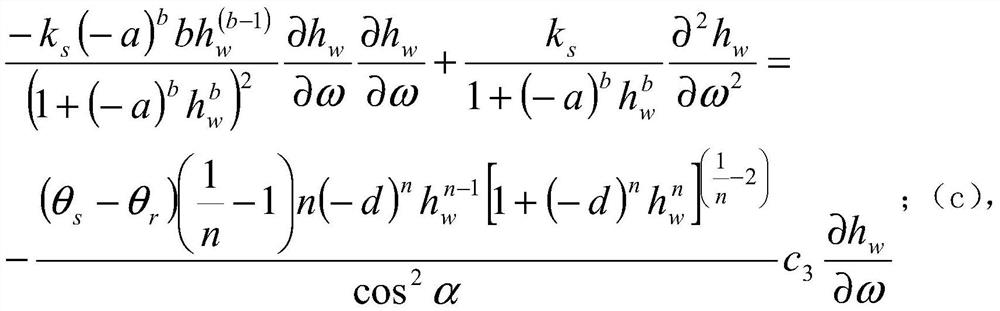Patents
Literature
77 results about "Darcy's law" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Darcy's law is an equation that describes the flow of a fluid through a porous medium. The law was formulated by Henry Darcy based on results of experiments on the flow of water through beds of sand, forming the basis of hydrogeology, a branch of earth sciences.
Tight oil flow simulation and permeability prediction method based on pore network model
ActiveCN108729908AThe flow is accurately describedFlow descriptionSurveyDesign optimisation/simulationData fileNetwork model
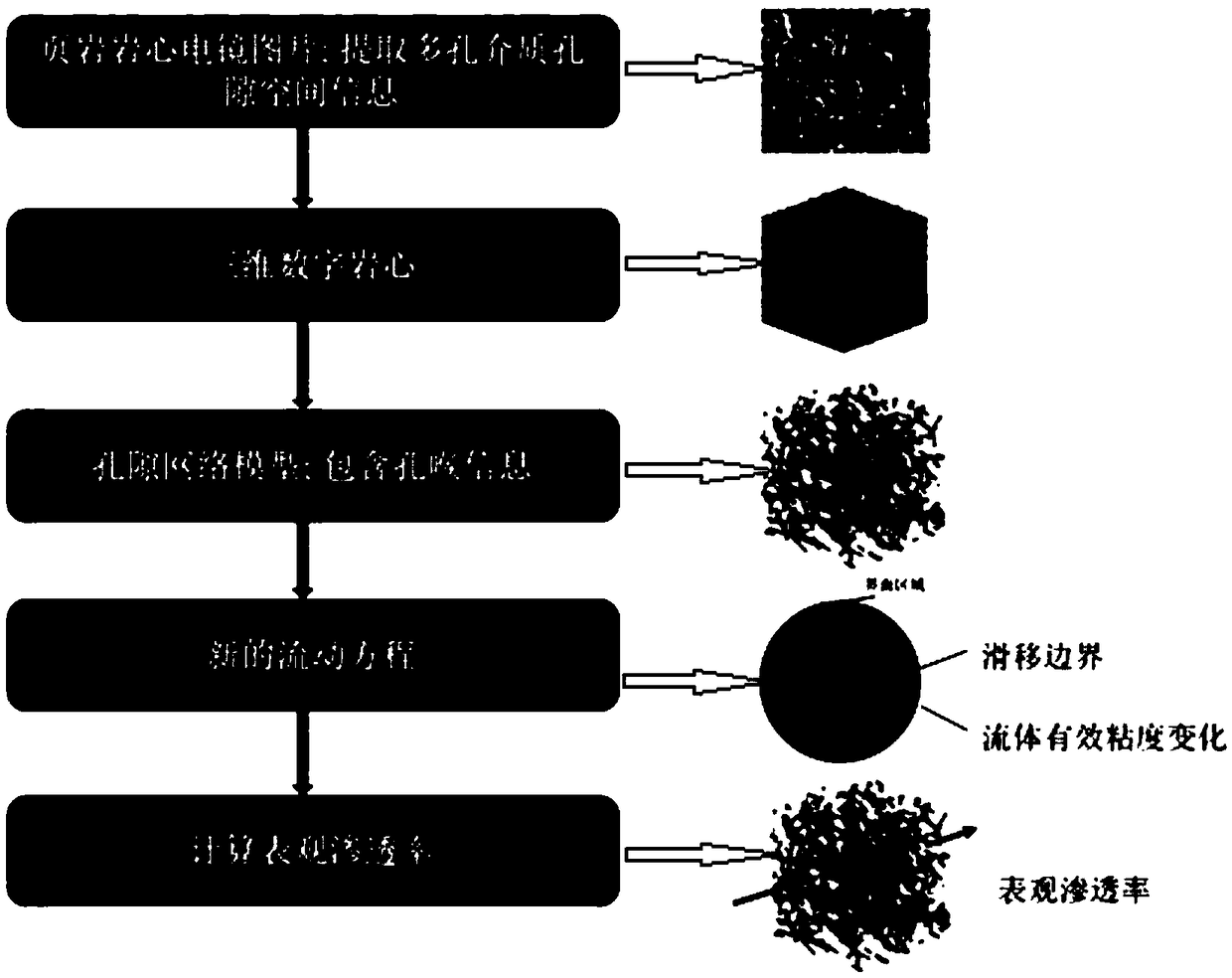
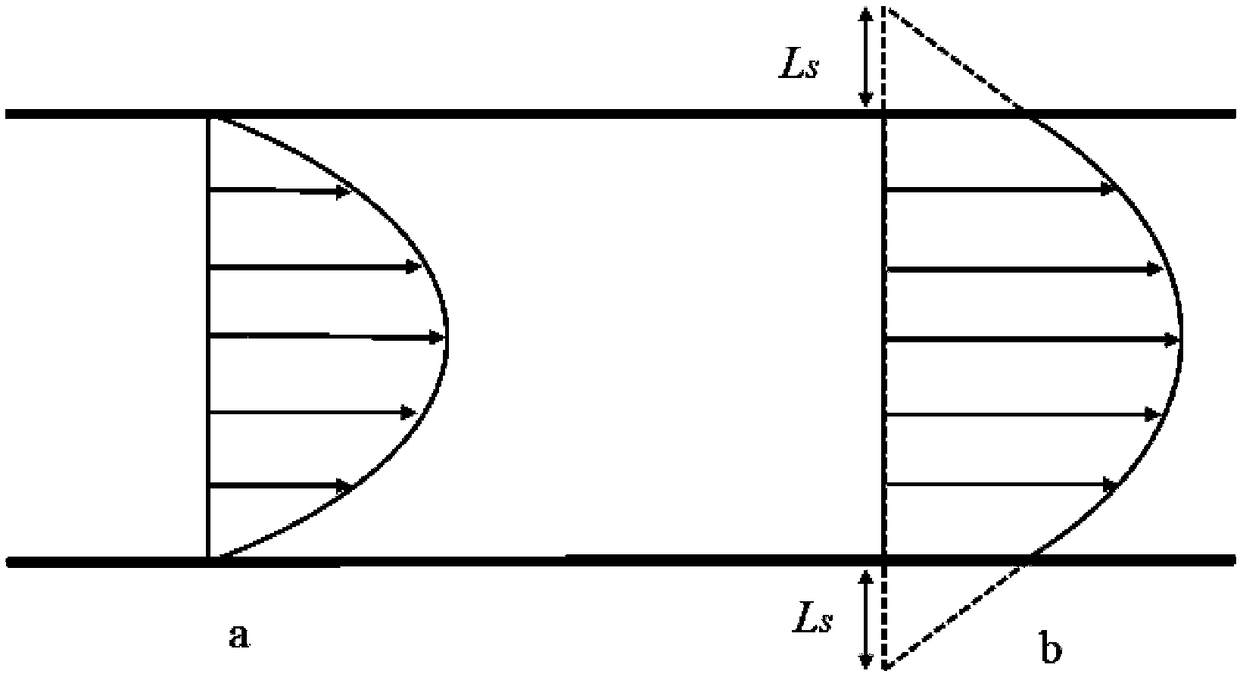
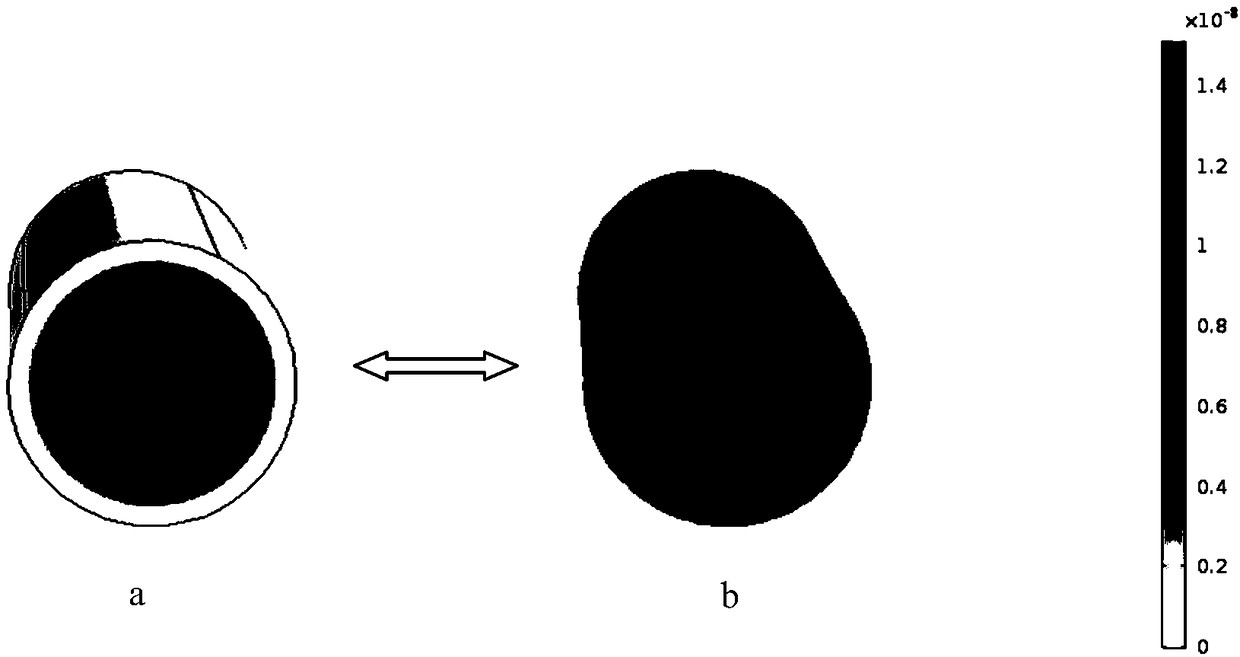
The invention relates to a tight oil flow simulation and permeability prediction method based on a pore network model. The method includes the following steps: (1) scanning a tight core to obtain a two-dimensional electron microscope image and obtain spatial geometric information of porous medium pores; (2) reconstructing a digital core to obtain a geometric data file of the digital core; (3) extracting the pore network model of the digital core to obtain a data file of the pore network model of the tight core; (4) obtaining the pressure at each pore and the volume flow rate at each pore throat position to further obtain the flowing condition of a fluid in the nano-scale pore network model; (5) obtaining the volume flow rate Q of the fluid at the outlet end of the pore network model and calculating the apparent permeability of the pore network model according to the Darcy law. The newly developed pore network model overcomes the shortcoming that the traditional pore network model cannot consider the boundary slip and the change of the effective viscosity of the fluid when the fluid flows in the nanopores.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
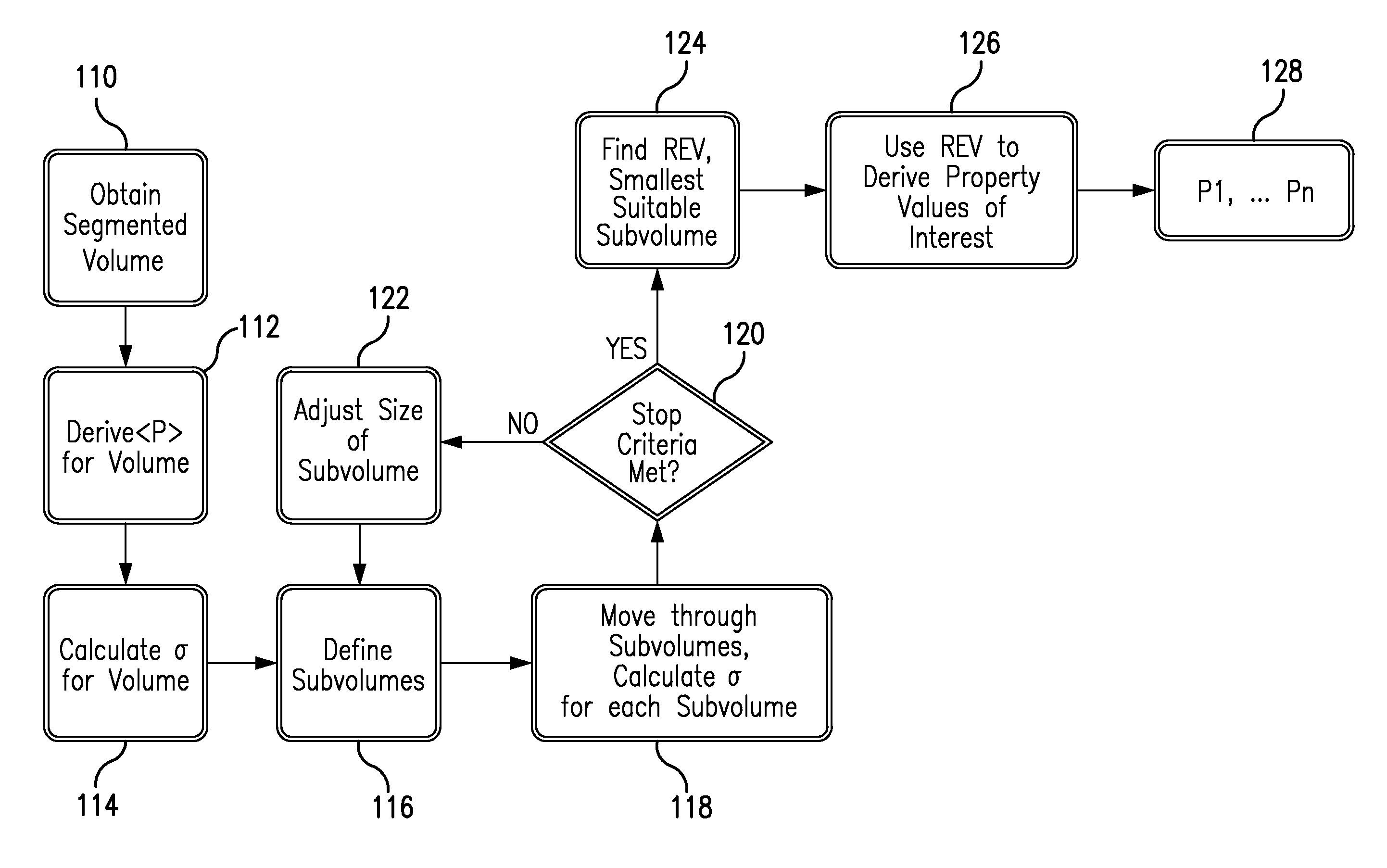
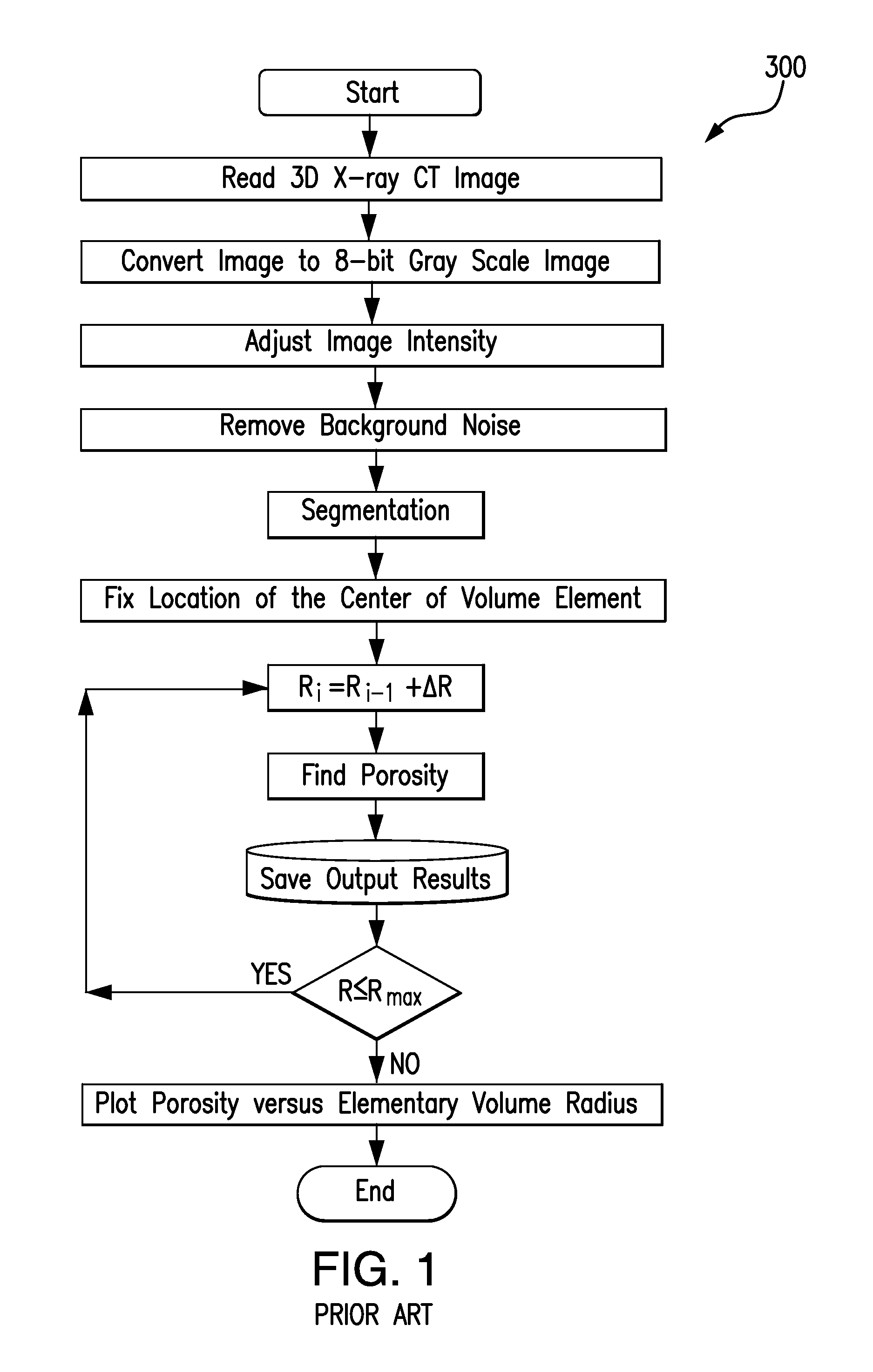
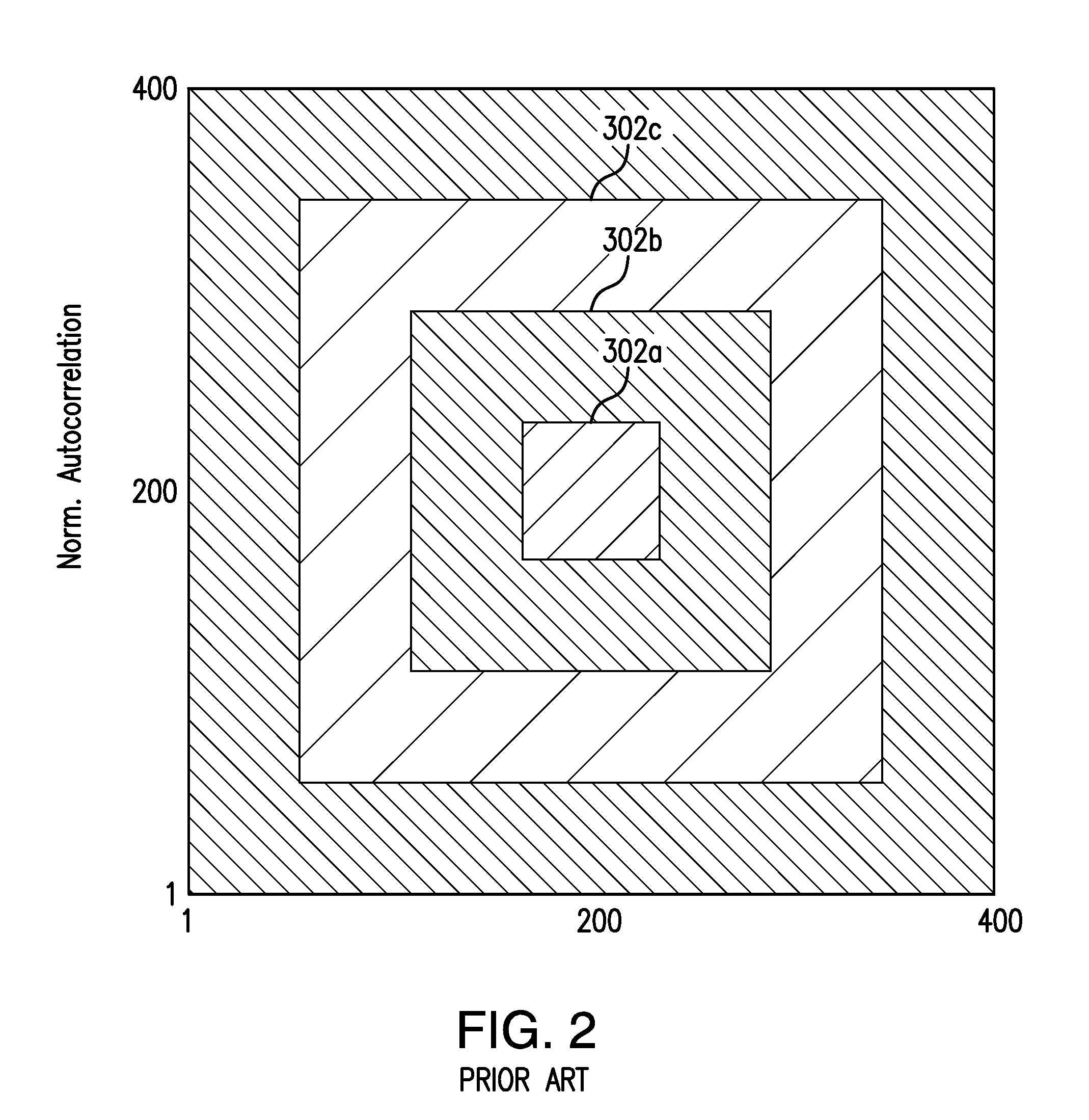
Efficient Method For Selecting Representative Elementary Volume In Digital Representations Of Porous Media
InactiveUS20130262028A1Effective estimateImprove approximationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMechanical area measurementsRepresentative elementary volumeDarcy's law
The present invention relates a method to estimate representative elementary volume (REV) in a sample of porous media wherein the sub-volume selected is a better approximation of the elementary volume than existing methods. REV in a sample of porous media such as rock can be defined wherein the REV is selected with respect to the expected direction of fluid flow through the porous media. The method can quantify how good is the digital representation of a rock and how accurate a description of a fluid flow through Darcy's law will be, and allows the evaluation of different length scales in different directions for the REV and an assessment of the anisotropy of the pores structures when the method is applied in different directions. The method also can determine a robust criteria to understand when a trend of porosity-permeability breaks down due to an insufficient size of the subsample.
