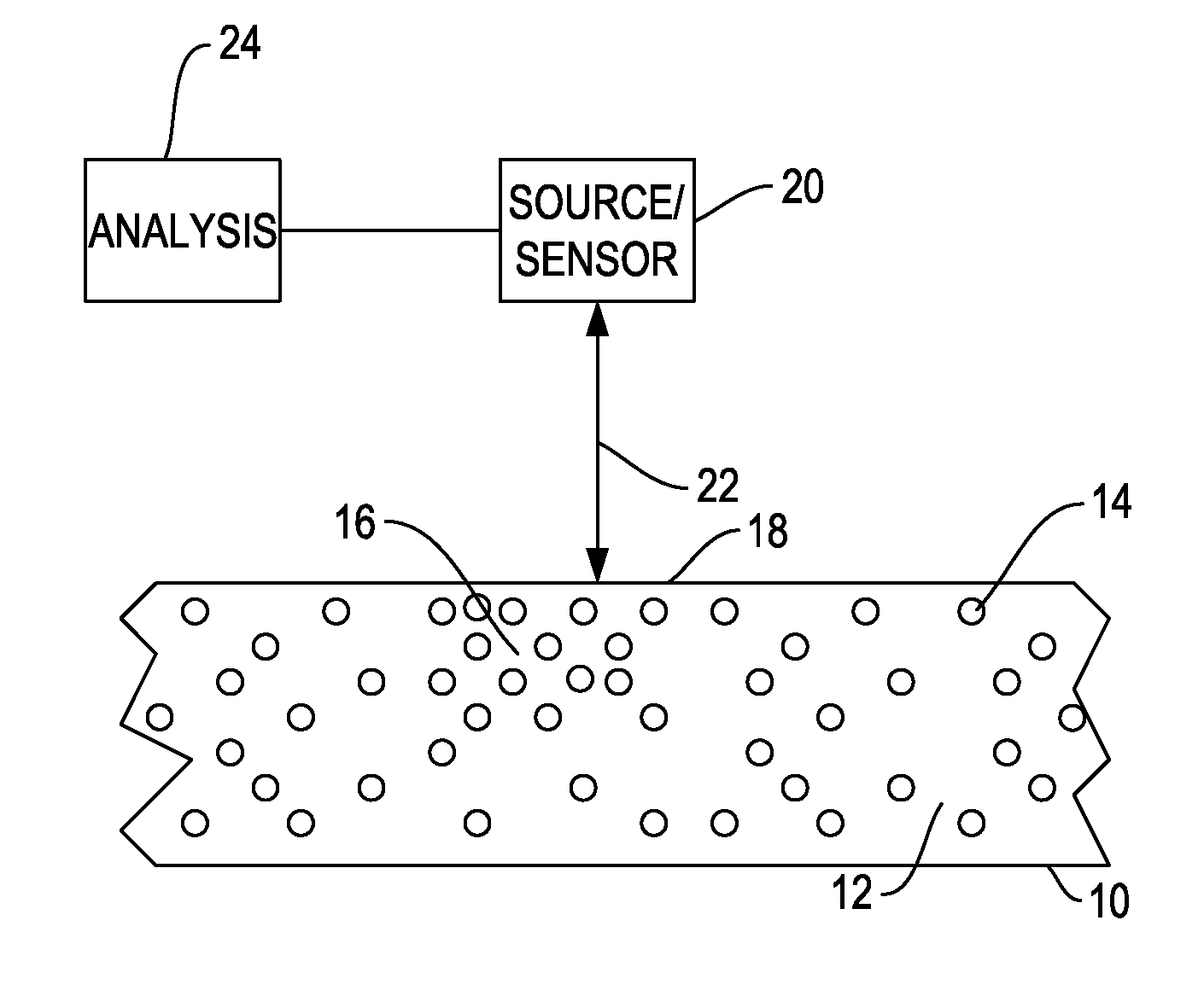
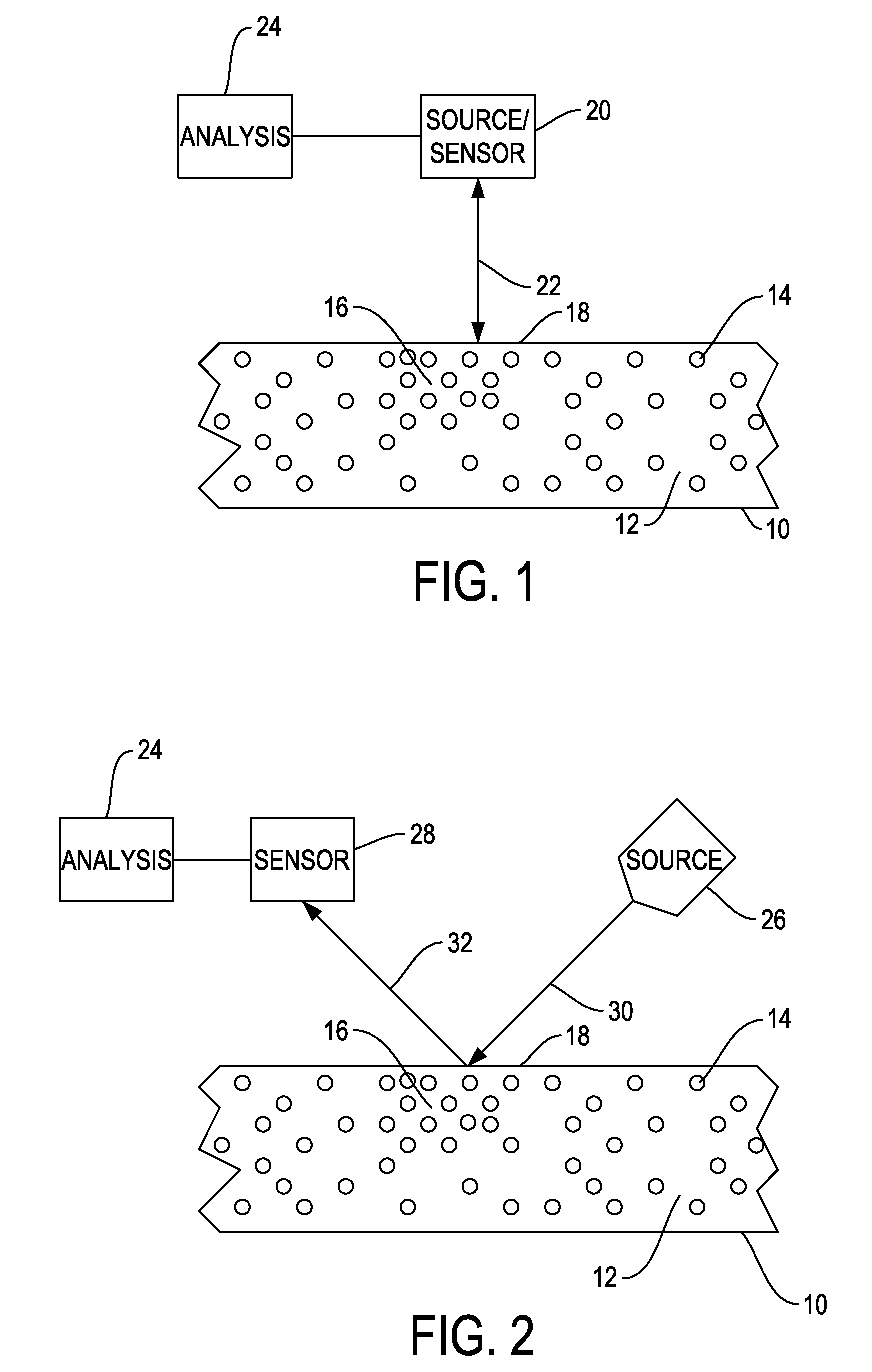
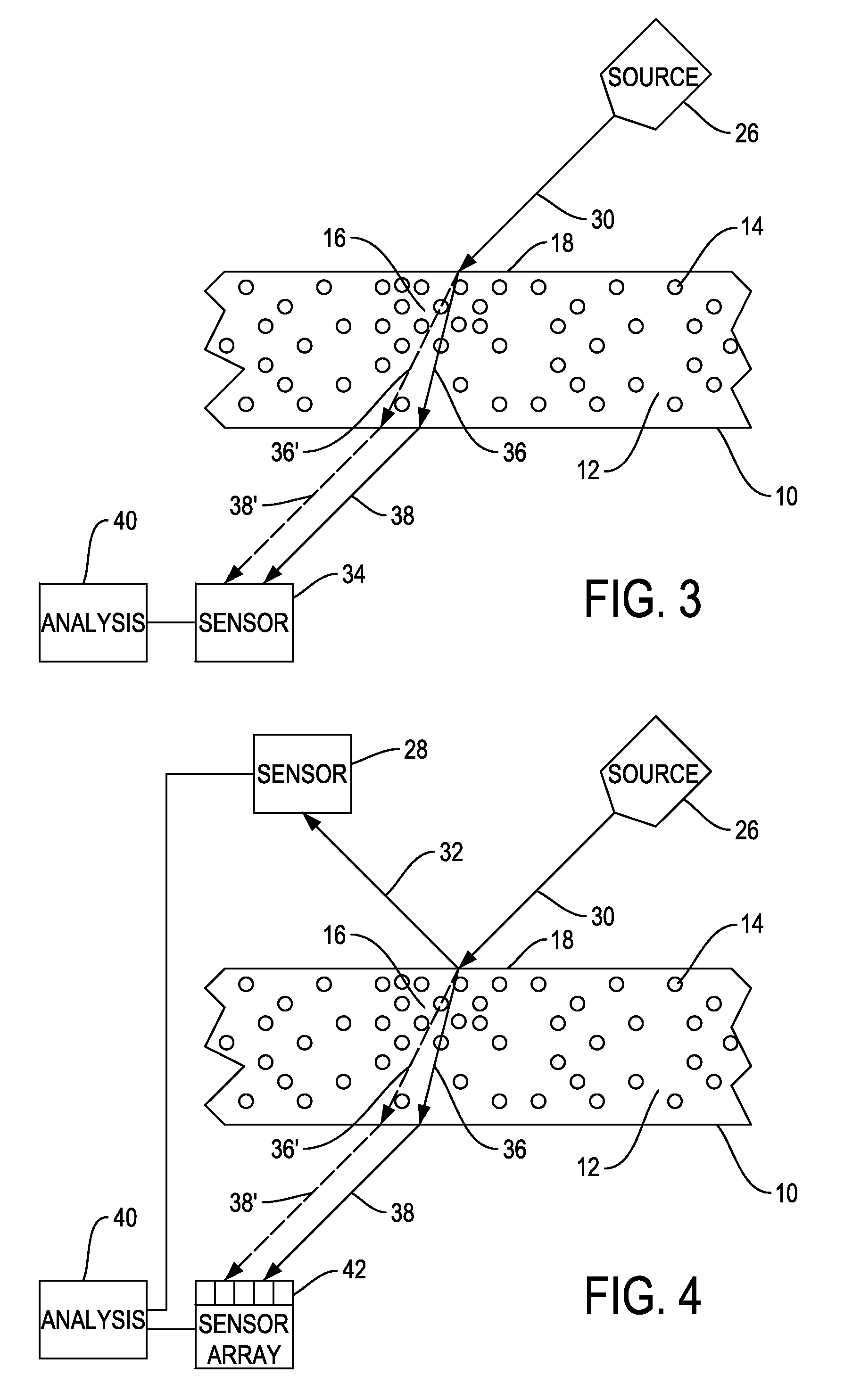
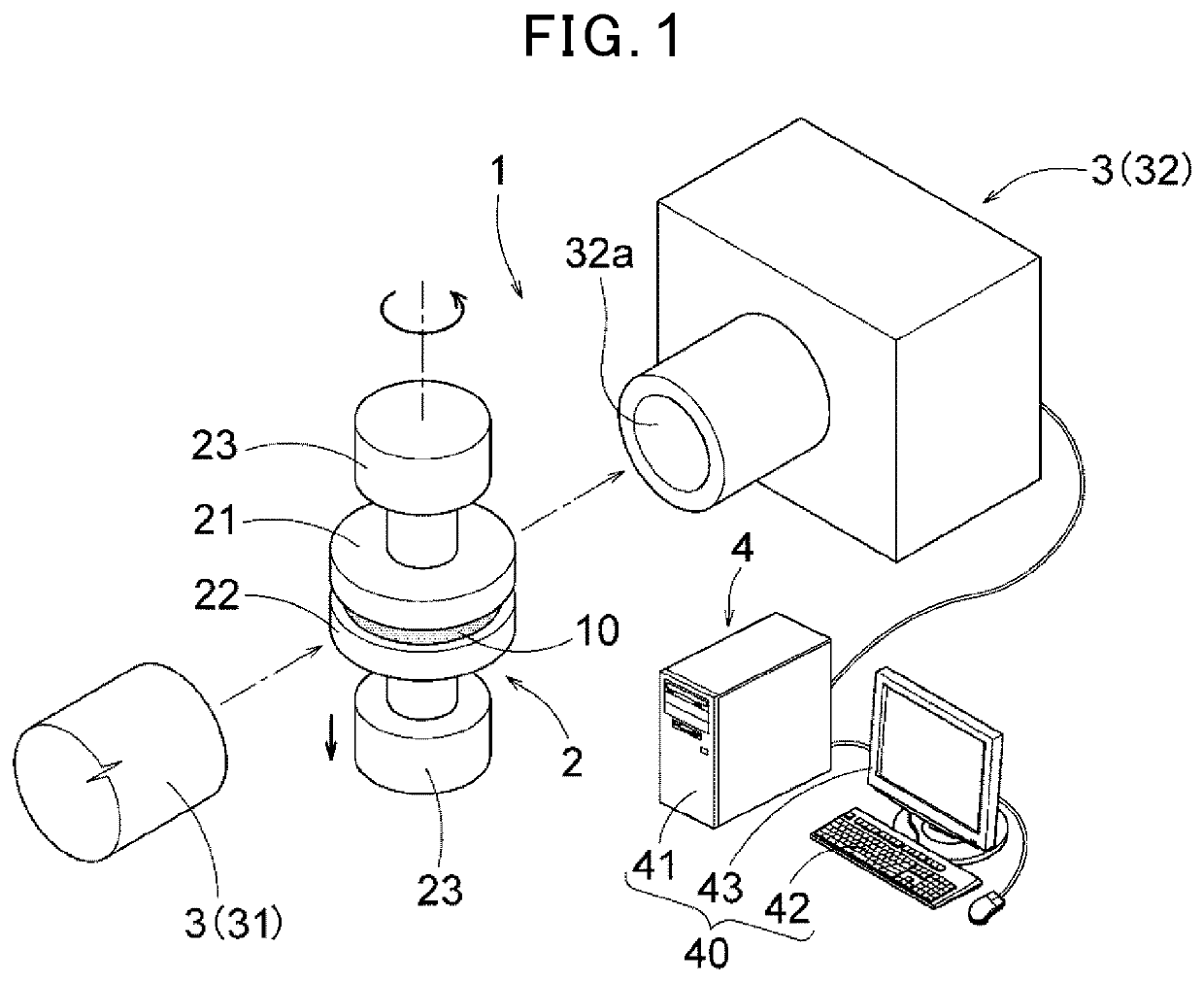
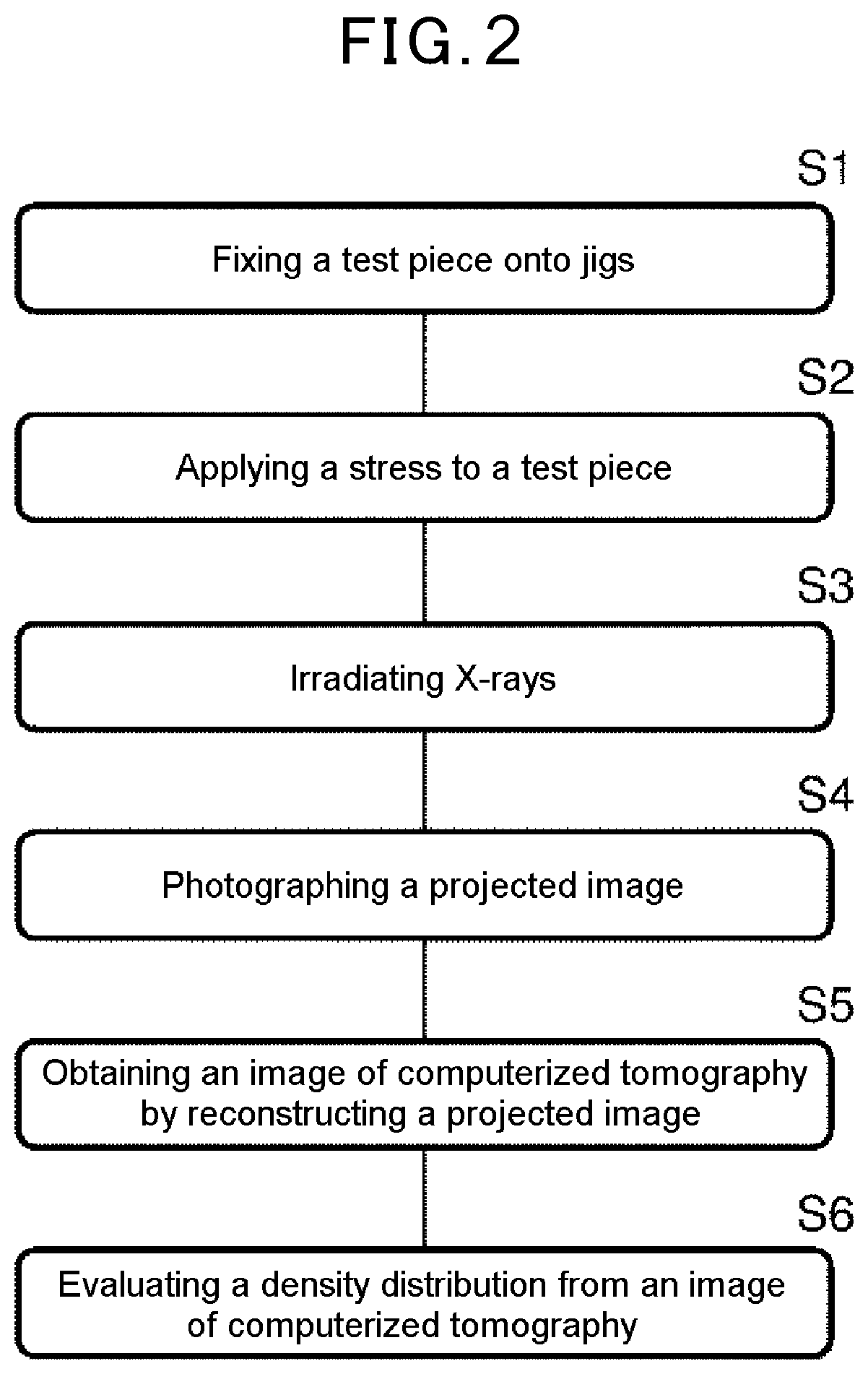
Patents
Literature
31results about "Solid dispersion analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
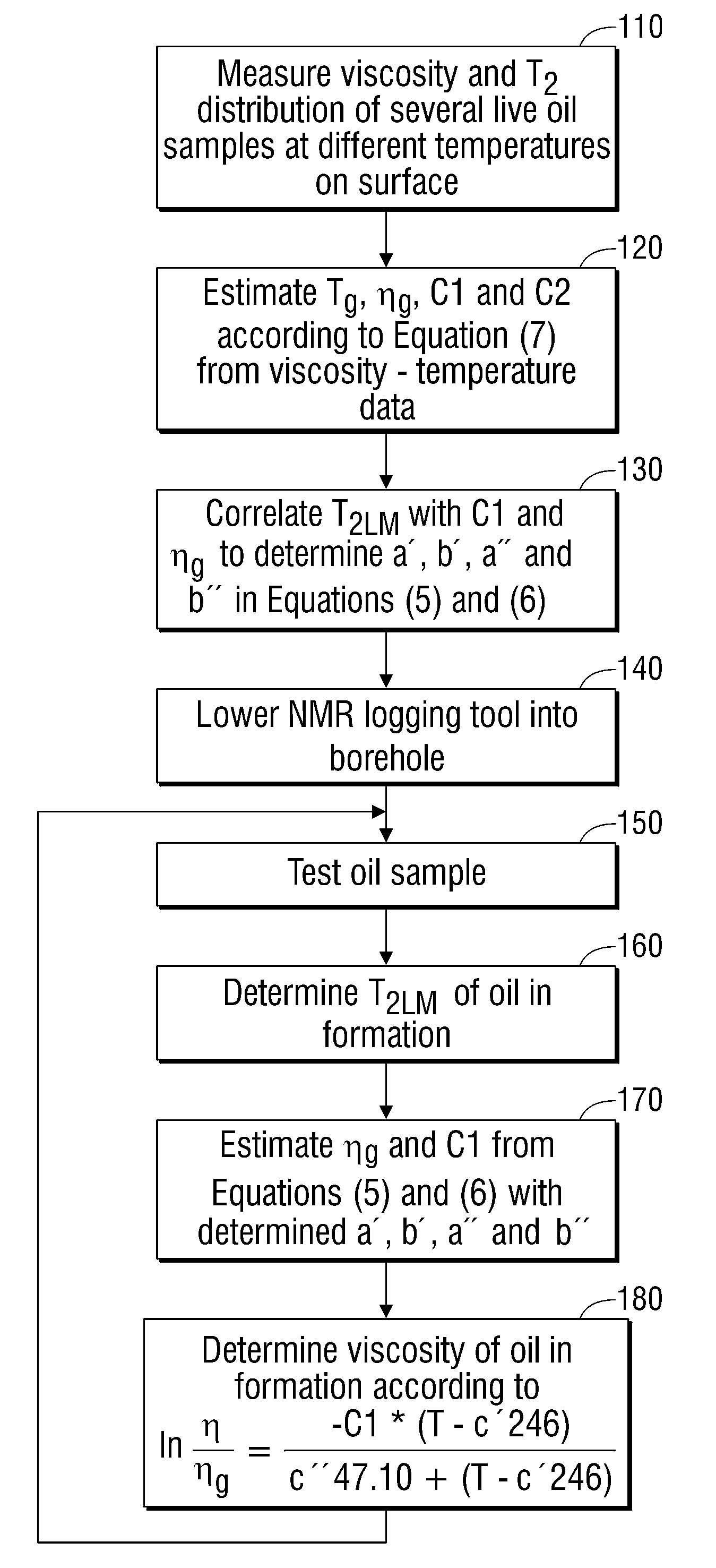
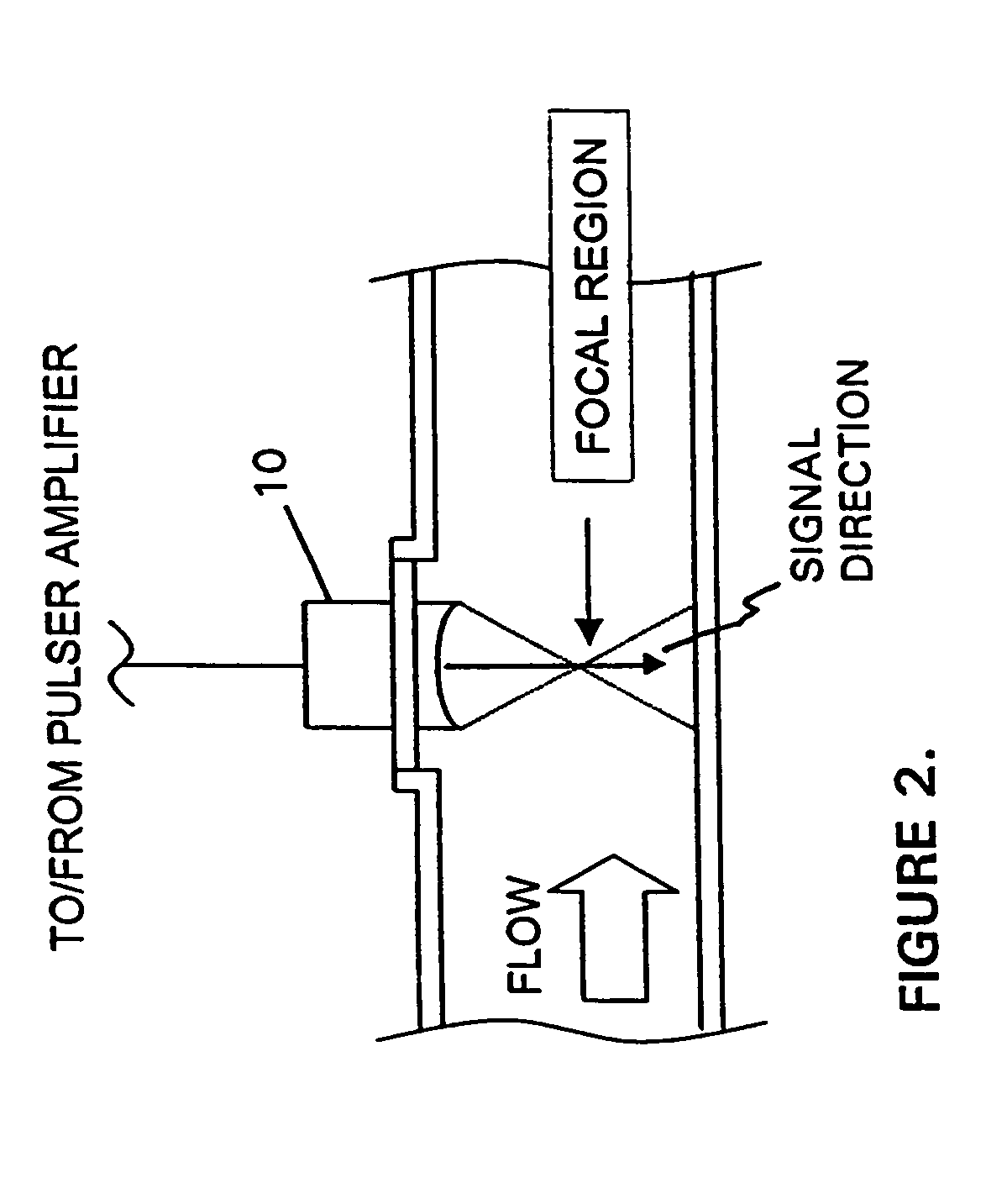
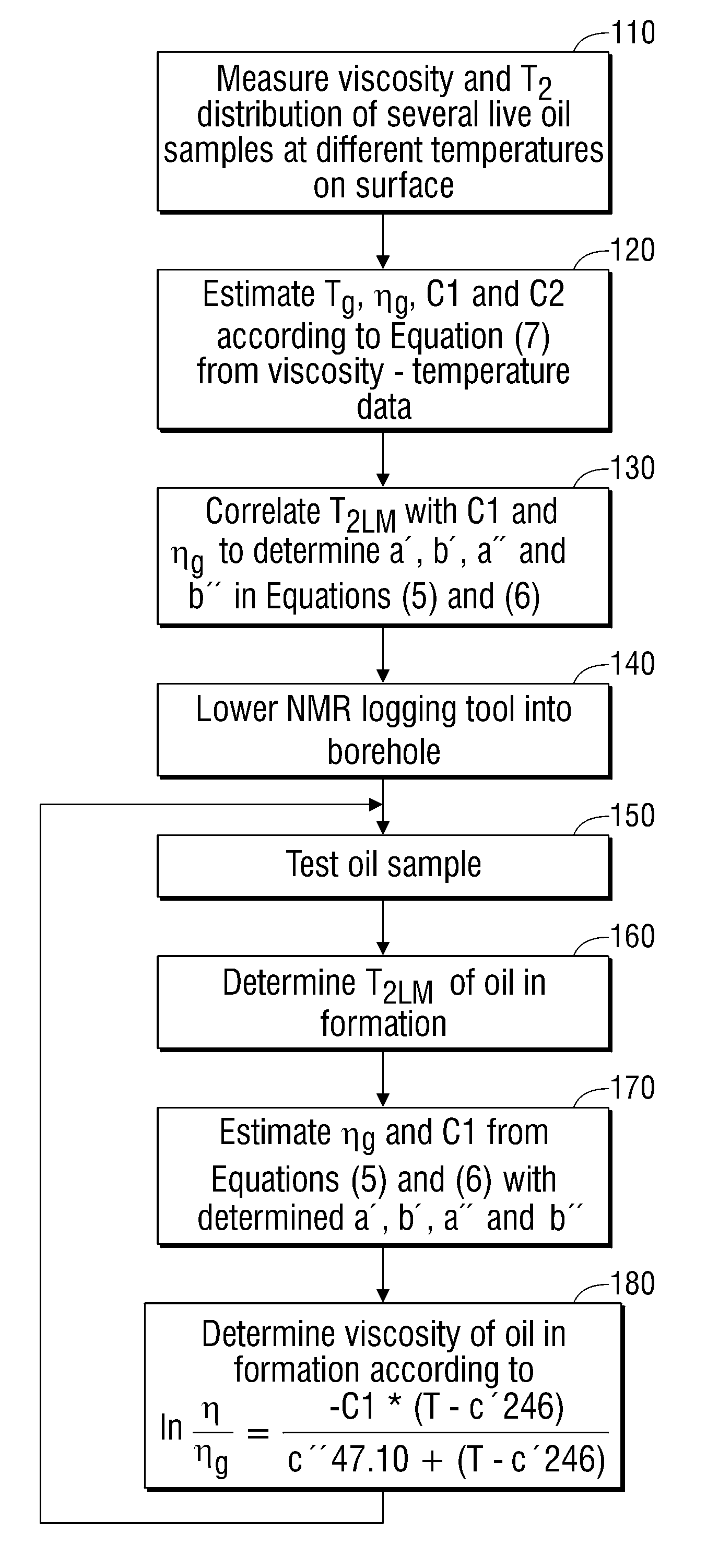
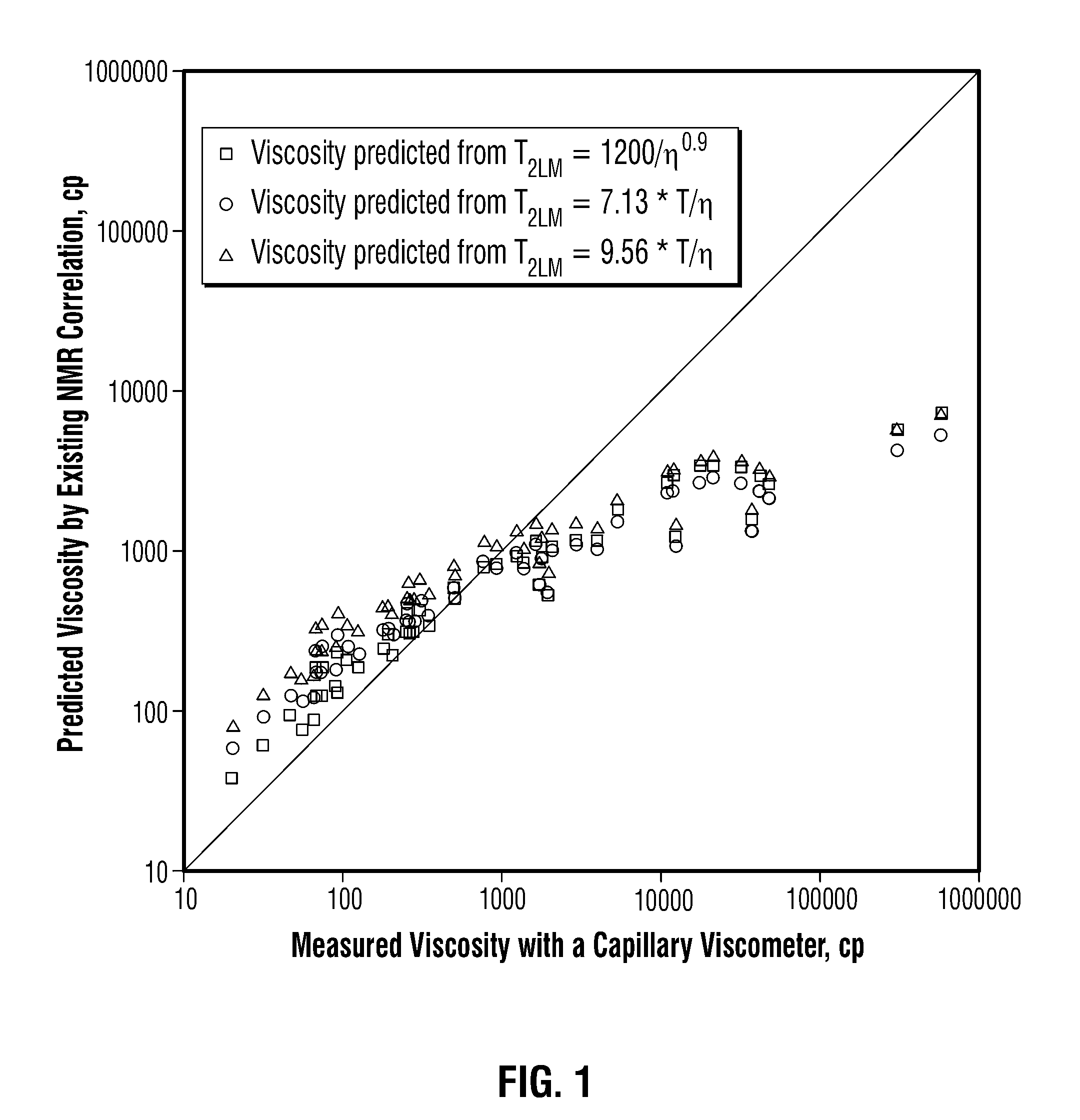
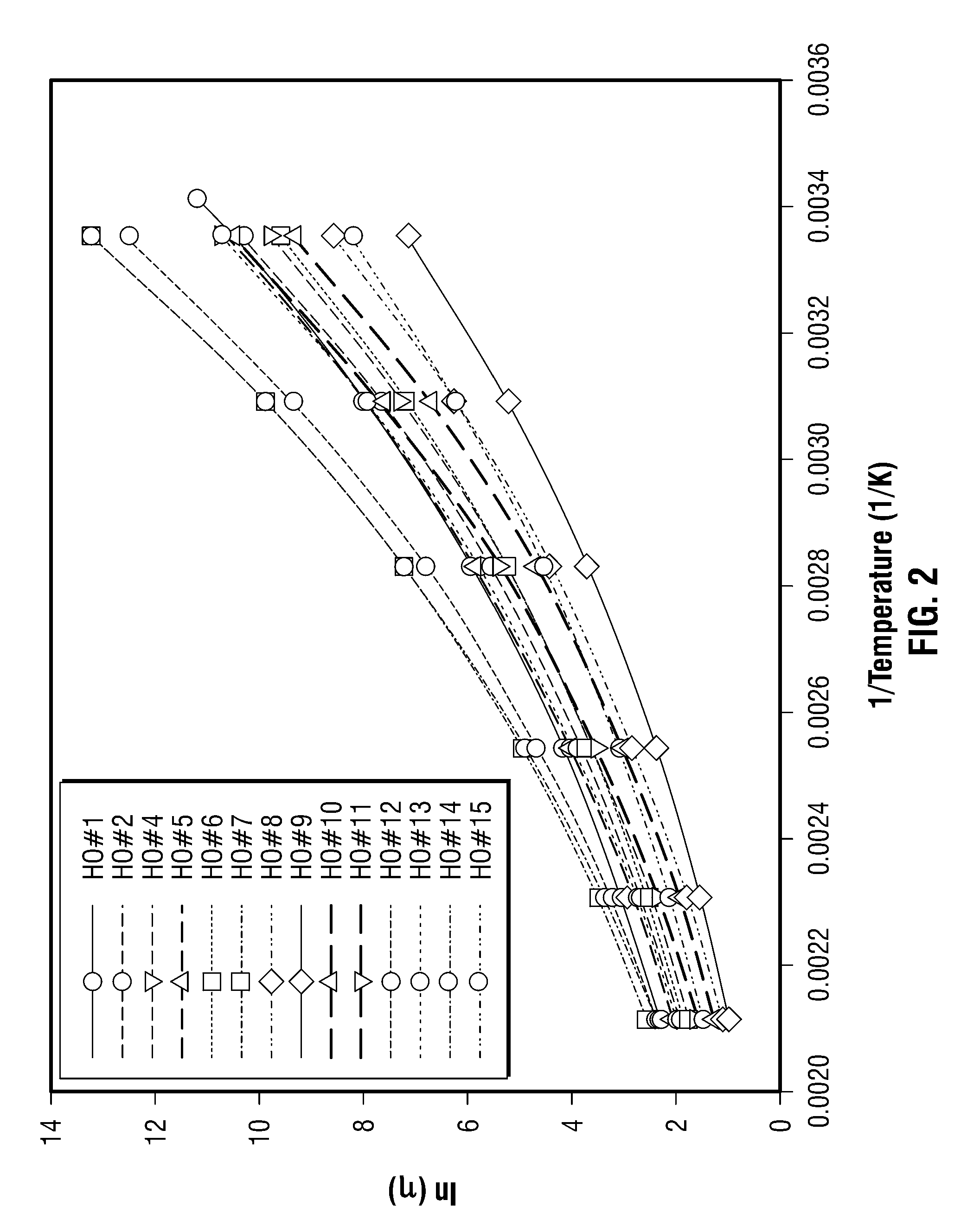
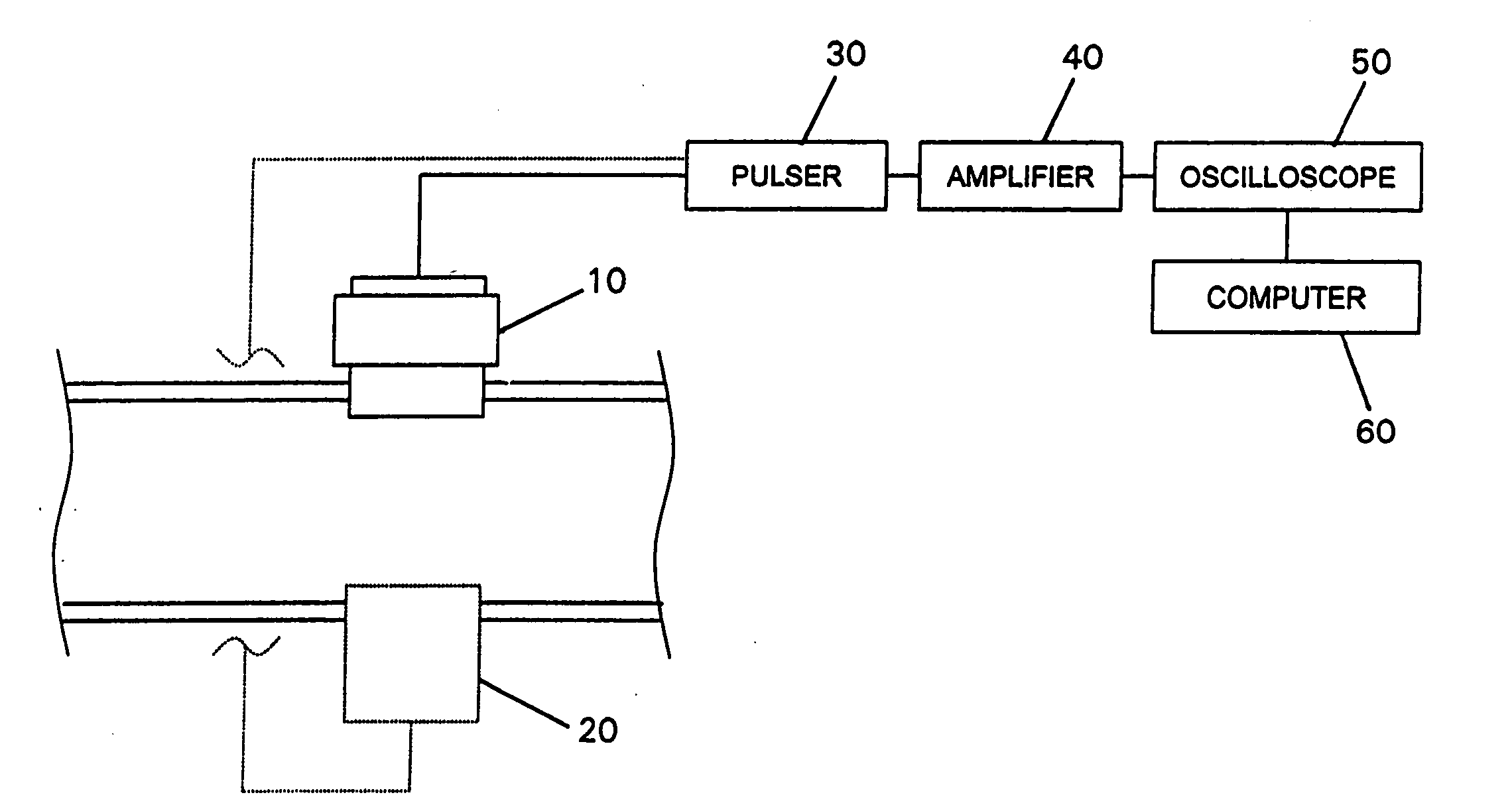
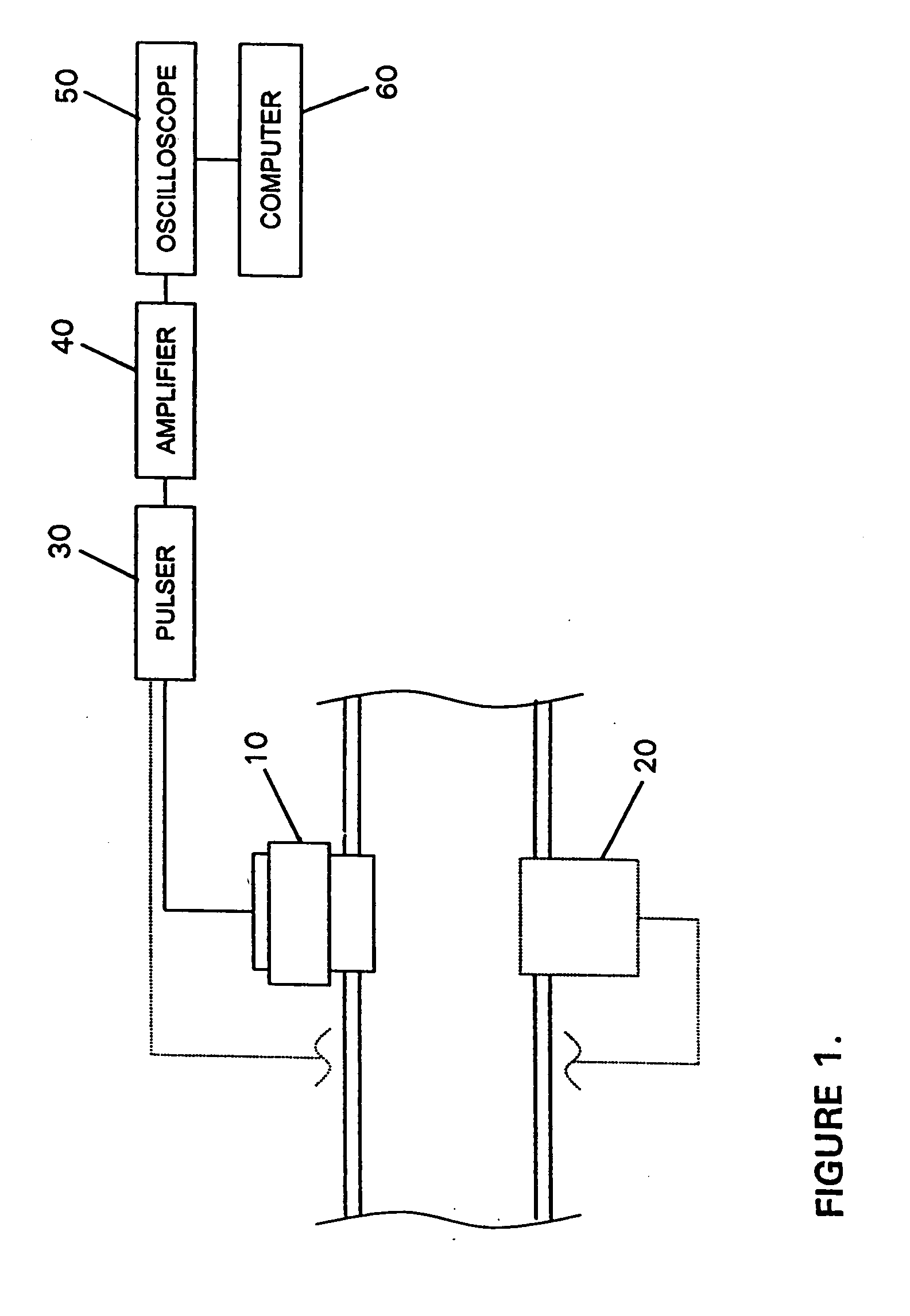
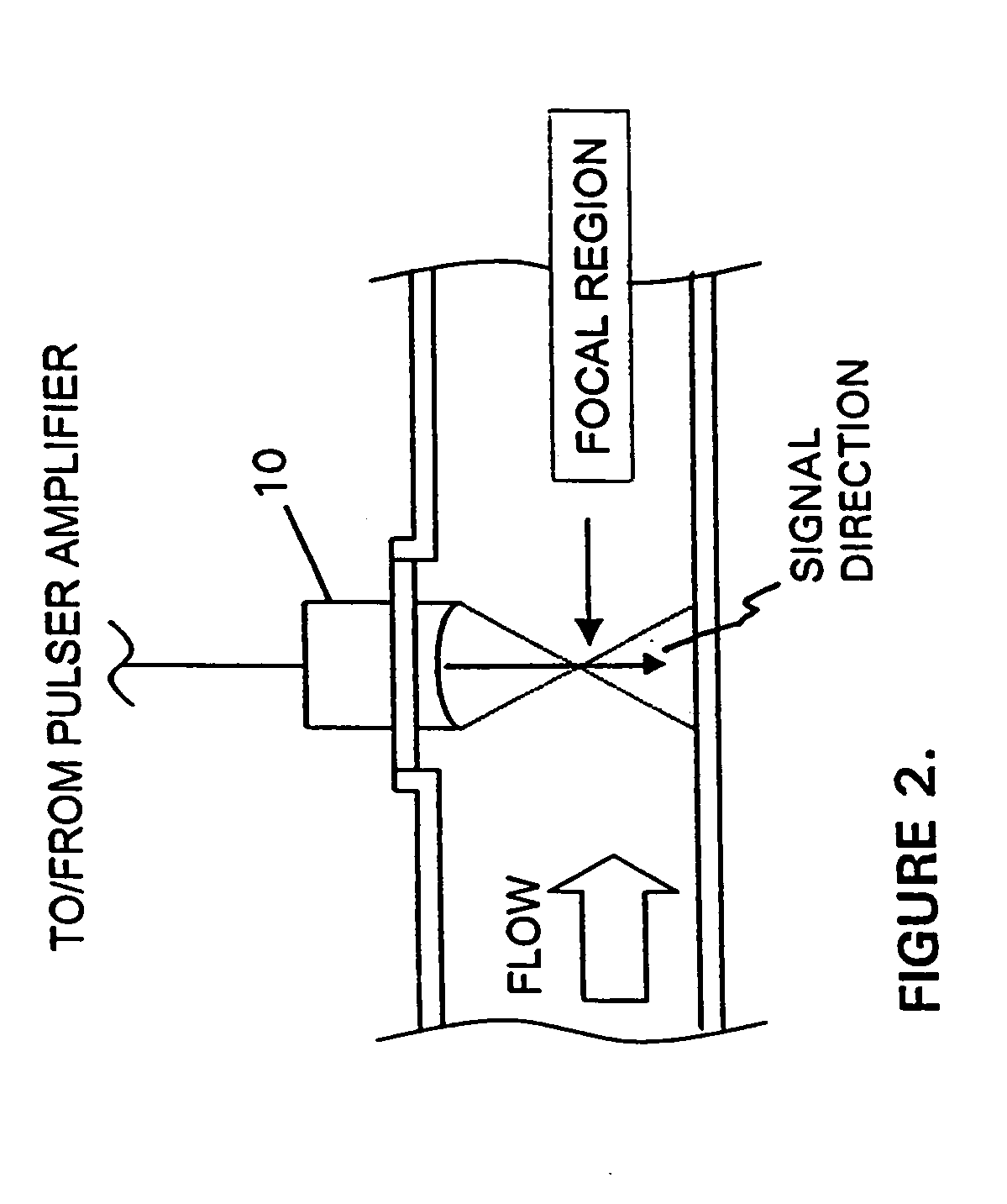
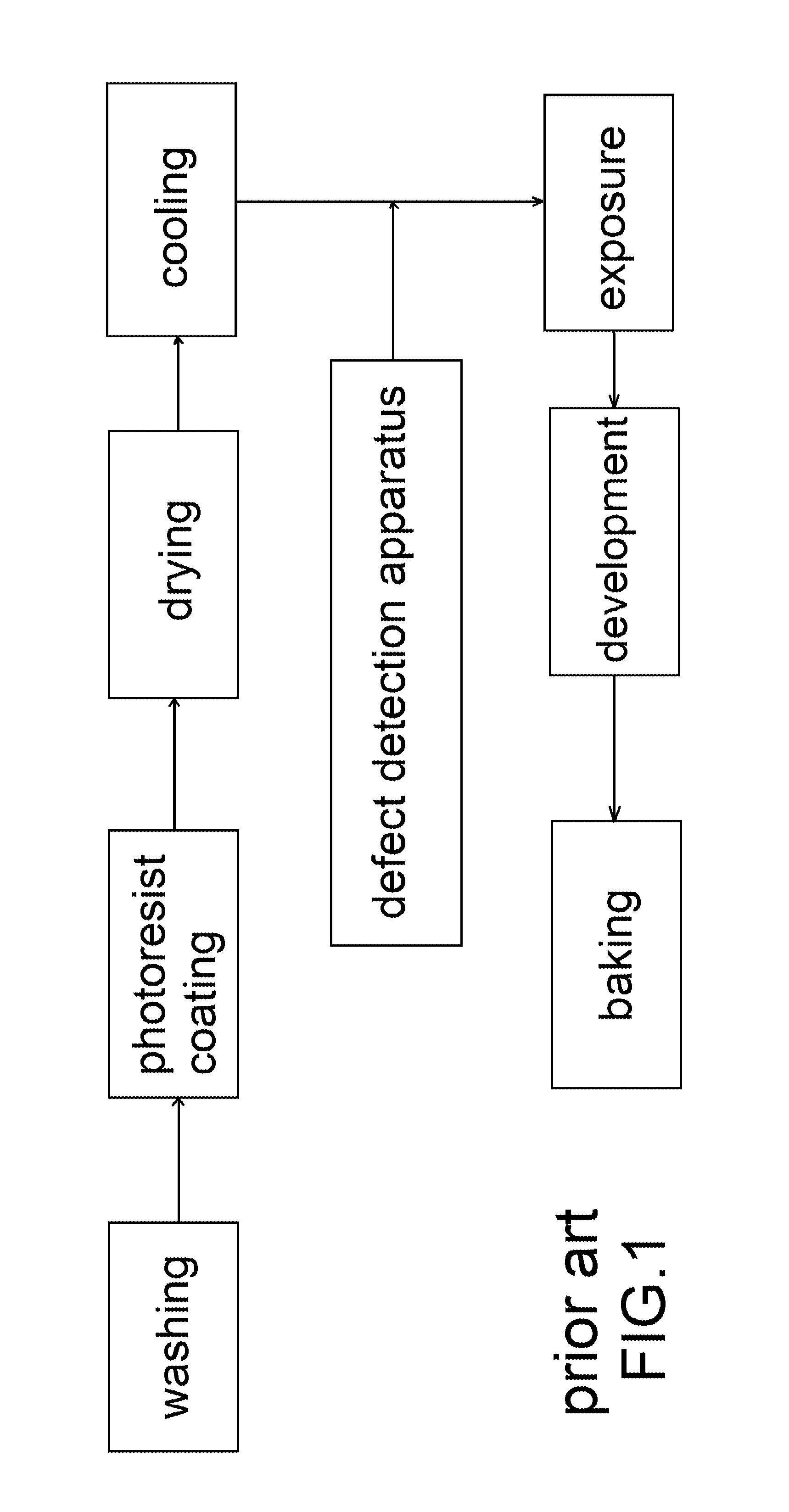
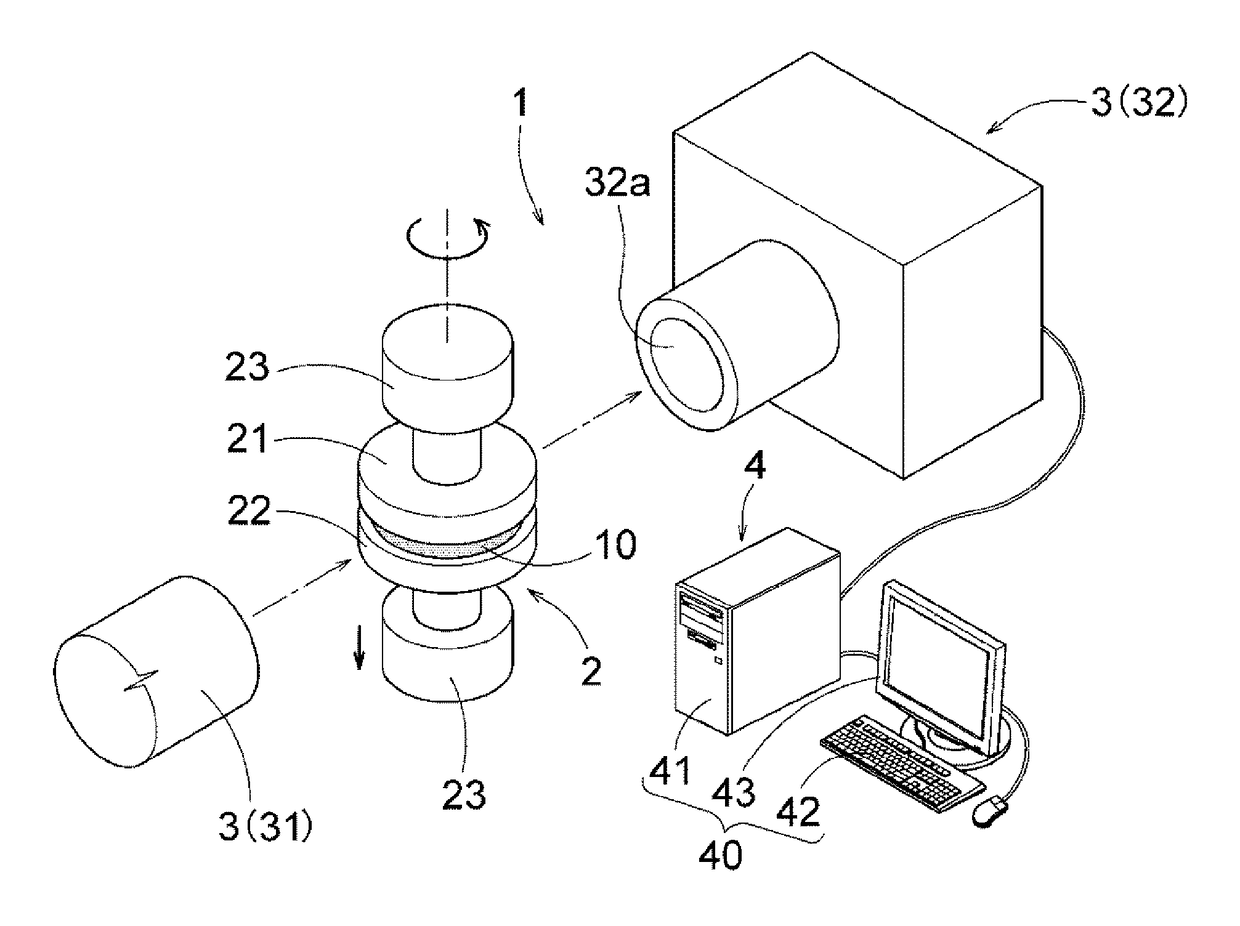
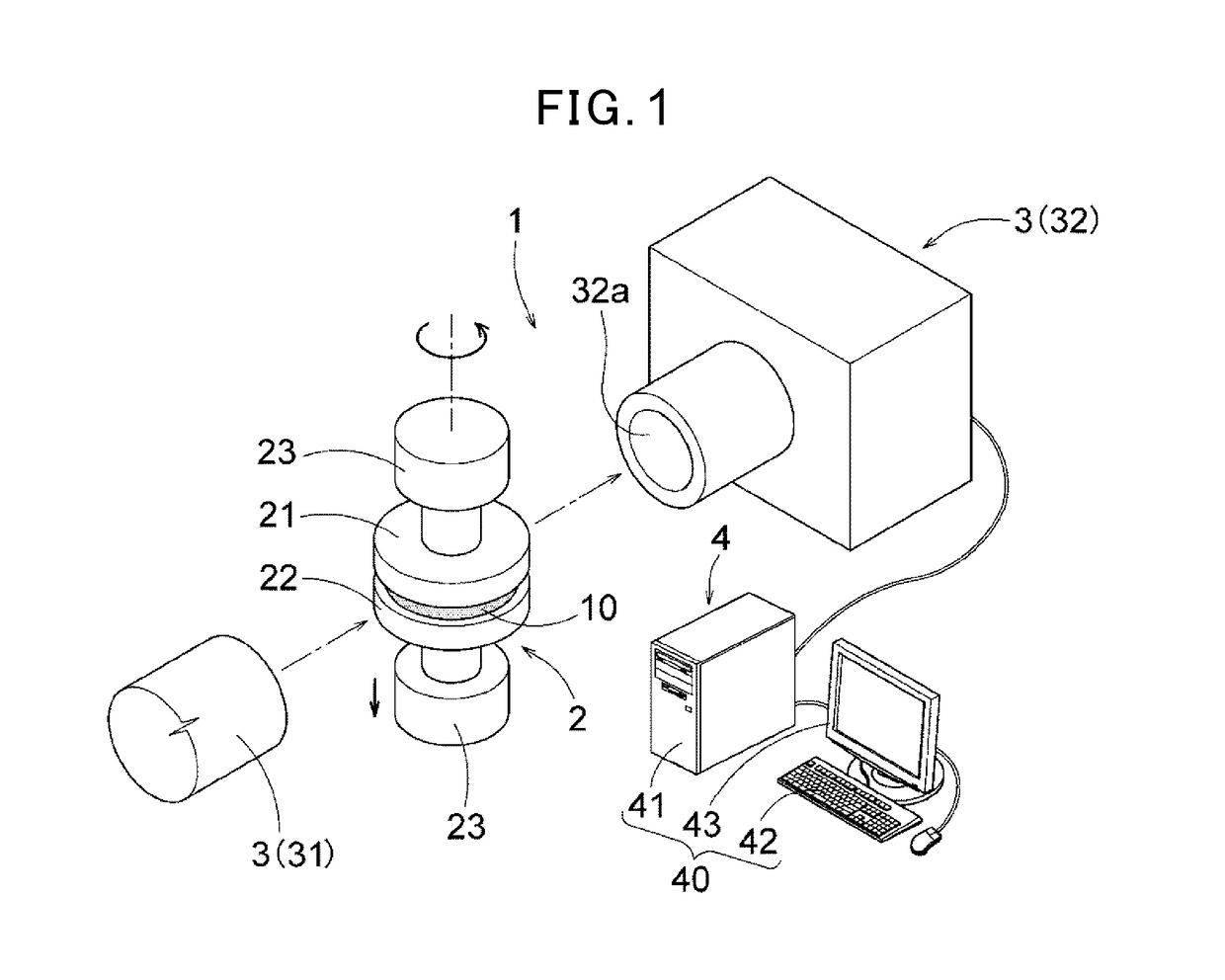
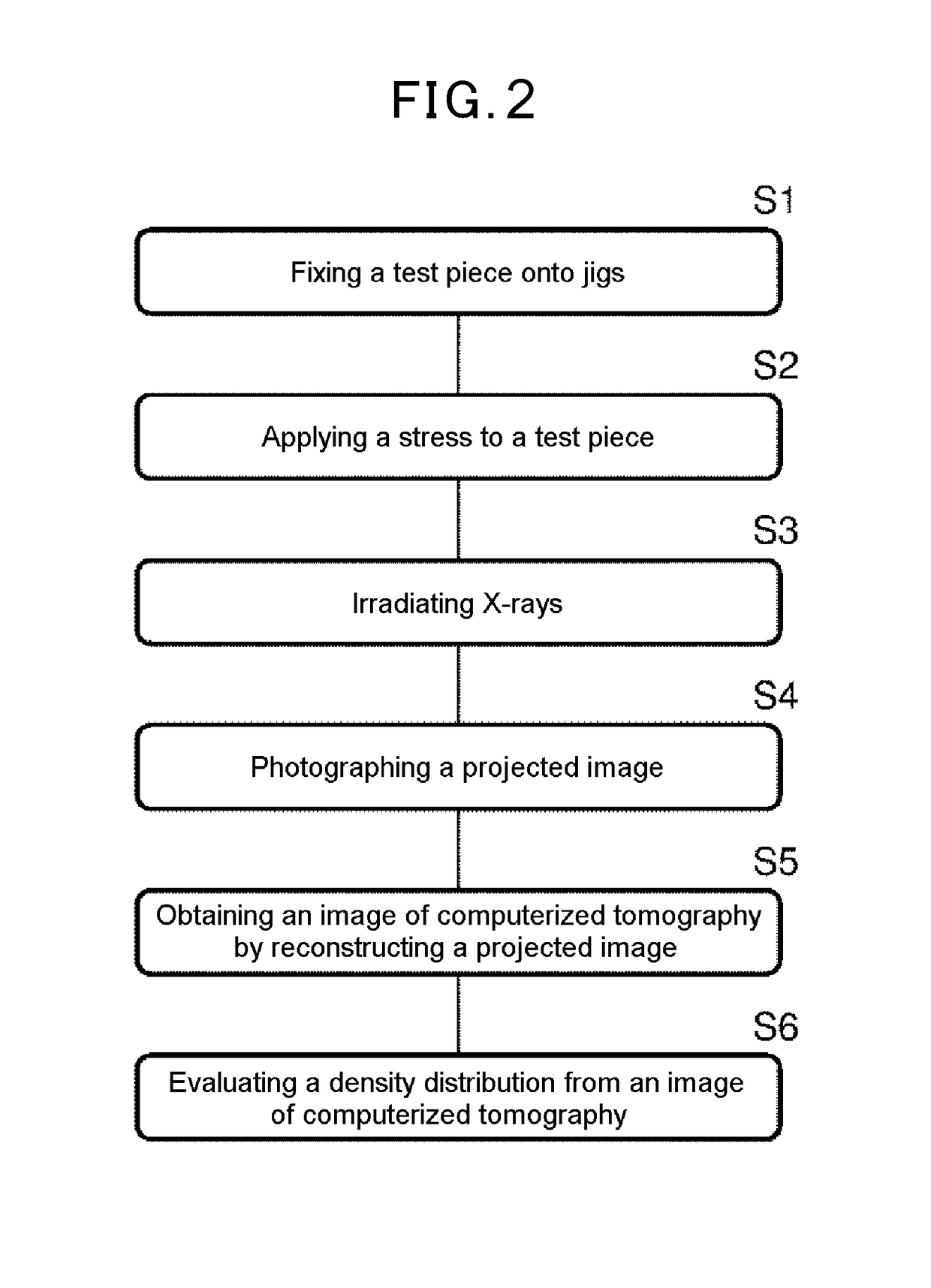
Methods for determining in situ the viscosity of heavy oil using nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time measurements
ActiveUS20100039109A1Solid dispersion analysisMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceGlass transition
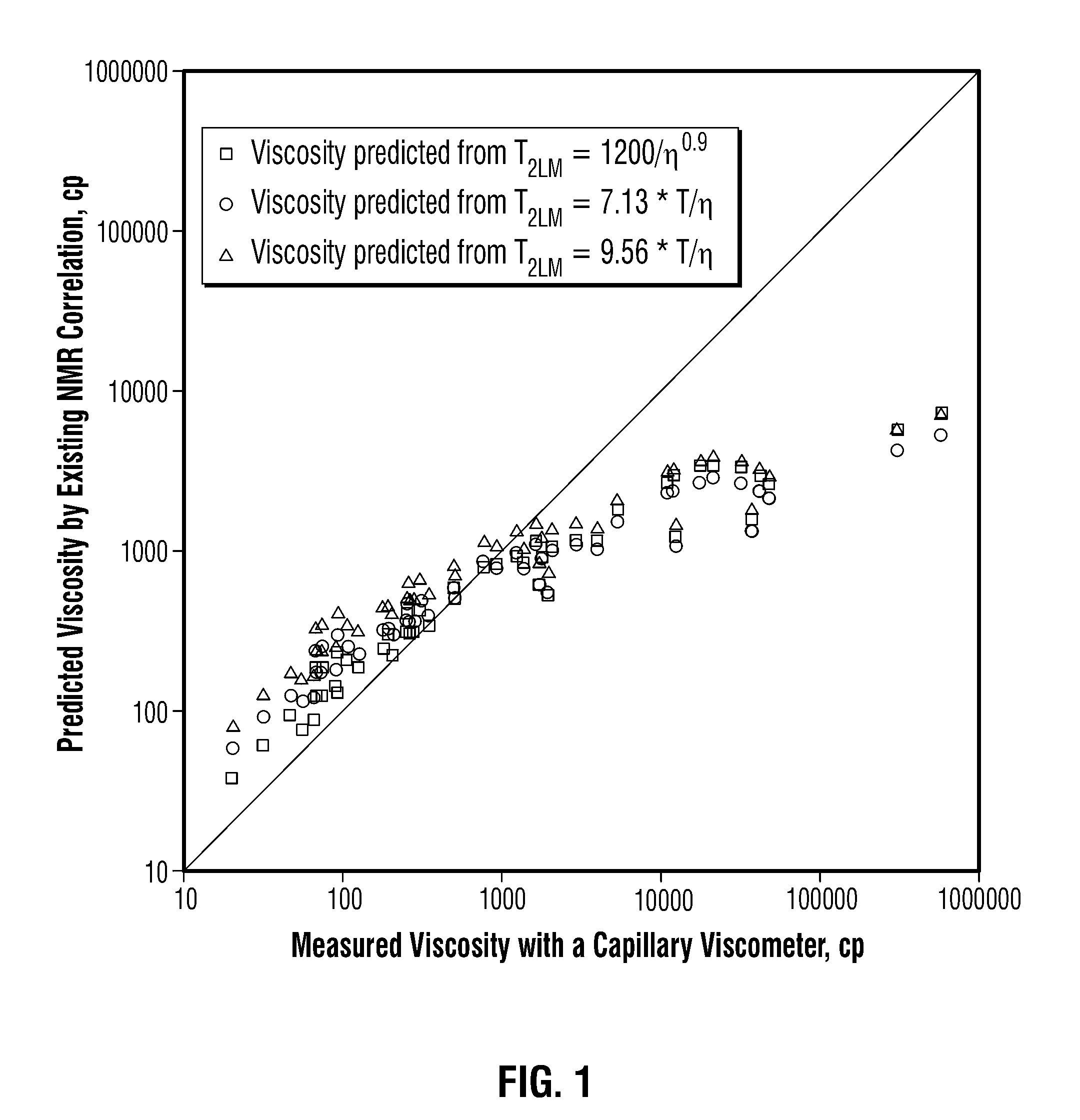
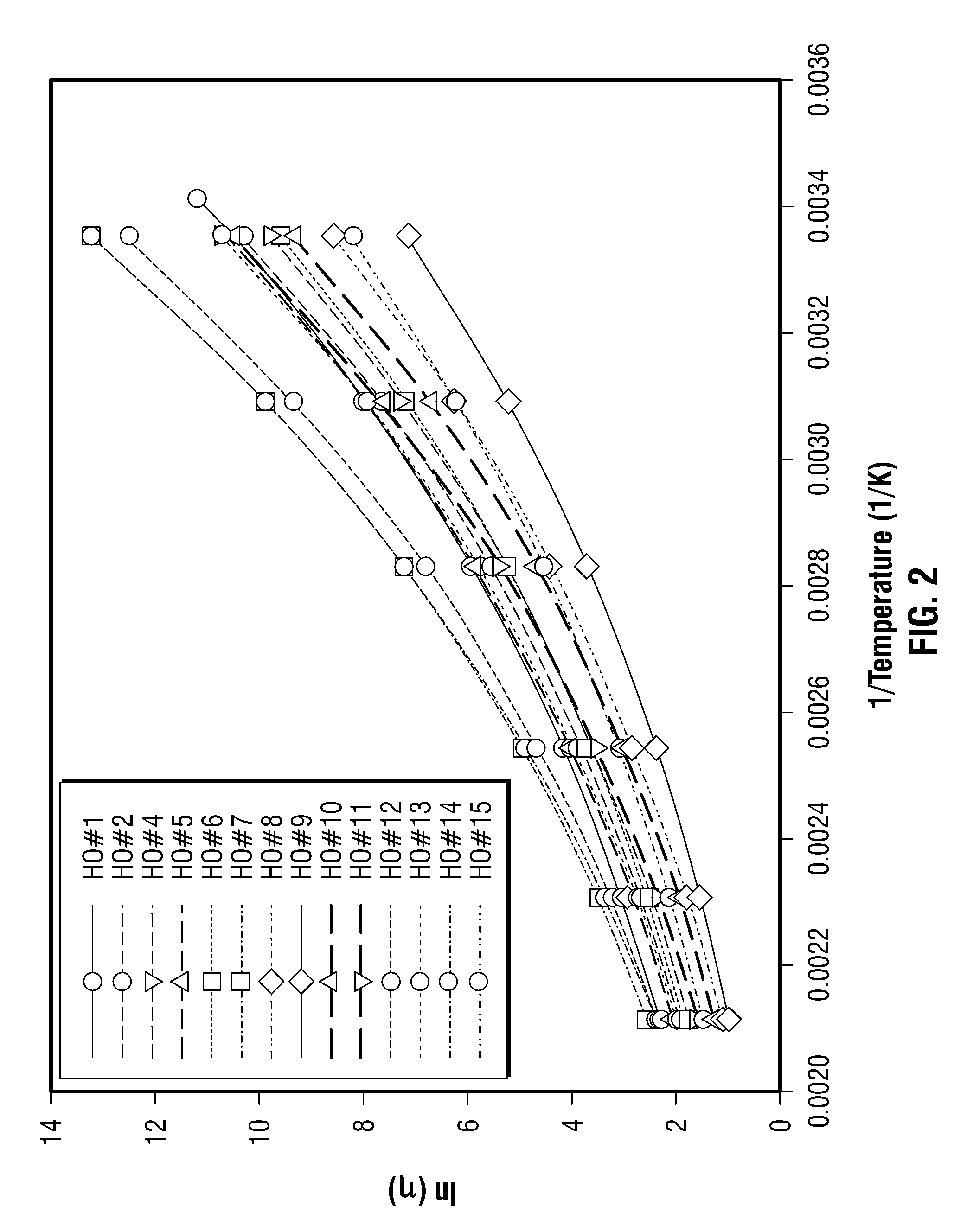
The viscosity η (in centipoise) of a heavy oil sample is determined according to an equation of the form lnηηg=-C1*(T-c′246)c″47.10+(T-c′246),where T is the temperature of the heavy oil, T2LM is the logarithmic mean of the T2 distribution of the sample obtainable from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements, c′=1.0±0.05, c″=1.0±0.04, ηg is the glass transition temperature viscosity of the heavy oil and a function of T2LM, and C1 is a variable which is a constant for the heavy oil and is a function of T2LM. Both C1 and ηg are considered functions of certain NMR values associated with the heavy oil sample, with ηg and C1 preferably estimated by empirically fitting data to the equations lnT2LM=a′+b′lnηg and lnT2LM=a″+b″C1, where a′, b′, a″ and b″ are constants.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
