Guide knocking cap and prosthesis knocking device for joint replacement
A technology of joint replacement and knock cap, applied in the direction of joint implants, joint implants, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing radial component force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
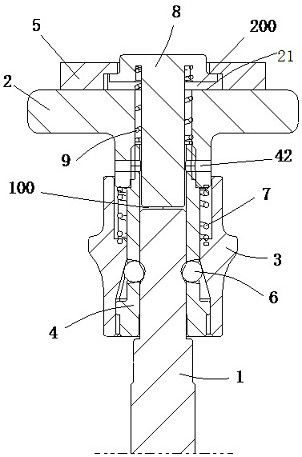
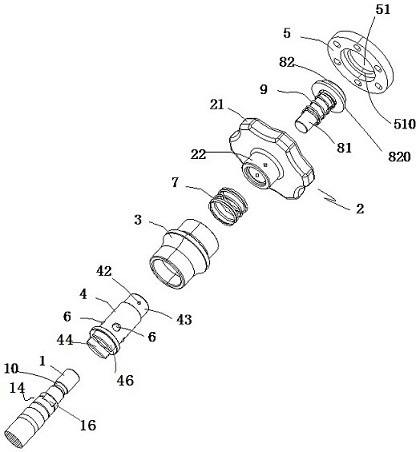
[0034] The striking device according to this embodiment further includes: a buffer sleeve, a flange end cover 5 of an impact rod 8 .
[0035] Here, the knocking portion 2 is configured as a T-shaped hollow sleeve structure with a mounting hole 20 formed therethrough in the axial direction, and includes an end portion 21 and a sleeve rod 22 . The upper end of the steel ball sleeve 4 penetrates into the stepped hole 32, and is connected with the lower end of the sleeve rod 22 extending into the stepped hole 32 through the tapered hole 42, and the outer axial direction of the steel ball sleeve 4 between the end of the sleeve rod 22 and the stepped hole 32 The sleeve is provided with a first spring 7 .
[0036] The impact rod 8 includes a rod portion 81 and a stepped head 82 . The lower end of the rod portion 81 passes through the mounting hole 20 and faces the end 11 of the knock rod 1 through the steel ball sleeve 4 to form an impact gap 100 . A buffer sleeve is axially sleeved...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The difference compared to Embodiment 1 mainly lies in the configurations of the buffer sleeve and the impact rod 8 .
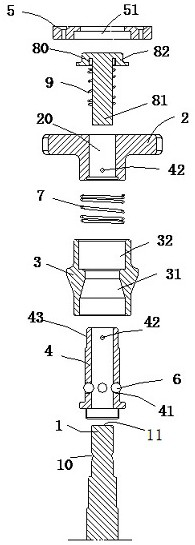
[0054] like Image 6 As shown, in addition to the second spring 9, a shock absorbing pad 91 in the form of a rubber gasket or the like is provided as a buffer sleeve. The shock-absorbing pad 91 is fitted into the mounting hole 20, and the inner peripheral wall thereof is formed as a tapered wall surface 94 whose diameter increases toward the head 82 or the proximal side. The rod portion 81 has a conical section 84 matched with the conical wall surface, and in the initial installation state, the conical section 84 fits with the conical wall surface 94 .
[0055] In this way, during the transmission of the radial force Fr, in addition to the second spring 9, the damping pad 91 will also serve as a radial support, buffering effect.
[0056] Image 6 The lower end of the shock-absorbing pad 91 shown in the figure is supported on the stepped surface 23 ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Figure 7 The difference between the shown buffer sleeve 93 and Embodiment 2 is that it is equivalent to the second spring 9 and the shock-absorbing pad 91 of Embodiment 2 being integrally connected in series, and part of the second spring 9 is upward from the shock-absorbing pad 91 . square out. This reduces assembly parts and simplifies assembly steps.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com