Owner:INGRAIN INC
Method for predicting extraction productivity of underground coal-seam gas
The invention provides a method for predicting extraction productivity of underground coal-seam gas, in which the actual change of permeability of a coal seam is considered and the extraction productivity of extraction drilling group can be predicted. The method comprises the following steps: 1) measuring original parameters of the coal seam to be measured; and 2) by calculating a model provided by the invention, acquiring the mean permeability after the extraction, the coal-seam gas pressure after the extraction, the coal-seam gas average content after the extraction and the coal-seam gas extraction quantity. In the method for predicting the extraction productivity of the underground coal-seam gas, based on Darcy's law of seepage, a mathematical model for predicting the extraction productivity of the underground coal-seam gas based on the permeability variation in the extraction process is established; and because the actual change of the permeability in the extraction process is considered in the mathematical model, the seepage situation of the coal-seam gas can be correctly reflected. In the further calculation step, the mathematical model is calculated by adopting a differencediscrete method, the convergence rate is high, the precision is high, the stability is high and the calculation accuracy and speed are improved.
Owner:CHINA COAL TECH ENG GRP CHONGQING RES INST
Method of determining the evolution of petrophysical properties of a rock during diagenesis
InactiveUS20100154514A1Enhanced recovery of hydrocarbonSolid dispersion analysisEarth material testingQuantitative determinationPhysical chemistry
A method for quantitative determination of the permeability and porosity evolution of a porous medium during diagenesis having application to oil reservoir development is disclosed. A diagenesis scenario and an initial structure of the pore network of the porous medium are defined.A representation of the pore network is constructed by a PNM model. The steps of the diagenesis scenario are determining the ion concentration on the pore and channel walls of the PNM model, for a precipitation or dissolution reaction according to the scenario, and deducing therefrom a geometry variation of the PNM model, the porosity is calculated geometrically and the permeability is calculated from Darcy's law for the modified PNM model; the foregoing steps are repeated according to the diagenesis scenario and a relationship is deduced between the permeability of the porous medium and the porosity of the porous medium during diagenesis.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Apparatus and method for testing permeability of porous material
ActiveCN105572013AEasy to operateHigh precisionPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityMaterials testing
The present invention discloses an apparatus and a method for testing permeability of a porous material, and belongs to the field of materials testing. According to Darcy's law, a test material is made into a cylinder / disk-shaped specimen, the cylinder / disk-shaped specimen is put into a syringe, hydraulic pressure is controlled by a material testing machine, and the permeability of the material can be obtained by testing and calculation of the speed of a liquid to pass through the material by. The method can be used as a method to test and characterize the porosity of the porous material and liquid permeability / penetrability. The testing technology is simple in operation and high in precision, is expected to promote as a testing technology for porosity characters of other porous materials, and has potential application value in material testing engineering filed.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Determination method and testing apparatus for permeability coefficient of cement-based material
InactiveCN105158136AGuaranteed tightnessAccurate control of constant pressurePermeability/surface area analysisPorosityTransducer
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
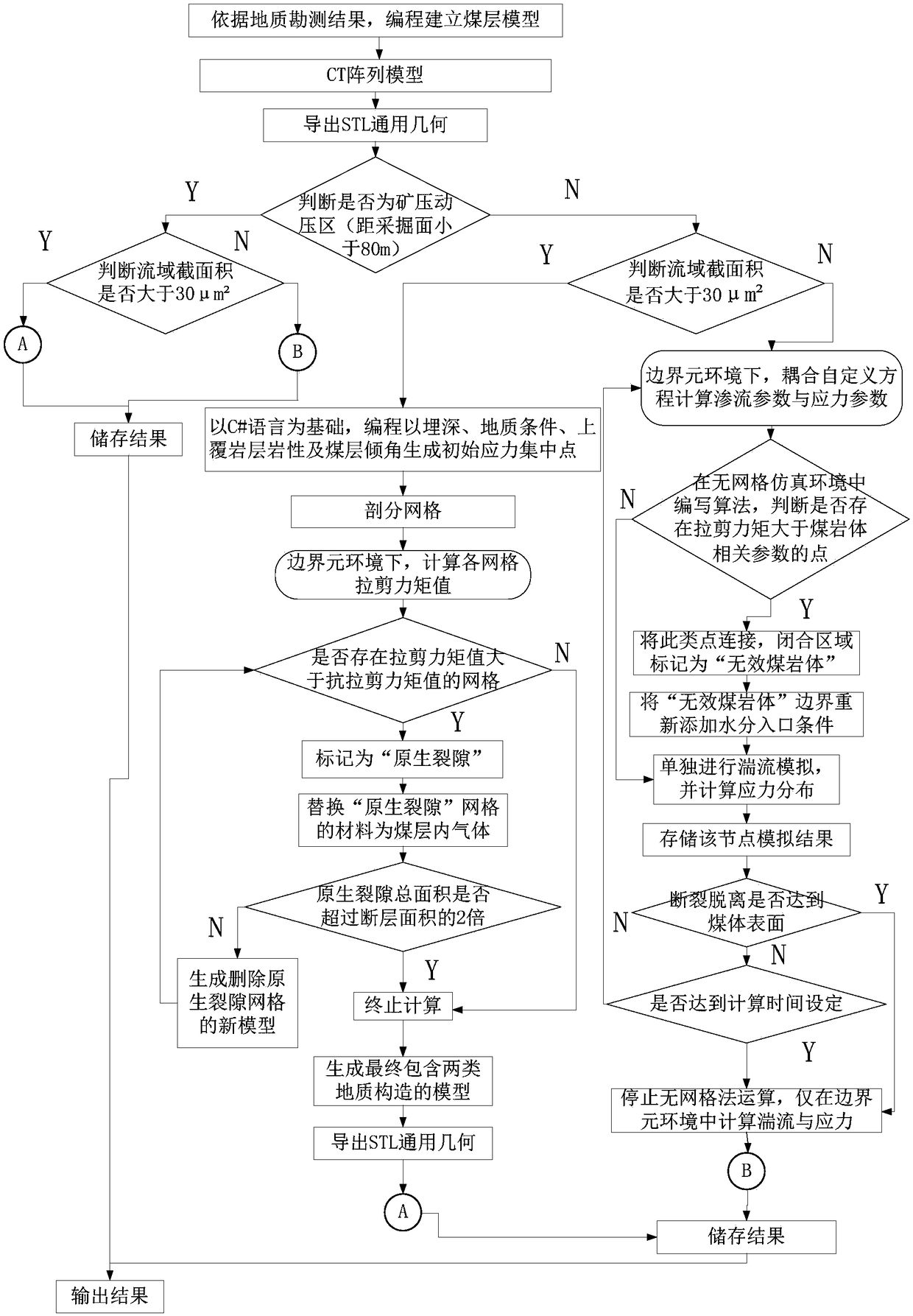
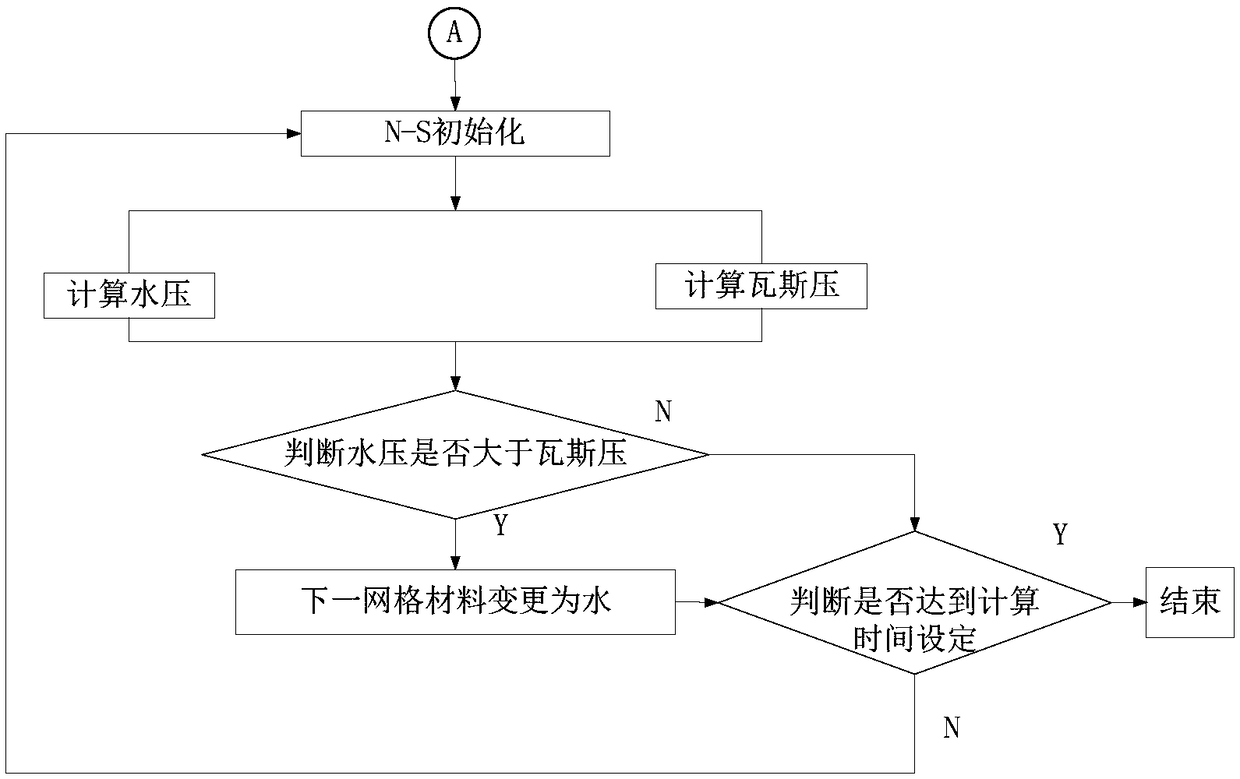
Coupling numerical simulation method of seepage-damage-stress for coal and rock mass water injection
ActiveCN109063257AEnsure safetyReduce productionUnderground miningDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelGeological survey
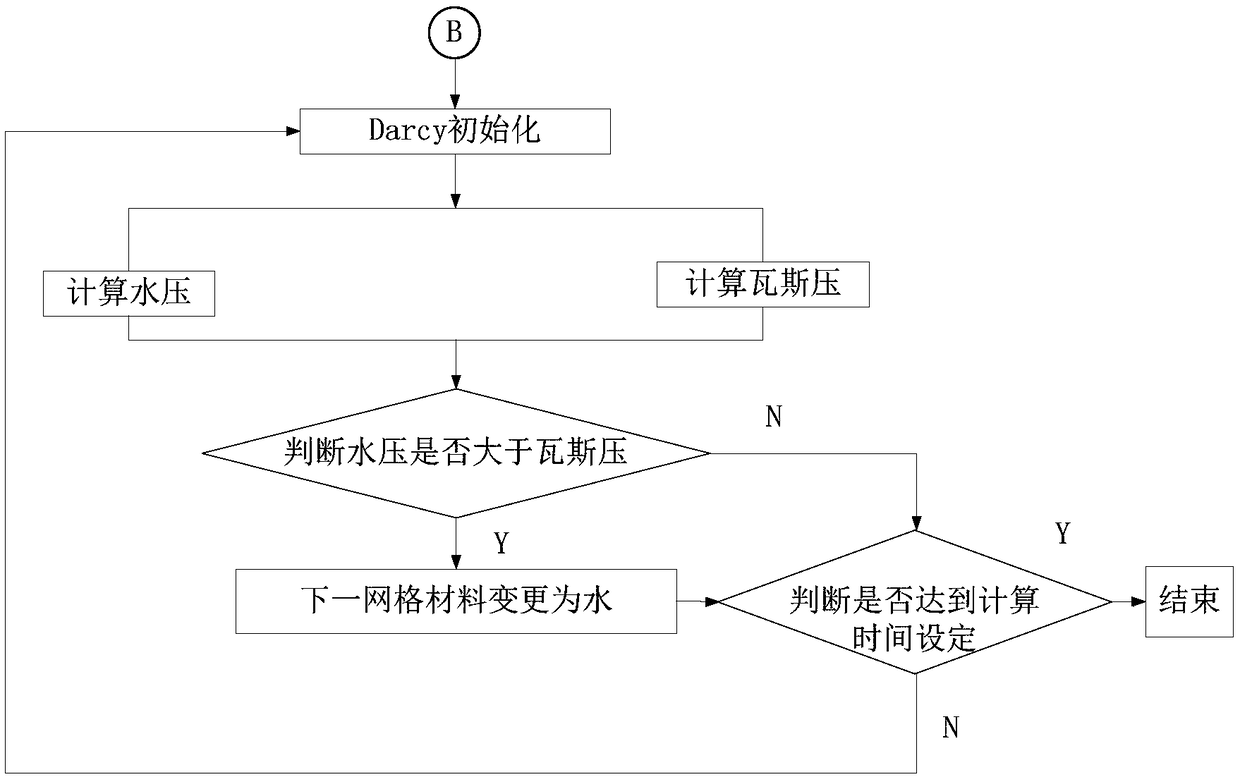
The invention discloses a water injection seepage flow in coal and rock mass zoning, damage-stress coupling numerical simulation method, according to the geological survey results, the coal seam modelis established; water injection seepage flow in coal and rock masses in non-mining affected area and mining affected area is simulated by zoning. In the non-mining influence area, the program can judge whether the coal body is deformed or even fractured under the action of water pressure stress by calculating and comparing the tensile and shear moments of each grid. At the same time, the meshlessmethod is used to simulate the fracture process of coal mass and the boundary element method is used to simulate the seepage process, which combines the advantages of the two methods on the micro-scale. In the mining-affected area, N-S equation and Darcy's law to accurately simulate the coal and rock mass water injection process in the coal and rock mass damage and moisture transport law. A soliddata basis for coal seam water injection is provided, greatly reducing the possibility of coal broken into dust particles, reducing the production of coal dust, ensuring the safety of coal seam mining.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Numerical simulation method for heterogeneous oil combination flooding system
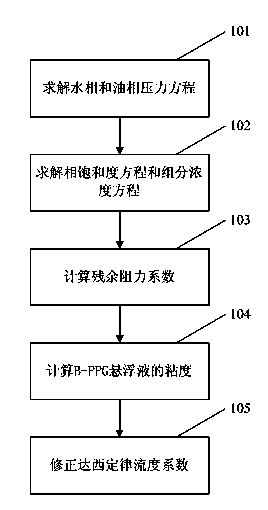
The invention provides a numerical simulation method for a heterogeneous oil combination flooding system. The method comprises the steps of solving a water phase pressure equation and an oil phase pressure equation; solving a phase saturability equation and a mass conservation equation of all components, and calculating the pre-crosslinked gel particle concentration under the current time step; calculating the pre-crosslinked gel particle residual resistance factor under the current time step in an interpolation mode according to a pre-crosslinked gel particle residual resistance factor curve; calculating the viscosity of pre-crosslinked gel particle suspension liquid; correcting the fluidity coefficient of the Darcy law, calculating water phase flowing speed according to the Darcy law, and carrying out phase pressure equation calculation of the next time step until the heterogeneous combination flooding simulation time is over. By means of the numerical simulation method for the heterogeneous oil combination flooding system, a mathematic model describing heterogeneous combination flooding blocking profile control and migration profile controlling and flooding, and the numerical simulation method effectively representing the pre-crosslinked gel particle displacement mechanism is provided.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
An efficient method for selecting representative elementary volume in digital representations of porous media
InactiveCN104335042AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEarth material testingRepresentative elementary volumeDarcy's law
The present invention relates a method to estimate representative elementary volume (REV) in a sample of porous media wherein the sub-volume selected is a better approximation of the elementary volume than existing methods. REV in a sample of porous media such as rock can be defined wherein the REV is selected with respect to the expected direction of fluid flow through the porous media. The method can quantify how good is the digital representation of a rock and how accurate a description of a fluid flow through Darcy's law will be, and allows the evaluation of different length scales in different directions for the REV and an assessment of the anisotropy of the pores structures when the method is applied in different directions. The method also can determine a robust criteria to understand when a trend of porosity-permeability breaks down due to an insufficient size of the subsample.