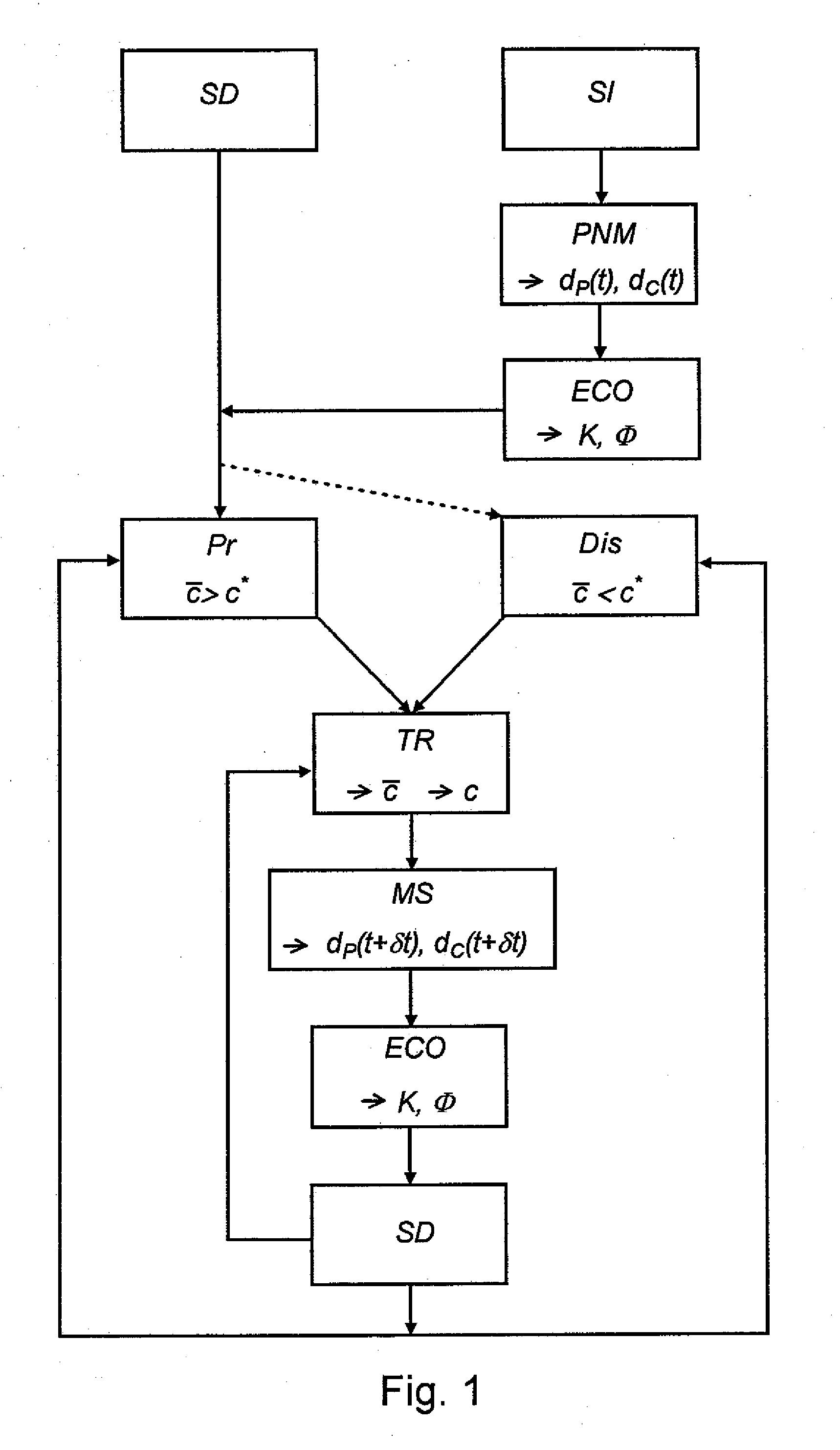
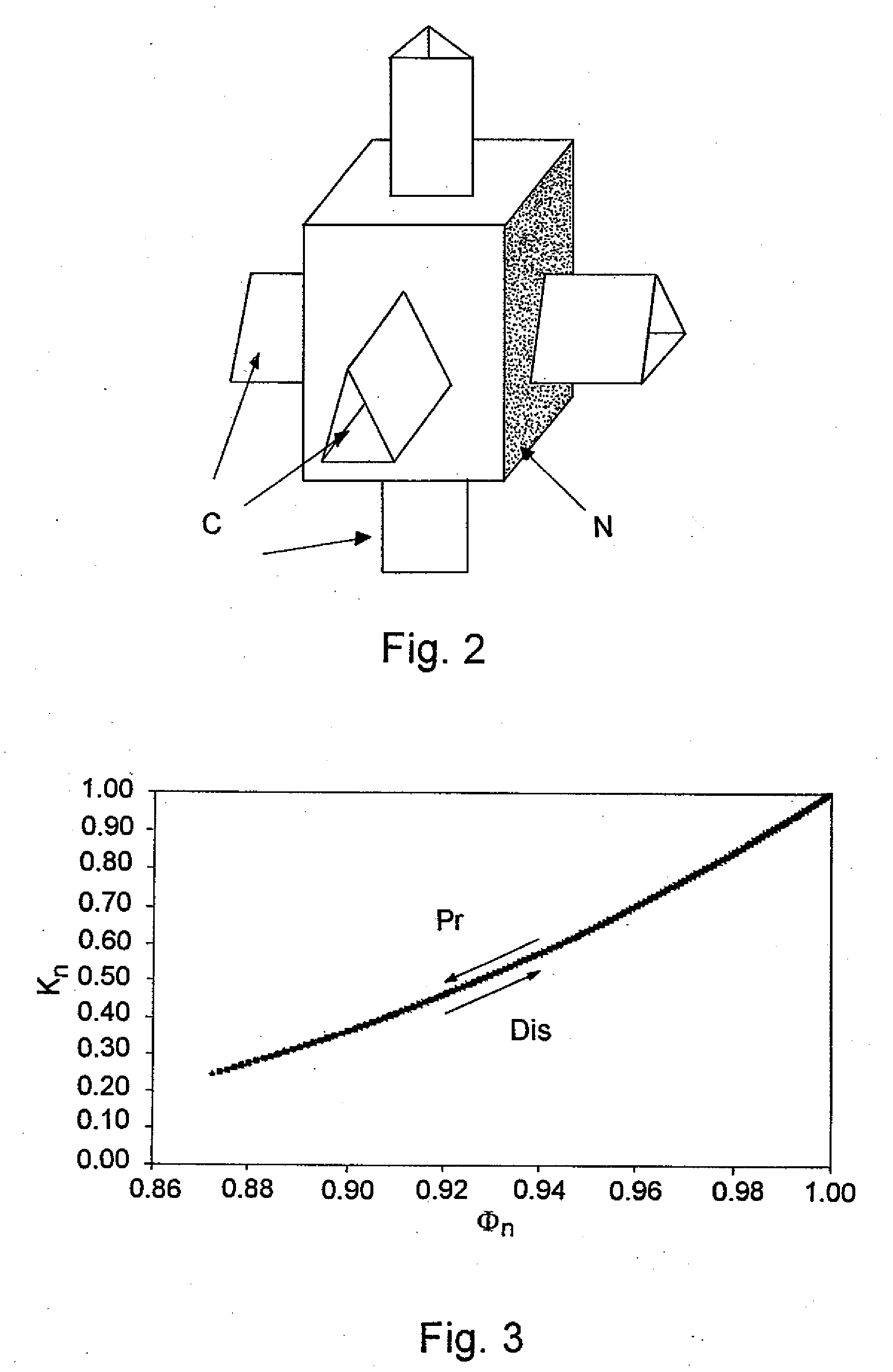
Method of determining the evolution of petrophysical properties of a rock during diagenesis
InactiveUS20100154514A1Enhanced recovery of hydrocarbonSolid dispersion analysisEarth material testingQuantitative determinationPhysical chemistry
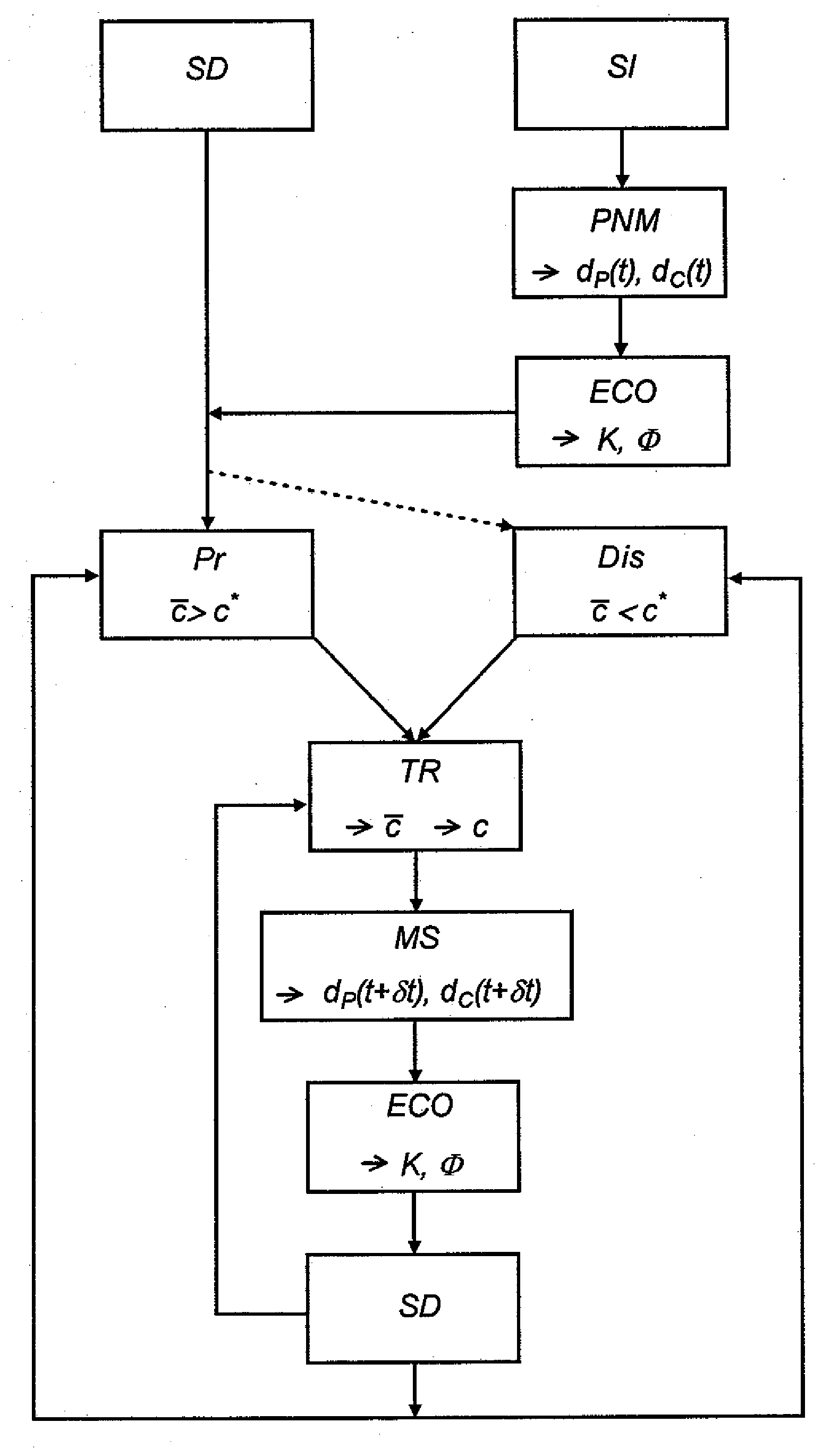
A method for quantitative determination of the permeability and porosity evolution of a porous medium during diagenesis having application to oil reservoir development is disclosed. A diagenesis scenario and an initial structure of the pore network of the porous medium are defined.A representation of the pore network is constructed by a PNM model. The steps of the diagenesis scenario are determining the ion concentration on the pore and channel walls of the PNM model, for a precipitation or dissolution reaction according to the scenario, and deducing therefrom a geometry variation of the PNM model, the porosity is calculated geometrically and the permeability is calculated from Darcy's law for the modified PNM model; the foregoing steps are repeated according to the diagenesis scenario and a relationship is deduced between the permeability of the porous medium and the porosity of the porous medium during diagenesis.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Full-view-field quantitative statistical distribution representation method of precipitated phase particles in metal material
ActiveCN108226159ARealize analysisEliminate statistical incompletenessImage enhancementImage analysisMathematical modelMetallic materials
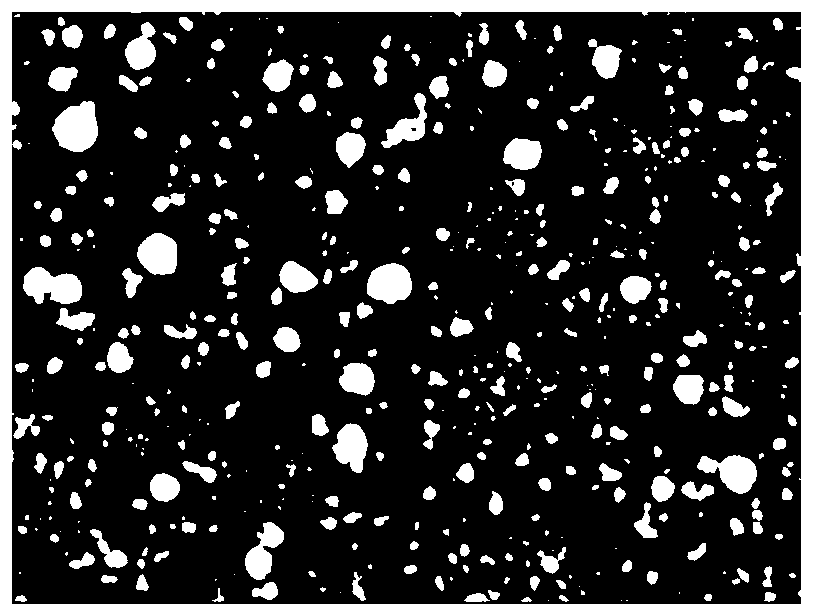
