputting values of rock core diameter and length into a computing chip; putting a rack core into a rubber sleeve, and applying confining pressure by a small-sized hand-cranking hydraulic pump; pushing a piston to a minimum calibration position of an inner cavity, and closing an emptying valve; setting the moving speed of the piston, starting a piston driving device, stopping working when the piston is moved to a maximum calibration position of the inner cavity, calculating the apparent permeability of rock core gas by the computing chip, and further calculating the rock core gas logging permeability to complete first-time measurement; opening the emptying valve, and then closing the emptying valve after the pressure of the inner cavity is balanced; repeating the previous steps, moving the piston to the minimum calibration position of the inner cavity, and carrying out measurement for the second time; and calculating the average value of the twice measured values by the computing chip to obtain the final rock core gas logging permeability. According to the measurement method, the rock core gas logging permeability can be measured for two times in the back and forth movement process of the piston, so that the measurement method is high in measurement efficiency and high in measurement speed, and has an important significance for rapid evaluation of rock samples collected in the field.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
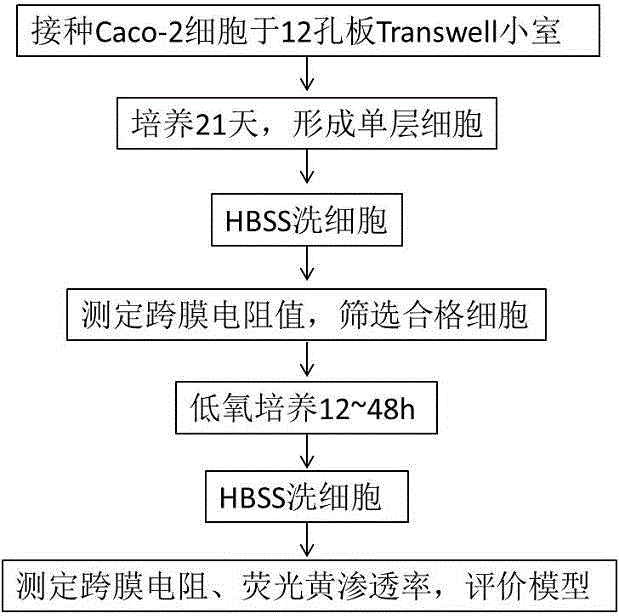
Establishing method for cell model used for researching drug absorption under plateau anaerobic condition
InactiveCN106701683AEasy to operateEnables high-throughput assaysTumor/cancer cellsOsmotic coefficientPlateau
The invention relates to an establishing method for a cell model used for researching drug absorption under a plateau anaerobic condition. The establishing method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing Caco-2 cells in a high-sugar DMEM culture solution; (2) constructing a Caco-2 cell single-layer model on a filter membrane of a 12-pore plate Transwell cell by the Caco-2 cells obtained in the step (1); (3) washing the Caco-2 cell single-layer model by HBSS; (4) measuring transepithelial electrical resistance of the Caco-2 cell single-layer model obtained in the step (3), and determining the Caco-2 cell single-layer model as a qualified Caco-2 cell single-layer model when the transepithelial electrical resistance is greater than 400 ohm; (5) performing anaerobic culture on the qualified Caco-2 cell single-layer model; (6) cleaning the Caco-2 cell single-layer model subjected to the anaerobic culture in the step (5); and (7) measuring the transepithelial electrical resistance and an fluorescein apparent permeability coefficient of the Caco-2 cell single-layer model obtained in the step (6), and completing model evaluation. The establishing method is simple to operate, is economic and scientific, can realize high-throughput measurement, administrates drugs for highland people in an individualized mode, and has relatively great promotion effect on reasonable drug administration.
Owner:王荣
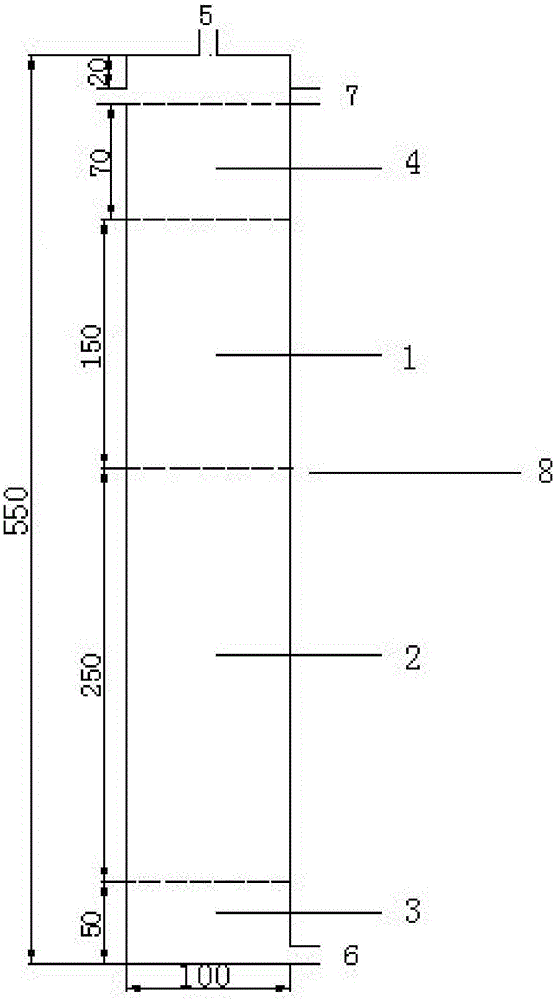
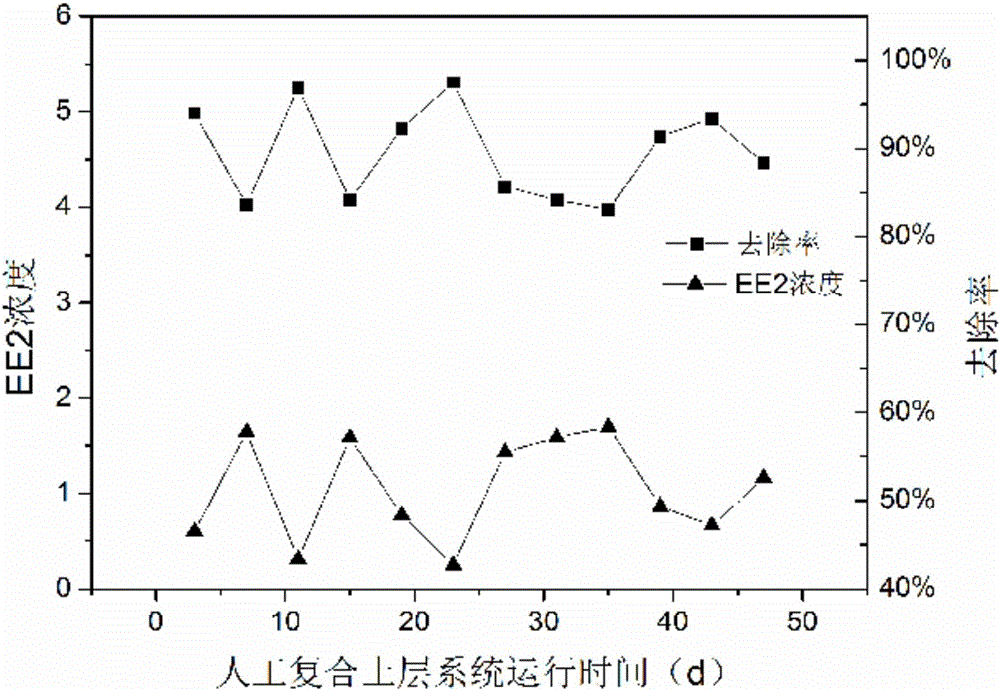
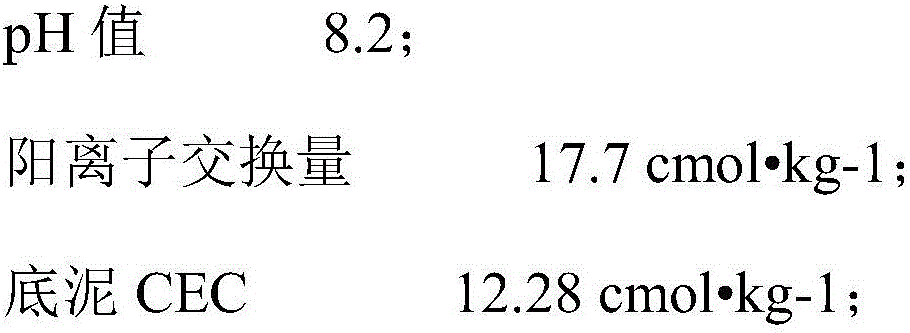
Artificial soil layer quick infiltration system and method for removing ethinylestradiol in water with high hydraulic load
InactiveCN106587382AEfficient removalIncrease hydraulic loadWater contaminantsTreatment involving filtrationHigh concentrationPerturbateurs endocriniens