Owner:领英股份有限公司
Cubic spline multi-scale finite element method for simulating two-dimension flow movement
InactiveCN105354362AGuaranteed continuityHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALMatrix method
The present invention discloses a cubic spline multi-scale finite element method for simulating two-dimension flow movement. The method comprises: firstly converting a problem that needs resolution into a variational version; determining a boundary condition of a research area, setting a coarse grid cell dimension h, dissecting the research area to obtain a coarse grid cell, and dissecting the coarse grid cell into a fine grid cell; resolving a degradation elliptic problem on each coarse grid cell to construct a basis function; resolving a total rigidity matrix and a right-hand side simultaneous equations system by using an effective calculation matrix method; obtaining a water head of each node (the coarse dimension) on the research area; obtaining a coarse dimension water head derivative by using the cubic spline technique, and obtaining Darcy flow velocity of the coarse dimension according to Darcy's Law; obtaining a water head of each node (the fine dimension) by using the basis function and an interpolation formula; and obtaining a fine dimension water head derivative by using the cubic spline technique, and obtaining Darcy flow velocity of the fine dimension according to the Darcy's Law. Compared to the prior art, the method disclosed by the present invention has similar precision, but has higher calculation efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for predicting shale nanopore permeability based on fractal theory
ActiveCN110567858AReduce forecasting costsAccurate predictionPermeability/surface area analysisSpecial data processing applicationsAnalytical expressionsDarcy's law
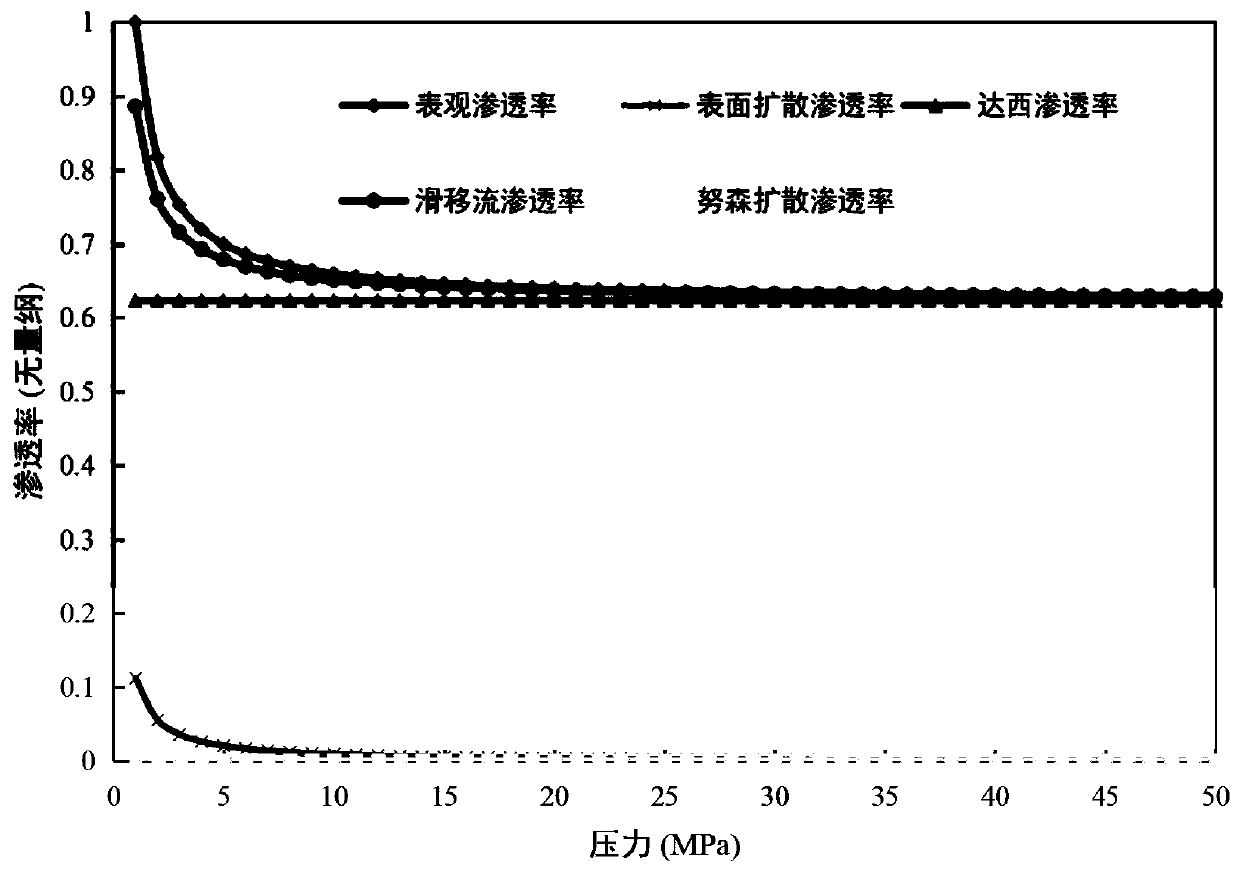
The invention discloses a fractal theory-based shale nanopore permeability prediction method, which comprises the following steps: establishing an expression of a flow section and a length scale expressed by fractal dimension based on a fractal theory and a capillary bundle model; based on the fractal theory, according to different flow state characteristics in a shale reservoir and the Hastelloy-Poisson's law, establishing a single round pipe gas mass flux integral expression including slip flow, free flow and surface flow; based on the Darcy law, establishing a total expression of the mass flow of the porous medium gas; substituting the mass flux integral expression and the flow section expression into the total expression to obtain a shale nanopore permeability analytical expression considering the multi-scale flow state; and calculating the nano-pore permeability of the shale in different flow states through the shale nanopore permeability analytical expression. According to the method, the permeability of the unconventional reservoir tight shale gas nanopores can be rapidly and accurately predicted.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
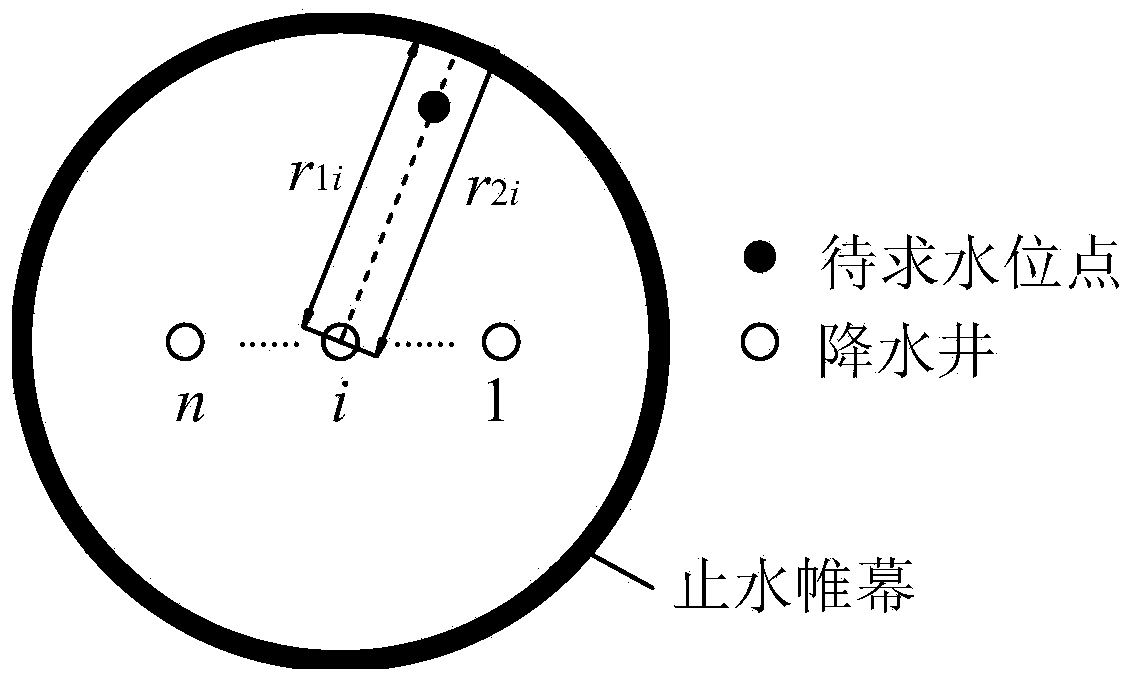
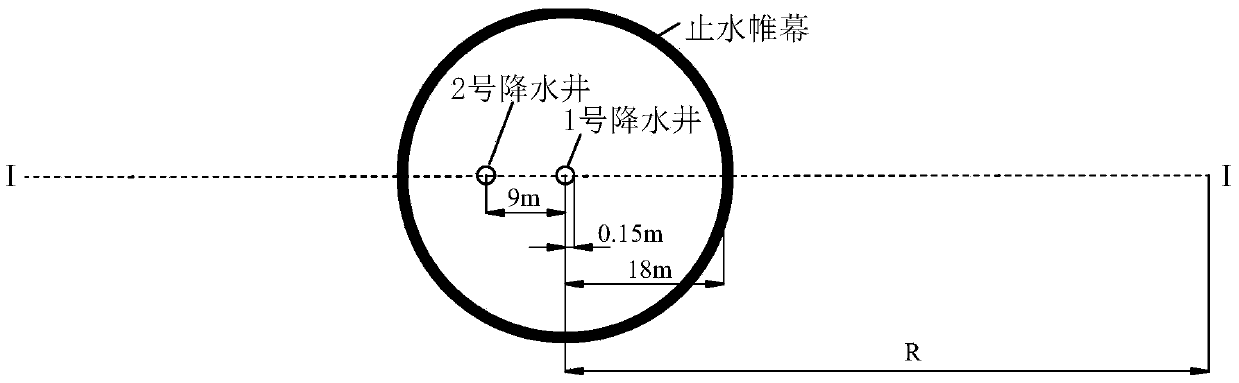
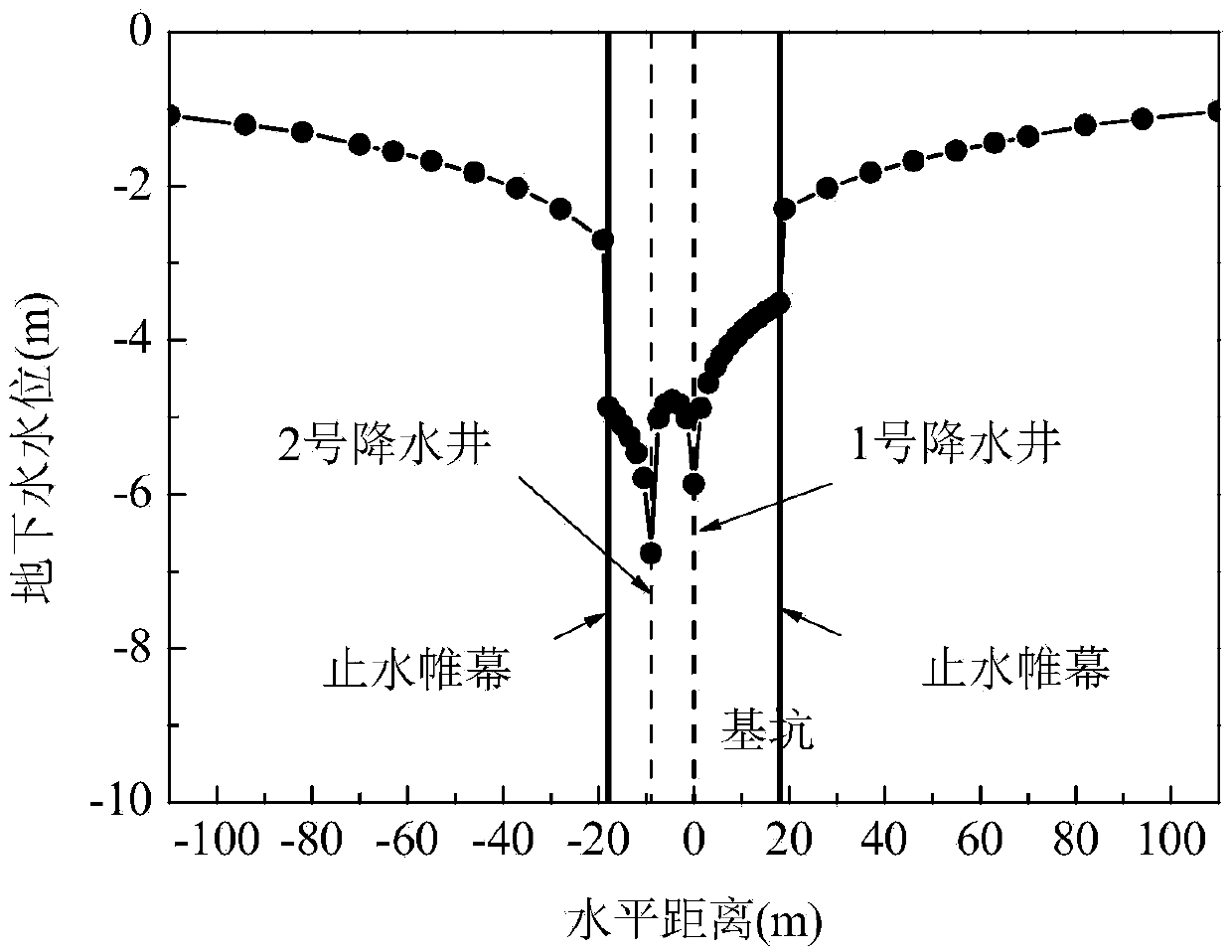
Pressure bearing water level determining method for constant-flow water pumping of lower foundation pit of suspension type waterproof curtain
The invention provides a pressure bearing water level determining method for constant-flow water pump of a lower foundation pit of a suspension type waterproof curtain. According to the method, the ground water level when the waterproof curtain doesn't enter an aquifer and the ground water level change caused by the waterproof curtain are determined in a constant-flow water pumping process based on obtained soil layer information and water pumping information of the pressure bearing aquifer and according to the Darcy law and the water volume conservation principle. Thus, pressure bearing water levels in and out the lower foundation pit of the suspension type waterproof curtain in constant-flow water pump can be determined. By means of combination of the Darcy law, the water volume conservation principle and the ground water percolation theory, the distribution of pressure bearing water levels in and out the foundation pit can be visually reflected in foundation pit dewatering. Therefore, basis for analyzing effects of foundation pit dewatering on the surroundings is provided. The method is simple, practical, convenient to popularize and large in application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
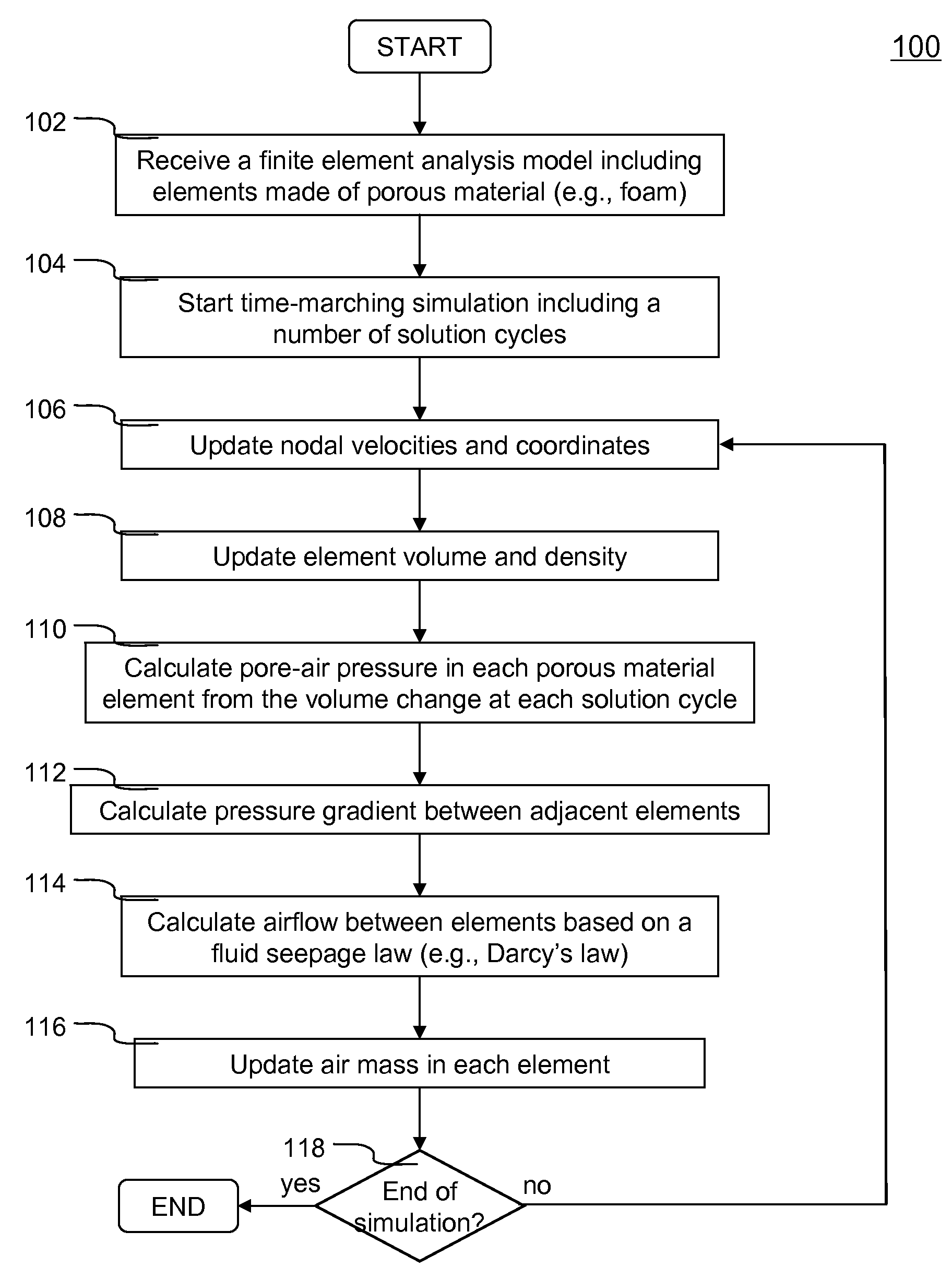
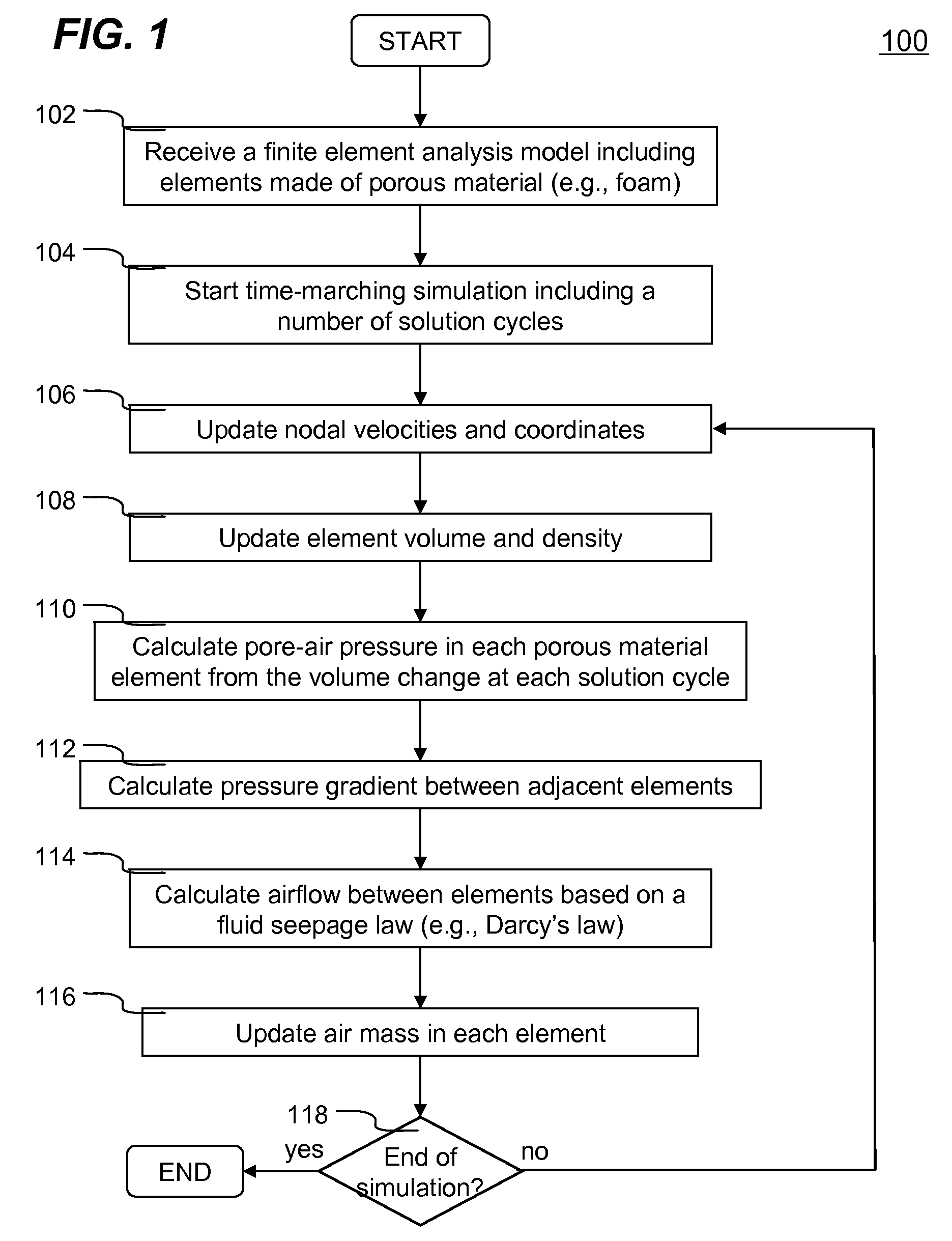
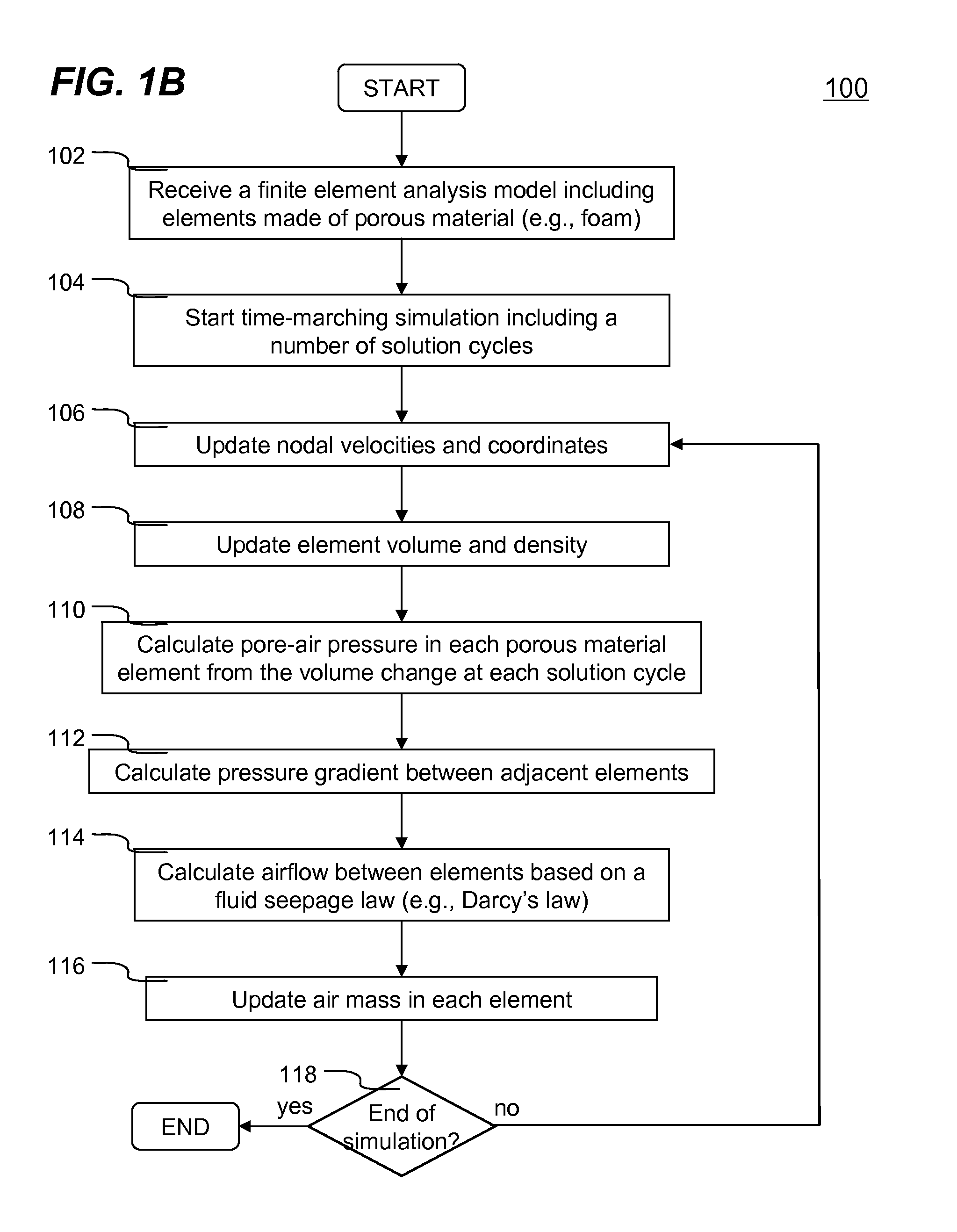
Numerical simulation of airflow within porous materials
InactiveUS20110010137A1Realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materialsComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationVolume variationElement analysis
