Optical modulator and method for controlling optical modulator
An optical modulator and optical modulation technology, applied in optics, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as modulation schemes that cannot be applied to optical duobinary modulation, and achieve reliable detection, compensation of operating point drift, and reduction of chirp sound effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
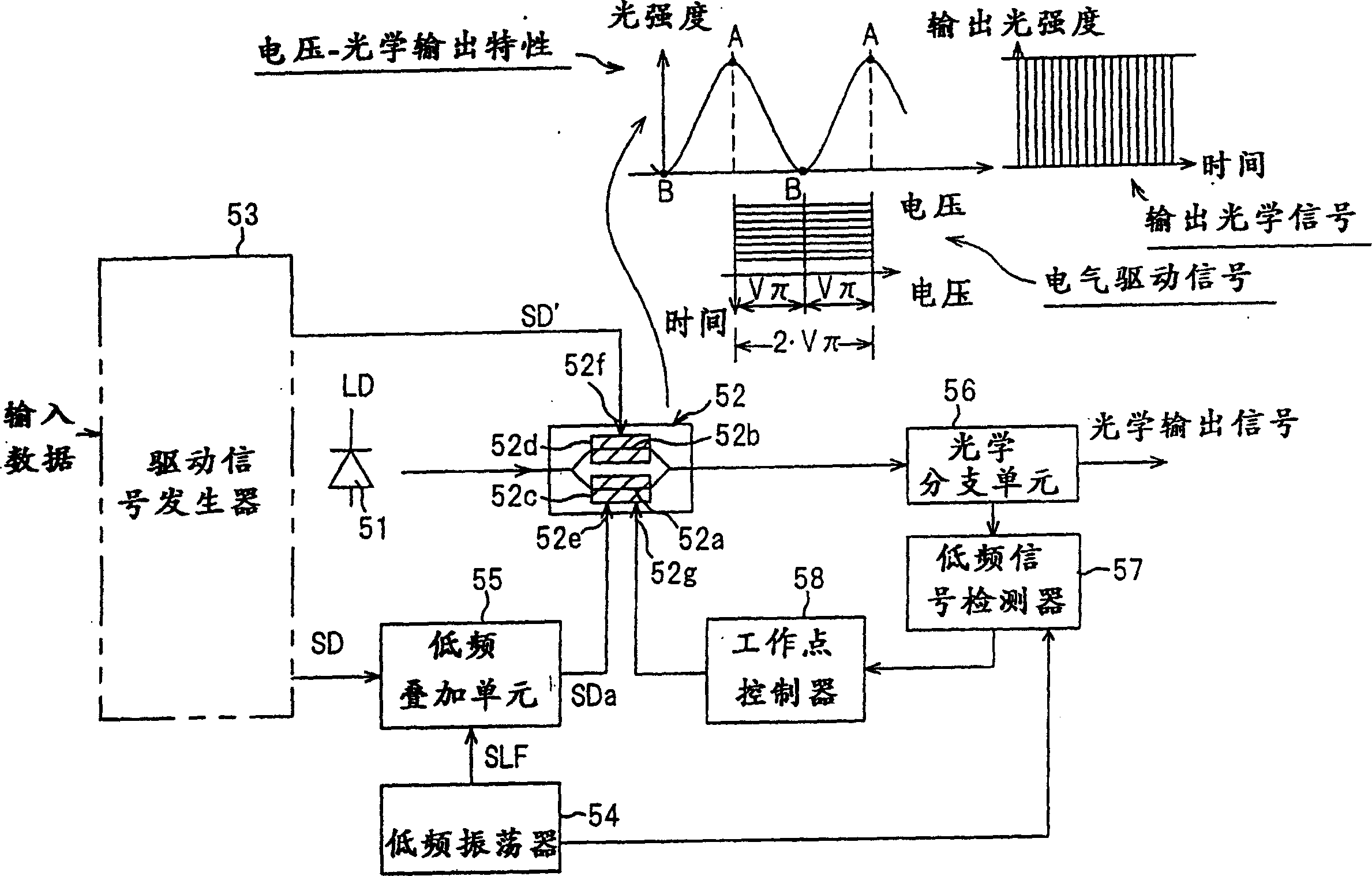
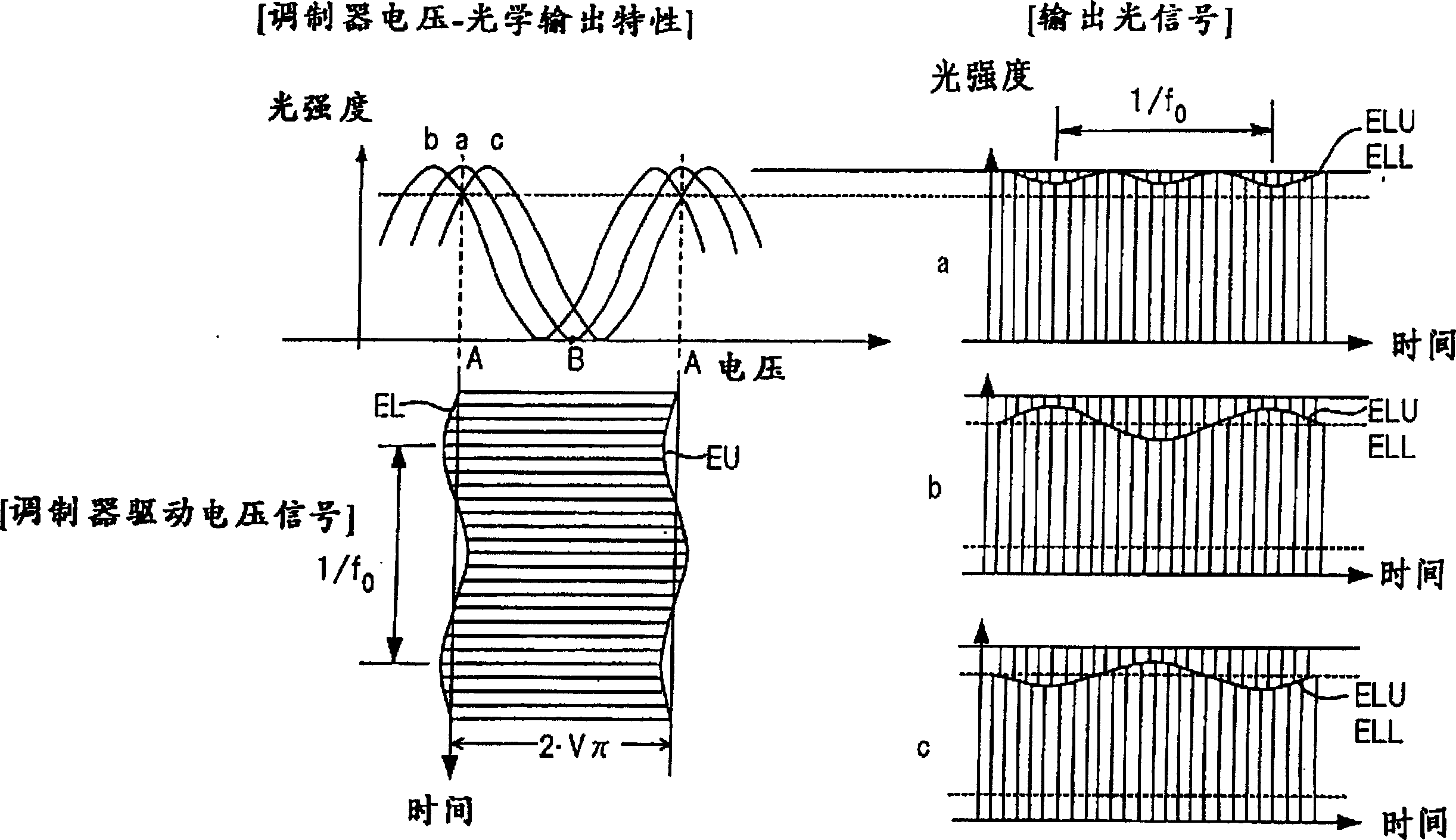
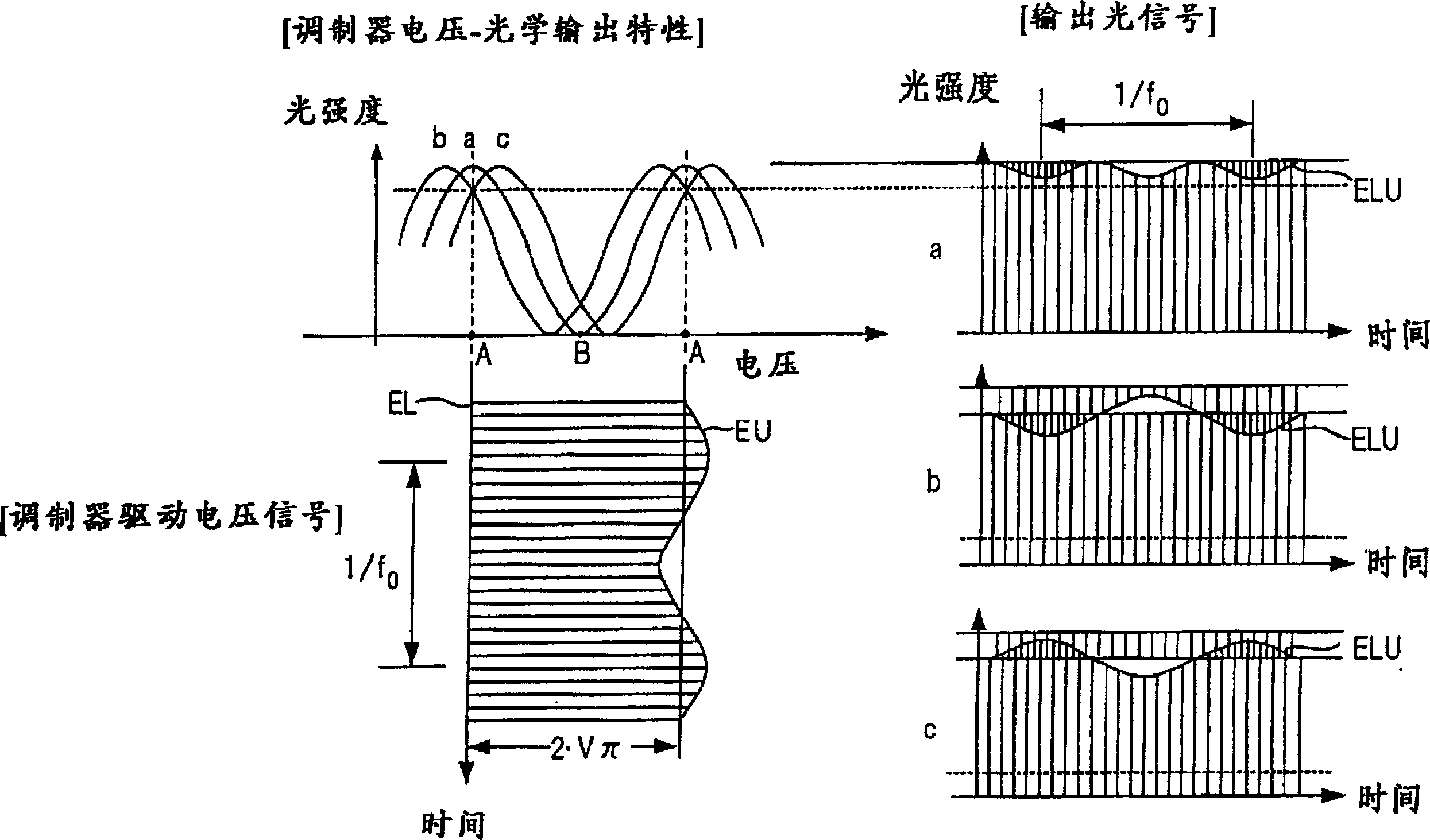
[0124] Figure 7 is a diagram showing the configuration of an optical modulation device according to the first embodiment. This is an example where a LN optical modulator (MZ type optical modulator) configured for two-sided drive (i.e. the modulator has drive electrodes on both sides) is used as the optical modulator, and low frequency is achieved in such a way modulated so that the envelopes on the on and off sides of the modulator voltage drive signal applied to the optical modulator respectively have the same phase (see figure 2 ). Figure 8 With Figure 7 Waveform diagram of the signal concerned.