The invention belongs to the technical field of the quantitative statistical distribution analysis of characteristic chromatograms of microstructures and precipitated phases in metal materials, and relates to a full-view-field quantitative statistical distribution representation method of precipitated phase particles in a metal material. The method comprises the following steps of electrolytic corrosion of a metallic material sample, automatic collection of a characteristic chromatogram of a metallurgical structure, automatic splicing and fusion of the characteristic chromatograms of full-view-field metallurgical structures, automatic identification and segmentation of the precipitated phase particles and quantitative distribution representation of the large-range full-view-field precipitated phase particles. According to the full-view-field quantitative statistical distribution representation method, through establishing a mathematic model, the automatic splicing and fusion of the characteristic chromatograms of the full-view-field large-area metallurgical structures in a characteristic region and the automatic segmentation and identification of the precipitated phase particles are realized; the quantitative statistical distribution representation information of the full-view-field morphology, quantity, size, distribution and the like of plentiful precipitated phases in a larger range is quickly obtained, and the method has the features of being accurate and high-efficiency and large in quantitative distribution representation information quantity, and has much more statistical representativeness compared with conventional single-view-field quantitative image analysis.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Detection of discontinuity densities in composite materials
ActiveUS8618485B1Radiation pyrometrySolid dispersion analysisRefractive indexElectromagnetic radiation