The invention relates to an artificial soil layer quick infiltration system and method for removing ethinylestradiol in water with high hydraulic load, and the main structure of the system adopts an organic glass column as a carrier. Overall height of the column is 55cm, including overflow space with a height of 10 cm and dense filling of artificial mixed soil and gravel filter materials with a height of 45 cm. Fillers, from top to bottom, include a mixture of silty clay, medium-fine sand and volcanic rocks with a thickness of 15 cm, zeolite with a thickness of 25 cm, and coarse sandy gravel with a thickness of 5 cm. Endocrine disruptor ethinylestradiol can be removed from the to-be-treated water successively through the column, and through the degradation of soil natural microorganisms and the physical adsorption of the filter materials. Through the system, the removal rate of ethinylestradiol in reclaimed water is 99% or above, and the average removal rate is about 90% for high-concentration distribution water containing 10 <mu>g / L of EE2. The average of operation apparent permeability of the system is 1.26cm / s, the system is high in hydraulic load and low in site condition requirements. Plugging is an important factor affecting the application of artificial soil layer rapid infiltration system engineering. The system can operate for a long time under high hydraulic load, and can effectively remove the target pollutant EE2.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Shale reservoir permeability dynamic prediction method under synergistic effect of complex mechanism
ActiveCN111208051AImprove accuracyFacilitate mastery of dynamic development rulesPermeability/surface area analysisPorous mediumStream flow
The invention discloses a dynamic prediction method for shale reservoir permeability under the synergistic effect of a complex mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: correcting a non-circular pore with a pore section of a shale reservoir into a circular pore; carrying out quantitative characterization on pore size evolution by utilizing a pore equivalent diameter; determining a poresize fractal factor based on a fractal coarsening theory; calculating the length of a hollow billet and the number of pores in a preset range according to the pore size fractal factor, calculating thesectional area of the porous medium and the volume flow of a hollow billet bundle by utilizing a real-time pore equivalent radius and the pore number in the preset range; calculating the shale apparent permeability of the pores with different sections by utilizing hollow billet length, hollow billet bundle volume flow and the porous medium sectional area, and calculating the shale apparent permeability according to the proportions of the pores with different sections and the apparent permeability of the pores with different sections. The method can quantitatively characterize the influence ofcomplex multi-scale pores, reservoir modes, stress sensitivity and other characteristics of the shale reservoir on seepage, and realize the effective dynamic prediction of the permeability of the shale reservoir.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Flow-state evaluation method capable of considering shale multiscale effect
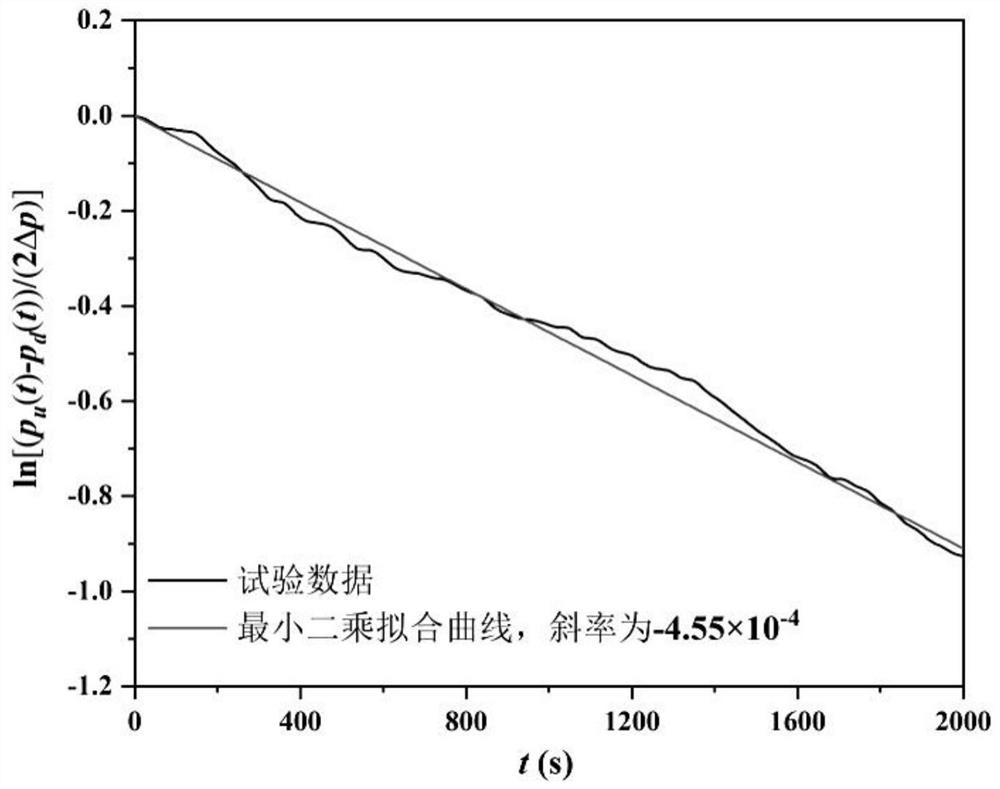
The invention discloses a flow-state evaluation method capable of considering the shale multiscale effect. The method comprises the following steps that S1, a shale core basic parameter is collected;S2, an apparent permeability calculation model capable of considering the multiscale effect is built; S3, four seepage flow models which exist at the same time are built, and a related algorithm is combined to obtain pressure response curves of an upstream chamber and a downstream chamber; S4, a pulse decay method experiment is used for measuring the pressure response curves of the upstream chamber and the downstream chamber; S5, in combination with the shale core pressure response modes of different development conditions, fitting of the experiment data is carried out to obtain the pressure response curves of the upstream chamber and the downstream chamber through calculation, and the shale core parameter is obtained through calculation; and the four seepage flow models which simultaneously exist in the shale core and consider an adsorption and desorption matrix and matrix + natural fracture development are built, the pressure response curves in the upstream chamber and the downstreamchamber are obtained through calculation, the pressure response curves obtained through calculation and the pressure response curves measured through the experiment are subjected to fitting, and related parameters and distributions of four flow states in the shale core can be obtained.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