Systems and methods of numerically simulating airflow within porous materials are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, engineering product represented by a finite element analysis model containing in part porous material with permeability. In each solution cycle of a time-marching simulation, each of the elements of porous material is evaluated with airflow in conjunction with the traditional mechanical response. Each element's volume change results into different air-pore pressure hence a pressure gradient, which in turn is used for airflow calculated in accordance with a fluid seepage law that depends upon permeability of the porous material. Therefore, a more realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materials can be achieved. The volume change and pressure of each element of porous material is evaluated using ideal gas law. A general form of Darcy's law includes user control parameters is used for evaluating airflow based on the pressure gradient and permeability.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
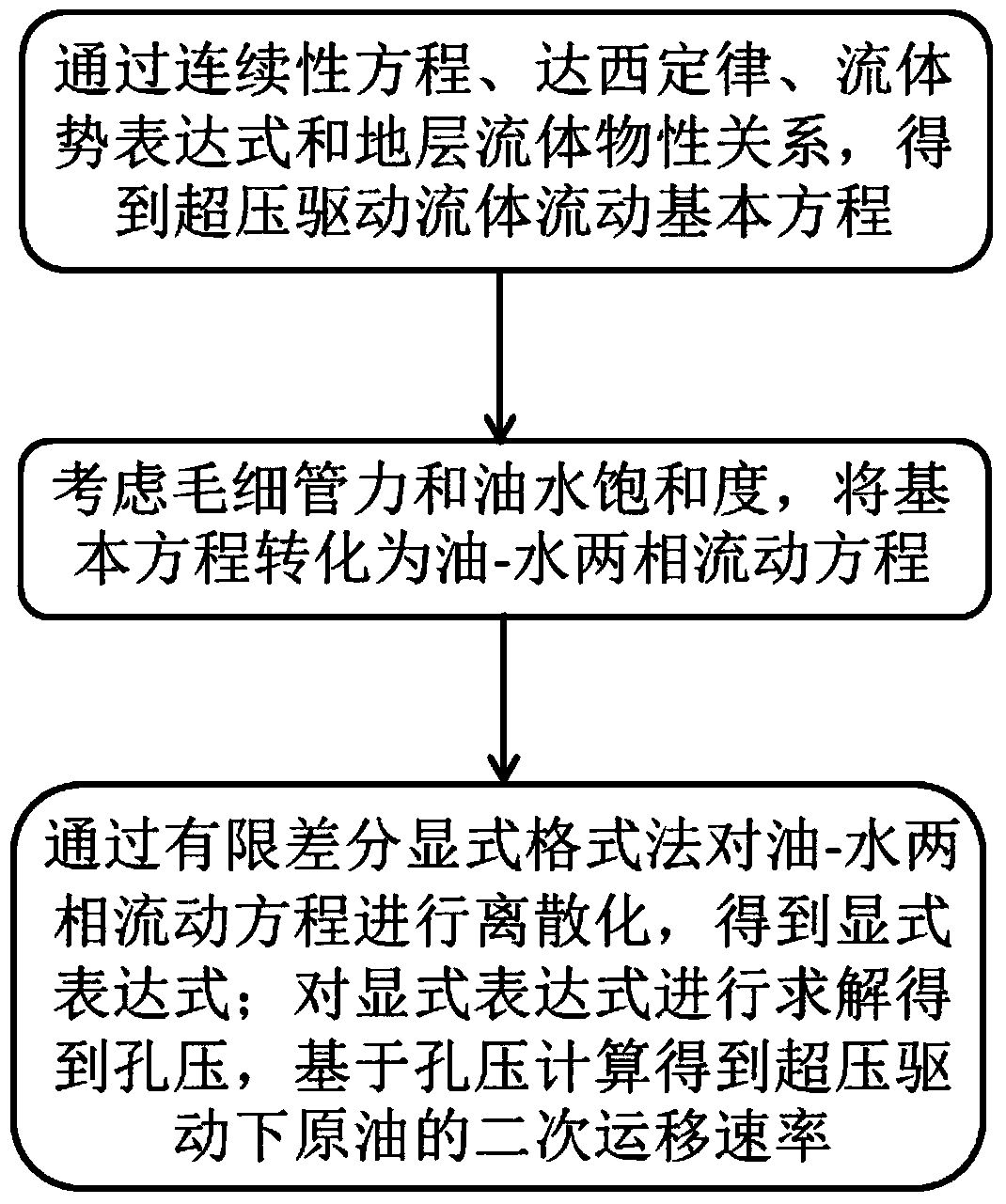
Method for calculating secondary migration rate of crude oil driven by overpressure
The invention relates to the technical field of geological prospecting and discloses a method for calculating secondary migration rate of crude oil driven by overpressure. The method includes: acquiring an overpressure driven fluid flowing basic equation through a continuity equation, a Darcy law, a fluid potential expression and a formation fluid physical property relation, and converting the basic equation into an oil-water two-phase flowing equation by taking capillary pressure and oil-water saturation degree into consideration; discretizing the flowing equation through a finite difference explicit format method to acquire an explicit expression; solving the explicit expression to acquire hole pressure, and calculating on the basis of the hole pressure to acquire the secondary migration rate of the crude oil driven by overpressure. The secondary migration rate of the crude oil driven by overpressure in an overpressure reservoir is calculated by combining flowing characteristics and physical property characteristics of fluid in the overpressure reservoir through geological modeling, mathematical deduction and solving, migration distance of overpressure driven oil gas and crude oil distribution range can be acquired further, and a scientific basis is provided for geological evaluation and exploration of oil gas and finding of new oil gas reserves.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN) +1
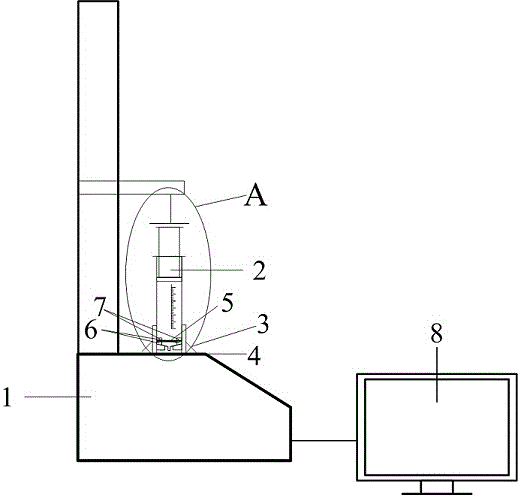
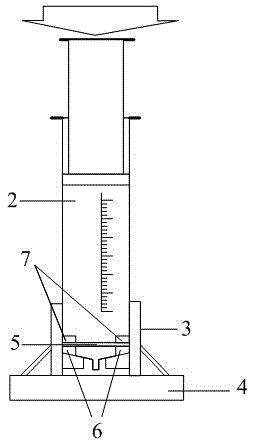
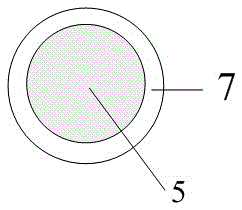
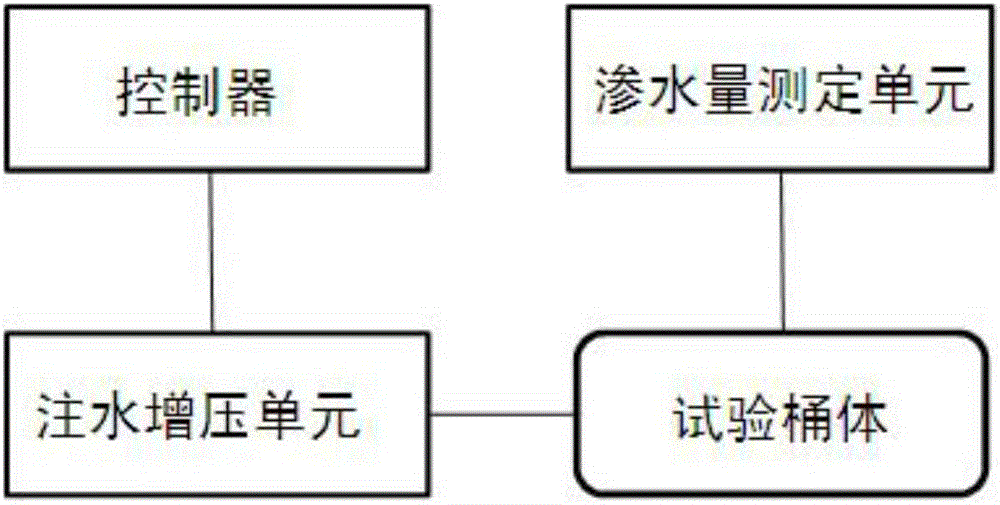
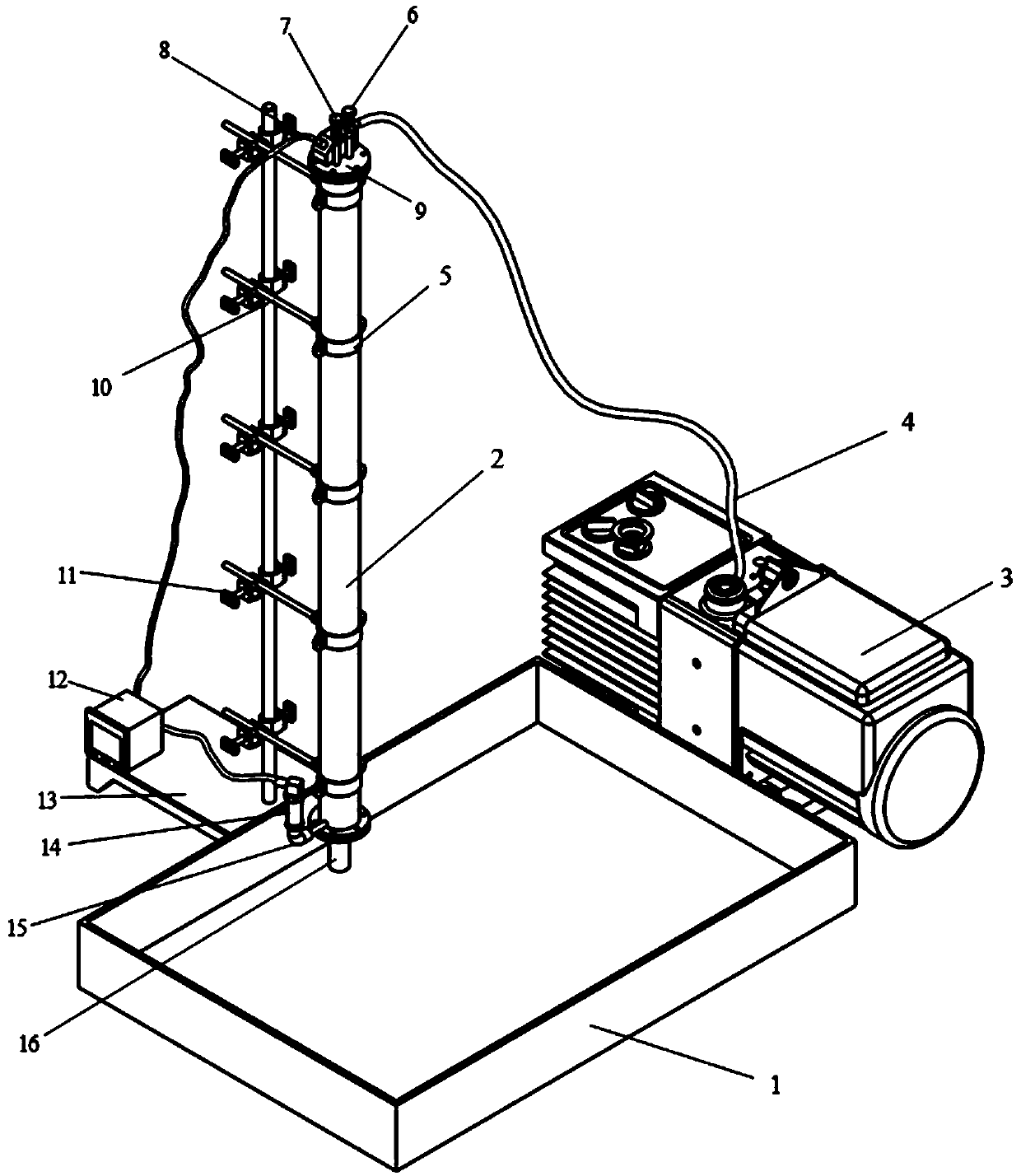
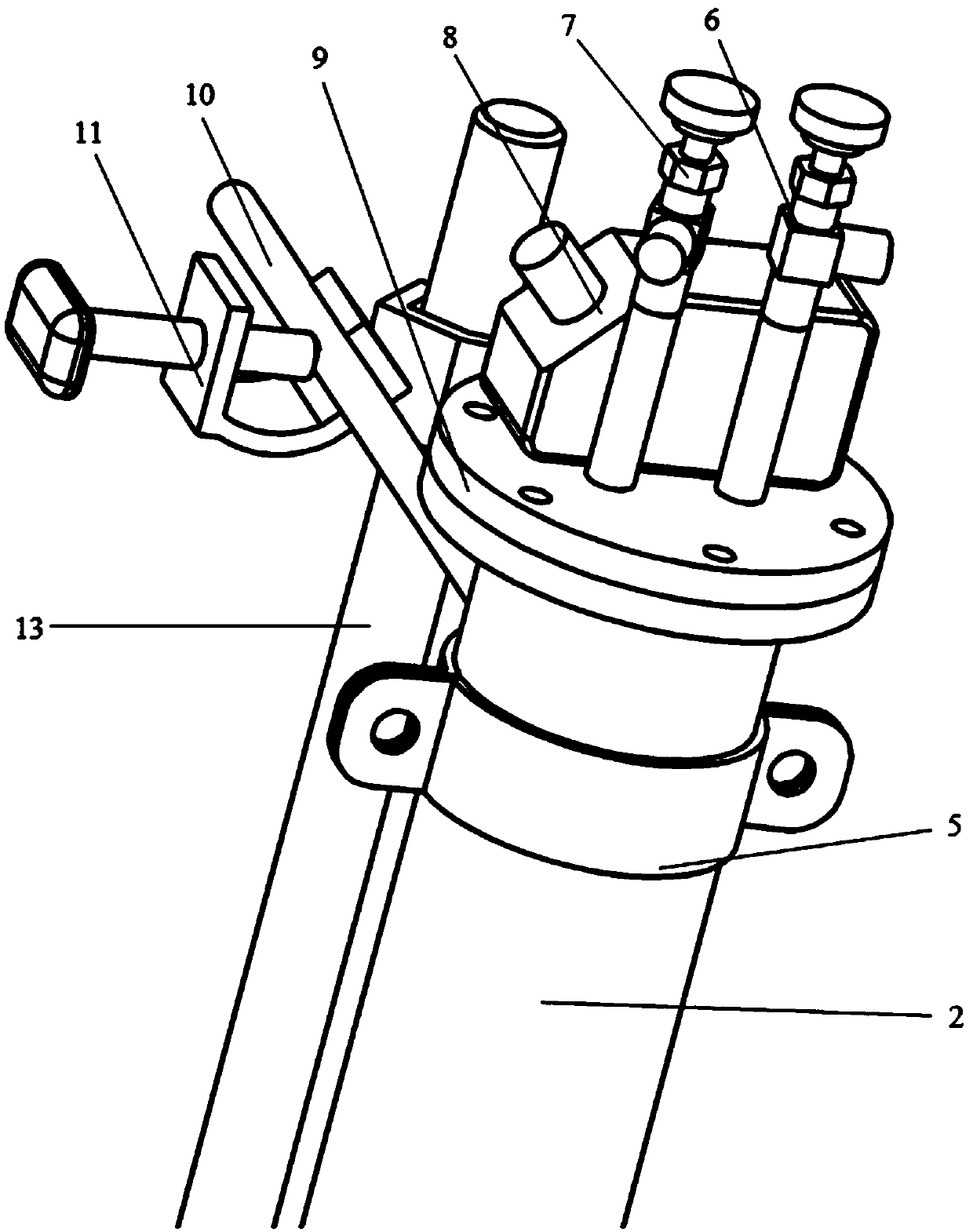
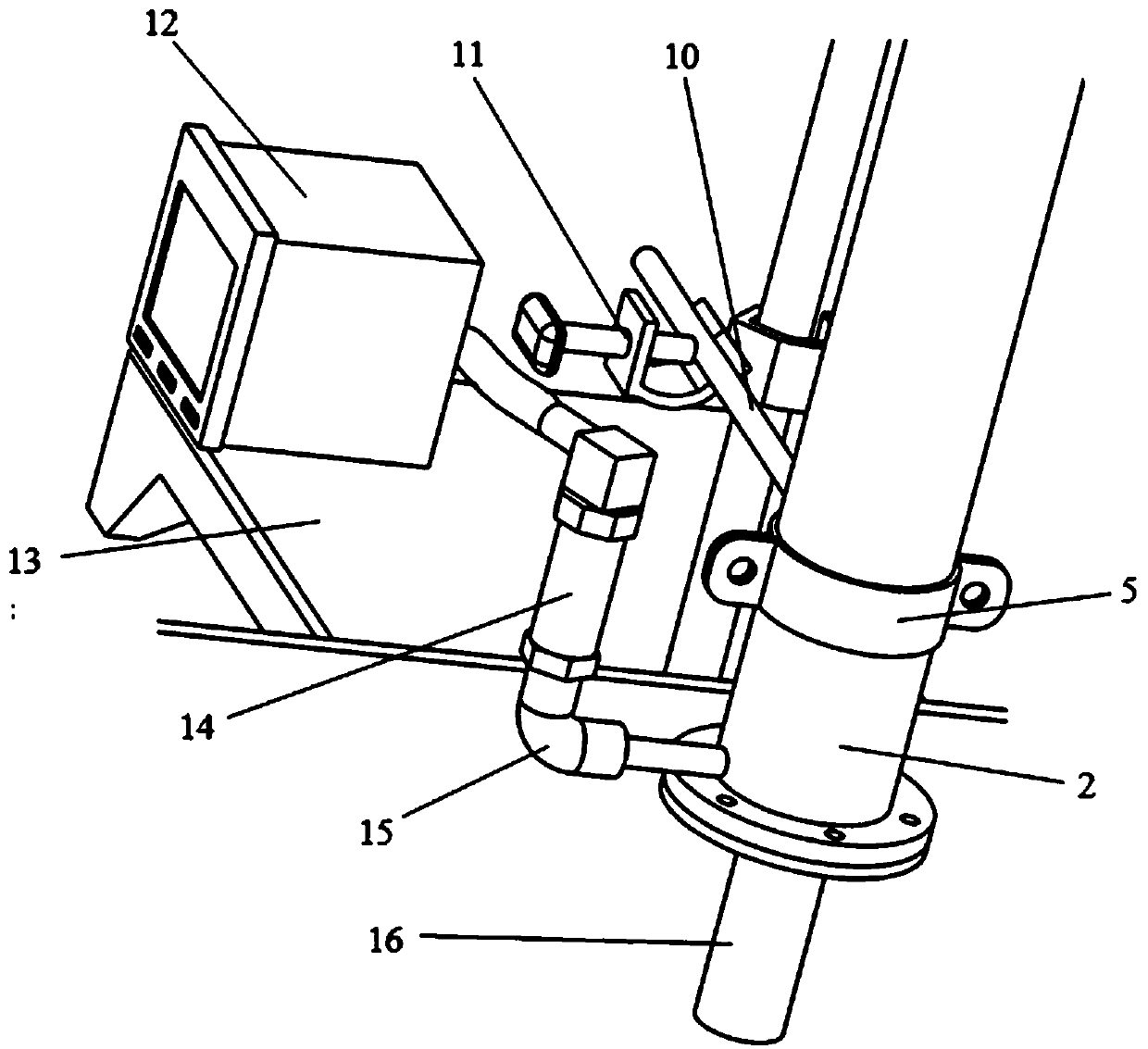
Fully-automatic Darcy law experiment system
InactiveCN107121369AAvoid askingSmall footprintPermeability/surface area analysisData acquisitionWater flow
The invention relates to a fully-automatic Darcy law experiment system which is characterized by comprising a water supply system, an infiltration system and a data acquisition and processing system; the work of the fully-automatic Darcy law experiment system is realized through the steps of initial numerical measurement, water pump water supply, water infiltration, data acquisition, data calculation and the like; through the automatic whole-process control Darcy law experiment system, the numerical measurement accuracy and precision are greatly improved, and the experiment efficiency of the Darcy law experiment system is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Rock soil penetration air pressure solidification testing method
InactiveCN106769500ASmall footprintEasy loadingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPermeability/surface area analysisGraduated cylinderExhaust valve
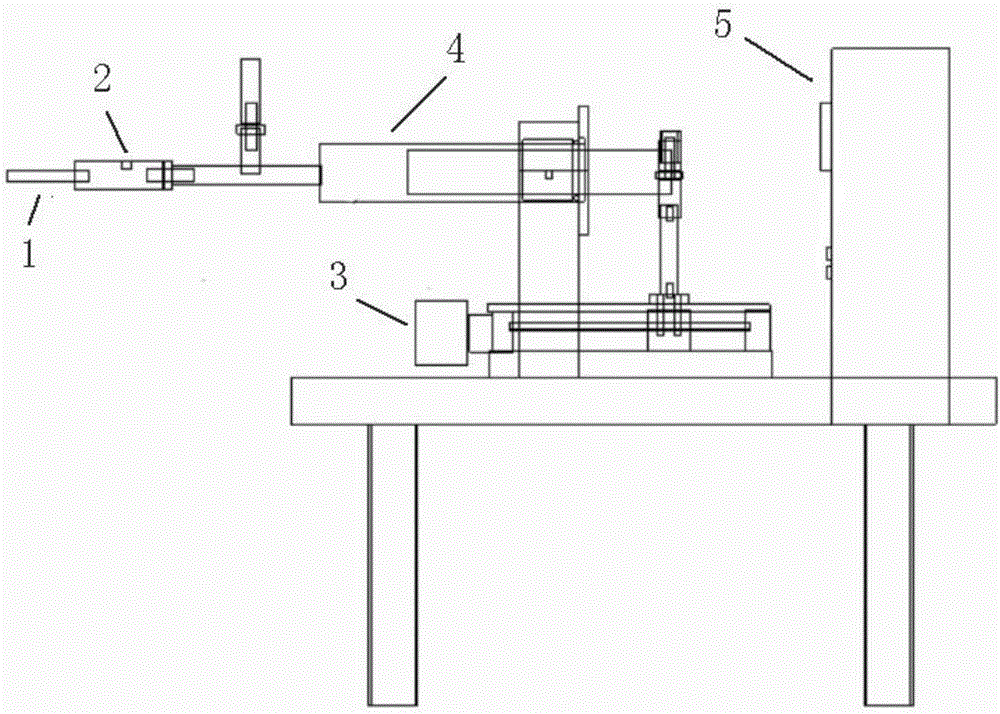
The invention discloses a rock soil penetration air pressure solidification testing method. An adopted solidification instrument comprises a base 5, a cover plate 15, a scale water storage tank 7, a measuring cylinder 23, a pressure application device and a computer 6, wherein the cover plate 15 is supported on the base 5 through a supporting piece. The testing method comprises the following steps: before a test, turning on the computer, filling the scale water storage tank with water, recording a scale reading, sheathing soil samples with soft sheaths, and placing the soil samples between an upper permeable stone and a lower permeable stone; emptying air in the cavity of the base; switching off an exhaust valve of the base, and switching on an air inlet valve and an air suction valve so as to enable an air bag in an air bag cavity to be in contact with a wall of the air bag cavity, wherein an air gauge displays the value of the applied confining pressure; enabling the bottom of a pressure application shaft to be in full contact with the upper permeable stone, and applying weights on a jack; determining the solidification time according to geo-technical testing procedures; and after the test is over, recording the water yield in unit time, and calculating the permeability coefficient according to the Darcy law.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Sample preparation device and sample preparation method for sand-soil contact surface test sample as well as osmotic coefficient determination method
