Permanet magnet type rotary electric machine
A technology of rotating electrical machines and permanent magnets, applied to synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuits, etc., can solve the problems of hindering the insertion of armature windings and small cross-sectional area, etc. Achieve the effect of reducing harmonic components, reducing torque pulse and low noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
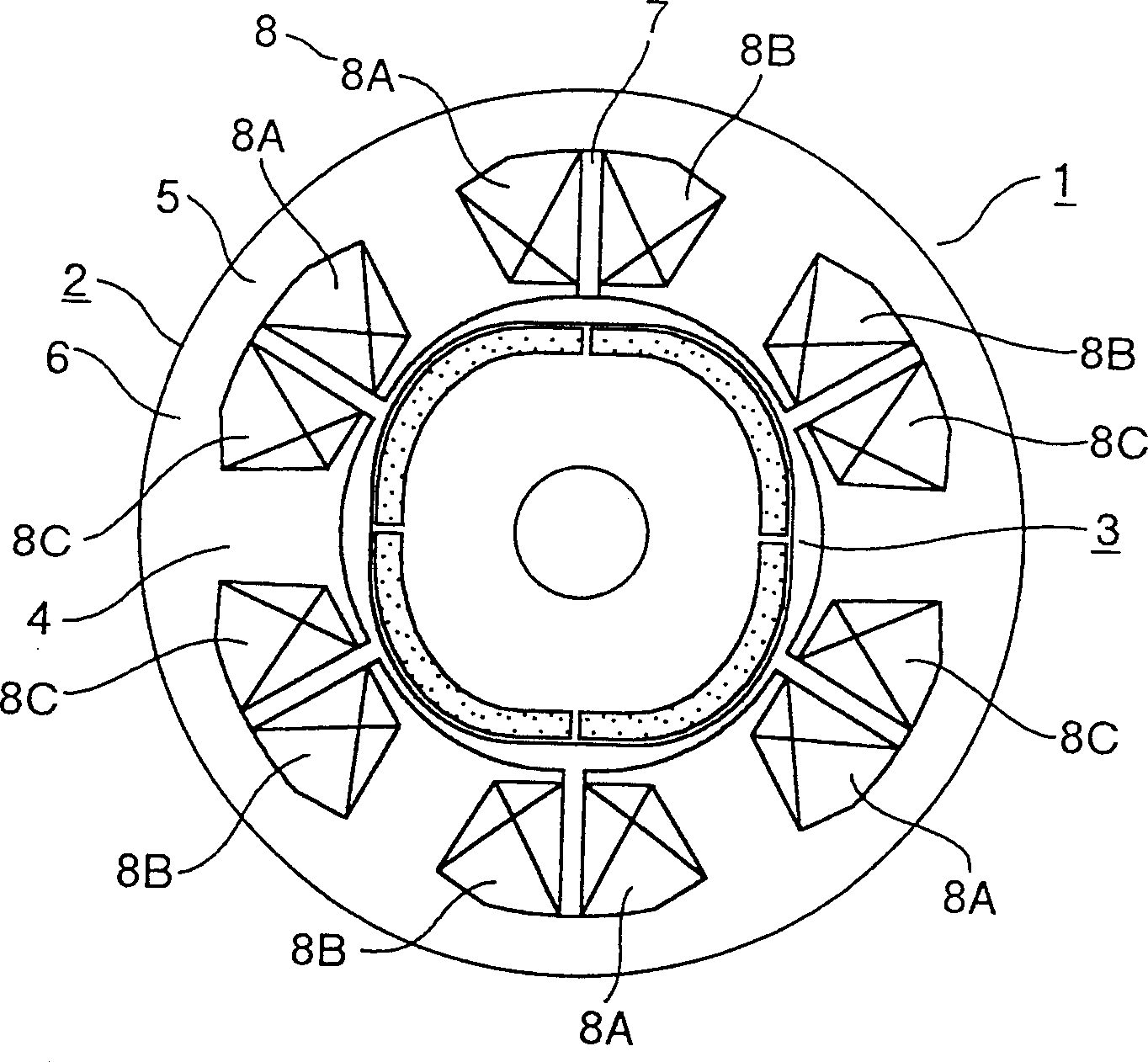
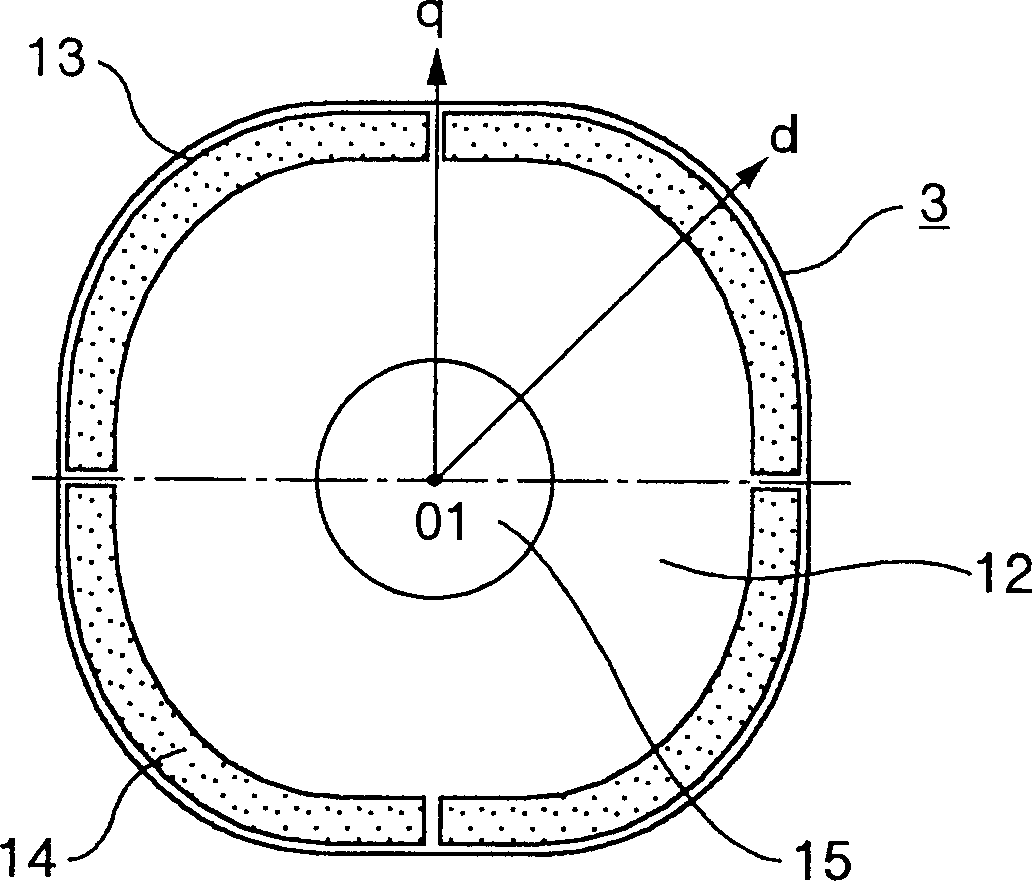
[0023] figure 1 Showing the radial cross-sectional shape of Embodiment 1 of the permanent magnet type rotating electrical machine according to the present invention, figure 2 represents the radial cross-sectional shape of the rotor according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, image 3 is a cross-sectional view of the outer peripheral shape of the rotor according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention; Figure 4 A waveform representing the induced electromotive force of the permanent magnet type rotating electric machine according to the present invention; Figure 10 It is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of a comparative example of a permanent magnet type rotating electrical machine.
[0024] A permanent magnet type rotating electrical machine 1 includes a stator 2 and a rotor 3 . The stator 2 includes a stator core 6 including teeth 4 and a core back 5, and concentric armature windings 8 (three-phase windings including a U-phase winding 8A, a V-phase ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Figure 5 It is a cross-sectional view of the outer peripheral shape of the rotor in Embodiment 2 of the permanent magnet type rotating electric machine according to the present invention.