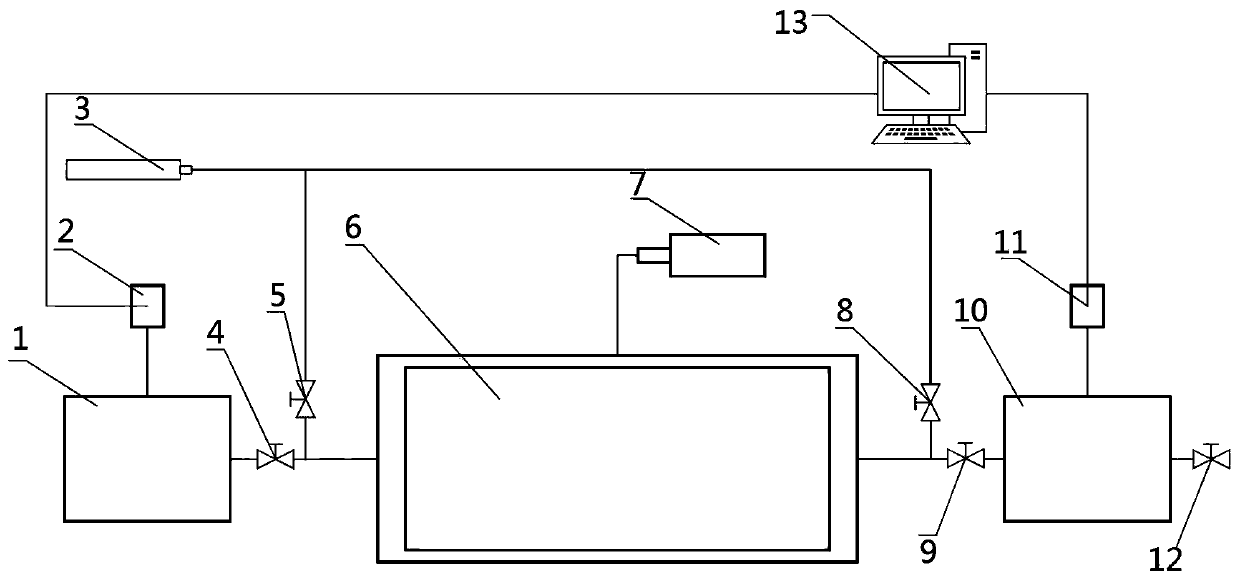
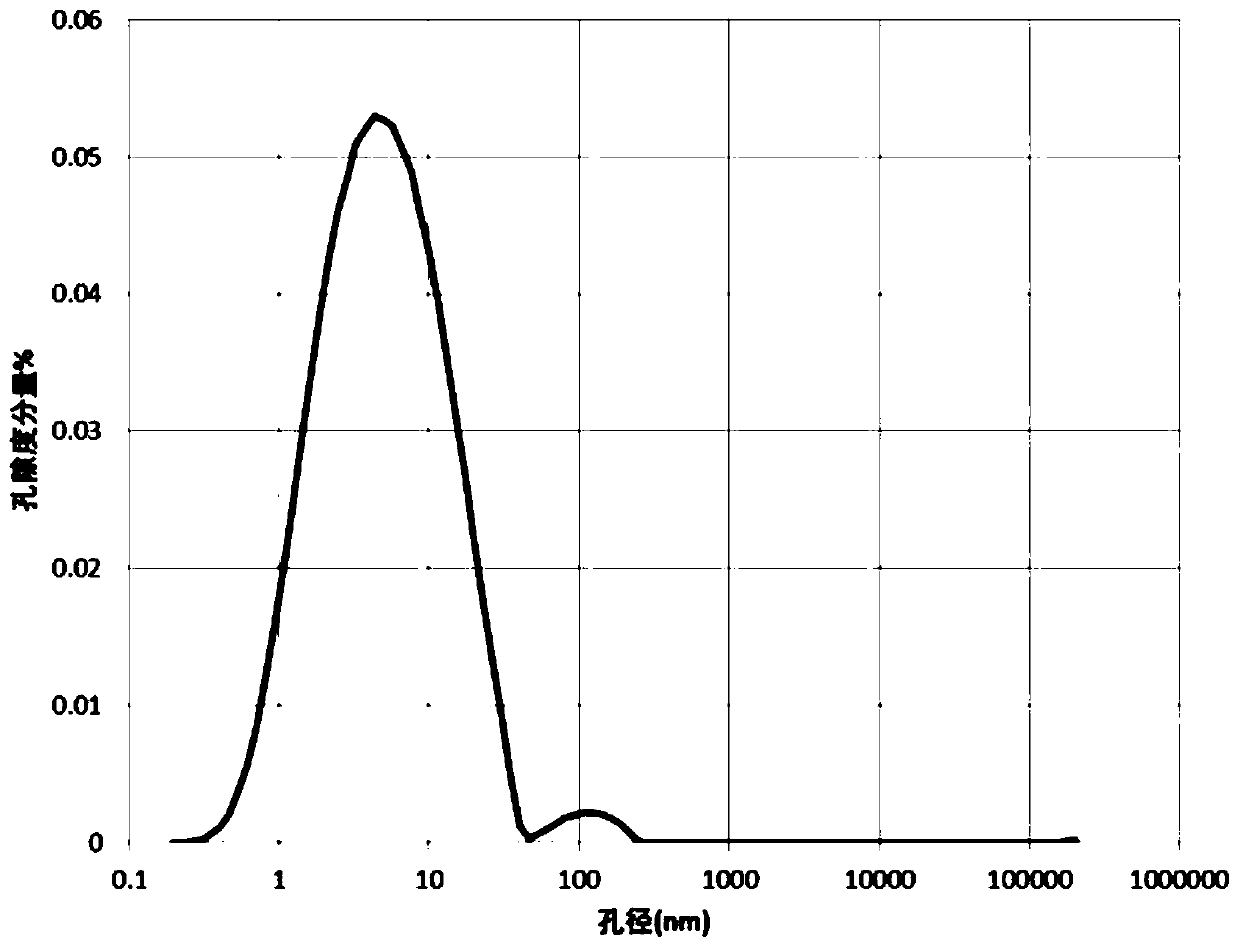
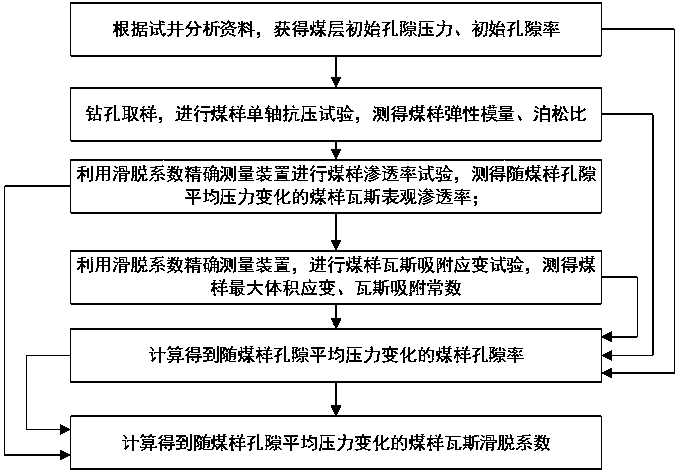
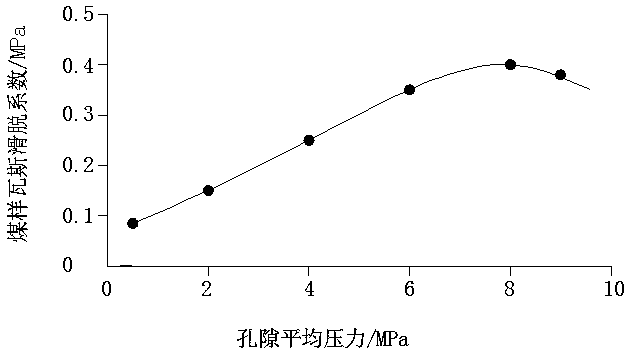
Method for precisely measuring gas slippage coefficient of low-permeability coal seam
ActiveCN110487703AImprove the shortcomings that can only be solved by linear fittingAccurate measurementPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityAnalysis data
The invention discloses a method for precisely measuring a gas slippage coefficient of a low-permeability coal seam. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring initial pore average pressure and initial porosity of the coal seam according to well testing analysis data of a coal-bed gas well; drilling and sampling the coal seam, carrying out a uniaxial compression test, and measuring an elasticitymodulus and a Poisson's ratio of a coal sample; carrying out a coal sample permeability test by using a low-permeability coal seam gas slippage coefficient precise measuring device, and measuring a gas apparent permeability of the coal sample; carrying out a coal sample gas adsorption strain test by utilizing the low-permeability coal seam gas slippage coefficient precise measuring device, and measuring maximum volume strain and adsorption gas constants of the coal sample; calculating to obtain porosity and pore radius of the coal sample changing along with the average pore pressure; and calculating to obtain the coal sample gas slippage coefficient changing along with the average pore pressure. The method is convenient and reliable, easy to operate, high in precision and high in safety,realizes the precise measurement of the gas dynamic slippage coefficient in the coal-bed methane production process, and provides an important theoretical basis for precise prediction of the productivity in the coal-bed methane exploitation process.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Shale reservoir induced heterogeneity dynamic evolution prediction method
ActiveCN111340298AHelps to masterDeepen understandingForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationSoil scienceReservoir pressure
The invention discloses a shale reservoir induced heterogeneity dynamic evolution prediction method. The method comprises the following steps: correcting a pore with a non-circular cross section of ashale reservoir into a circular pore; carrying out quantitative characterization on pore size evolution by utilizing the pore equivalent diameter; calculating apparent permeability of different sections of the shale reservoir; calculating the apparent permeability of the shale reservoir by utilizing the apparent permeability of different sections and the pore proportions of different sections; obtaining a material balance equation of the shale reservoir based on the Darcy law of the apparent permeability; and solving the material balance equation to obtain the change relationship of the apparent permeability of the shale reservoir at different positions in the matrix along with time, and quantitatively characterizing the heterogeneous response and evolution in the matrix by utilizing the change relationship to realize the prediction of the induced heterogeneous dynamic evolution of the shale reservoir. According to the method, the development of the induced heterogeneity dynamic evaluation technology in the shale reservoir pressure relief development process can be promoted, and the understanding of the unsteady-state law in the shale reservoir development process is facilitated.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
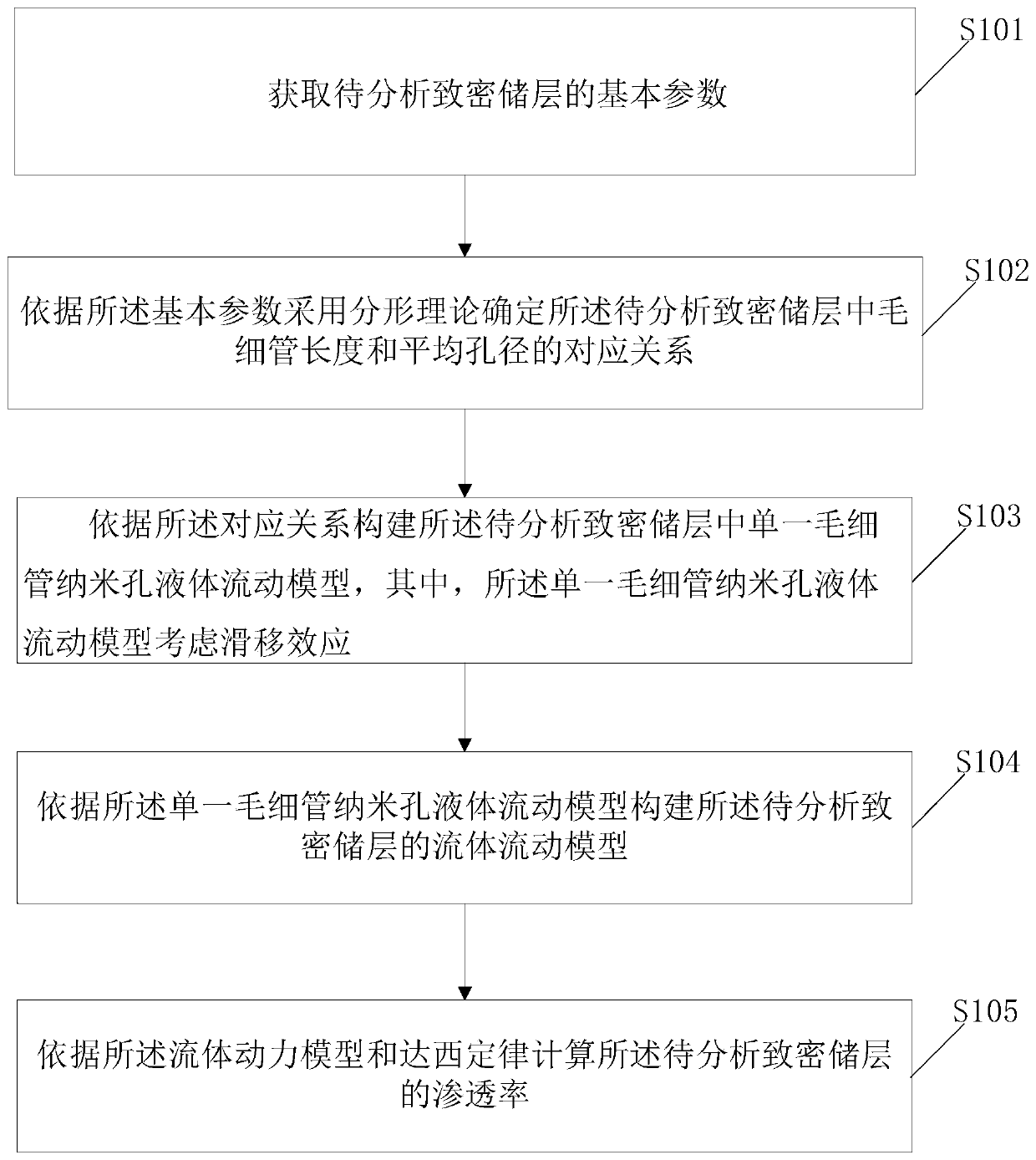