InactiveCN104655468ASolving Permeability Measurement ProblemsLow costPreparing sample for investigationPermeability/surface area analysisTest sampleEngineering
The invention discloses a sample preparation device and a sample preparation method for a sand-soil contact surface test sample as well as an osmotic coefficient determination method. The sample preparation device mainly comprises an outer barrel and an inner barrel which are coaxially arranged; the part between the inner barrel and the outer barrel is filled with sand by layers and is impacted; the inner barrel is slowly upwards lifted to a certain height and then is fixed; a certain amount of clay is weighed and is poured into the inner barrel; the clay is impacted to a pre-set height and then the inner barrel is slowly upwards lifted; the clay is poured and impacted, and the step is repeated for multiple times to reach a pre-set sample height; and the sample preparation device is detached and a test sample is taken out; the sand adhered to the surface of the test sample is slightly brushed off by a soft hairbrush, namely the sand-soil contact surface cylindrical test sample which is tightly filled with the sand at the periphery can be obtained. Then the thickness and the sand content of a sand-soil contact surface are measured by adopting a parallel test. Furthermore, a flexible wall test can be utilized and water in each sand-soil contact surface test sample permeates along two paths of the middle clay and the sand-soil contact surface; and the osmotic coefficient of the sand-soil contact surface can be calculated according to a Darcy law.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Apparatus for measuring saturated hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media
ActiveUS20160076987A1Simple configurationEasy disposalPermeability/surface area analysisIn situ soil foundationMeasurement deviceWater flow
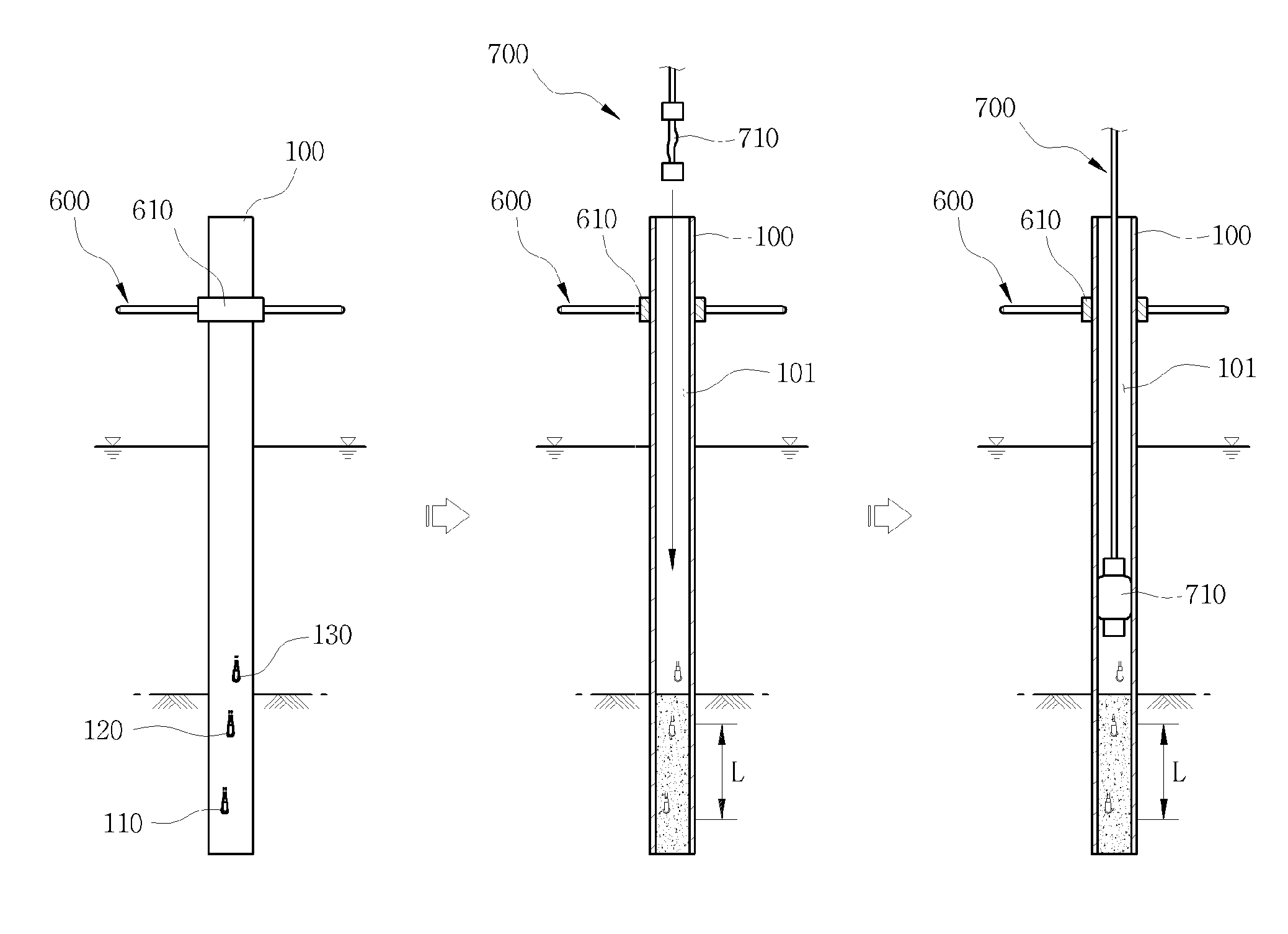
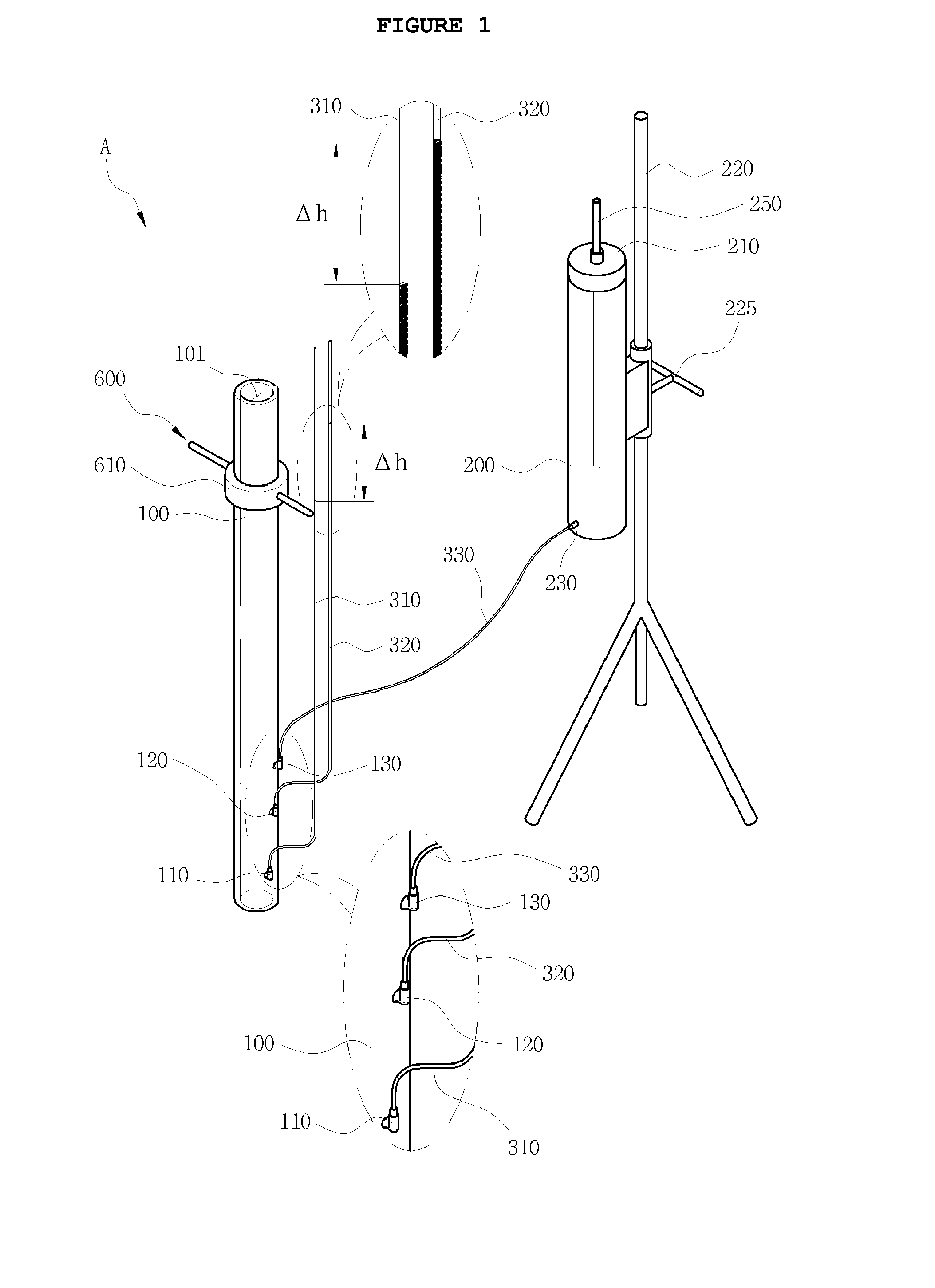
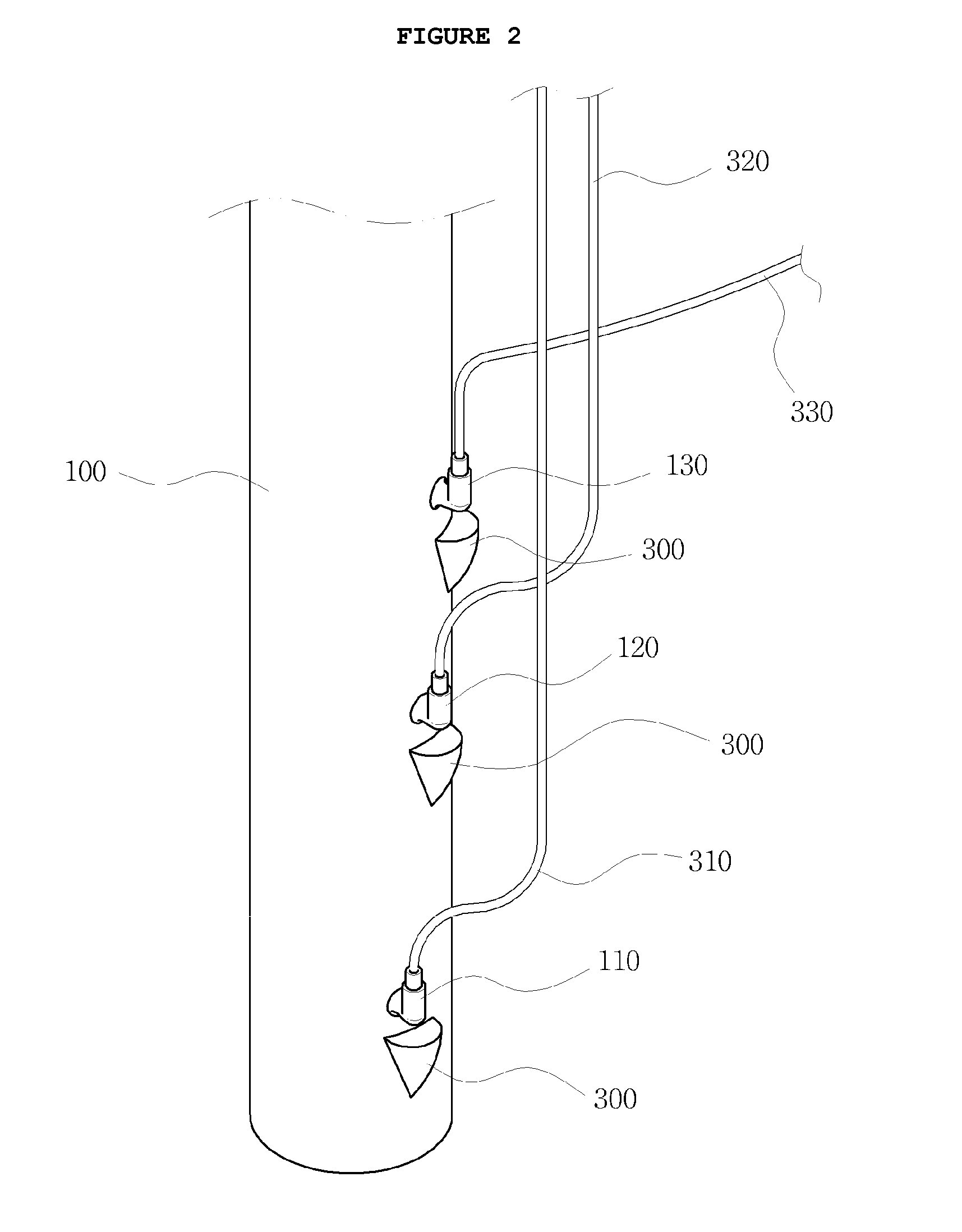
A apparatus for measuring saturated hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media in an unsaturated zone of the earth. The measuring apparatus includes a cylinder member inserted into the porous media in a position in which the upper and lower ends of the cylinder member are open, a means for supplying a constant flow rate of water to the cylinder member, and a pressure measuring means for measuring the hydraulic head in response to water flowing into the cylinder member. The measuring apparatus can easily measure the vertical hydraulic conductivity of a foundation based on Darcy's Law in the field. It is possible to accurately measure the hydraulic conductivity of a sedimentary layer in the natural state and easily determine geological characteristics of the soil. It is possible to obtain very accurate information regarding the process of dispersion and movement of contaminants.
Owner:KOREA INST OF GEOSCI & MINERAL RESOURCES
Method for directly testing permeability of underground coal seam
InactiveCN104345022AImprove permeabilityData shortcutPermeability/surface area analysisNitrogenRock tunnel
A method for directly testing the permeability of an underground coal seam sequentially includes the following steps: (1) constructing a crossing seam hole with the diameter of D and the radius of r and vertical to a coal seam in a coal mine underground rock tunnel as an gas supplying hole; (2) uniformly constructing six gas outlet holes in the circumference having a distance R to the boring centerline of the gas supplying hole; (3) respectively firmly sealing the gas supplying hole and the six gas outlet holes; (4) connecting the six gas outlet holes through a sealed gas outlet pipeline together, connecting to an gas outlet tube, directly connecting the gas outlet tube to underground gas, windpipe, the trachea and underground gas directly connected, allowing the pressure to be unchanged and p2, and installing a sensor for monitoring the flow and the concentration of nitrogen on the gas outlet tube; (5) connecting high-pressure high-purity nitrogen with the gas supplying hole through an gas supplying connecting pipeline; (6) recording the flow qk when a gas flowing out of the gas outlet tube is high purity nitrogen; and (7) calculating by adopting a steady flow process based on Darcy's law to obtain the real data of the permeability of the underground coal seam. The method has the advantages of fast data obtaining, reality and reliability.
Owner:HENAN COAL CHEM IND GROUP INST
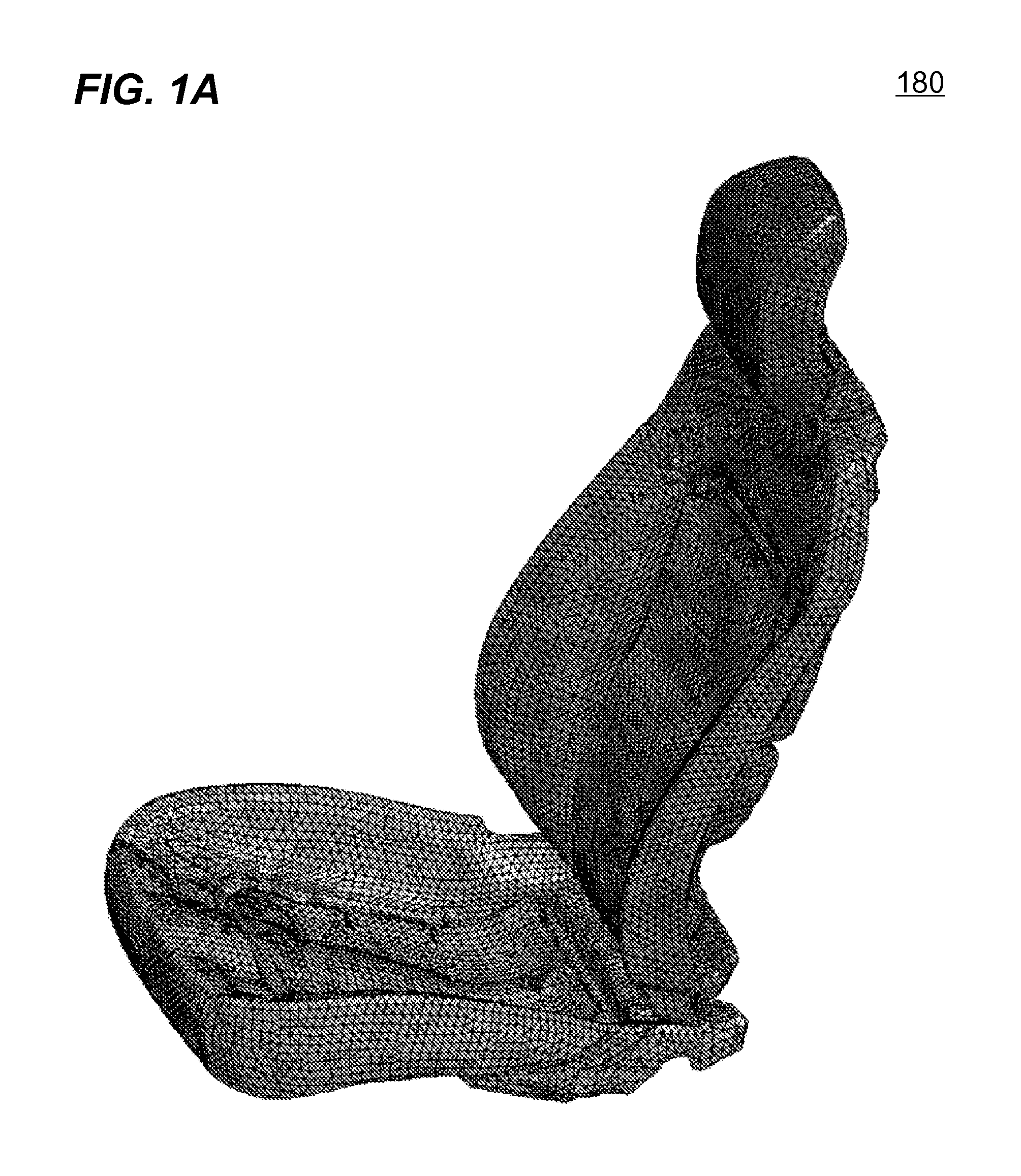
Numerical simulation of airflow within porous materials
InactiveUS20110282637A1Reduce needFeasible solutionGeometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationCar seatElement analysis