A method for detecting suspended discontinuity densities in a material is provided. The method includes transmitting terahertz electromagnetic radiation toward a surface of the material. This radiation is received at an expected location after interacting with the material. The power level of the received radiation is measured and deviation from the expected value is used to determine a suspended discontinuity density gradient in the material. The method can be used with either reflected radiation or transmitted radiation. Embodiments of the method can calculate the index of refraction in the material and correlate this with the suspended discontinuity density of the material.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Detecting inclusions in transparent sheets
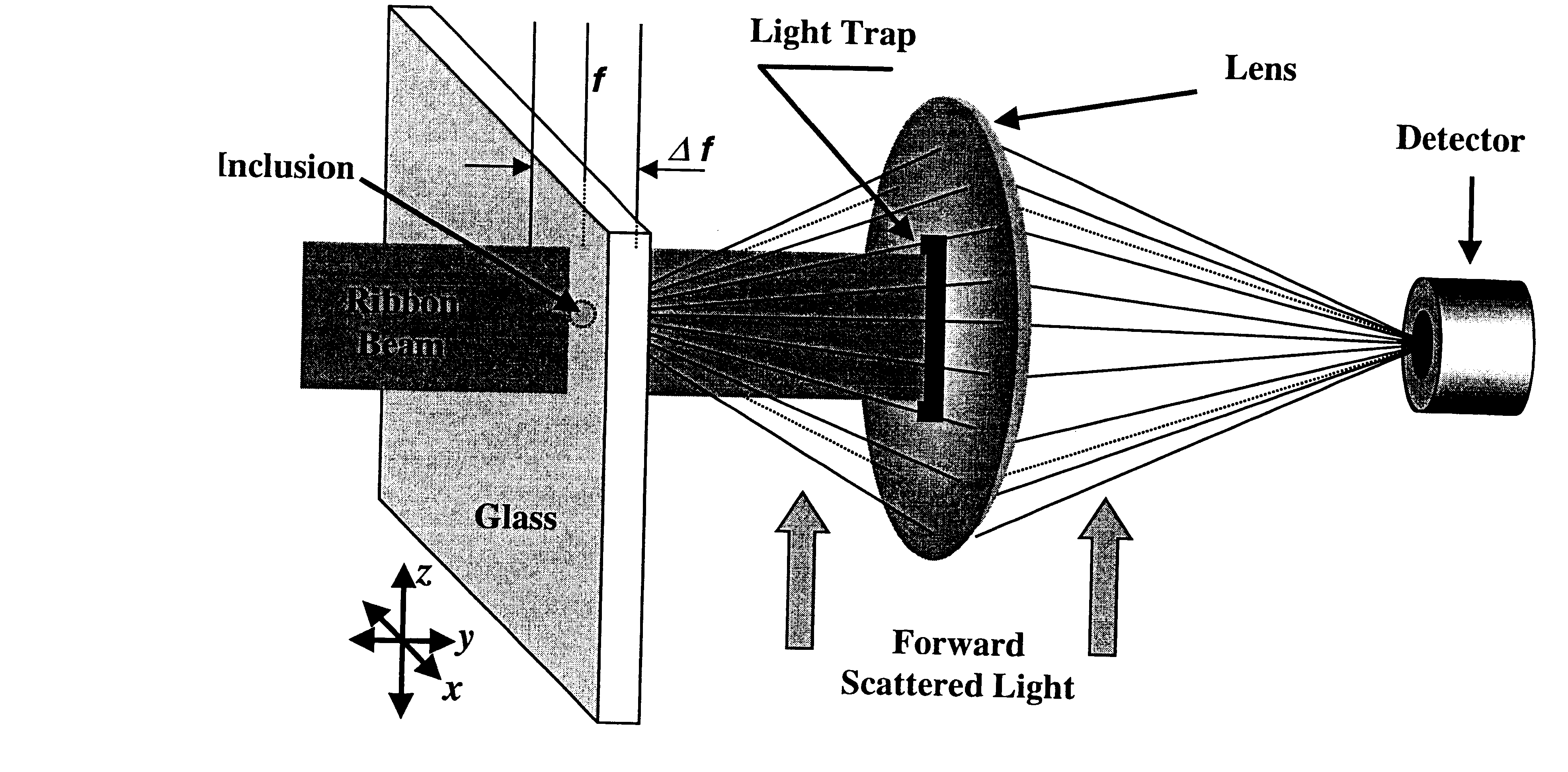
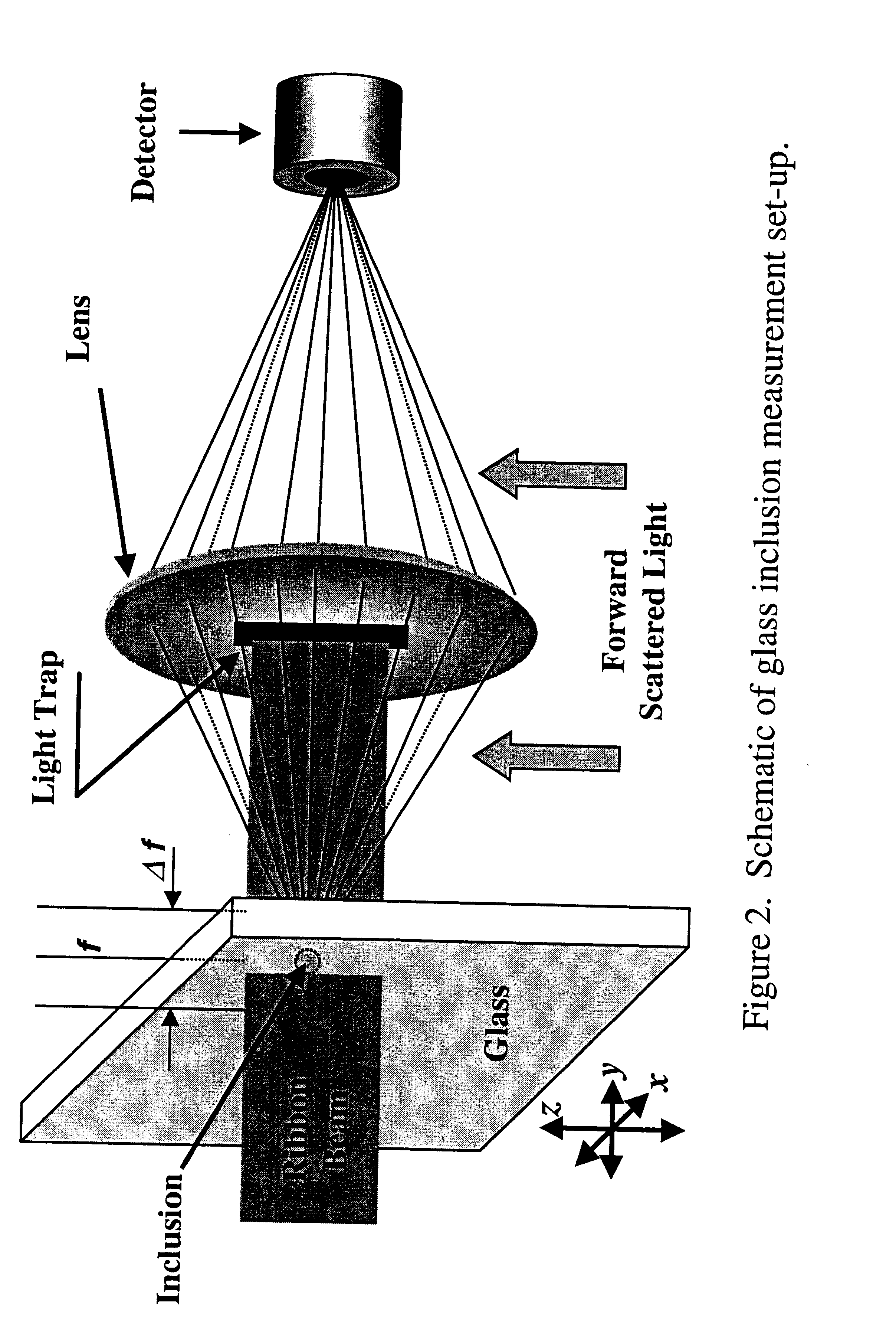
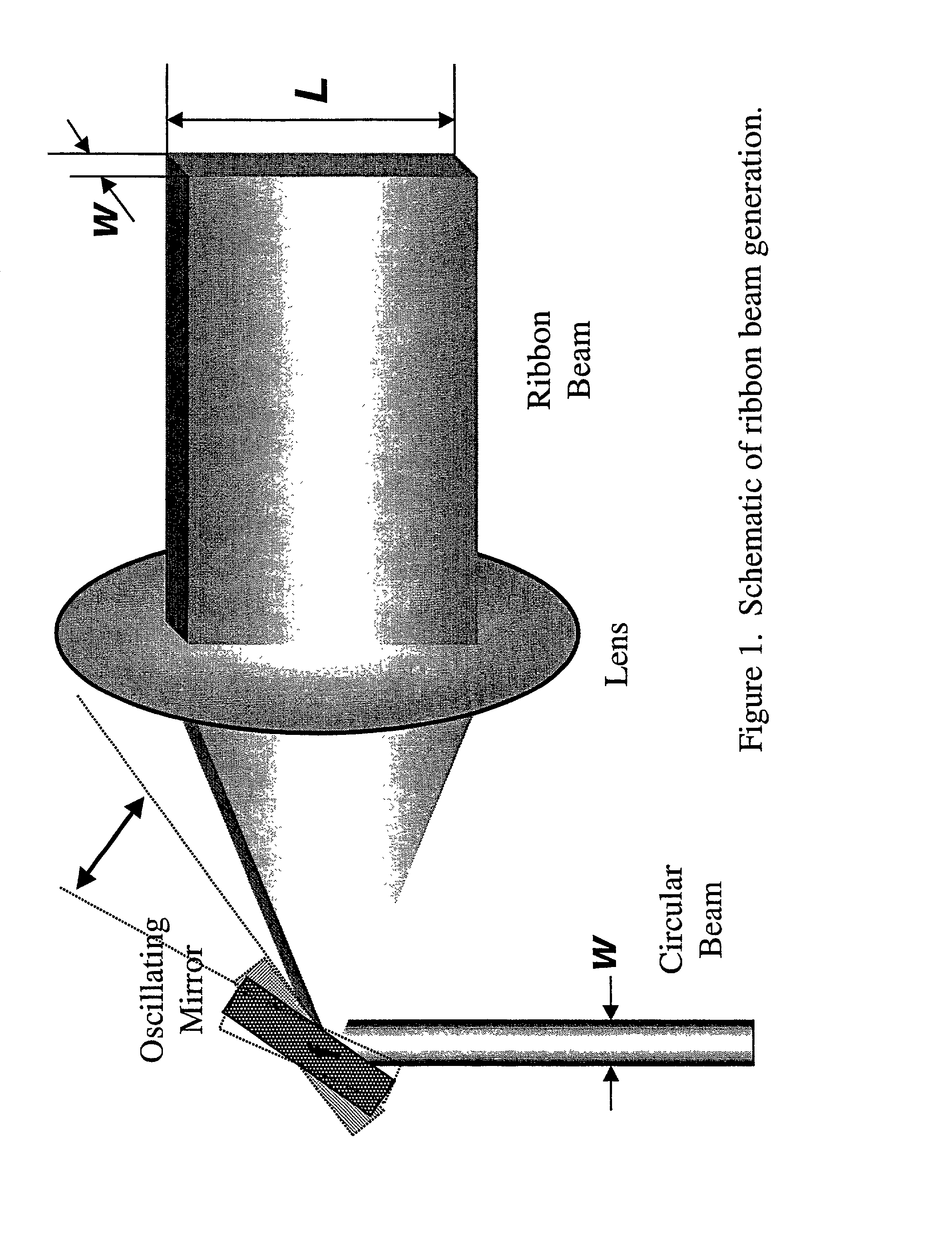
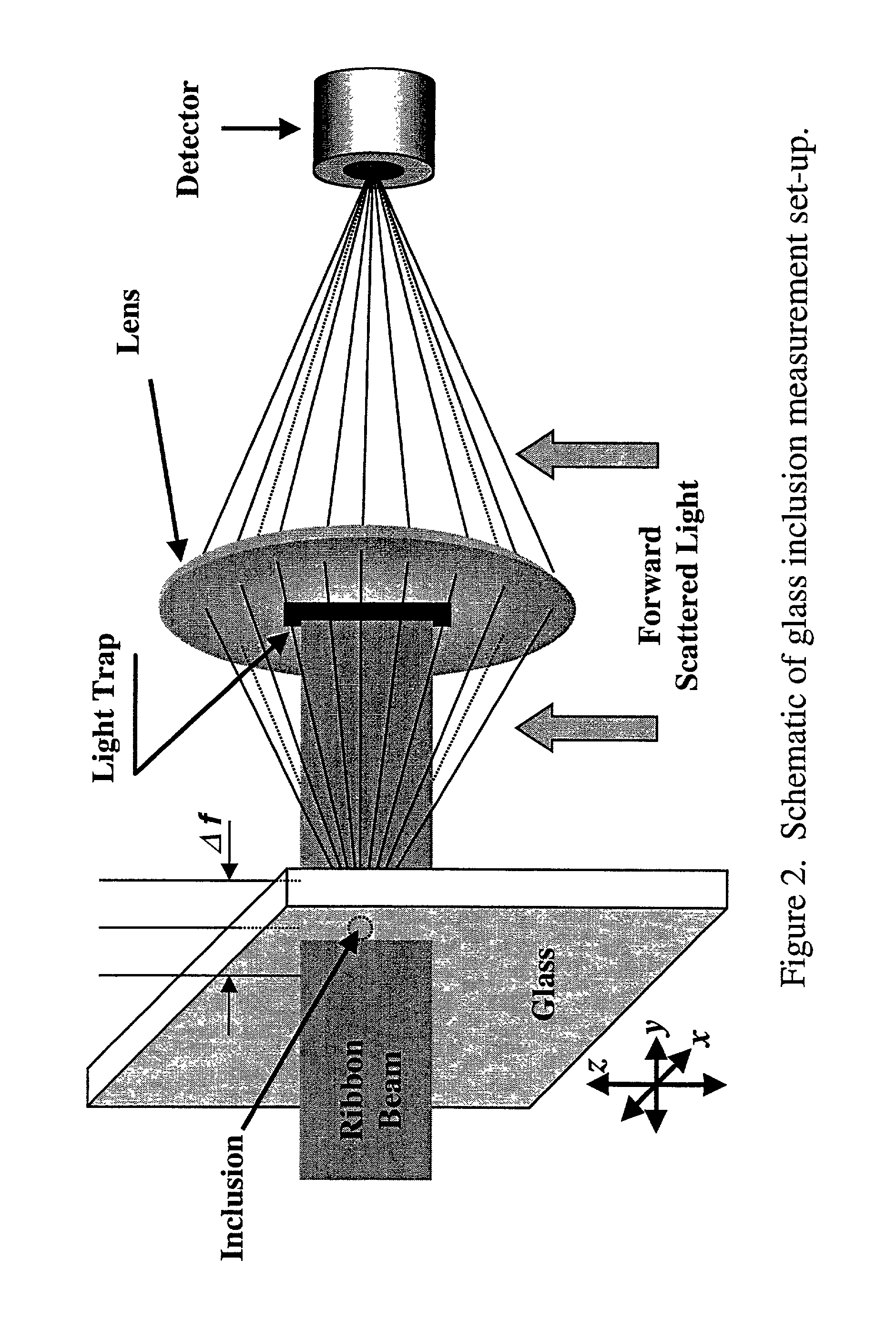
InactiveUS6388745B2Solid dispersion analysisOptically investigating flaws/contaminationRefractive indexLaser beams
This light scattering technique for size measurement is based on the fact that an illuminated particle (inclusion) serves as a secondary radiation source in a manner which is related to its size. This technique allows for detection of inclusions in the interior of transparent solid media, such as bulk glass. When illuminated with a beam of monochromatic light such as a laser beam as the primary light source, the angular distribution of the scattered intensity originated from the inclusion in the micron to submicron range, is a function of intensity, wavelength and index of refraction. A lens and light trap block the primary light for reaching a detector. The light trap, however, allows the secondary scattered light to reach the detector.