Tight reservoir liquid phase apparent permeability calculation method and device
ActiveCN111291521AReduce biasImprove accuracyFlow propertiesDesign optimisation/simulationChemical physicsFluid phase
The invention discloses a tight reservoir liquid phase apparent permeability calculation method and device. The method comprises the steps of acquiring basic parameters of a tight reservoir to be analyzed, determining the corresponding relationship between the capillary length and the average pore diameter in the tight reservoir to be analyzed by adopting a fractal theory according to the basic parameters, constructing a single capillary nanopore liquid flow model in the tight reservoir to be analyzed according to the corresponding relationship, wherein the single capillary nanopore liquid flow model considers a slip effect, constructing a fluid flow model of the tight reservoir to be analyzed according to the single capillary nano-pore liquid flow model, and calculating the permeability of the tight reservoir to be analyzed according to the hydrodynamic model and a Darcy law. According to the calculation method, the slip effect is considered, so that the deviation generated by predicting the apparent permeability of the tight reservoir by adopting continuous fluid mechanics and slip-free boundary conditions is reduced, and the calculation accuracy of the liquid-phase apparent permeability of the tight reservoir is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Quantitative characterization and parameter acquisition method for reservoir and seepage space of shale oil reservoir
ActiveCN114428040AEasy to controlStrong representativeSurface/boundary effectScanning probe techniquesRock corePorous medium
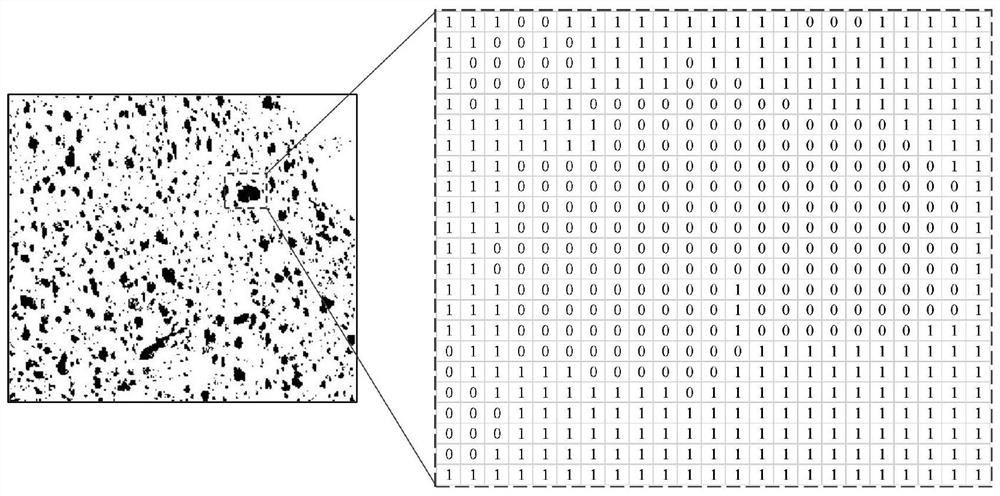
The invention discloses a shale oil reservoir reservoir seepage space quantitative characterization and parameter acquisition method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring image information of a real rock core of a shale reservoir in a target area, and processing the image information to obtain statistical characteristics of a micro-pore structure of a reservoir-seepage space; s2, generating a porous medium model based on the statistical characteristics and multi-level constraints; s3, obtaining characteristic parameters of the porous medium model, wherein the characteristic parameters comprise pore connectivity, pore size, pore morphology and porosity; and S4, performing fluid flow simulation in the porous medium model to obtain the apparent permeability of the fluid in the seepage of the porous medium model. The method has the technical effect that the porous medium model with higher representativeness and finer performance can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Prediction method for dynamic evolution of induced heterogeneity in shale reservoirs
ActiveCN111340298BHelps to masterDeepen understandingForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationSoil scienceDarcy's law
The invention discloses a shale reservoir induced heterogeneity dynamic evolution prediction method, which corrects the shale reservoir pore cross section from non-circular pores to circular pores; uses the pore equivalent diameter to quantitatively characterize the pore size evolution; calculates The apparent permeability of different sections of shale reservoirs; the apparent permeability of shale reservoirs is calculated by using the apparent permeability of different sections and the proportion of pores in different sections; based on Darcy's law of apparent permeability, the shale The material balance equation of the reservoir; by solving the material balance equation, the relationship between the apparent permeability of the shale reservoir at different positions in the matrix and the change with time is obtained, and the change relationship is used to quantitatively characterize the response and evolution of heterogeneity in the matrix to realize Prediction of dynamic evolution of induced heterogeneity in shale reservoirs. The invention can promote the development of the induced heterogeneity dynamic evaluation technology in the shale reservoir development process of pressure relief, and contribute to the understanding of the unsteady law in the shale reservoir development process.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