Systems and methods of numerically simulating airflow within porous materials are disclosed. Engineering product (e.g., car seat) represented by a finite element analysis model containing in part porous material with permeability. In each solution cycle of a time-marching simulation, each of the elements of porous material is evaluated with airflow in conjunction with the traditional mechanical response. Each element's volume change results into different pore air pressure hence a pressure gradient, which in turn is used for airflow calculated in accordance with a fluid seepage law that depends upon permeability of the porous material. Therefore, a more realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materials can be achieved. The volume change and pressure of each element of porous material is evaluated using ideal gas law. A general form of Darcy's law includes user control parameters is used for evaluating airflow based on the pressure gradient and permeability.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
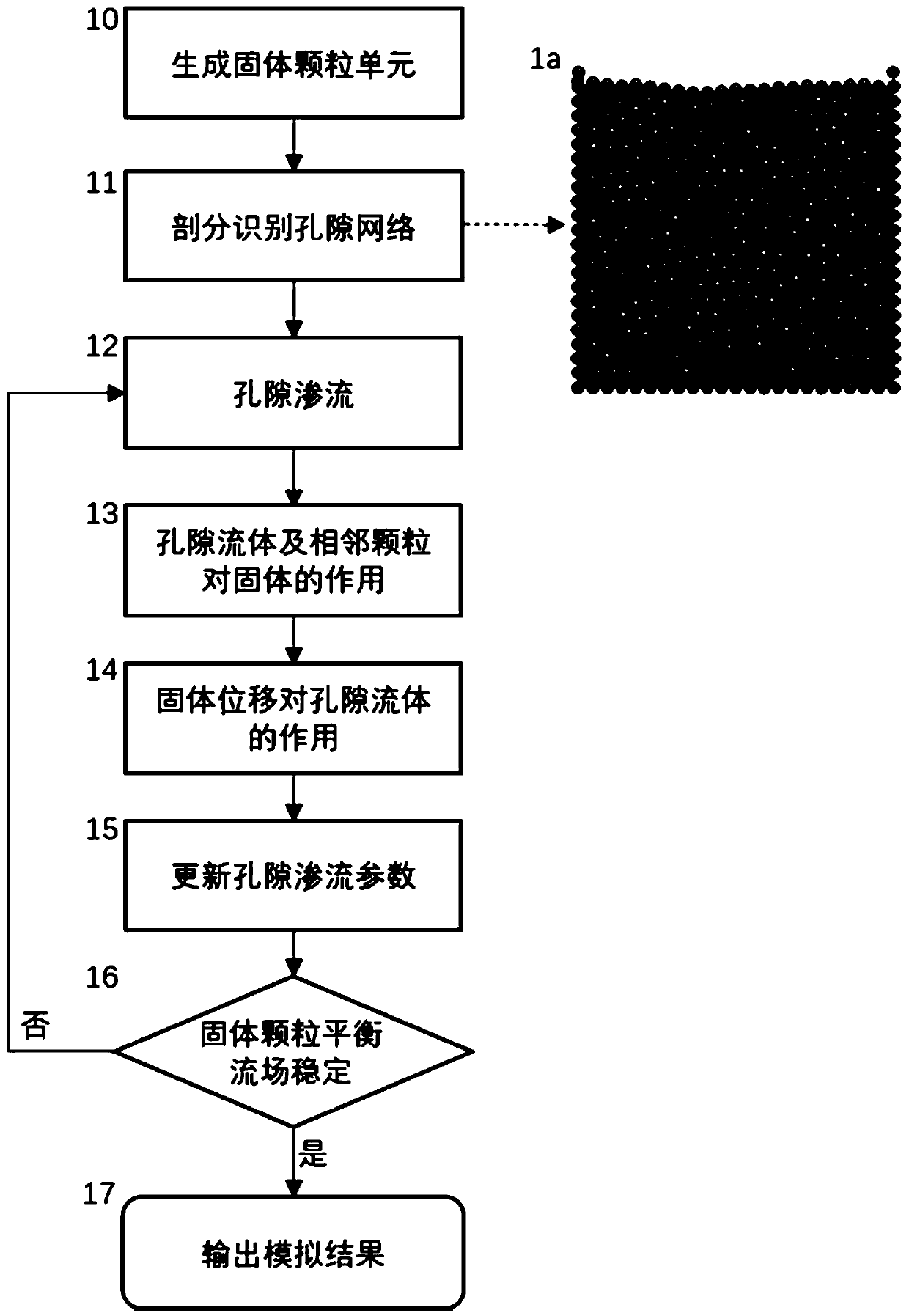
Rock-soil body discrete element fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation method based on pore density flow
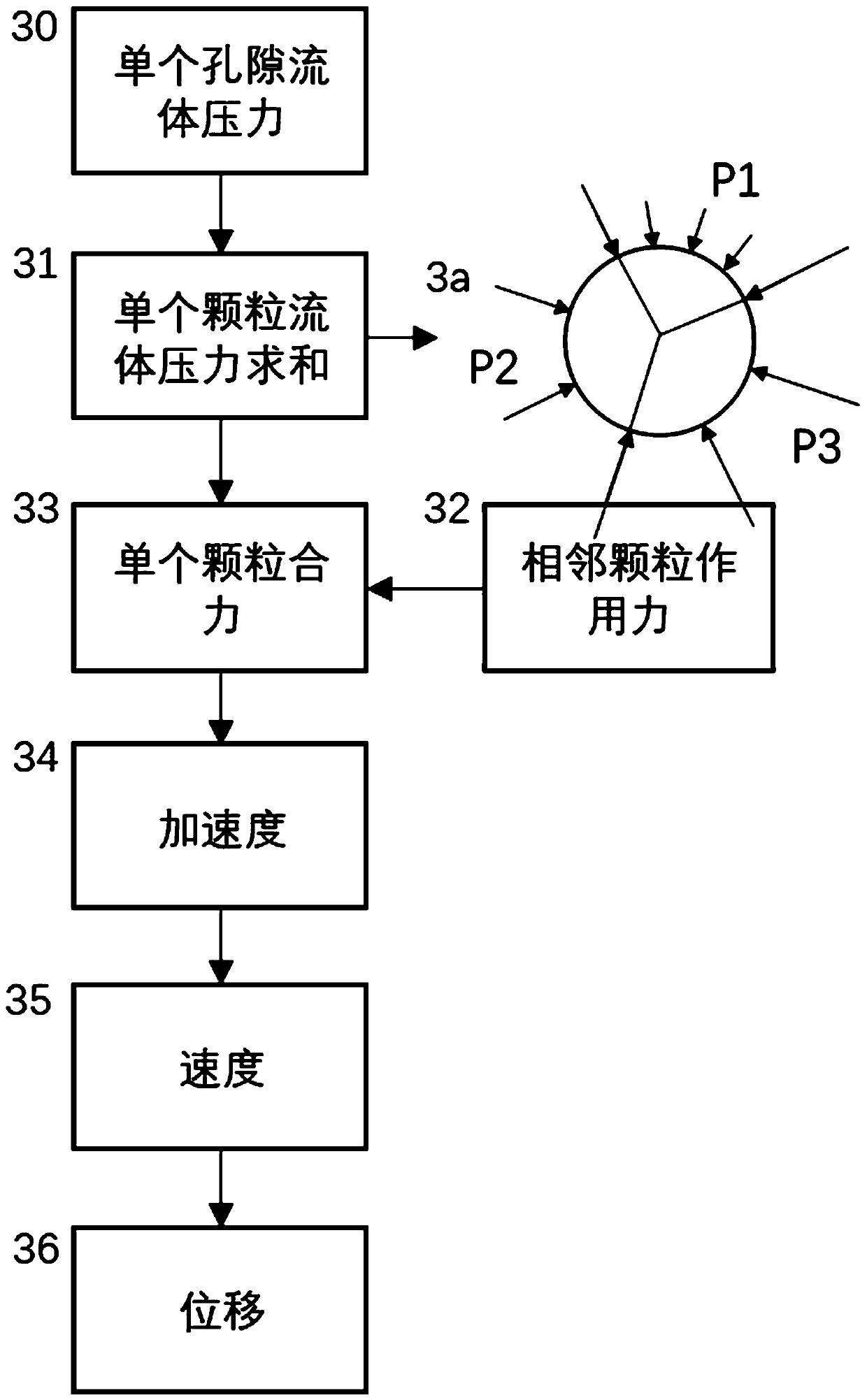
ActiveCN110263362AUniform physical propertiesSmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scalePore fluid
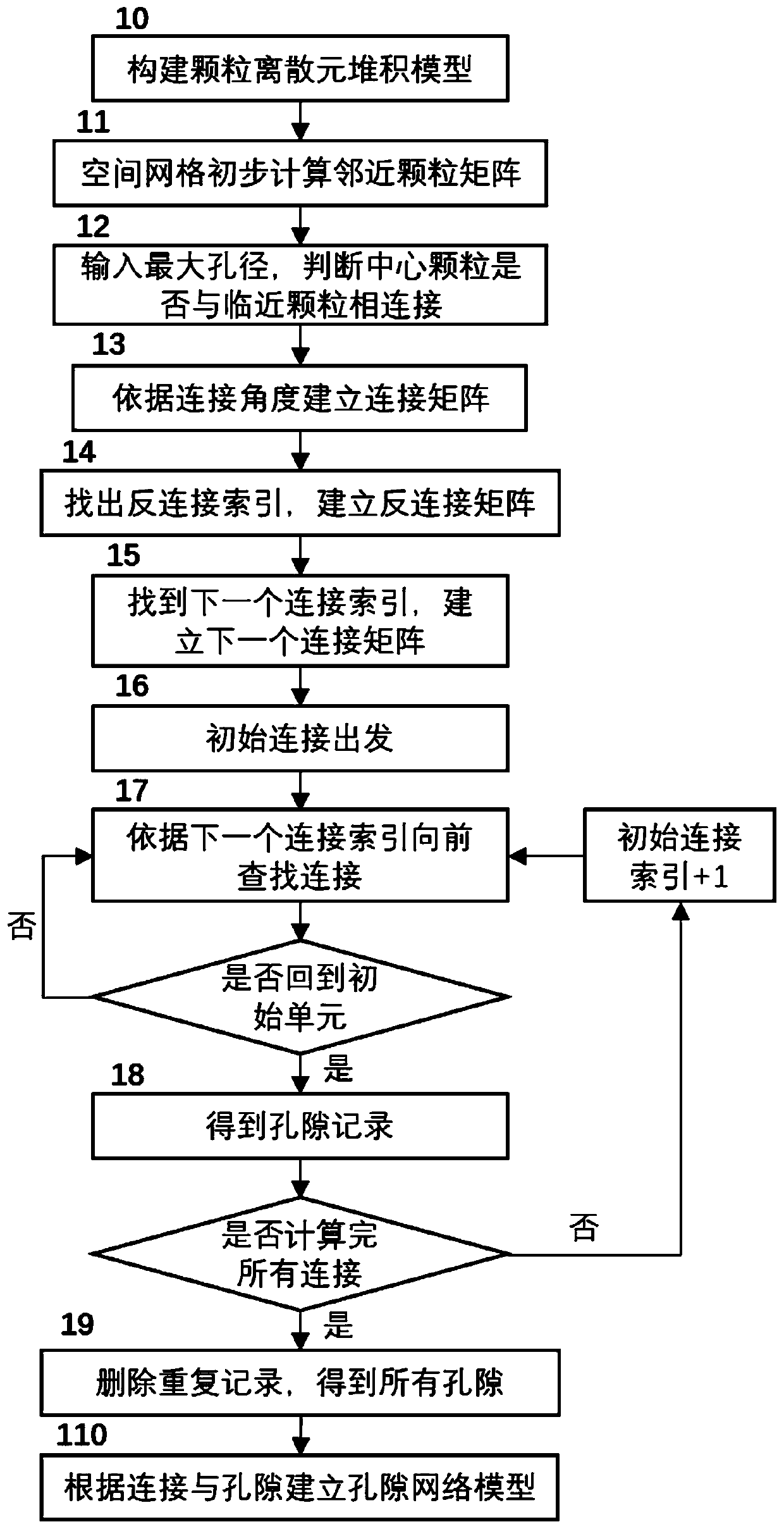
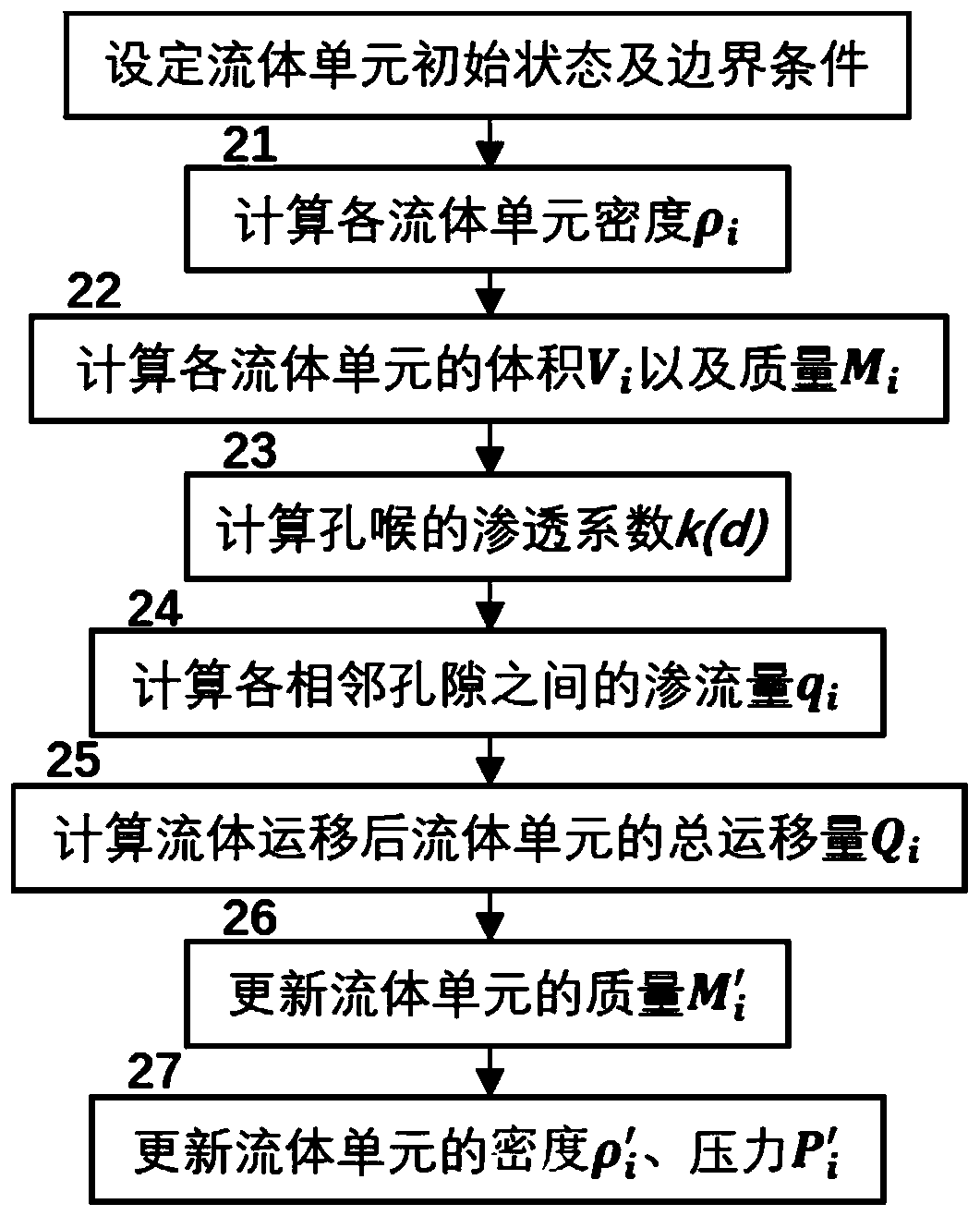
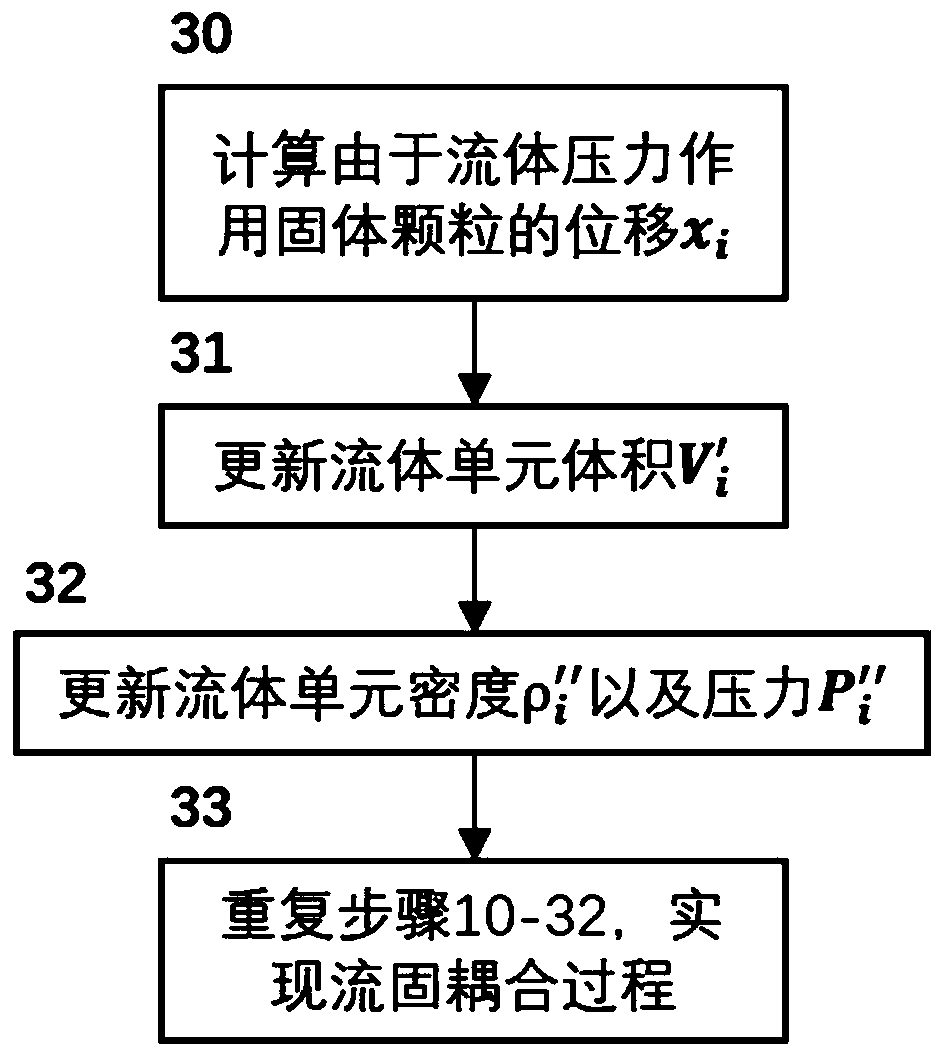
The invention discloses a rock-soil body discrete element fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation method based on pore density flow. The method comprises the steps of generating a solid particle random accumulation model, subdividing and identifying a pore network, establishing a pore seepage equation, acting on solids by pore fluid and adjacent solid particles, acting on the pore fluid by solid displacement, and updating pore seepage parameters; repeating the steps until the solid particles are balanced and the seepage of the pore fluid is stable. According to the method, the calculated amount is greatly reduced, the pore fluid state equation is established, the temperature field and the seepage field are naturally coupled through density, the microscopic seepage equation is established by analogy of the macroscopic Darcy law to achieve pore seepage calculation, and the complex macroscopic phenomenon can be efficiently simulated based on the pore scale energy.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSTIY SUZHOU HIGH TECH INST
Method for simulating standard suction of smoking machine by stepping motor
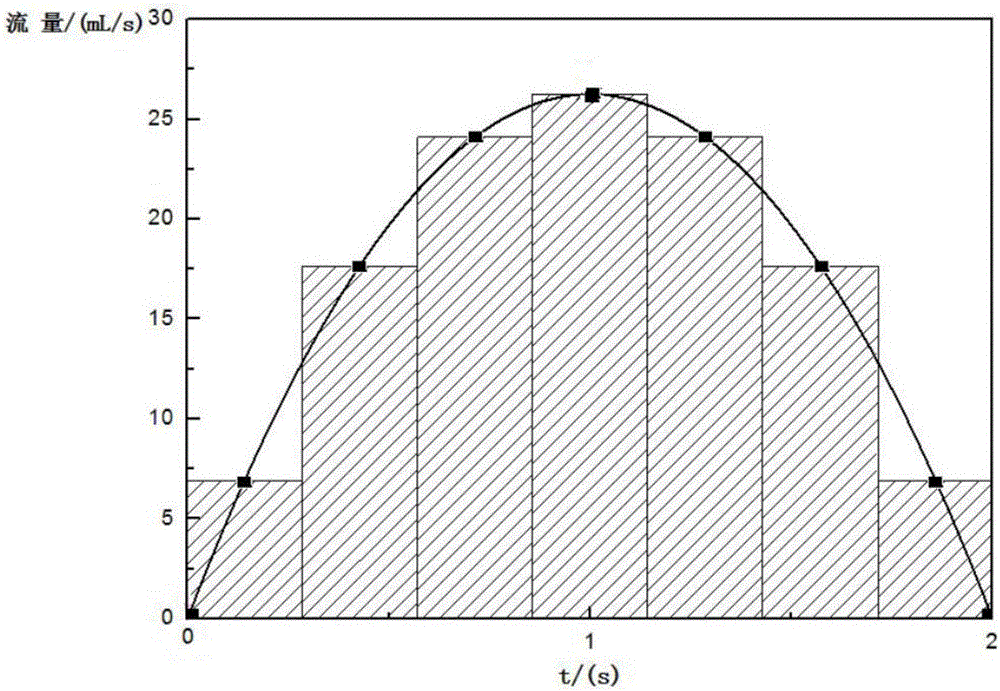
InactiveCN107525648AEasy to adjust the operating speedEasy to adjust running timeHydrodynamic testingEngineeringDarcy's law
The invention discloses a method for simulating standard suction of a smoking machine by a stepping motor. The standard suction speed of a common smoking machine is 35ml in two seconds, and the standard suction frequency is one time every 60 seconds. A smoke testing machine which is constructed by means of the stepping motor verifies a fact that the motion frequency of the stepping motor is proportional to the motion frequency of the stepping motor and pressure of a smoke branch outlet through experiments. According to a Darcy's law, on the condition of relatively low smoke speed, the pressure at the smoke branch outlet is proportional to the speed. Therefore the suction frequency of the stepping motor is proportional to the speed of the smoke branch outlet. The method comprises the steps of firstly, approximating a standard suction bell-shaped flow graph to a parabola Q=At2+Bt, then equally dividing the parabola to seven equal time segments along the transverse coordinate, taking the intermediate time of each equal time segment, calculating corresponding flows Q1, Q2, . . . Q7, setting the frequency of the stepping motor to corresponding H1, H2, . . .H3, setting the time to T1=T2=...T7=0.286, and furthermore in a time period of 2s, the stepping motor rightly sucks 35ml.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
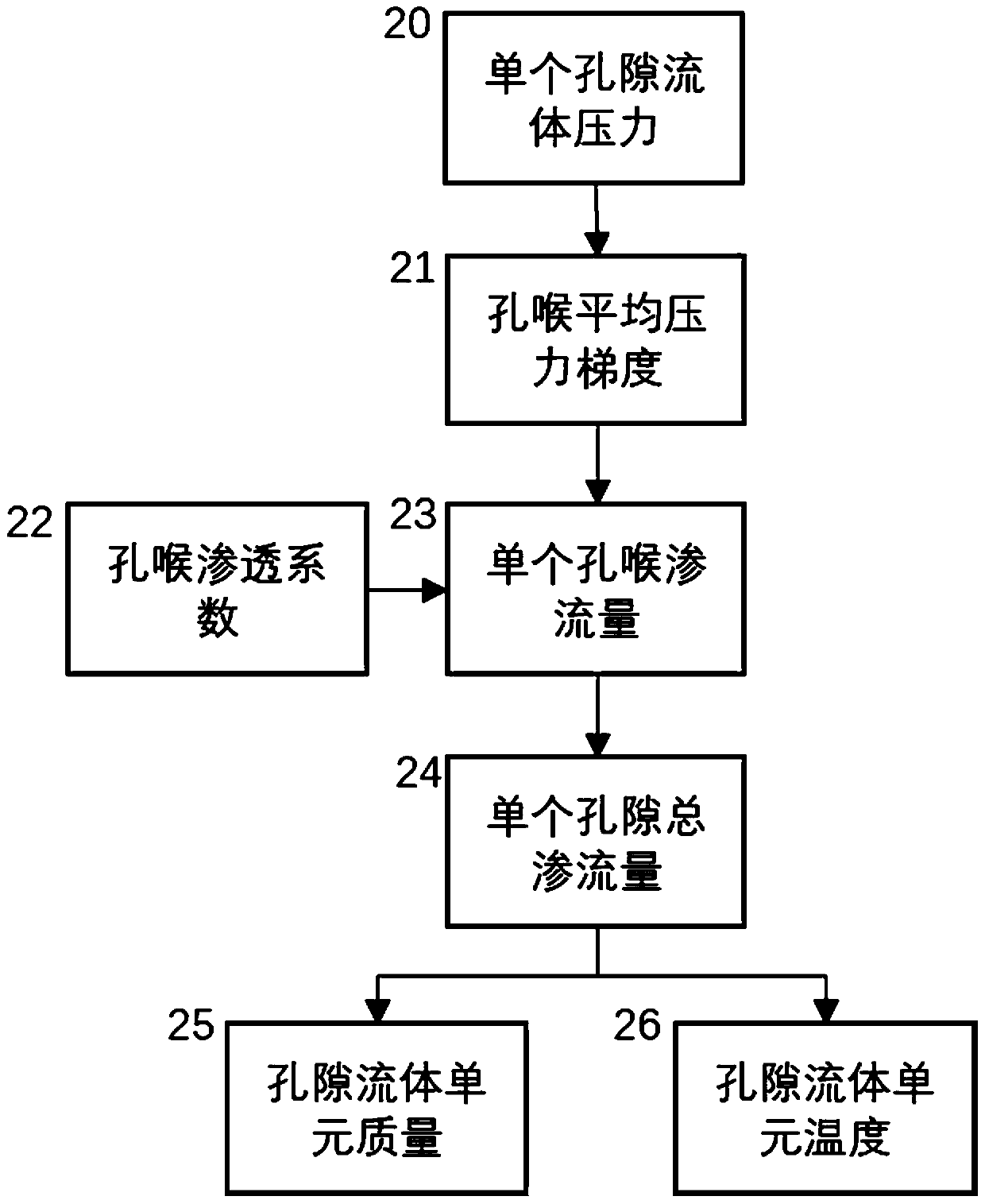
Discrete element fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation method and system based on GPU matrix
PendingCN111507024ARealize dynamic simulationIncrease computing speedDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingSoil massPore water pressure
The invention discloses a discrete element fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation method and a discrete element fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation system based on a GPU matrix. The discreteelement fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation method comprises the steps of: establishing a pore network model; establishing a fluid unit migration model, wherein fluid units in pores are connected through pore throats among particle units, permeation of the fluid units obeys the Darcy law, the flow of the fluid units is determined by rock and soil mass properties, pore throat diameters and the like, and water pressure, temperature and density have a function relational expression; and exerting fluid-solid coupling effect, wherein pore water pressure acts on the particles, and the particlemovement changes the pore volume, so that a fluid-solid coupling effect is realized. According to the discrete element fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation method, dynamic simulation of a large-scale fluid-solid coupling system can be realized, and the calculation speed and the calculation quantity of discrete element fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation are remarkably improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