Owner:CORNING INC
Measurement and control of asphaltene agglomeration in hydrocarbon liquids
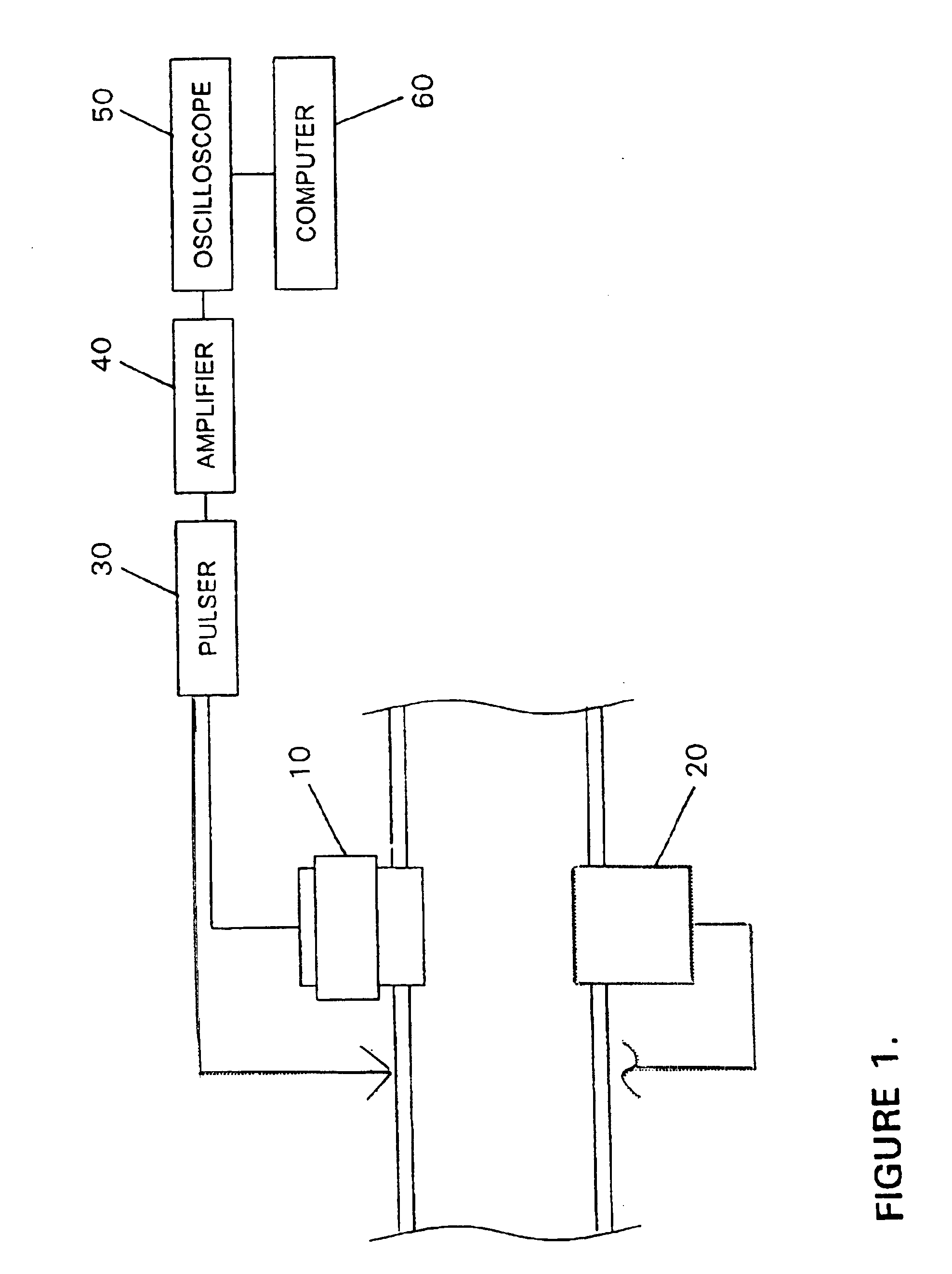
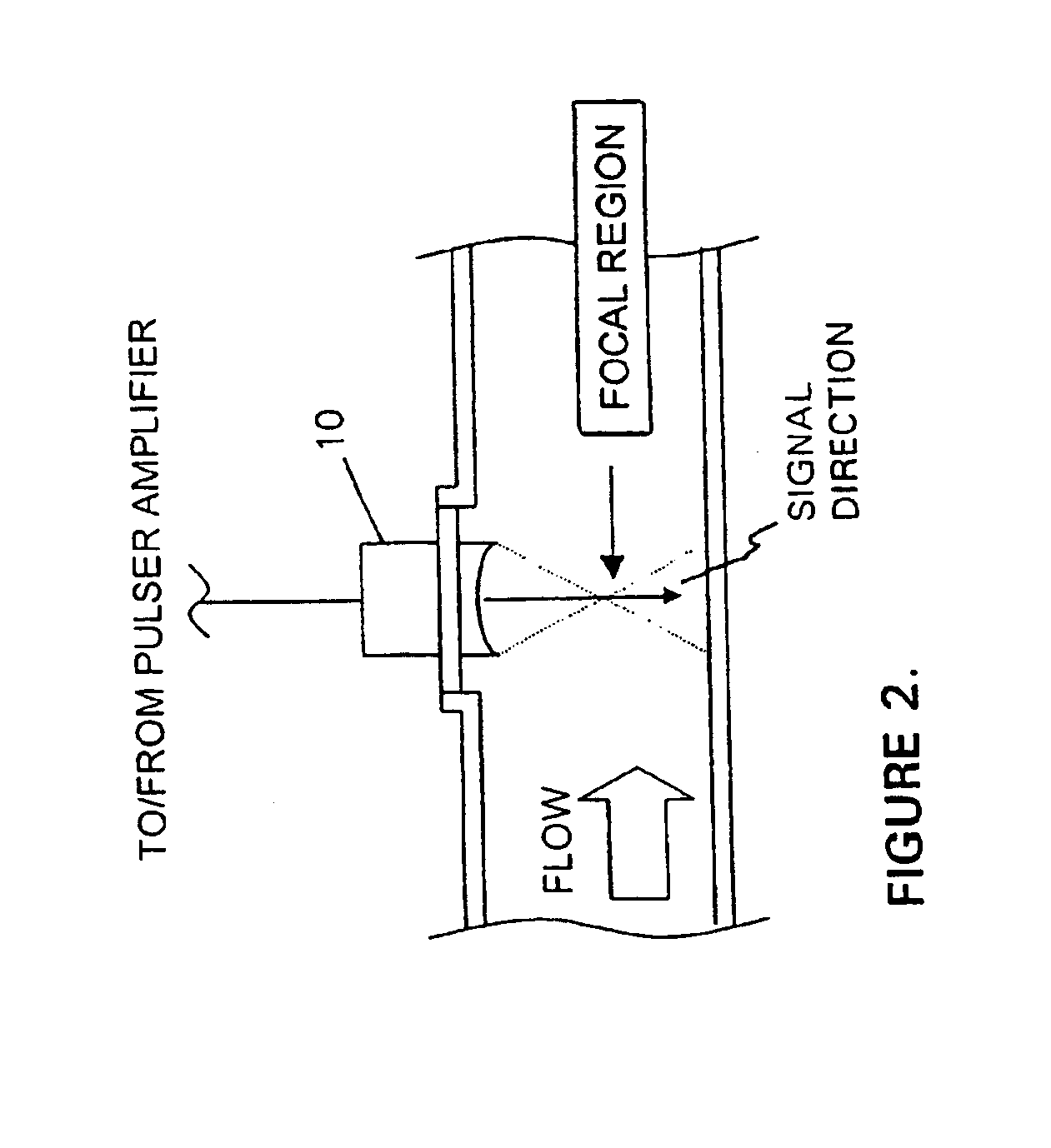
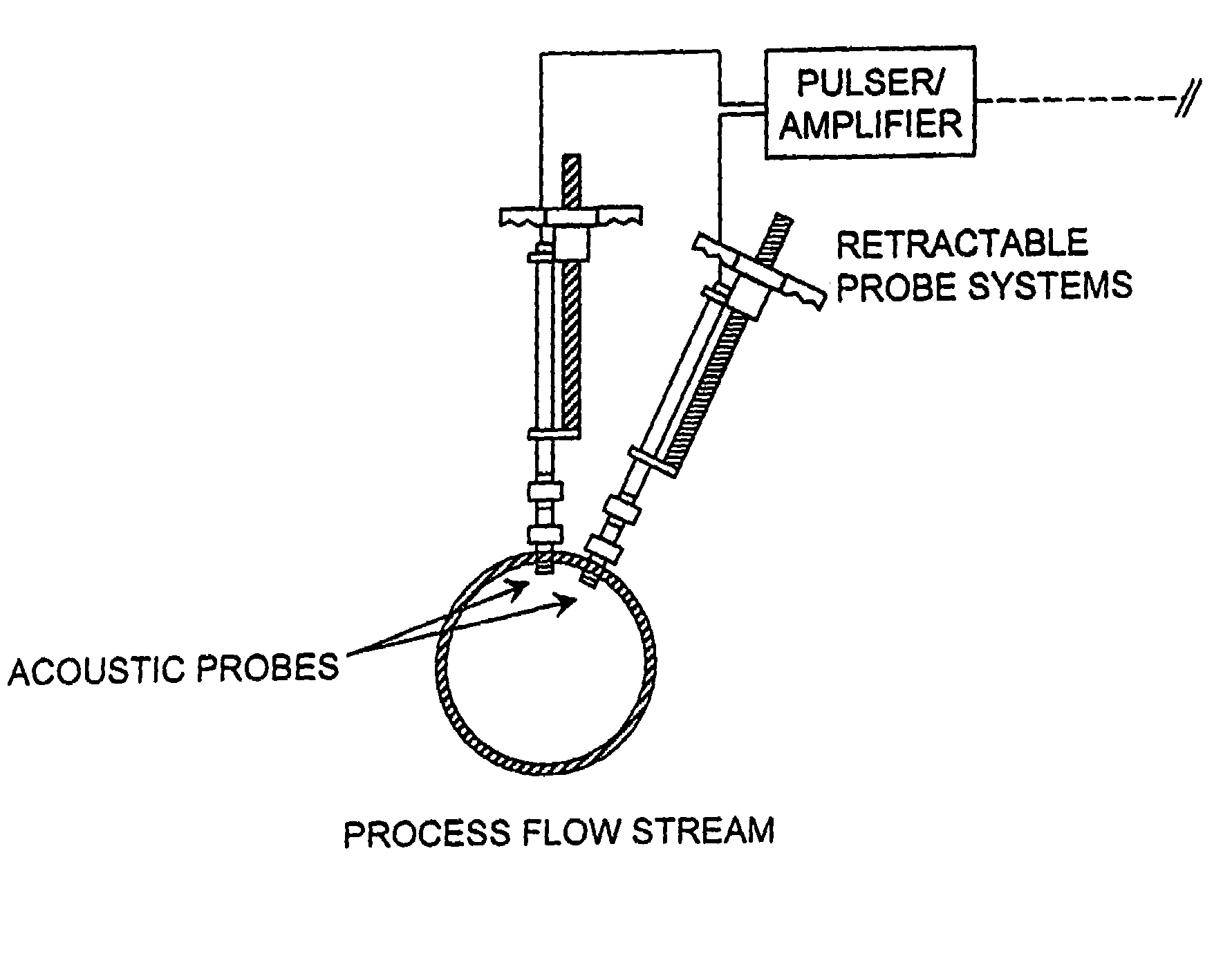
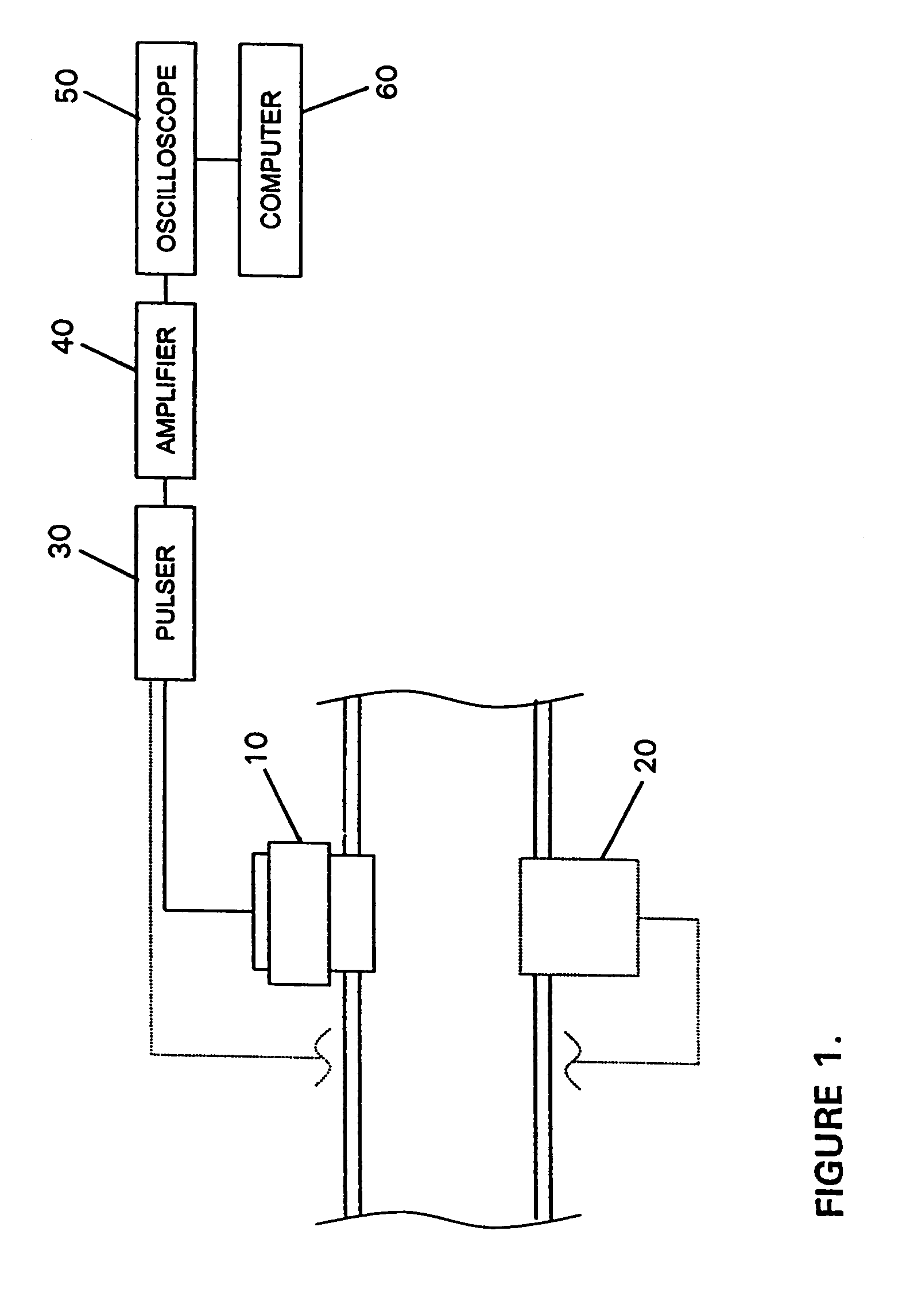
InactiveUS6945096B1Easy to operateBroaden applicationAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationAcoustic energyAsphaltene
A method is provided for measuring the agglomerative state of asphaltenes in oil by applying an acoustic signal to the oil, detecting the scattered acoustic energy and using this detected signal to determine the relative particle size distribution of the asphaltene particles in the oil and / or their state of agglomeration. A method for controlling the agglomerative state of the asphaltenes which is based on the acoustic measurement technique is also provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC +1
Measurement and control of asphaltene agglomeration in hydrocarbon liquids
InactiveUS7360403B2Easy to operateSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationAcoustic energyAsphaltene
A method is provided for measuring the agglomerative state of asphaltenes in oil by applying an acoustic signal to the oil, detecting the scattered acoustic energy and using this detected signal to determine the relative particle size distribution of the asphaltene particles in the oil and / or their state of agglomeration. A method for controlling the agglomerative state of the asphaltenes which is based on the acoustic measurement technique is also provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
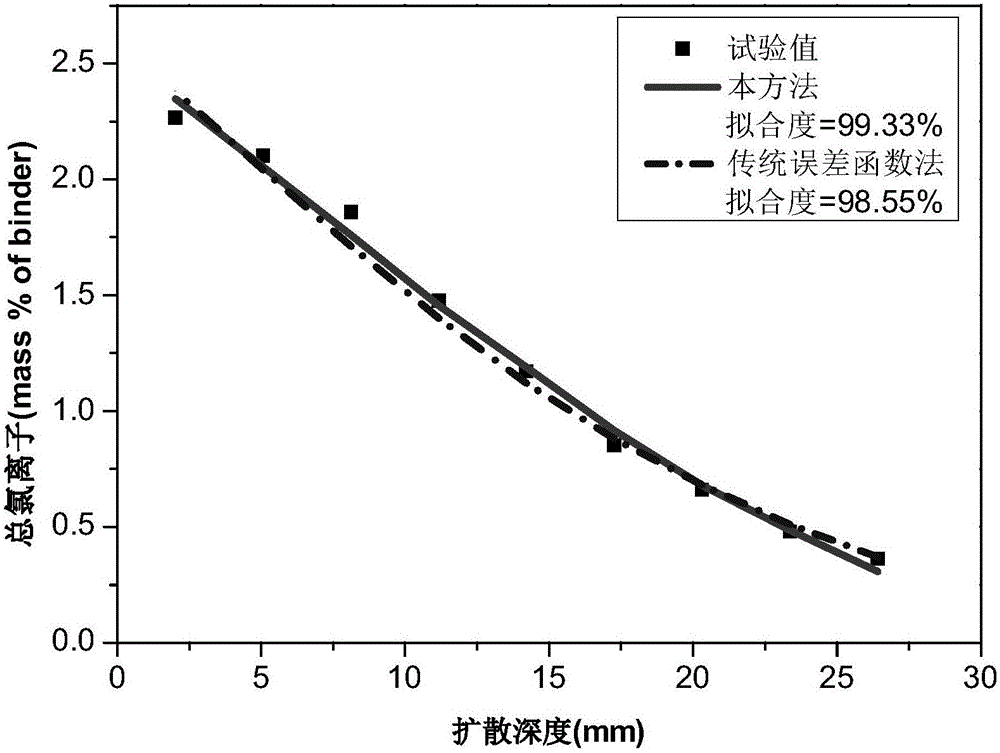
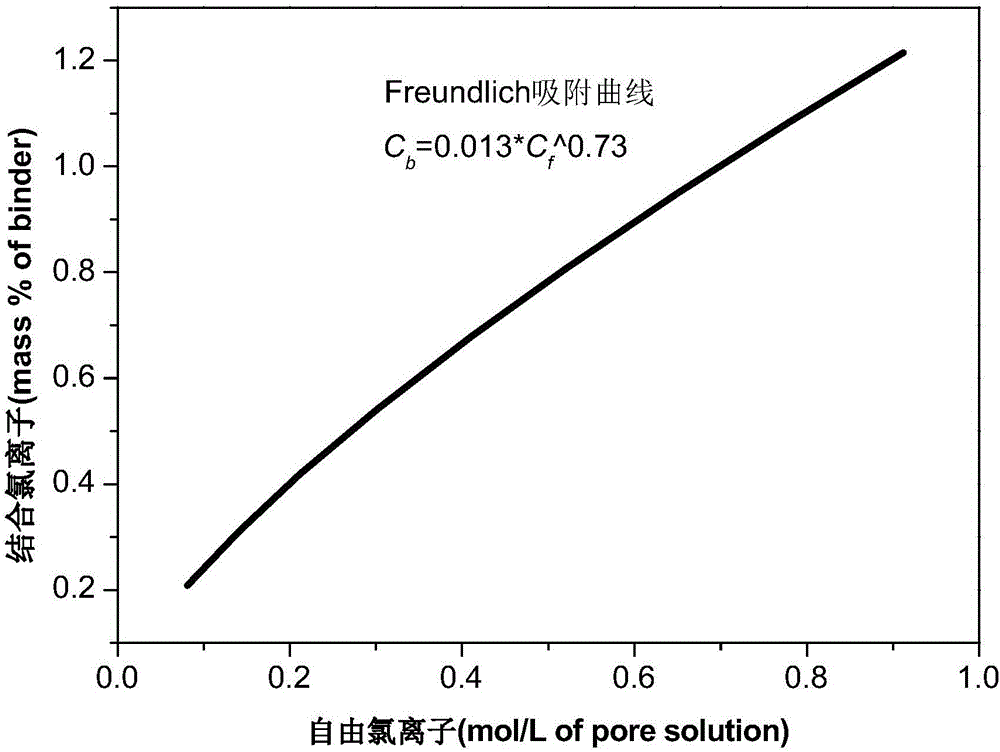
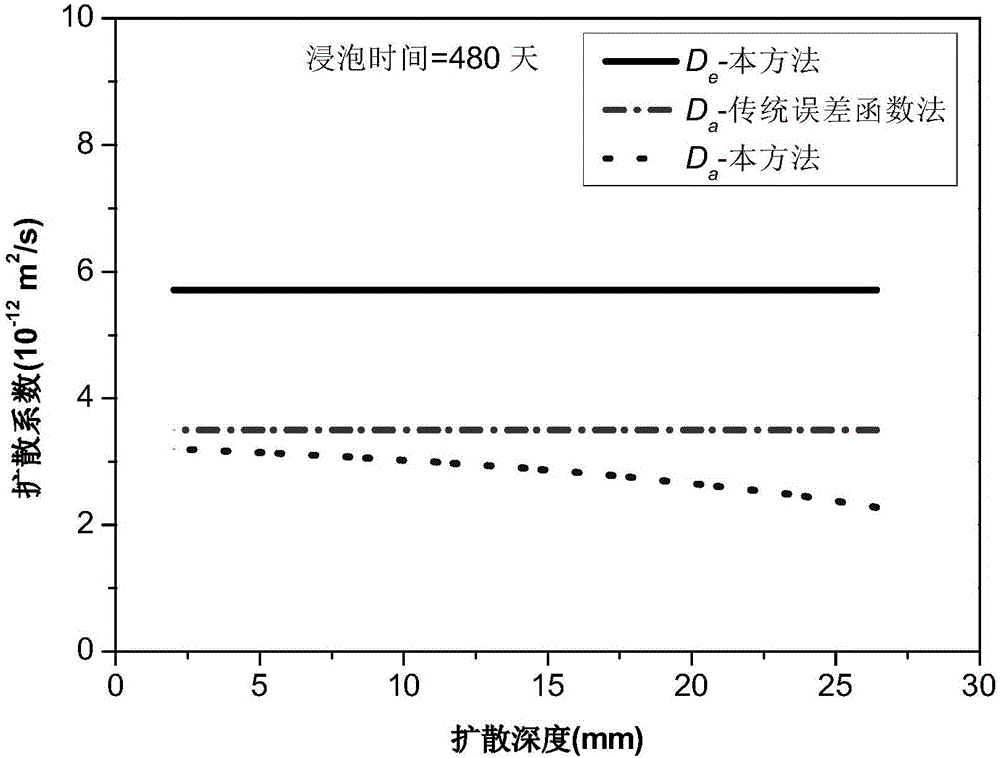
Method for obtaining chlorine ion diffusion and combination parameters in cement-based material
InactiveCN105973757AAvoiding problems with experimentally measuring free chloride concentrationsThe result is accurateWeather/light/corrosion resistanceSolid dispersion analysisDiffusionConfidence interval
The invention discloses a method for obtaining chlorine ion diffusion and combination parameters in a cement-based material. The method only needs a total chlorine ion concentration curve, and can simultaneously obtain a chlorine ion effective diffusion coefficient and adsorption isothermal curve parameters through regression calculation. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a total chlorine ion concentration distribution curve by a non-steady state diffusion test; trying different combinations of to-be-obtained parameters, calculating to obtain a theoretical total chlorine ion concentration distribution curve; carrying out fitting regression of the theoretical curve and the experimental curve by a nonlinear least square method, to obtain a set of parameter values with the highest fitting degree; calculating the confidence interval of each parameter; and further calculating to obtain an adsorption curve, distribution curves of an apparent diffusion coefficient along with the time and space, and distribution curves of total chlorine ions, combined chlorine ions and free chlorine ions in the time and space. The method not only can obtain the diffusion parameter and the combination parameter, but also can obtain the intervals of the parameters.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
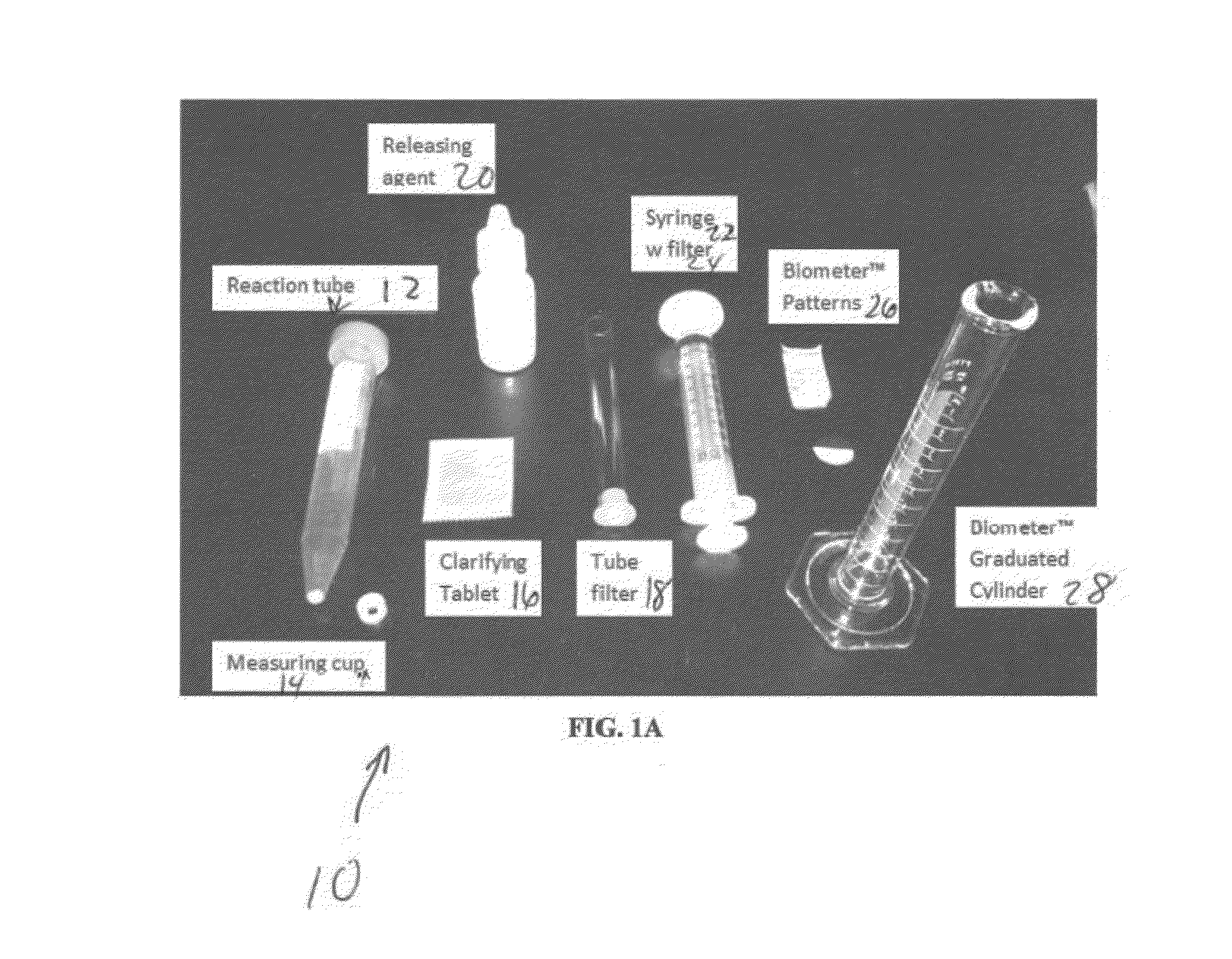
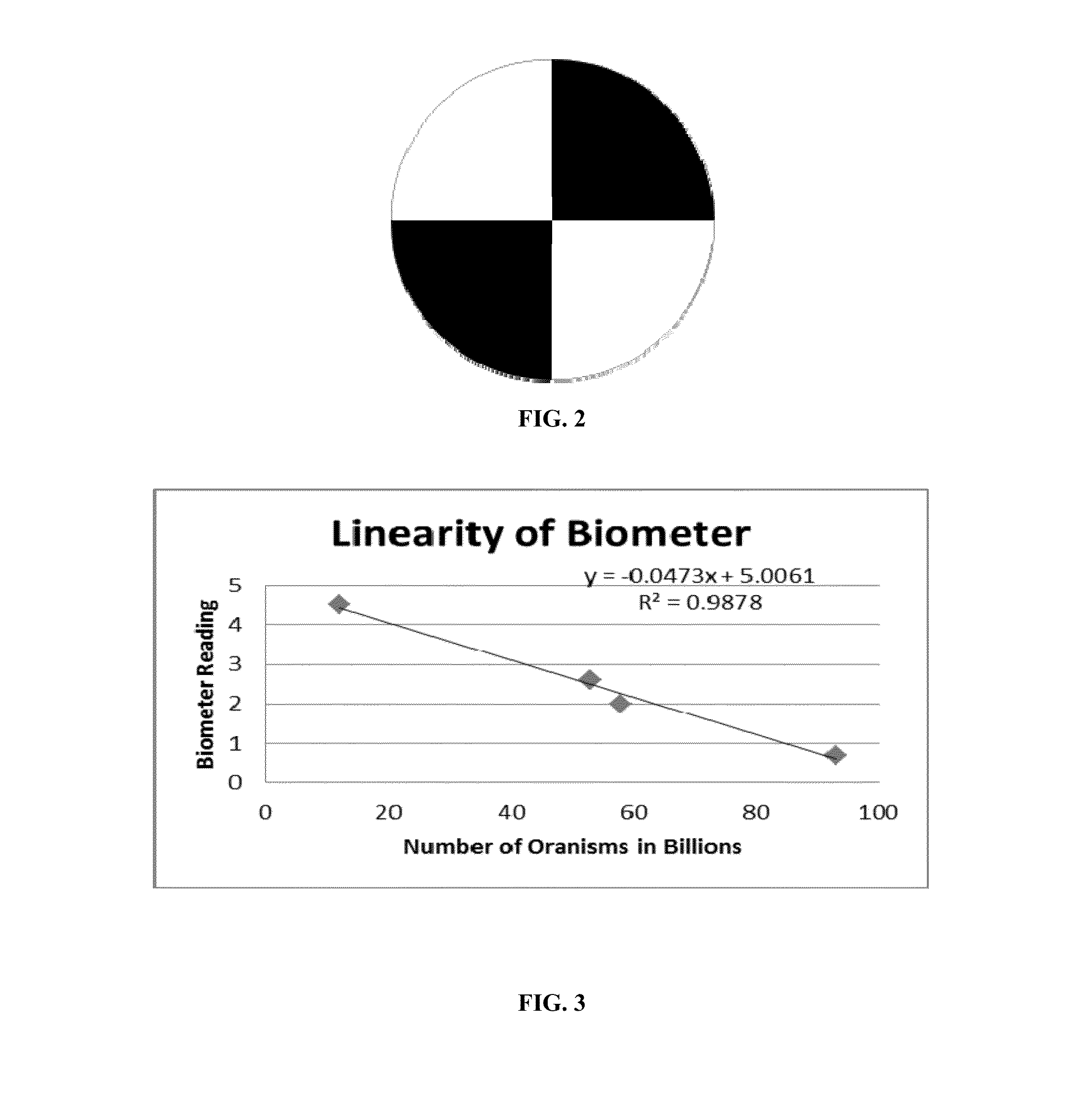
Methods and compositions for estimating soil microbial load
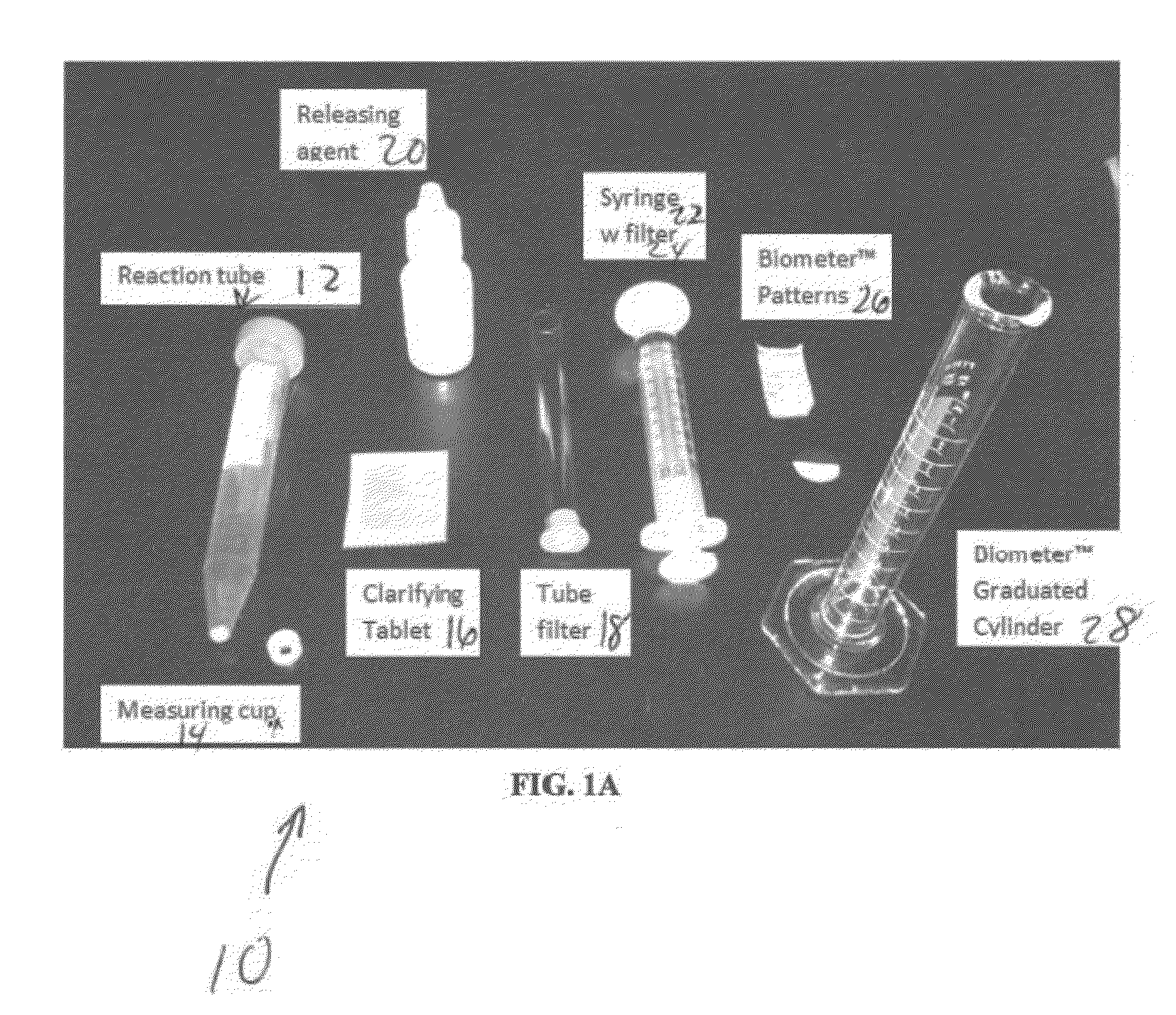
ActiveUS20140220623A1Effective timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTurbiditySecchi disk
Methods and compositions for the preparation of soil samples and the determination of the number of microbes within a soil sample are disclosed. The methods include measuring, solubilizing, bleaching and filtering soil samples and measuring the turbidity of the filtered solution. The turbidity of the sample can be determined by visual inspection of a Secchi disk viewed through the column liquid sample in a transparent tubular cylinder, or by using a cell phone camera and application. Devices and kits for the rapid, cost efficient determination of microbial numbers in the field setting are disclosed. The disclosed devices and methods can also be used for applications other than determination of microbial numbers.
Owner:PROLIFIC EARTH SCI
Methods for determining in situ the viscosity of heavy oil using nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time measurements