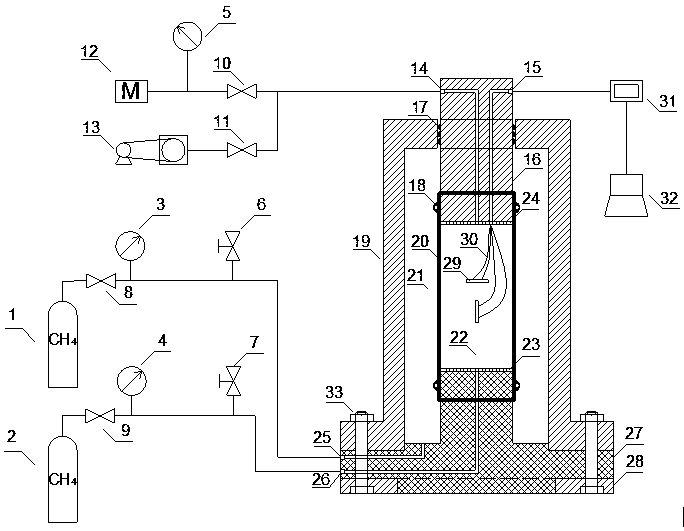
Device and method for rapidly and accurately measuring seepage law of gas in compact rock core
ActiveCN111929223AEasy to operateAccurate measurementPermeability/surface area analysisRock coreAxial pressure
The invention discloses a device and a method for rapidly and accurately measuring a seepage law of gas in a compact rock core. The device comprises a triaxial rock core holder, a pipeline system, a seepage system, a pressure system, a valve system and a data acquisition and processing system. The method comprises the following steps that the apparent permeability of a compact rock core is measured; by keeping the axial displacement of the compact rock core unchanged, the axial pressure and confining pressure applied to the compact rock core are adjusted, and the Biot coefficient of the compact rock core is measured; according to the measured Biot coefficient, the effective stress of the compact rock core is kept unchanged, and the Klinkenberg coefficient of gas seepage in the compact rockcore is measured. The method can accurately and quickly determine the seepage law of the gas in the compact rock core, are simple to operate, and have important significance for exploration and development of compact gas reservoirs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for calculating liquid apparent permeability of dual-wettability shale
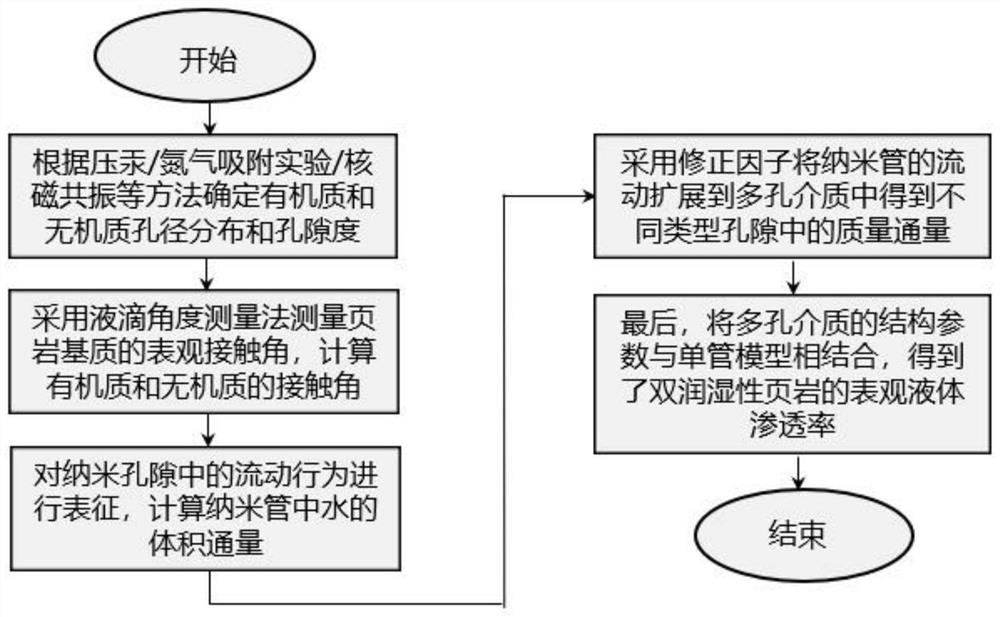
PendingCN114136862AChemical property predictionComputational theoretical chemistryMacroscopic scaleSoil science
The invention discloses a method for calculating liquid apparent permeability of dual-wettability shale. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring related parameters of a dual-wettability shale matrix and liquid; determining organic matter pore size distribution, inorganic matter pore size distribution and porosity of the dual-wettability shale; measuring an apparent contact angle of the dual-wettability shale matrix, and calculating an organic matter contact angle and an inorganic matter contact angle according to the apparent contact angle; and finally, calculating the liquid apparent permeability of the dual-wettability shale. According to the method, the transmission mechanism of organic matters and inorganic matters is considered, and parameters such as velocity distribution, density distribution, apparent viscosity, slippage length, shale pore tortuosity, porosity and the like are introduced into macroscopic permeability characterization of a shale matrix; and then, the structure parameters of the porous medium are combined with the single-tube model, various transport mechanisms are coupled, a unified liquid apparent permeability model is established, key input parameters are provided for accurate numerical simulation of shale gas, and the method has important theoretical and practical significance.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
A method for calculating the apparent permeability of porous media in shale reservoirs
ActiveCN108710723BApparent permeability is accurateAccurate calculation of apparent permeabilityDesign optimisation/simulationPermeability/surface area analysisPorous mediumUnconventional oil