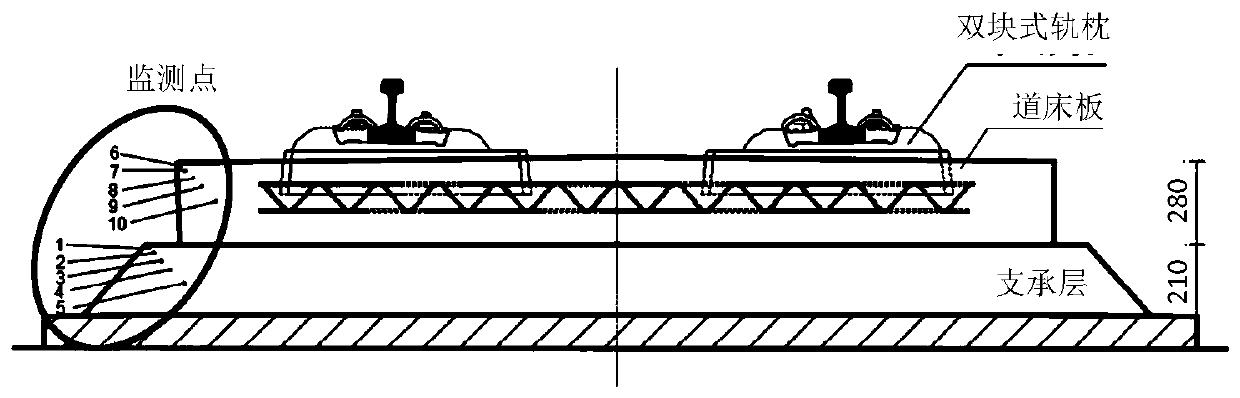
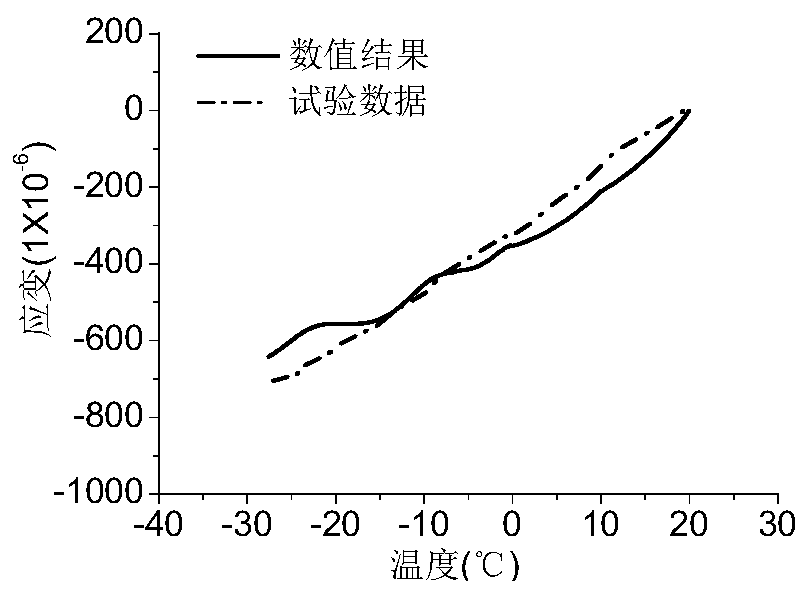
Ballastless track freezing and damage behavior calculation method
ActiveCN110390176ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFreeze thawingDarcy's law
The invention discloses a ballastless track freezing and damage behavior calculation method which comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring a porous framework volume compression modulus of a pouredconcrete test piece according to a dynamic elastic wave test, and calculating to obtain a Biot coefficient; S2, acquiring pore structure distribution parameters and overall porosity of concrete testpieces according to CT scanning and image recognition technologies; S3, according to pore structure distribution parameters, acquiring temperature-freezing rate relation curve in freezing process of concrete test pieces through calculation; S4, according to a Young-Laplace equation ice-unfrozen water balance and ice-adsorbed water film balance relationship, constructing a function relationship among the average pore pressure, the temperature and the pore structure; and S5, Based on porous medium mechanics, Darcy's law of water migration in a porous medium and Friour's law of heat conduction ofa porous system, constructing a coupling control equation of a porous medium stress field, a temperature field and a seepage field to obtain an interaction relationship among structural stress, heattransfer and water migration in the ballastless track in the freeze-thaw process.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
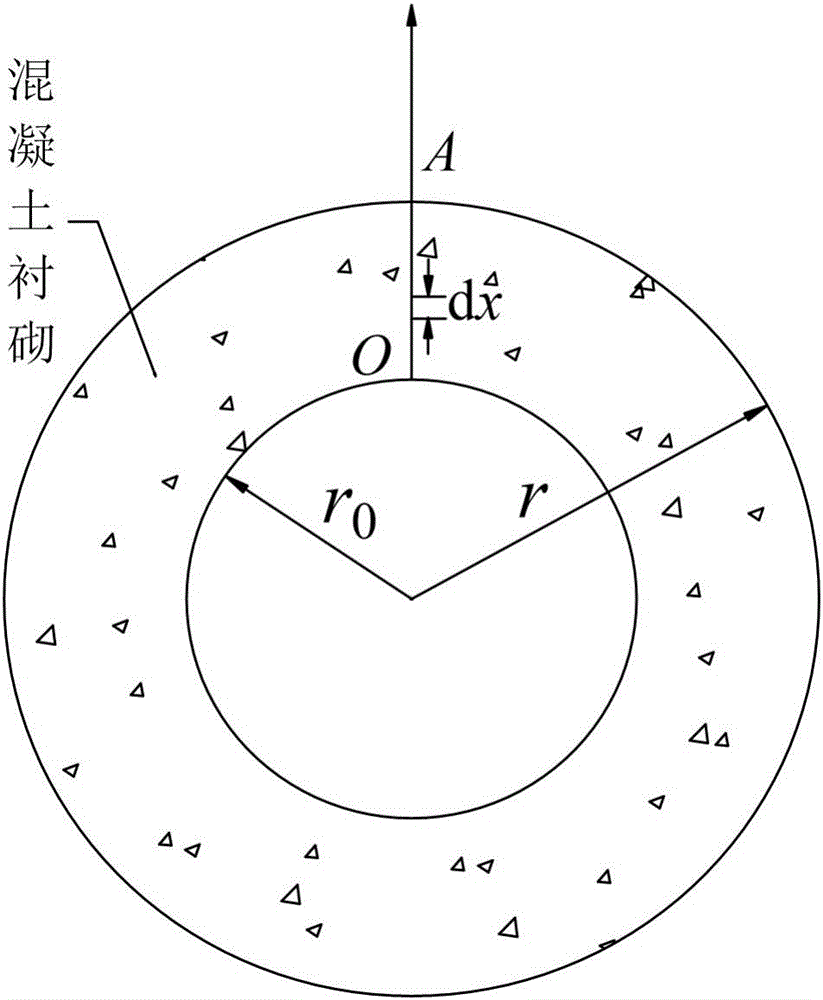
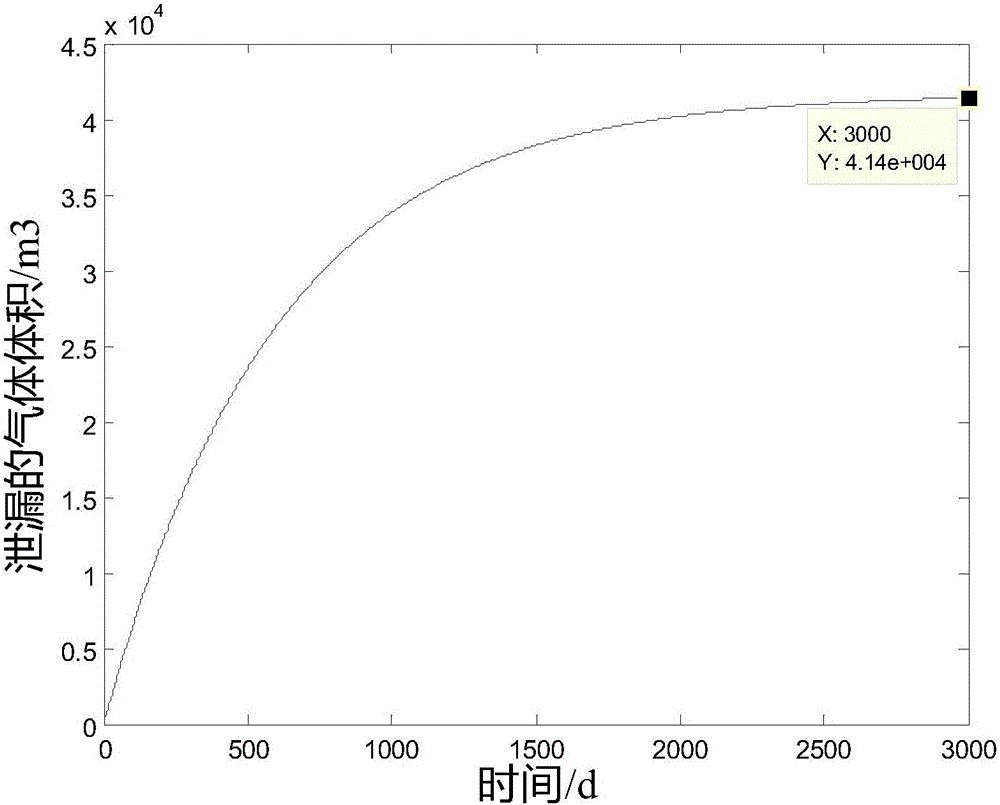
Method for computing air impermeability of gas storage cavity
ActiveCN106092469AGuaranteed air tightnessUnderstand the purposeMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateProduct gasPressure difference
The invention discloses a method for computing the air impermeability of a gas storage cavity. The method comprises steps of: S1, setting seepage velocity computational formulas 1 for different seepage distances according to a Darcy law; S2, setting a computational formula 3 of the pressure difference [delta]px inside the cavity according to an ideal gas state equation computational formula 2; S3, supposing that the seepage velocity of a seeped gas is uA(t) when the gas reaches the outer surface of concrete, setting the leaked gas volume computational formula 4 within time dt; S4, setting the pore volume capable of containing air as V pore and obtaining a V pore computational formula 5; S5, setting the time when the gas just seep to a position A as a time start point and setting the volume of the seeped gas at the time t as [delta]V(t), setting a computational formula 6 of a pressure difference inside the cavity; and S6, integrating the computational formula 5 to obtain a differential equation, and solving the differential equation to obtain an expression of the volume of the leaked gas about time. The method may provide gas leakage cases with different lining permeability, and guarantees the air impermeability of the gas storage cavity by controlling the permeability of the lining.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST
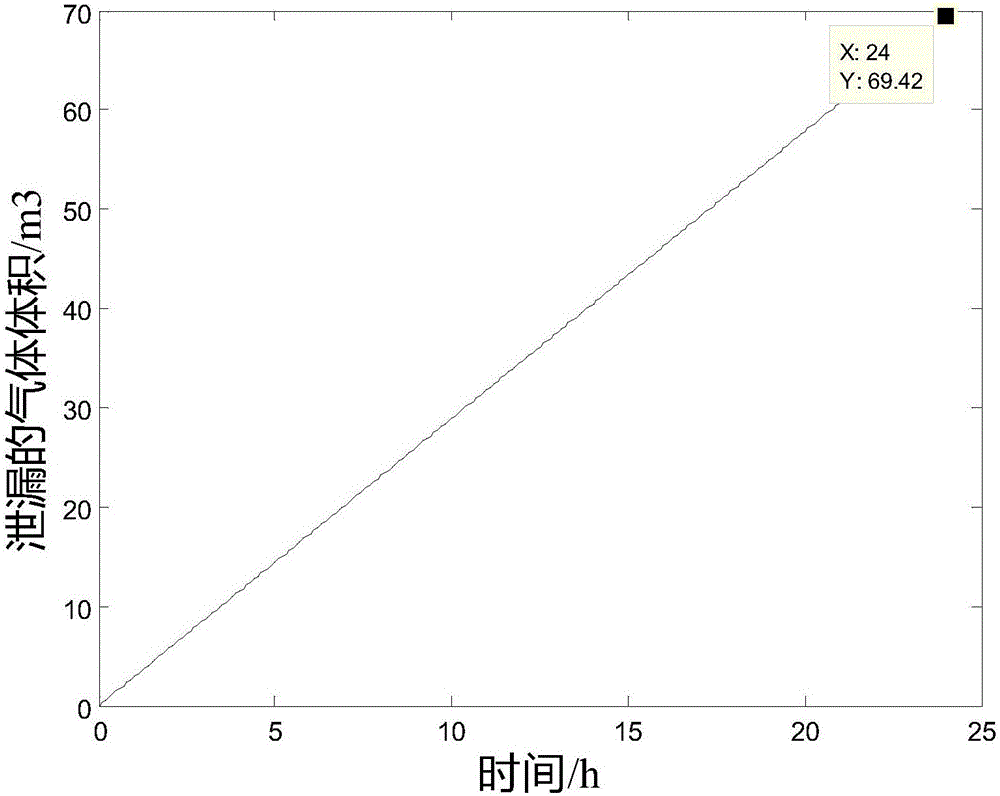
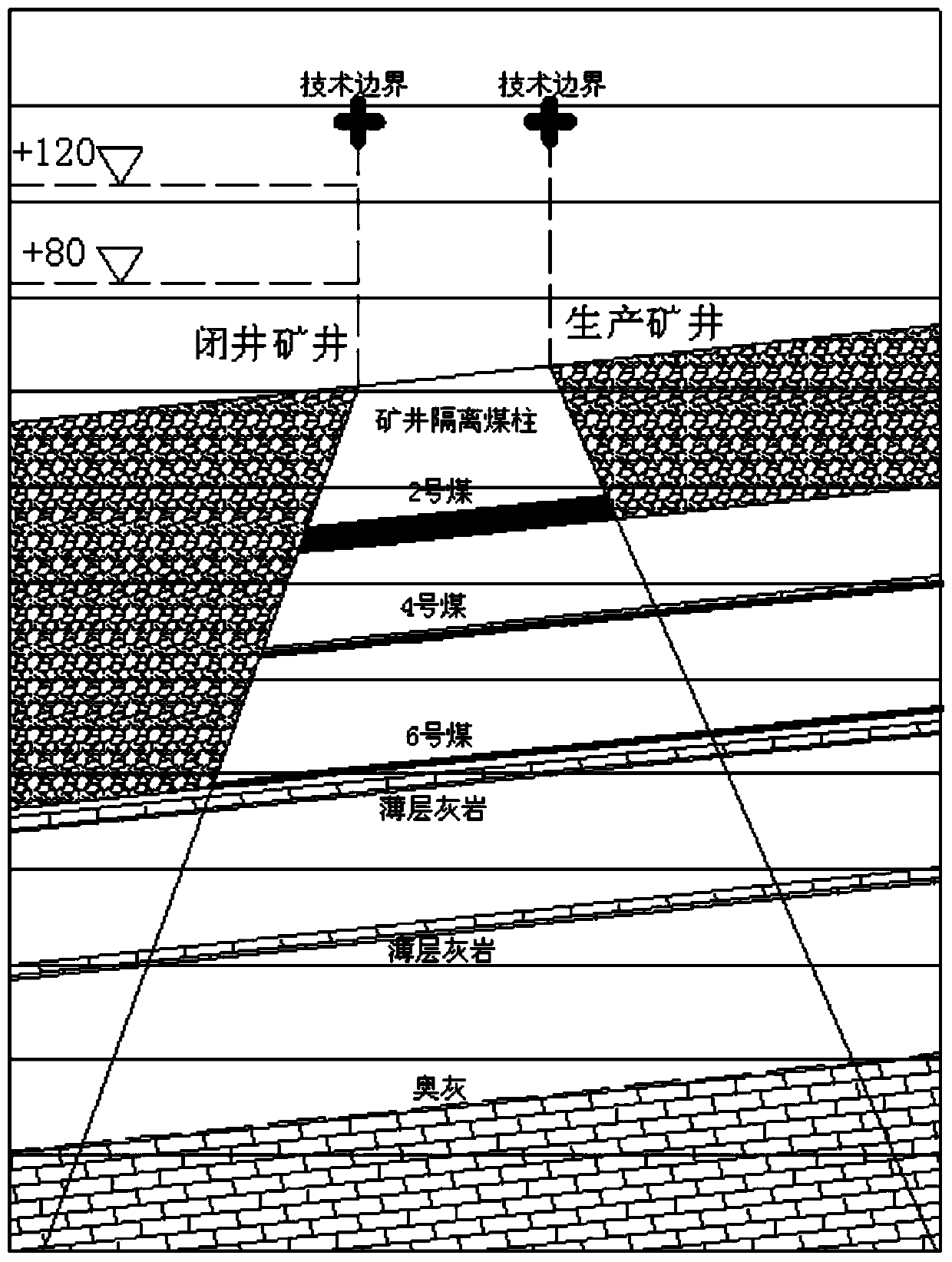
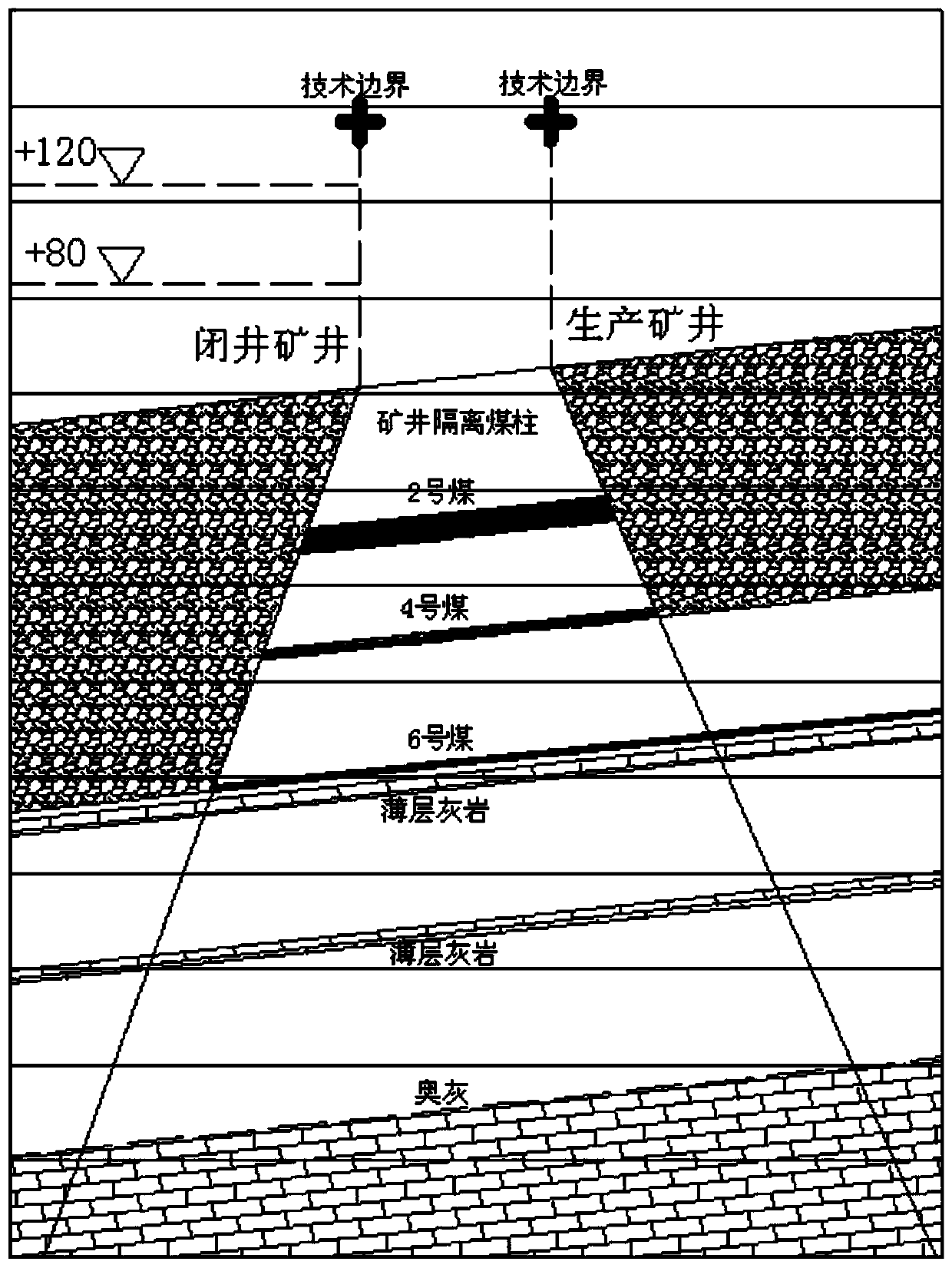
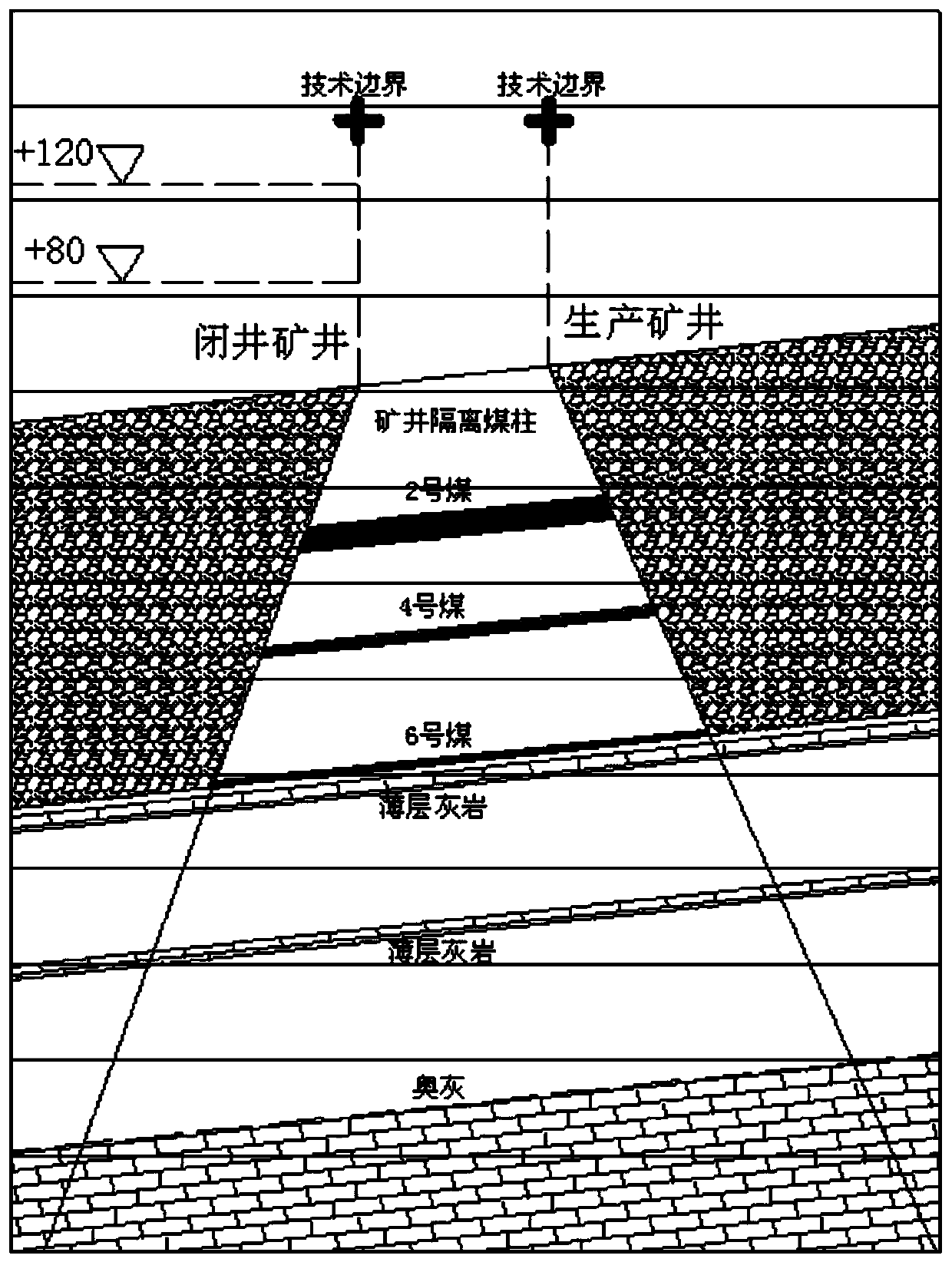
Water inflow prediction and calculation method based on hydrogeological model of adjacent mines after mine closing
ActiveCN110567854ARealisticReduce analysisEducational modelsPermeability/surface area analysisHydrologyDarcy's law
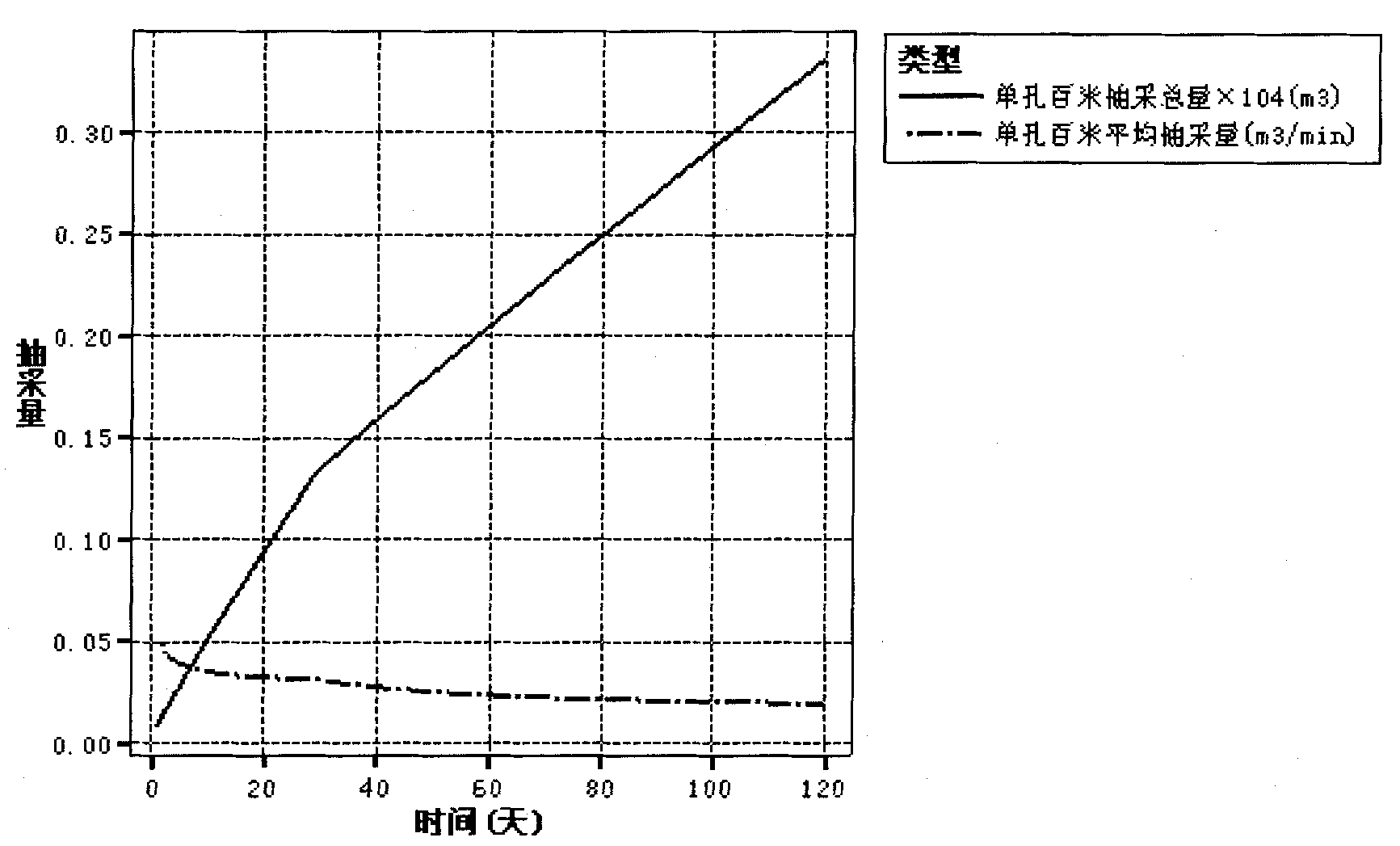
The invention provides a water inflow prediction and calculation method based on a hydrogeological model of adjacent mines after mine closing. The method comprises the steps: 1, establishing the hydrogeological model of the adjacent mines after mine closing; and 2, predicting and calculating the water inflow based on the hydrogeological model of the adjacent mines after mine closing. The step 1 further comprises the following steps: 11, analyzing a water filling condition after pit closing of the mine; and 12, determining the water filling condition after pit closing of the mine. The boundarycondition in the step 11 comprises that a natural geological boundary of a relatively large fault is used as a boundary; or an artificial technical boundary is taken as the boundary. In the step 1, seepage motion of the hydrogeological model of the adjacent mines after mine closing conforms to the Darcy law of the hydrogeological theory, and in the step 2, a Darcy formula is adopted to predict andcalculate influence of pit closing of the mine on mining of the adjacent mine and the water inflow. The Darcy formula is Q = KIF, wherein Q represents the water inflow in the unit of m3 / min, F represents the seepage section area in unit of m2, I represents the hydraulic gradient, and K represents a permeability coefficient.