ActiveUS8013601B2Solid dispersion analysisElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceGlass transition
The viscosity η (in centipoise) of a heavy oil sample is determined according to an equation of the form lnηηg=-C1*(T-c′246)c″47.10+(T-c′246),where T is the temperature of the heavy oil, T2LM is the logarithmic mean of the T2 distribution of the sample obtainable from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements, c′=1.0±0.05, c″=1.0±0.04, ηg is the glass transition temperature viscosity of the heavy oil and a function of T2LM, and C1 is a variable which is a constant for the heavy oil and is a function of T2LM. Both C1 and ηg are considered functions of certain NMR values associated with the heavy oil sample, with ηg and C1 preferably estimated by empirically fitting data to the equations ln T2LM=a′+b′ ln ηg and ln T2LM=a″+b″C1, where a′, b′, a″ and b″ are constants.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Measurement and control of asphaltene agglomeration in hydrocarbon liquids
InactiveUS20060156820A1Easy to operateSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationAcoustic energyAsphaltene
A method is provided for measuring the agglomerative state of asphaltenes in oil by applying an acoustic signal to the oil, detecting the scattered acoustic energy and using this detected signal to determine the relative particle size distribution of the asphaltene particles in the oil and / or their state of agglomeration. A method for controlling the agglomerative state of the asphaltenes which is based on the acoustic measurement technique is also provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Methods and compositions for estimating soil microbial load
Methods and compositions for the preparation of soil samples and the determination of the number of microbes within a soil sample are disclosed. The methods include measuring, solubilizing, bleaching and filtering soil samples and measuring the turbidity of the filtered solution. The turbidity of the sample can be determined by visual inspection of a Secchi disk viewed through the column liquid sample in a transparent tubular cylinder, or by using a cell phone camera and application. Devices and kits for the rapid, cost efficient determination of microbial numbers in the field setting are disclosed. The disclosed devices and methods can also be used for applications other than determination of microbial numbers.
Owner:PROLIFIC EARTH SCI
Detecting inclusions in transparent sheets
InactiveUS20010040678A1Solid dispersion analysisOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhysicsScattered light
This light scattering technique for size measurement is based on the fact that an illuminated particle (inclusion) serves as a secondary radiation source in a manner which is related to its size. This technique allows for detection of inclusions in the interior of transparent solid media, such as bulk glass. When illuminated with a beam of monochromatic light such as a laser beam as the primary light source, the angular distribution of the scattered intensity originated from the inclusion in the micron to submicron range, is a function of intensity, wavelength and index of refraction. A lens and light trap block the primary light for reaching a detector. The light trap, however, allows the secondary scattered light to reach the detector.
Owner:CORNING INC
Apparatus for detecting heights of defects on optical glass
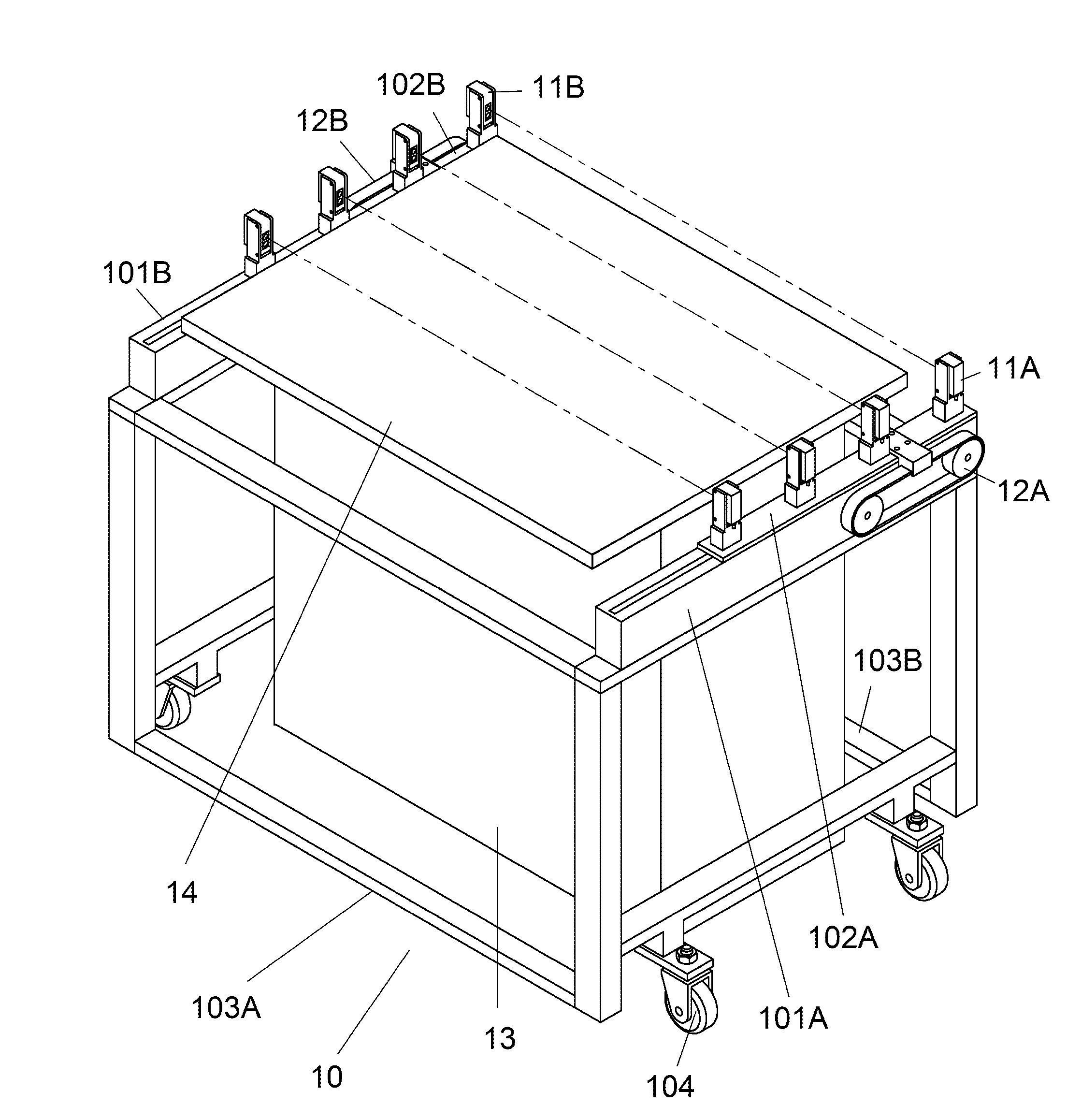
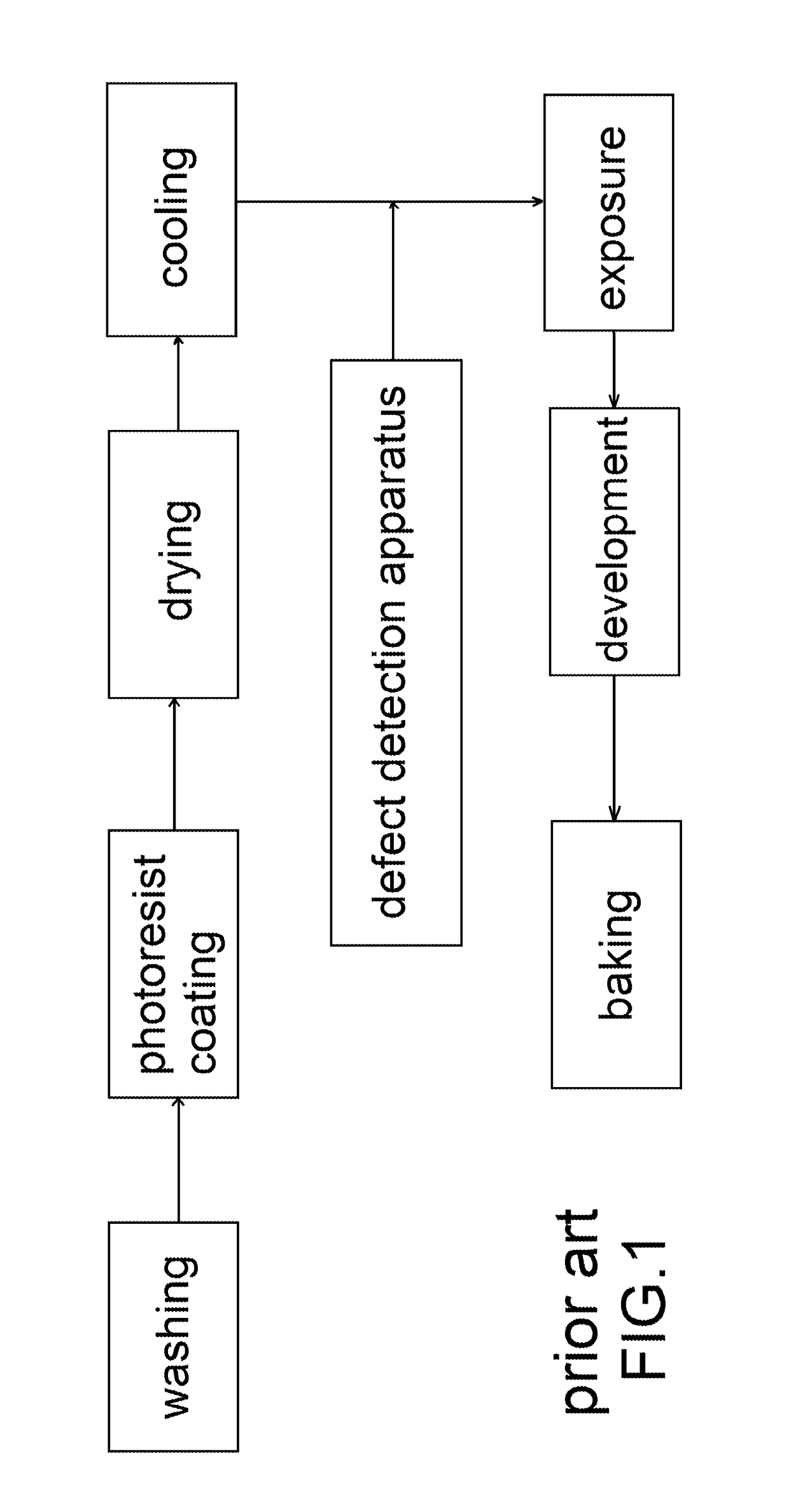
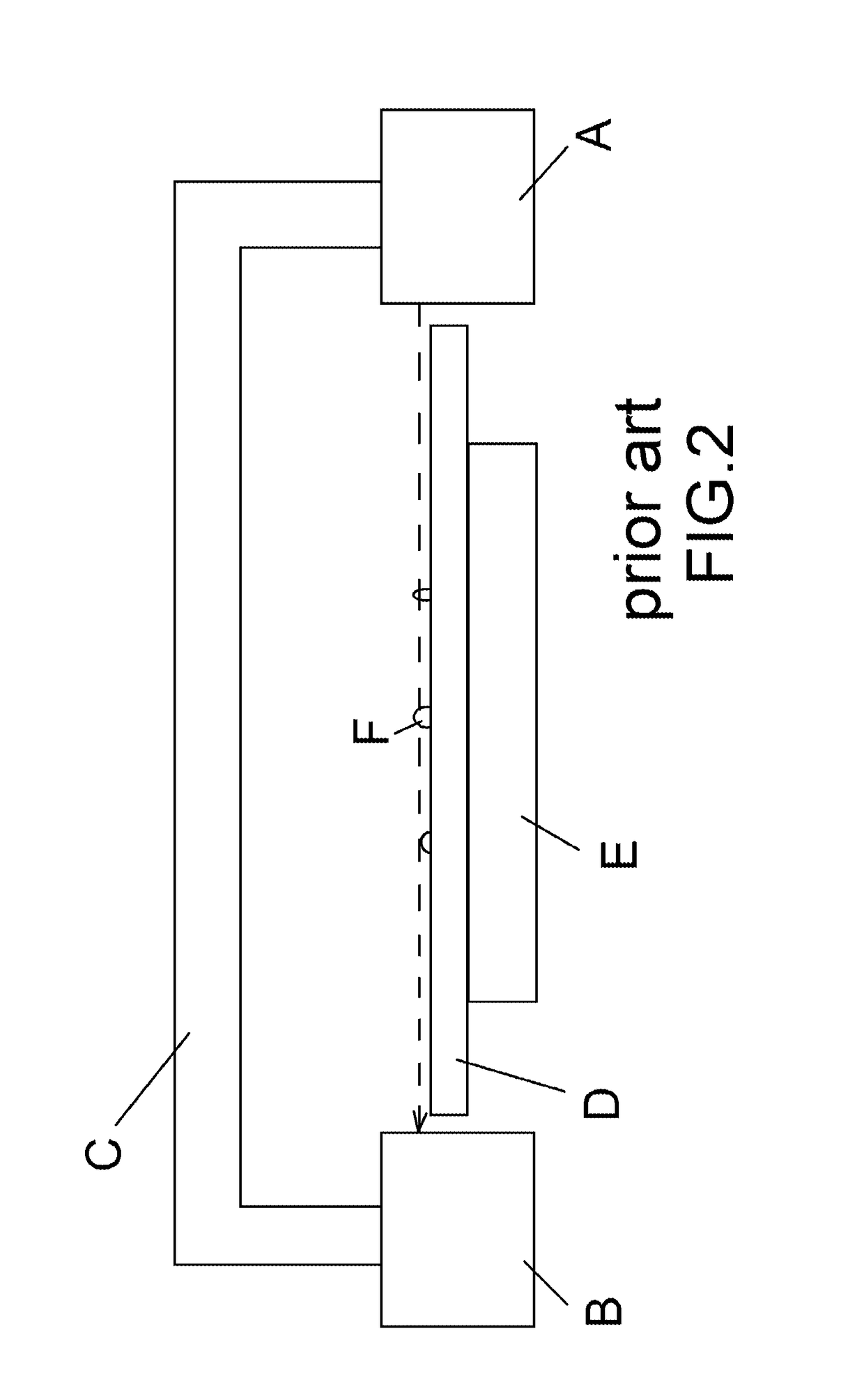
InactiveUS20160061584A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSolid dispersion analysisOptical glassLaser beams
A detection apparatus includes four sets of transmitter and receiver wherein the transmitters are on a first sliding member of a frame and the receivers are on a second sliding member of the frame; and drives for moving the first and second sliding members back and forth. During the movements of the first and second sliding members, each transmitter emits laser beam toward the receiver of the same set by passing through a space above a photoresist-coated optical glass by 100 μm, no signal is generated at the receiver if the laser beam is not blocked, and a signal is generated at the receiver if the laser beam is blocked by at least one of a plurality of particles on the photoresist-coated optical glass.