The present invention belongs to the technical field of unconventional oil and gas development, and relates to a method for calculating apparent permeability of porous media of shale reservoir. The method includes the steps of: S1, collecting basic parameters of shale gas reservoir, calculating to obtain a Knudsen coefficient and a contribution coefficient; S2, utilizing the Knudsen coefficient tojudge the flow state of the gas in the capillary tube, and establishing the corresponding gas mass transport equation; S3, according to the water saturation of the reservoir rock sample, determiningthe effective flow radius corresponding to the capillaries of different sizes; S4, establishing unified mass transport equation of gas in different flow states in capillary tubes; S5. according to theunified mass transport equation, calculating the apparent permeability of the capillary tube, and superposing the apparent permeabilities of the capillary tubes with different sizes to obtain the apparent permeability of the whole shale core. The method of the invention takes into account the influence of different capillary sizes, distribution frequencies and water saturation of shale, and the method provided by the invention is closer to the real situation of the reservoir and obtains more accurate data.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Measuring method of gas core permeability
ActiveCN104266949BDerivation is simpleReliable resultsPermeability/surface area analysisStopped workRock core
The invention discloses a measurement method of rock core gas logging permeability. The method comprises the following steps of inputting values of rock core diameter and length into a computing chip; putting a rack core into a rubber sleeve, and applying confining pressure by a small-sized hand-cranking hydraulic pump; pushing a piston to a minimum calibration position of an inner cavity, and closing an emptying valve; setting the moving speed of the piston, starting a piston driving device, stopping working when the piston is moved to a maximum calibration position of the inner cavity, calculating the apparent permeability of rock core gas by the computing chip, and further calculating the rock core gas logging permeability to complete first-time measurement; opening the emptying valve, and then closing the emptying valve after the pressure of the inner cavity is balanced; repeating the previous steps, moving the piston to the minimum calibration position of the inner cavity, and carrying out measurement for the second time; and calculating the average value of the twice measured values by the computing chip to obtain the final rock core gas logging permeability. According to the measurement method, the rock core gas logging permeability can be measured for two times in the back and forth movement process of the piston, so that the measurement method is high in measurement efficiency and high in measurement speed, and has an important significance for rapid evaluation of rock samples collected in the field.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Shale reservoir permeability prediction method based on improved kozeny-carman model
ActiveCN111208052BImprove accuracyFacilitate mastery of dynamic development rulesPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityPredictive methods
The invention discloses a shale reservoir permeability prediction method based on the improved Kozeny-Carman model, which corrects the shale reservoir pore cross section from non-circular pores to circular pores; uses the pore equivalent diameter to quantitatively characterize the pore size evolution ; Determine the pore size fractal factor based on the fractal coarsening theory; calculate the capillary length and the number of pores in the preset range according to the pore size fractal factor, calculate the pore volume by using the real-time pore equivalent radius and the capillary length, and use the capillary length and the preset range The matrix volume is calculated by the number of pores, the dynamic porosity is calculated by using the pore volume and the matrix volume, and the apparent permeability of a single capillary of different sections is calculated by using the real-time equivalent pore radius. Permeability calculates the apparent permeability of shale. The invention comprehensively considers the characteristics of the shale reservoir, dynamically characterizes the porosity of the shale reservoir based on the fractal theory, and applies the dynamic porosity to the quantitative characterization of the permeability of the shale reservoir.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