Owner:JIZHONG ENERGY FENGFENG GRP
Exploitation dynamic calculation method under multilayer joint-exploitation oil deposit fixed liquid volume production condition
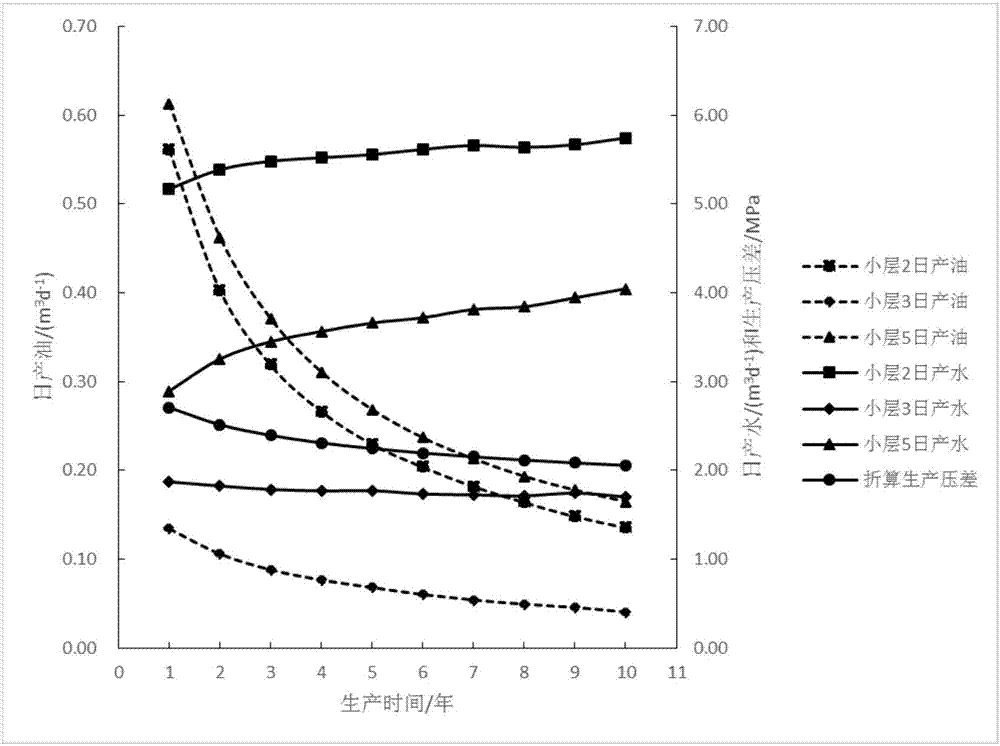
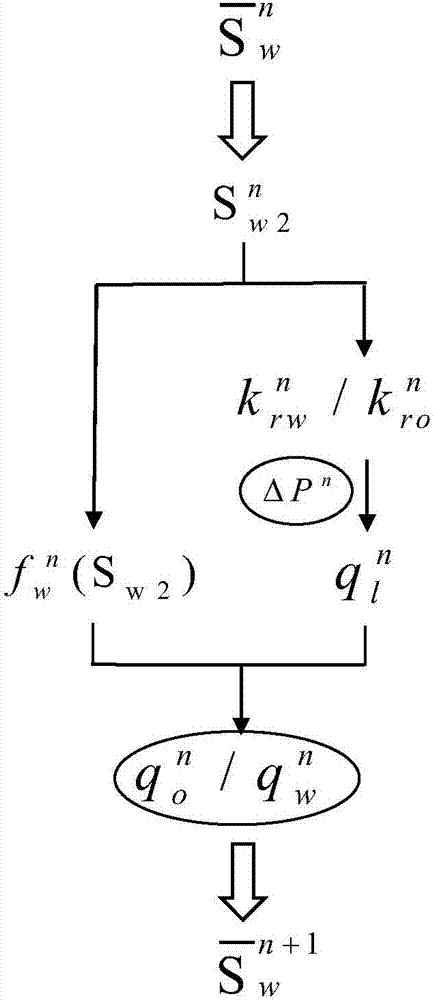
ActiveCN107169684ATotal seepage resistance decreasesClimate change adaptationResourcesCurve fittingWater production
The invention discloses an exploitation dynamic calculation method under the multilayer joint-exploitation oil deposit fixed liquid volume production condition, and belongs to the technical field of oilfield development. The method comprises the steps: 1, knowing reservoir physical property and fluid parameters of each single layer; 2, knowing the mean water saturation degree of the layers at a moment n, solving the water saturation degree of an outlet, and solving the oil and water relative permeability and water content through a relative permeability curve fitting fractional flow equation; 3 knowing the total liquid production capacity and the oil and water relative permeability at the moment n, and solving a corresponding production pressure difference delta Pn at the moment n under the fixed liquid volume production condition through iteration; 4, solving the liquid production capacity at the moment n through the generalized Darcy's law, and determining the water production capacity and oil production capacity through the water content fwn(Sw2); 5, obtaining the mean water content (shown in the description) at the moment (n+1) according to the material balance law; 6, repeatedly carrying out the steps (2)-(5) till (n+1) is equal to N, and ending the calculation. According to the invention, the method achieves the calculation of the developing dynamic of multilayer joint-exploitation fixed liquid volume production, and can provide guide for the production of an oilfield.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Pavement structure multi-physical field coupling numerical simulation method based on finite element
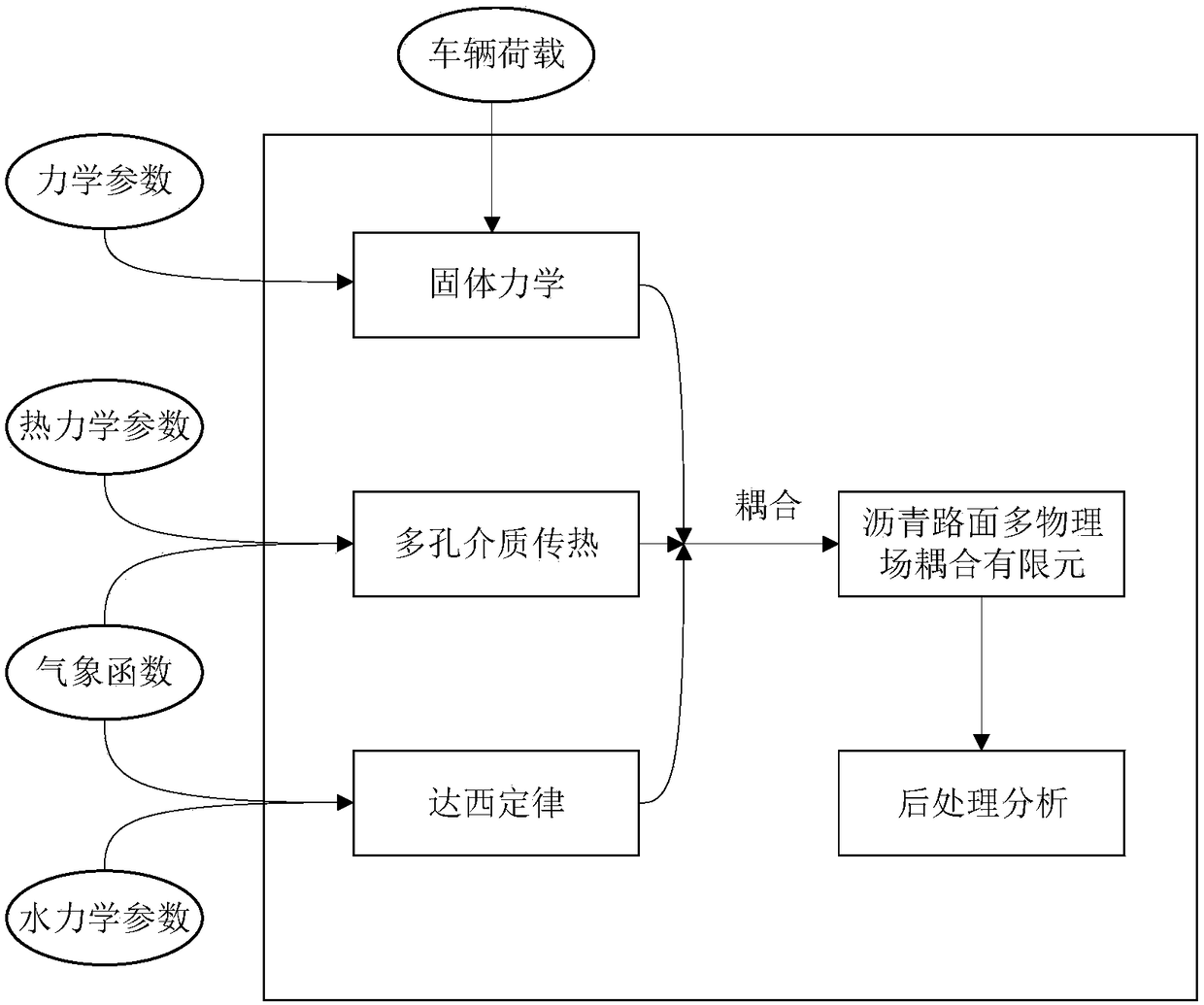
ActiveCN109241636AAccurate analysis of usabilityGeometric CADSustainable transportationMultiphysics couplingPhysical field
The invention discloses a pavement structure multi-physical field coupling numerical simulation method based on finite element, which comprises the following steps: defining mechanical, thermodynamicand hydraulic parameters; Defining vehicle loads and meteorological functions; Adding a solid mechanics module, applying a load and setting boundary conditions; Adding a porous medium heat transfer module, referring a weather function and setting boundary conditions; Adding Darcy's law module, referring a weather function and setting boundary condition; Adding a multi-physical field coupling module to couple the multi-physical fields; Calculating and performing post-processing analysis. The invention couples the stress field, the temperature field and the hydraulic field, and comprehensively studies the influence of multiple physical fields on the road performance. The invention has good guiding significance for the selection and analysis of the pavement structure.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
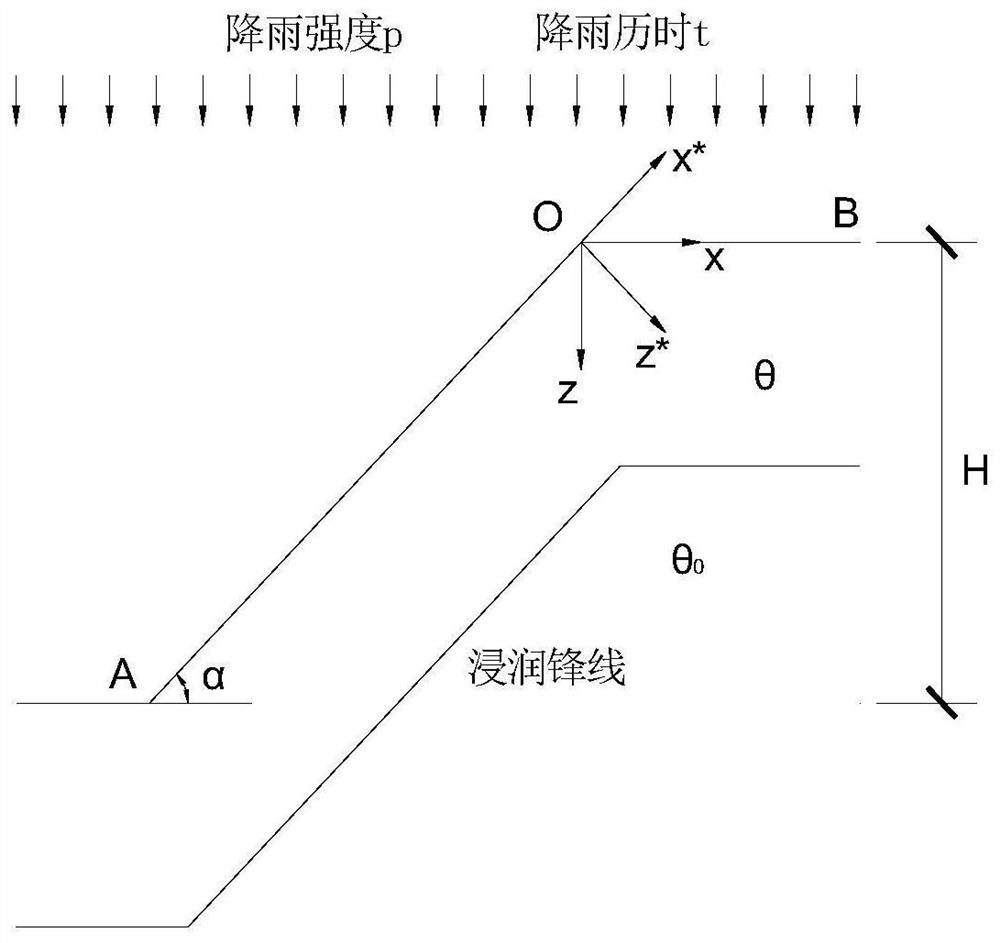
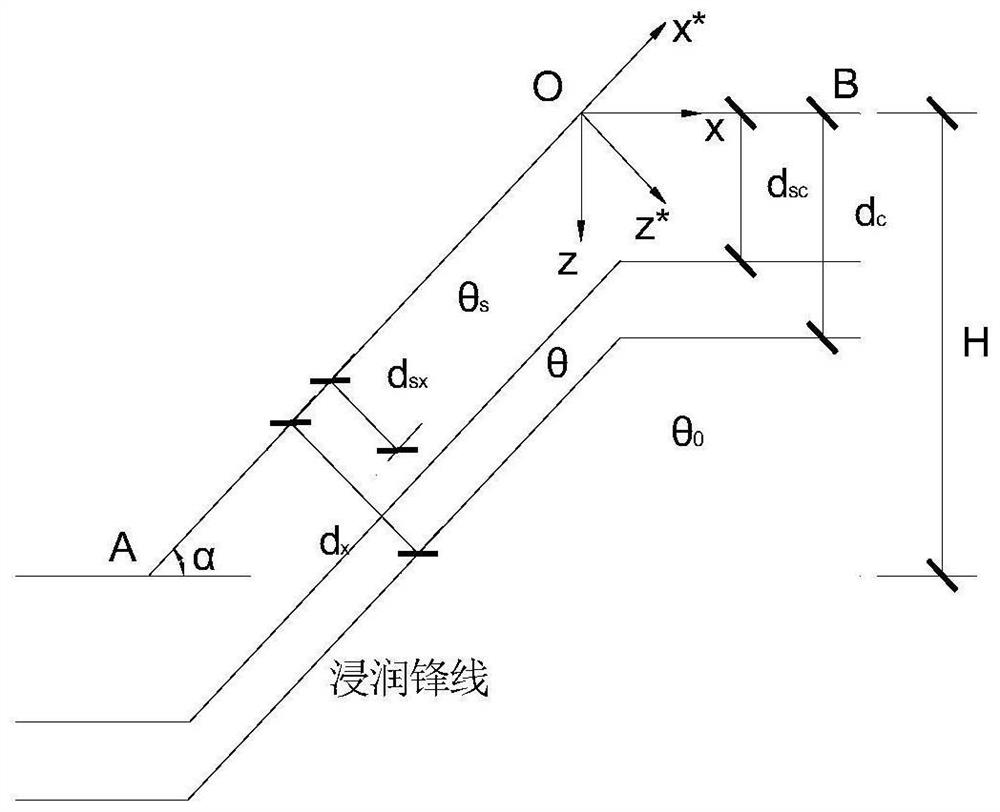
Method for calculating seepage control equation of unsaturated loess slope under rainfall infiltration
PendingCN112685874ADetermining the penetration depthSolve the difficulty of analytical calculation of seepage fieldDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingSoil scienceDarcy's law
The invention discloses an unsaturated loess slope seepage control equation calculation method under rainfall infiltration. The method comprises steps of 1, building a loess slope seepage field analysis model of a horizontal slope surface and an inclined slope surface through reasonable assumption according to the damage influence factors of a loess slope under the rainfall infiltration condition, a two-dimensional unsaturated loess seepage control equation being obtained through a porous medium theory and a hydraulics theory; 2, converting coordinate systems in the vertical rainfall direction and the horizontal direction into a direction along the slope surface and a direction perpendicular to the slope surface to obtain an unsaturated loess seepage control equation after coordinate conversion and simplification; and 3, according to the soil-water characteristic curve, the permeability coefficient equation and the Darcy law, an analytical solution of the transient moisture content in the loess slope in the rainfall process being derived, and the rainwater infiltration depth and the saturated infiltration depth being determined. The method has the effect of solving problems that the seepage field of the rainwater infiltration side slope is difficult to analyze and calculate and the calculation parameters of the unsaturated soil are inaccurate.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Porous metal support permeability testing device and surface cleaning device as well as porous metal support permeability testing method and surface cleaning method
InactiveCN109632599ASimple and fast operationImprove test accuracyPermeability/surface area analysisCleaning using liquidsHuman bodySurface cleaning
The invention discloses a porous metal support permeability testing device and surface cleaning device as well as a porous metal support permeability testing method and surface cleaning method. The porous metal support permeability testing device comprises a water tank, a sample fixing table for fixing a sample, a vacuum tube, a vacuum pump and a data receiving recorder, wherein the water tank isused for containing liquid, the sample fixing table is connected with the vacuum tube, the vacuum tube is connected with the vacuum pump, a water outlet of the sample fixing table is immersed in the liquid of the water tank, and a sensor used for measuring displacement changes of the liquid level in the vacuum tube and a sensor used for measuring pressure changes in the vacuum tube are arranged onthe vacuum tube correspondingly. The surface cleaning device only needs to replace the data receiving recorder in the testing device with a high-pressure air pump, so that the surface of a porous metal support can be cleaned. The permeability testing method simulates the flowing environment for the porous metal support in a human body, judges the laminar flow state of the liquid by utilizing theReynolds number, and therefore calculates the permeability size of the porous metal support by using the Darcy's law.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com