Owner:TAIWAN NANO TECH APPL CORP
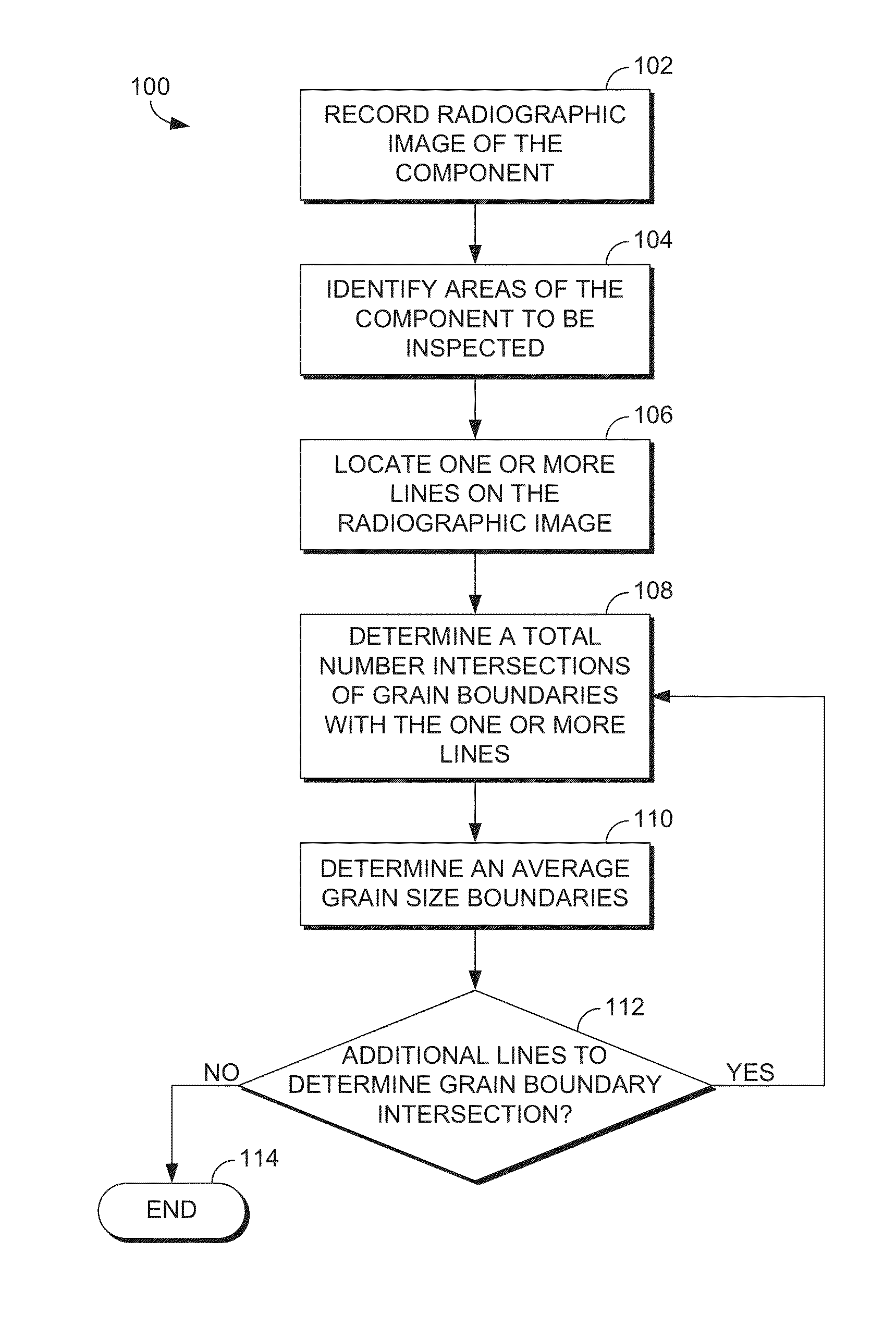
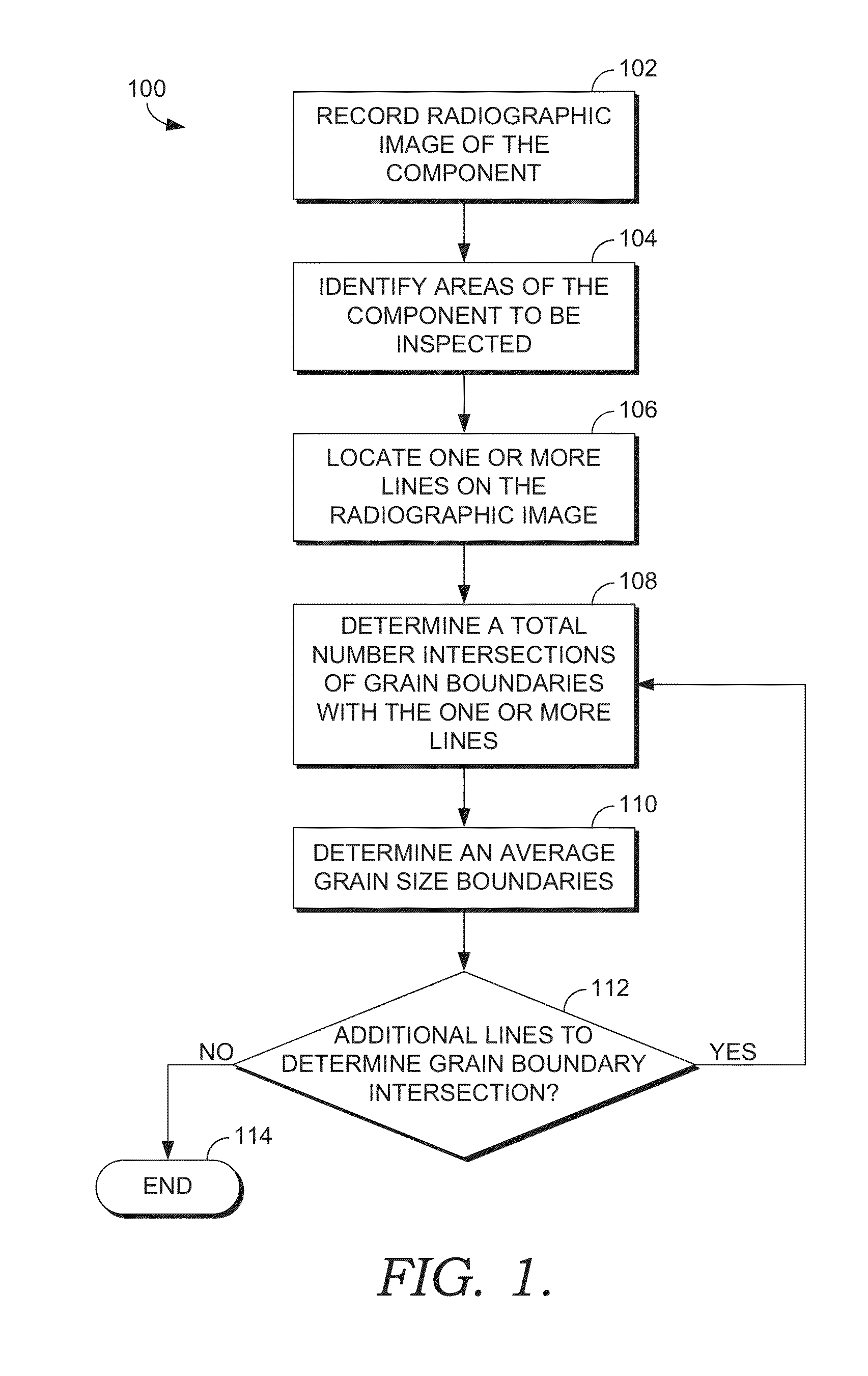
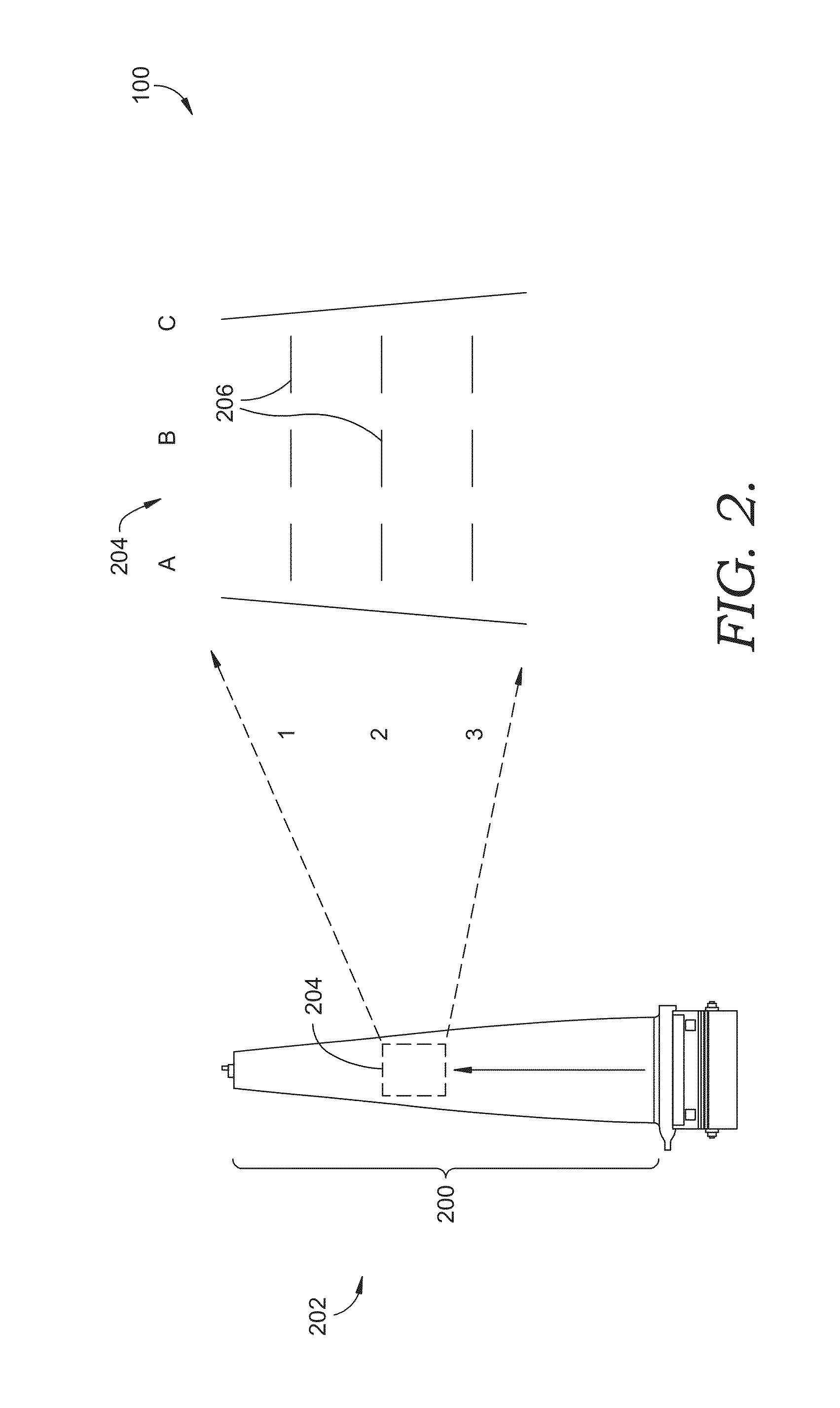
Grain size inspection of a gas turbine component by x-ray refraction
InactiveUS20140270072A1Quick identificationSolid dispersion analysisParticle size analysisX ray refractionAlloy
A system and method for inspecting a grain size of a cast alloy component while maintaining the structural integrity of the cast alloy component is disclosed. The method includes recording a radiographic image of the component, identifying areas of the component to be inspected, and locating one or more lines having a pre-determined length on the radiographic image at an area to be inspected. Then, a total number of intersections with the one or more lines are determined and an average grain size is calculated.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
Full-field Quantitative Statistical Distribution Characterization Method of Precipitated Phase Particles in Metallic Materials
ActiveCN108226159BQuantitative retention cannot be guaranteedAnalytical inefficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisMathematical modelFull field
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Pneumatic tire and crosslinked rubber composition
ActiveUS20180297404A1Good dispersibilityGood dispersionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSolid dispersion analysisShear modulusEngineering
The pneumatic tire of the present invention characterized by comprising: bead cores, a carcass ply, an inner liner disposed at an inner side than the carcass ply in a direction of a tire diameter, and a tread disposed at an outer side than the carcass ply in a direction of a tire diameter and having a volume of the low density region of 35% or more at elongation by an applied stress of 1.5 MPa, a volume of the void portion of 7.5% or less at elongation by an applied stress of 3.0 MPa and a filler dispersibility index ΔG* shown by the following equation (I) of 3 or less and the crosslinked rubber composition having a volume of the low density region of 35% or more at elongation by an applied stress of 1.5 MPa, a volume of the void portion of 7.5 or less at elongation by an applied stress of 3.0 MPa and a filler dispersibility index ΔG* shown by the following equation (I) of 3 or less are excellent in abrasion resistance.ΔG*=(G*(4%)−G*(256%)) / G*(256%) (I)In the equation (I), G* (n %) indicates a shear modulus when an n % strain is applied.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Detection method for content of nitric acid insoluble substances in high-purity silver ingot
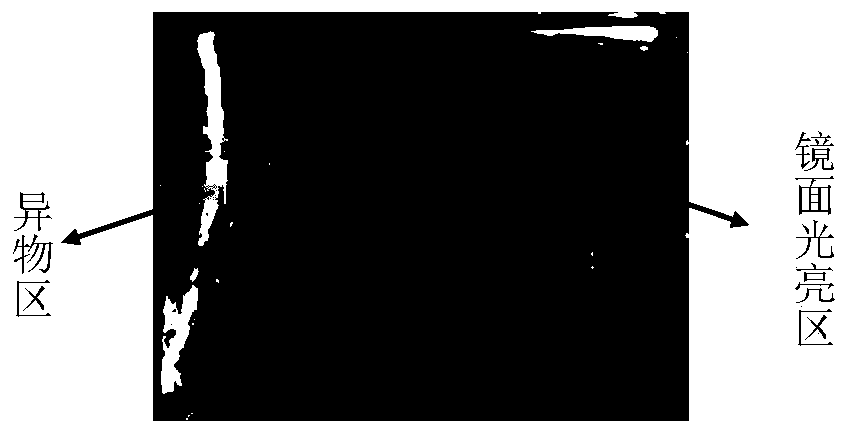
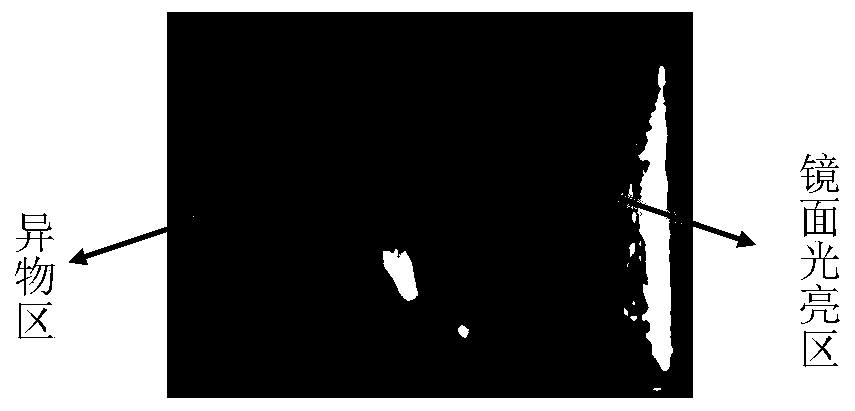
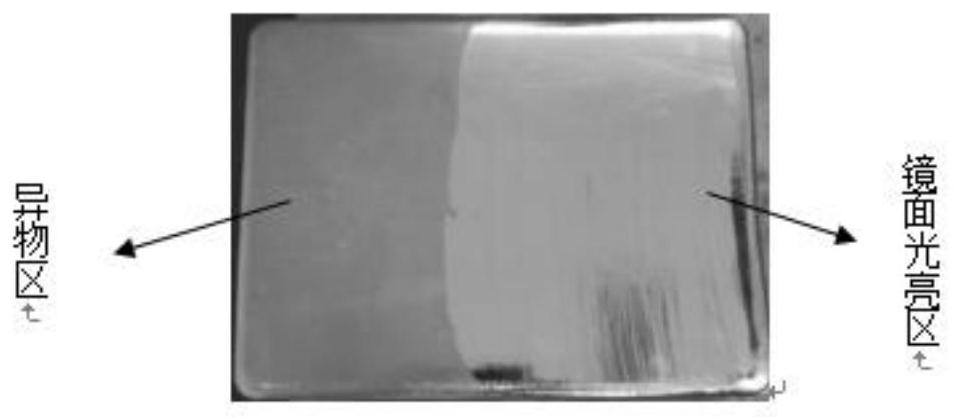
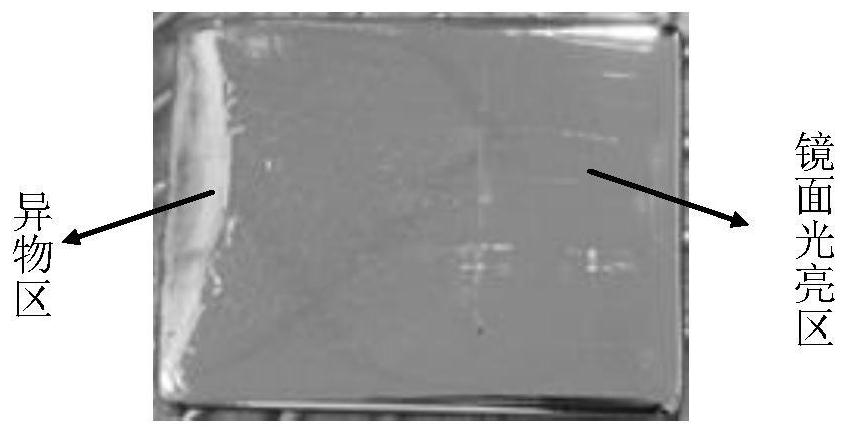
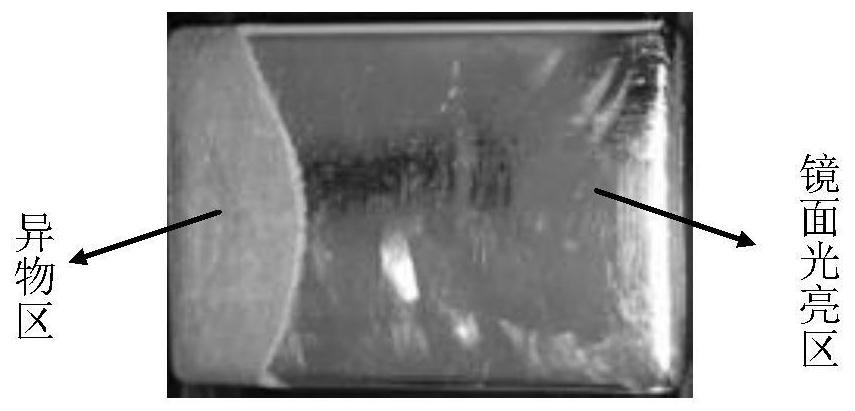
ActiveCN110044763AAvoid wastingReduce usageWeighing by removing componentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationForeign matterShielding gas
The invention discloses a detection method for the content of nitric acid insoluble substances in a high-purity silver ingot, belongs to the technical field of impurity detection, and solves the problems that an existing detection method for the content of nitric acid insoluble substances in a high-purity silver ingot is likely to cause high detection cost and detection inaccuracy. The high-puritysilver ingot comprises 99.99wt% of silver. The detection method comprises the following steps that: carrying out fusion on the high-purity silver ingot under the atmosphere of protection gas, and carrying out intermittent movement on the high-purity silver ingot in a fusion process; after fusion is finished, cooling to obtain a discharged silver ingot, and forming a foreign matter region and a mirror surface bright region on the upper surface of the discharged silver ingot; and according to a ratio of the area of the foreign matter region to the quality of the high-purity silver ingot, determining the content of nitric acid insoluble substances in the high-purity silver ingot. The detection method disclosed by the invention is convenient and simple, and the waste of the sliver ingot is avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FUDA ALLOY MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
Method for quantifying solute transport in soil through CT scanning technology and ion tracing technology
PendingCN114235860AReduce disturbanceAvoid damageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSolid dispersion analysisImaging interpretationIodide potassium
The invention discloses a method for quantifying solute transport in soil through a CT scanning technology and an ion tracing technology. The method comprises the steps that a sample is subjected to saturation standing; preparing a potassium iodide solution as a tracer agent; performing first CT scanning on the sample; adding a tracer agent to carry out second CT scanning on the sample; adding a tracer agent to carry out third CT scanning on the sample; after scanning is finished, a CT scanning image is extracted through VG Studio software, and image interpretation is conducted through Avizo software. According to the method for quantifying the solute transport in the soil through the CT scanning technology and the ion tracing technology, the ion tracing technology is combined with a CT scanning instrument and professional three-dimensional analysis software, and the solute transport in the soil is quantified on the premise that the soil structure is not damaged; in addition, compared with a traditional brilliant blue dyeing method, damage to the environment can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pneumatic tire and crosslinked rubber composition
ActiveUS10639932B2Good dispersibilityGood dispersionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSolid dispersion analysisTire beadShear modulus
The pneumatic tire of the present invention characterized by comprising: bead cores, a carcass ply, an inner liner disposed at an inner side than the carcass ply in a direction of a tire diameter, and a tread disposed at an outer side than the carcass ply in a direction of a tire diameter and having a volume of the low density region of 35% or more at elongation by an applied stress of 1.5 MPa, a volume of the void portion of 7.5% or less at elongation by an applied stress of 3.0 MPa and a filler dispersibility index ΔG* shown by the following equation (I) of 3 or less and the crosslinked rubber composition having a volume of the low density region of 35% or more at elongation by an applied stress of 1.5 MPa, a volume of the void portion of 7.5 or less at elongation by an applied stress of 3.0 MPa and a filler dispersibility index ΔG* shown by the following equation (I) of 3 or less are excellent in abrasion resistance.ΔG*=(G*(4%)−G*(256%)) / G*(256%) (I)In the equation (I), G* (n %) indicates a shear modulus when an n % strain is applied.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
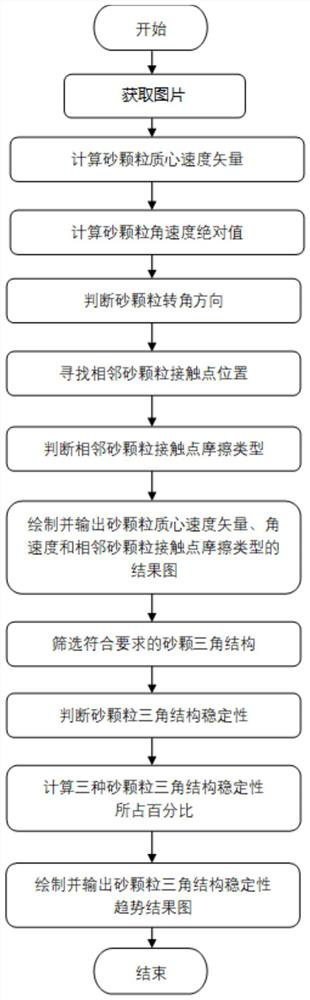
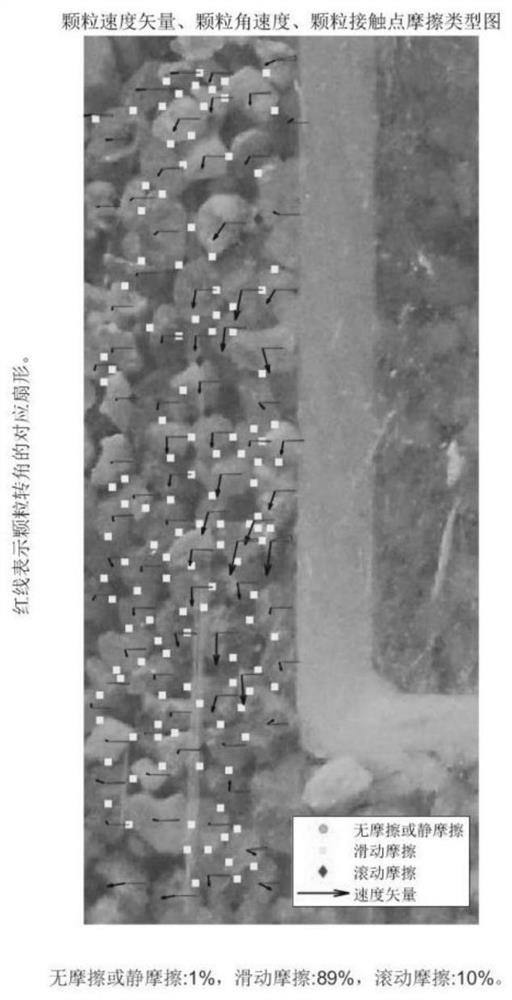
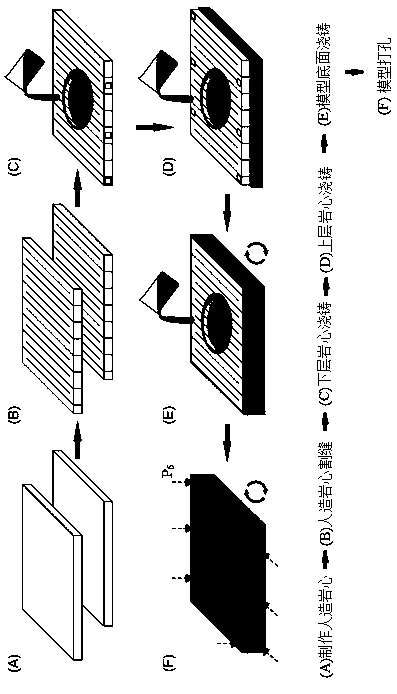
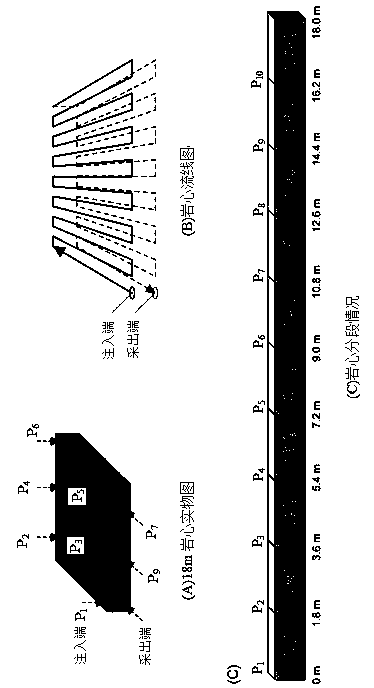
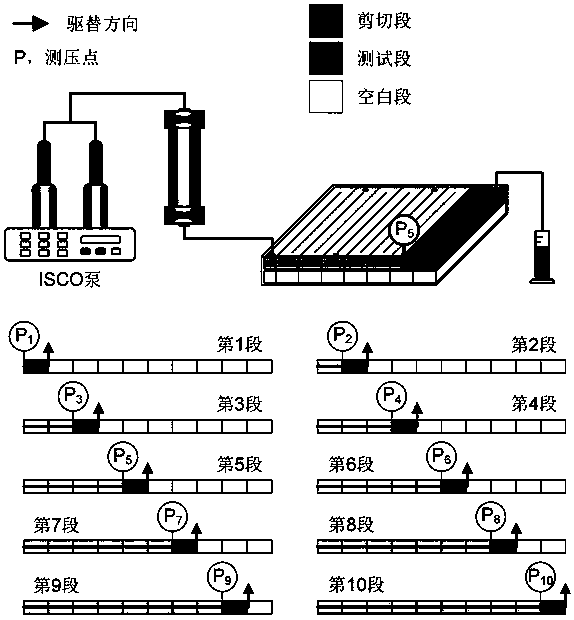
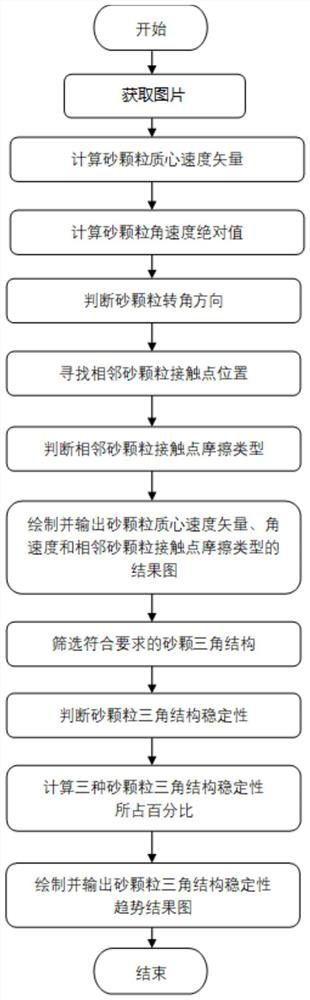
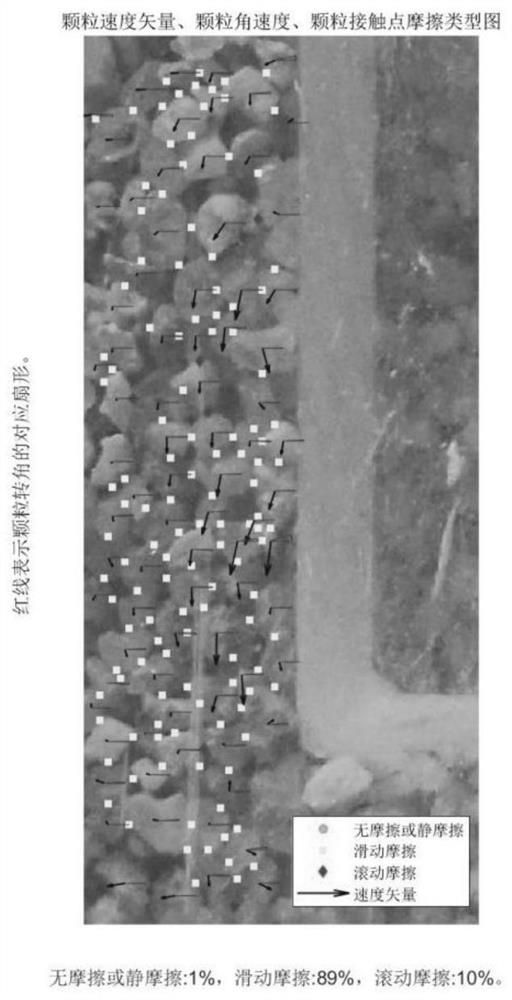
Method for analyzing microstructure motion state of sand particles at structural interface
ActiveCN111665172AShow clear and richCalculation speedSolid dispersion analysisGraphicsClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a microstructure motion state of sand particles at a structural interface. The method comprises the following steps: calculating kinematic parameters ofsand particles according to a shot structural interface sand particle loading motion process image, and calculating positions of contact points of adjacent sand particles; according to the positions of the adjacent sand particle contact points and a preset judgment rule, determining the friction types of the adjacent sand particle contact points; constructing the kinematic parameters of the sand particles and a friction type result graph of contact points of the adjacent sand particles; and according to the kinematics parameters of the sand particles, acquiring a sand particle triangular structure meeting a preset triangular rule, and constructing a sand particle triangular structure state trend chart. The method for analyzing the microstructure motion state of the sand particles at the structural interface is achieved; meanwhile, the calculation speed is high, result graphics are displayed clearly and richly, the application range is wide, and an effective theoretical basis can be provided for analyzing the interaction characteristic of the structural interface and a soil body.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Simulation method for evaluating deep migration characteristics of polymer microspheres in porous medium
ActiveCN110927026ASolve the problem that the length is difficult to meet the experimental requirementsGood choiceSolid dispersion analysisParticle size analysisPolymer scienceRock core
The invention relates to a simulation method for evaluating deep migration characteristics of polymer microspheres in a porous medium. The simulation method comprises: manufacturing a long rock core model; testing resistance coefficients and residual resistance coefficients of the polymer microspheres at different migration depths in the long core model; representing a matching relationship between the polymer microspheres and core pores by adopting a matching coefficient; drawing a relation curve of the injection pressure, the resistance coefficient, the residual resistance coefficient and the displacement depth of the polymer microsphere, finding out the displacement depth at which the injection pressure, the resistance coefficient and the residual resistance coefficient reach the maximum value, and enabling the polymer microsphere to reach the optimal fluidity control and retention capacity at the depth; drawing a relation curve of the particle size and the matching coefficient of the polymer microspheres in the produced liquid and the displacement depth, and determining the particle size range and the matching coefficient range of the polymer microspheres in different migrationperiods. Long-distance migration of the polymer microspheres in a porous medium is simulated, and water plugging and profile control personnel can conveniently select the polymer microspheres of proper types according to the profile control depth.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Analytical method for the movement state of the sand particle mesostructure at the structure interface