A Permeability Evaluation Method for Unconventional Reservoir Based on Core Image
ActiveCN108829950BDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComputational scienceEvaluation result
The present invention provides a method for evaluating the permeability of unconventional reservoirs based on rock core images, which includes the following steps: using rock imaging technology to scan and identify real rock samples to obtain corresponding images, and divide the rock samples in the images into corresponding features; Extract the frequency spectrum of each feature separately, and then use the mixed fractal method to fit the analysis results to obtain the fractal parameters of each corresponding feature; combine the fitted fractal parameters to obtain a rock pore model based on the mixed fractal theory; through The pore connectivity algorithm calculates the connectivity probabilities between different types of pores in the rock pore model according to the connectivity probability matrix, and then the evaluation results of the apparent permeability of the current unconventional reservoir can be obtained. The invention starts from the real rock sample data and combines the pore connectivity algorithm to obtain the connectivity probability matrix between different types of pores, and finally realizes fast and accurate evaluation of the apparent permeability of unconventional reservoirs.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A flow regime evaluation method considering the multi-scale effect of shale
The invention discloses a flow state evaluation method considering multi-scale effects of shale, comprising the following steps: S1, collecting basic parameters of shale cores; S2, establishing an apparent permeability calculation model considering multi-scale effects; S3, establishing a simultaneous There are 4 kinds of seepage models, combined with related algorithms to obtain the pressure response curves of the upstream chamber and the downstream chamber; S4, using the pulse decay method to experimentally measure the pressure response curves of the upstream chamber and the downstream chamber; S5, combining the core pressure response of different development states Model, fit the experimental data to calculate the pressure response curves of the upstream chamber and downstream chamber, and calculate the core parameters. The present invention establishes four kinds of seepage models that simultaneously exist in the shale core that considers the matrix of adsorption and desorption and the matrix + natural fractures, and calculates the pressure response curves in the upper and lower chambers, the pressure response curves obtained through calculation and the pressure measured by experiments The response curves were fitted to obtain the relevant parameters and distributions of the four flow regimes in the rock.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
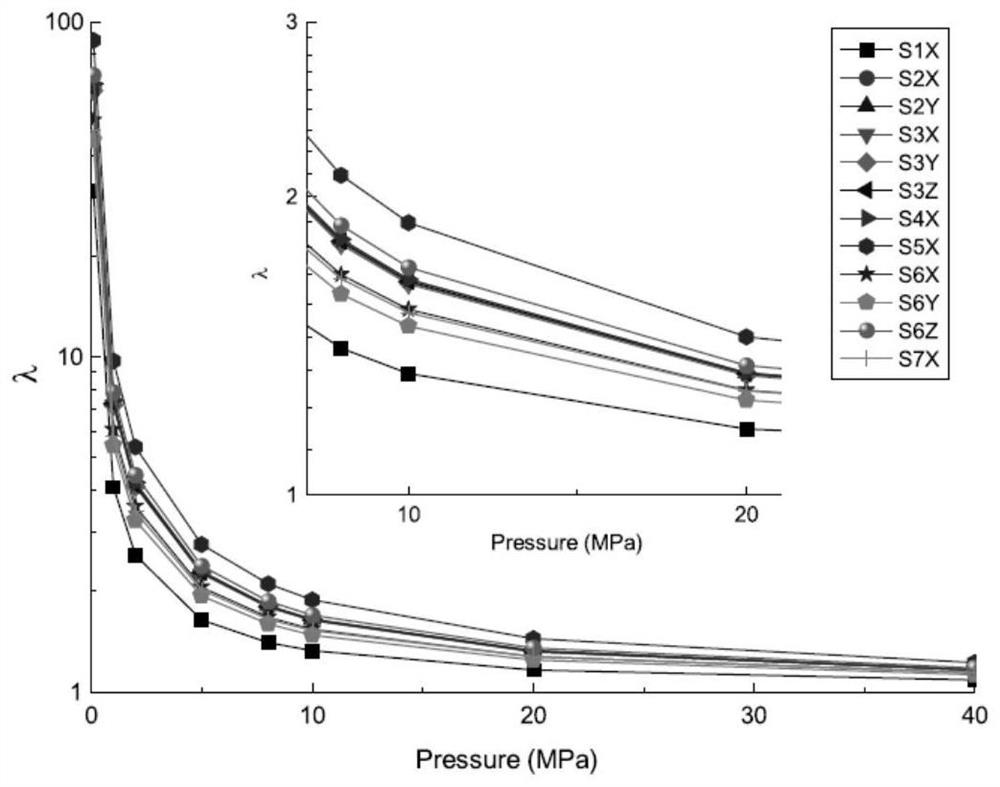
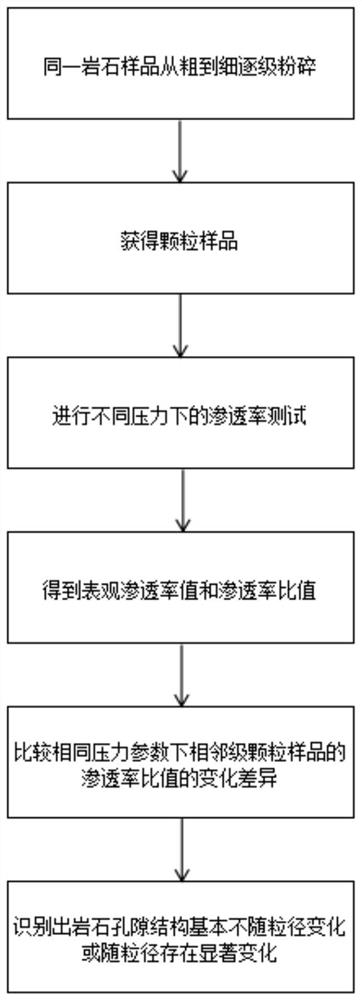
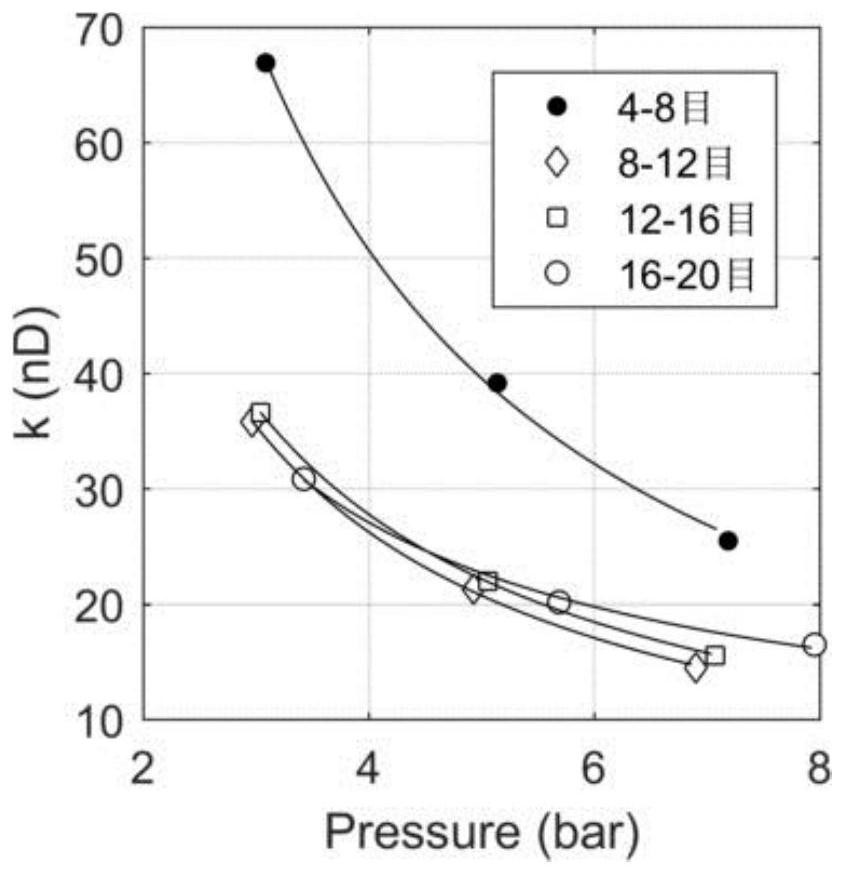
Method for judging whether rock pore structure changes along with particle size
The invention provides a method for judging whether a rock pore structure changes along with the particle size of particles, which comprises the following steps of: crushing the same rock sample step by step from coarse to fine, and obtaining particle samples in a mesh interval at each stage; the particle samples with the same mass are screened out at each stage, permeability tests under different pressures are carried out, and the apparent permeability values of the particle samples under different pressures and the permeability ratio of the particle samples at each stage are obtained; and comparing the change difference of the permeability ratios of the adjacent-level particle samples under the same