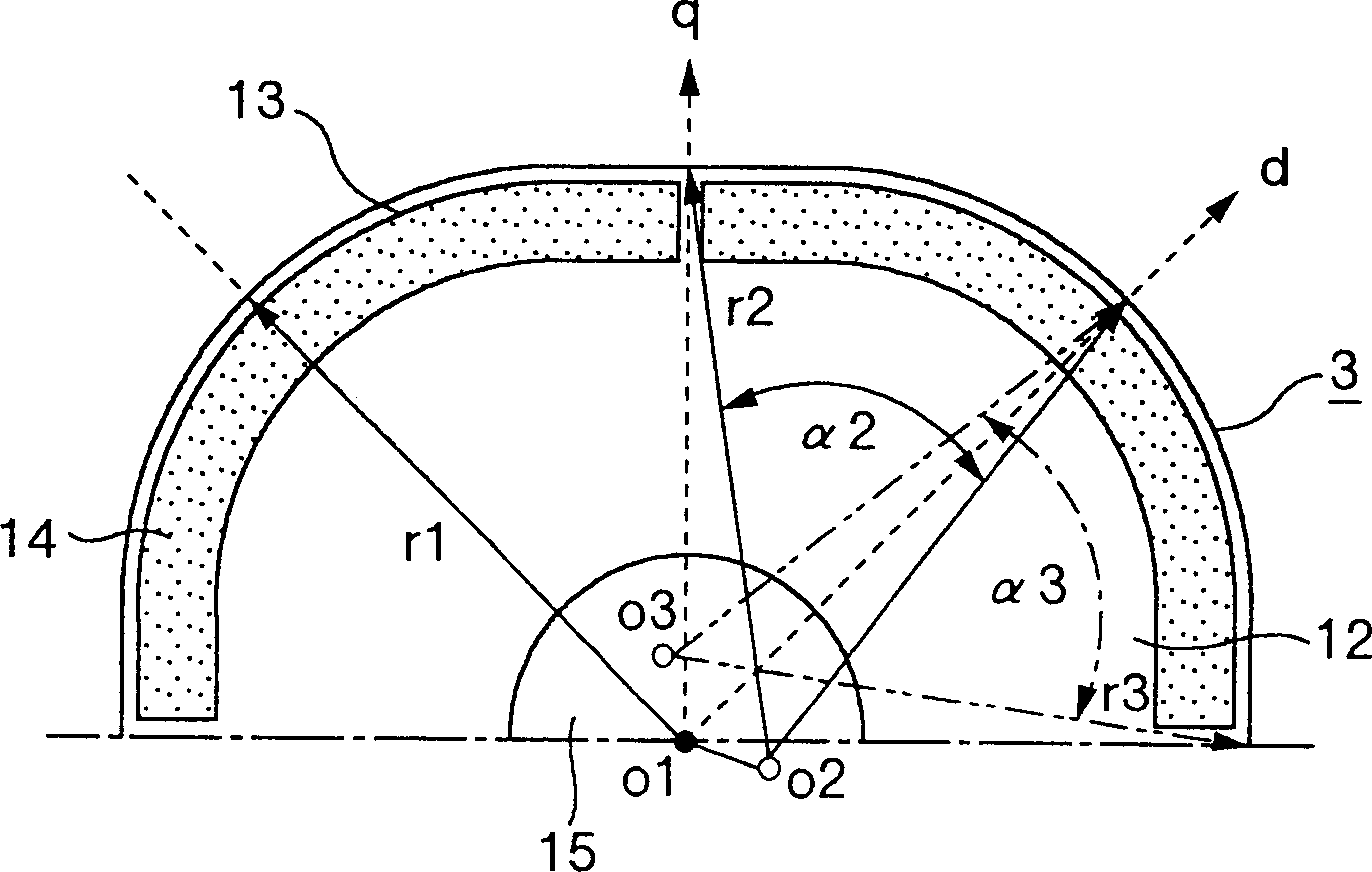
[0033] For the rotor in the attached figure, with image 3 Similar reference numerals are used for similar parts in , and therefore descriptions thereof are omitted. Figure 5 and image 3 The difference is that the outer peripheral shape of the rotor core 12 is a combination of an arc concentric with the center O1 of the rotor 3 and an arc not concentric therewith. Specifically, the shape of the rotor is a combination of arcs around points O2, O3 different from the center O1 and an arc around the center O1. In order to make the outer peripheral shape of the rotor symmetrical with respect to the d axis at each magnetic pole, the radius r2 of the arc around the point O2 is equal to the radius r3 of the arc around the point O3, and the circumferential angle α2 of the arc around the...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Image 6 It is a cross-sectional view of the outer peripheral shape of the rotor of Embodiment 3 of the permanent magnet type rotating electric machine according to the present invention.
[0038] For the rotor in the attached figure, with image 3 Similar components are shown with similar reference numerals, and descriptions thereof are omitted. Image 6 and image 3 The difference is that the outer peripheral shape of the rotor core 12 is a combination of elliptical arcs whose major axis is along the d-axis direction. In this structure, the radial distance from the center of the rotor 3 to the outer circumference of the rotor 3 still gradually decreases from the d-axis to the q-axis, and thus the same as image 3 Similar advantages are shown for the embodiment shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com