ActiveCN111665172BShow clear and richCalculation speedSolid dispersion analysisClassical mechanicsMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the motion state of the mesoscopic structure of sand particles at the structure interface, which includes calculating the kinematic parameters of the sand particles and calculating the contact point position of adjacent sand particles according to the photographed image of the sand particle loading motion process at the structure interface ; According to the contact point position of adjacent sand particles and the preset judgment rules, judge the friction type of adjacent sand particle contact points; construct the kinematic parameters of sand particles and the result map of friction type of adjacent sand particle contact points; according to the kinematics of sand particles parameter, obtain the triangular structure of sand particles conforming to the preset triangular rules, and construct the state trend diagram of the triangular structure of sand particles. The invention realizes the analysis method of the movement state of the mesoscopic structure of sand particles at the structure interface. At the same time, the invention has fast calculation speed, clear and rich graphic display of results, and wide application range, and can provide an effective theory for analyzing the interaction characteristics of the structure interface and soil in accordance with.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
High-speed railway foundation bed slurry-turning mud-emitting fine particle migration detection device
ActiveCN112595633APromote formationPromote evolutionSolid dispersion analysisEarth material testingEngineeringSlurry
The invention relates to a high-speed railway foundation bed slurry-turning mud-emitting fine particle migration detection device, and belongs to the field of railway slurry-turning mud-emitting detection. The device comprises a sample model box provided with a sample filling cavity, and a liquid inlet is formed in the bottom, corresponding to the sample filling cavity, of the sample model box; the loading mechanism is used for loading an impact load into the sample filling cavity; the water supply system feeds liquid into the sample filling cavity in the vertical direction through the liquidinlet; the plurality of collecting guide pipe are arranged at intervals along the vertical direction, each collecting guide pipe is horizontally arranged, and each collecting guide pipe is provided with a plurality of collecting holes at intervals along the horizontal direction; a reversing switch assembly is arranged on the collecting guide pipe and used for opening and closing the collecting holes, so that only one of the collecting holes in different positions is conducted; and according to the scheme, not only can the migration situation of the slurry-turning mud in the vertical directionbe detected, but also the migration situation of the slurry-turning mud in the transverse direction can be detected, and the influence of the boundary on the slurry-turning mud in the test process canbe reflected from the side face, so it is guaranteed that the migration result of fine particles of the slurry-turning mud in the test is relatively accurate.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
High-speed railway subgrade bed sloshing mud fine particle migration detection device
ActiveCN112595633BPromote formationPromote evolutionSolid dispersion analysisEarth material testingEngineeringMechanical engineering
The application relates to a detection device for fine particle migration detection of high-speed railway subgrade bed turbulence and mud discharge, which belongs to the field of railway slop and mud discharge detection. The mechanism loads the impact load into the sample filling chamber; the water supply system feeds liquid into the sample filling chamber along the vertical direction through the liquid inlet; There are multiple collection holes at intervals in the direction; the reversing switch assembly is arranged in the collection conduit to open and close the collection holes, so that only one of the collection holes in different positions is connected; through the above scheme, it is not only possible to detect the vertical It can also detect the migration of mud and mud in the lateral direction, and can reflect the influence of the boundary on mud and mud during the test from the side, so as to ensure that the results of fine particle migration of mud and mud in the test are relatively accurate.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Apparatus for detecting heights of defects on optical glass
A detection apparatus includes four sets of transmitter and receiver wherein the transmitters are on a first sliding member of a frame and the receivers are on a second sliding member of the frame; and drives for moving the first and second sliding members back and forth. During the movements of the first and second sliding members, each transmitter emits laser beam toward the receiver of the same set by passing through a space above a photoresist-coated optical glass by 100 μm, no signal is generated at the receiver if the laser beam is not blocked, and a signal is generated at the receiver if the laser beam is blocked by at least one of a plurality of particles on the photoresist-coated optical glass.
Owner:TAIWAN NANO TECH APPL CORP
A Simulation Method for Evaluating the Deep Migration Characteristics of Polymer Microspheres in Porous Media
ActiveCN110927026BSolve the problem that the length is difficult to meet the experimental requirementsGood choiceSolid dispersion analysisParticle size analysisPolymer scienceMicrosphere
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Mixture Segregation Testing Devices and Methods
Methods and devices are provided to measure segregation in solid particulate mixtures. Light energy is projected through a transparent barrier and reflected off a surface of a mixture volume. The constituent fraction in the mixture is determined by analyzing the mixture reflected light as a combination of the constituents' known reflected light spectral contents and intensities. This is accomplished at multiple surface locations to provide constituent fraction data over the mixture volume surface.
Owner:JOHANSON HLDG
A detection method of nitric acid insoluble content in high-purity silver ingots
ActiveCN110044763BReduce usageLow costWeighing by removing componentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationForeign matterPhysical chemistry
This application discloses a method for detecting the content of nitric acid insolubles in high-purity silver ingots, which belongs to the technical field of impurity detection, and solves the problems that the current detection method for the content of nitric acid insolubles in high-purity silver ingots is likely to cause high detection costs and inaccurate detection. The mass percentage of silver in the high-purity silver ingot is not less than 99.99%, and the detection method includes the following steps: melting the high-purity silver ingot under a protective gas atmosphere, moving the high-purity silver ingot intermittently during the melting process; After cooling, the silver ingot is obtained from the furnace, and the upper surface of the silver ingot from the furnace forms a foreign matter area and a mirror bright area; the content of nitric acid insoluble matter in the high-purity silver ingot is determined according to the ratio of the area of the foreign matter area to the quality of the high-purity silver ingot. The detection method of the present application is simple and convenient, and prevents the waste of silver ingots.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FUDA ALLOY MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
Fine particle cross-flow characteristic research method based on ore rock particle system structural characteristics
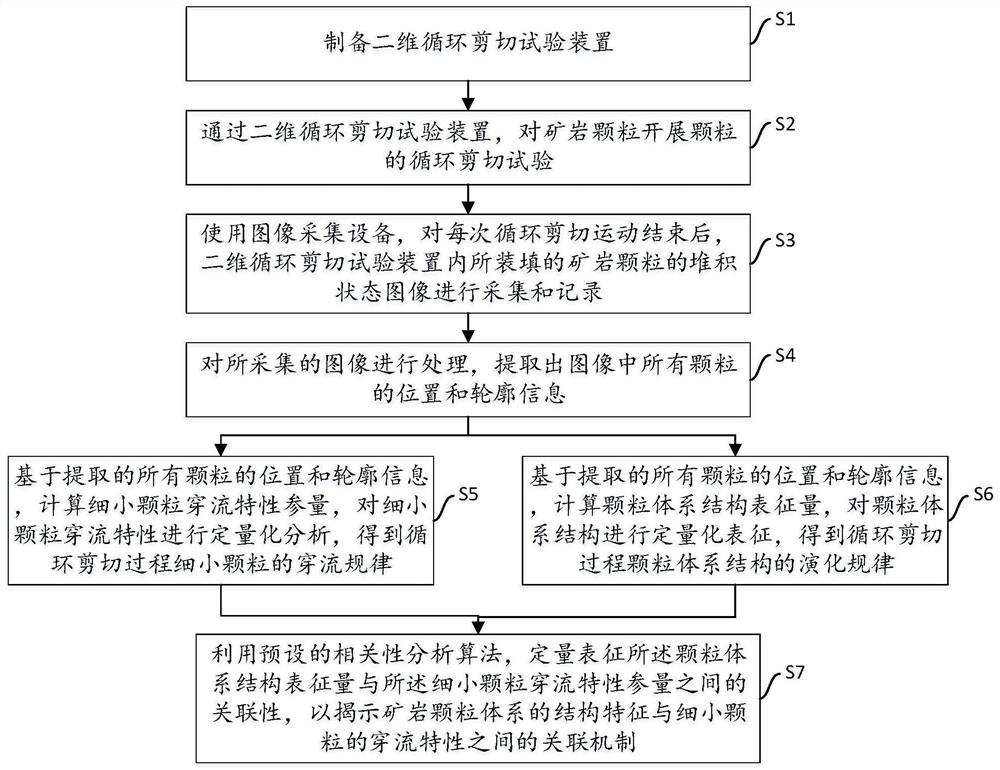
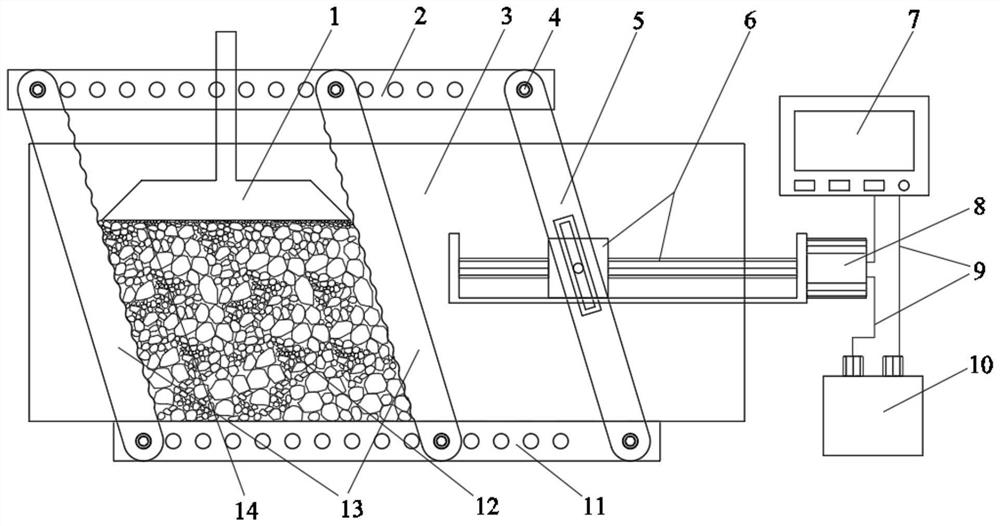
ActiveCN113899661AEasy to operateThe experimental process is visibleSolid dispersion analysisParticle flowImaging processing
The invention discloses a fine particle cross-flow characteristic research method based on ore rock particle system structural characteristics. The method comprises the steps: preparing a two-dimensional cyclic shear test device; carrying out a cyclic shear test on particles through the prepared cyclic shear test device; adopting image acquisition equipment for acquiring and recording accumulation state images of the ore rock particles filled in the cyclic shear test device after each cyclic shear motion is finished; processing the acquired image, and extracting position and contour information of all the particles; on the basis of an image processing result, calculating a fine particle flow characteristic parameter and a particle system structure characterization quantity; and quantitatively characterizing the relevance between the characterization quantity of the particle system structure and the flow-through characteristic parameter of the fine particles by using a relevance analysis algorithm. According to the method, the defects of existing research means are overcome, the correlation mechanism between the ore rock particle system structure characteristics and the fine particle flow characteristics can be disclosed, and a new method is provided for research on the fine ore rock particle flow characteristics.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Popular searches
Indirect flow property measurement Measurements using NMR Acoustic wave reradiation Permeability/surface area analysis Geological measurements Geometric image transformation Preparing sample for investigation Material analysis by optical means Character and pattern recognition Testing metal structures
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com