pressure parameter, and identifying that the pore structure of the rock basically does not change along with the particle size or obviously changes along with the particle size. By using the judgment method provided by the invention, the change characteristic differences of the apparent permeability values of the particles with different particle sizes along with the pressure are compared to identify that the pore structure basically does not change along with the particle size and obviously changes along with the particle size, and the judgment method has the advantages of easy operation and convenience; the problem that whether pore structures of a large number of particle samples change along with particle sizes is difficult to effectively judge is solved.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparent Permeability Interpretation Method and System for Low Permeability Reservoir in Formation
ActiveCN104237107BAccurate explanationPermeability/surface area analysisTest samplePermeability measurements
The invention discloses a method and system for interpreting the apparent permeability of low-permeability reservoirs in formations. Firstly, the curve of the permeability measurement value of the test sample as a function of gas pressure is determined, and then the Knudsen number of the test sample under different pressures is determined. The curve of the permeability measurement value of the test sample changing with the gas pressure is converted into the curve of the permeability measurement value of the test sample changing with the Knudsen number, and the curve of the permeability measurement value of the test sample changing with the Knudsen number Square method data fitting, determine the intrinsic permeability of the test sample, the wall influence parameters of the test sample, and the ratio of the slip distance of the test sample to the molecular mean free path, when determining the apparent permeability of the low-permeability reservoir in the formation , using the wall influence parameter of the test sample and the ratio of the test sample’s slip distance to the molecular mean free path to correct the wall slip effect, so as to more accurately explain the apparent permeability of low-permeability reservoirs in the formation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Dynamic prediction method of shale reservoir permeability under the synergistic influence of complex mechanisms
ActiveCN111208051BImprove accuracyFacilitate mastery of dynamic development rulesPermeability/surface area analysisSoil sciencePorous medium
The invention discloses a method for dynamic prediction of shale reservoir permeability under the synergistic influence of complex mechanisms, correcting the shale reservoir pore cross section from non-circular pores to circular pores; using the pore equivalent diameter to quantitatively characterize the pore size evolution; based on The fractal coarsening theory determines the fractal factor of the pore size; according to the fractal factor of the pore size, the capillary length and the number of pores in the preset range are calculated, and the cross-sectional area of the porous medium and the volume of the capillary bundle are calculated by using the real-time equivalent pore radius and the number of pores in the preset range Flow rate, using the capillary length, capillary bundle volume flow rate and porous medium cross-sectional area to calculate the apparent permeability of shale in different cross-section pores, and calculate the apparent permeability of shale according to the proportion of pores in different cross-sections and the apparent permeability of pores in different cross-sections. The invention can quantitatively characterize the influence of shale reservoirs on seepage due to complex multi-scale pores, storage methods, stress sensitivity and other characteristics, and realize effective dynamic prediction of shale reservoir permeability.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com