[0125] expressed in Figure 7 In the center are a semiconductor laser (DFB-LD) 51, and an MZ type optical modulator 52 whose voltage-optical output characteristic changes periodically. The optical modulator 52 includes: some optical waveguides 52a, 52b formed in LiNbO 3 On the substrate, and branched at the light input side and merged at the light output side; two signal ...
no. 2 example
[0149] Figure 13 is a diagram showing the configuration of the optical modulation device according to the second embodiment, and Figure 14 Indicates the relevant signal waveform. The second embodiment differs from the first embodiment in the method of superimposing low-frequency signals. and Figure 7 Elements identical to those shown in are indicated with like reference characters.
[0150] According to the first embodiment, the arrangement is such that the input side of the optical modulator 52 is equipped with a low-frequency superposition unit 55 to change the center voltage of the drive signal SD by a low-frequency signal. However, according to the second embodiment, the gain of the drive circuits 61, 62 is changed by a low frequency signal, whereby the drive signal is amplitude modulated by the low frequency signal.
[0151] expressed in Figure 13 Among them are: semiconductor laser (DFB-LD) 51; MZ type optical modulator 52; driving signal generator 53, which pro...
no. 3 example
[0163] Figure 17 is a diagram showing the configuration of an optical modulation device according to a third embodiment. and Figure 13 Elements that are the same as those of the second embodiment shown in FIG. 2 are indicated with like reference characters. In a second embodiment, the drive signals SD, SD' are both amplitude modulated by the low frequency signal, whereby the on and off sides of the modulator drive voltage signal are modulated by the low frequency signal having the same phase. In a third implementation, only one of the drive signals SD, SD' is amplitude modulated by the low frequency signal, whereby only the on or off side of the modulator drive voltage signal is modulated by the low frequency signal.
[0164] Figure 17 The third embodiment shown in differs from Figure 13 A second embodiment of the frequency f 0 The low frequency signal SLF is input to the gain control terminal of the driving circuit 61, and is used as the amplitude modulation signal S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com