A distributed fault-locating method in a total optical network
A fault location and distributed technology, applied in transmission monitoring/testing/fault measurement system, electromagnetic wave transmission system, electrical components, etc. Classification problems, to overcome the long time for fault location, avoid repetitive actions, and enhance the effect of modularization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
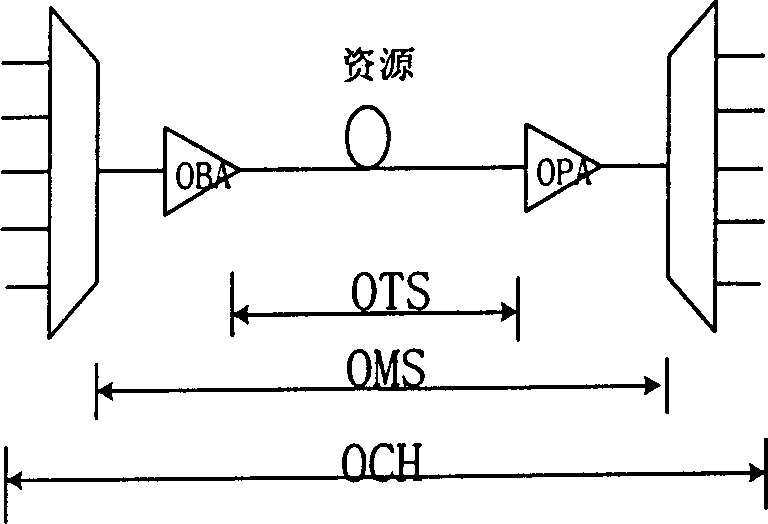
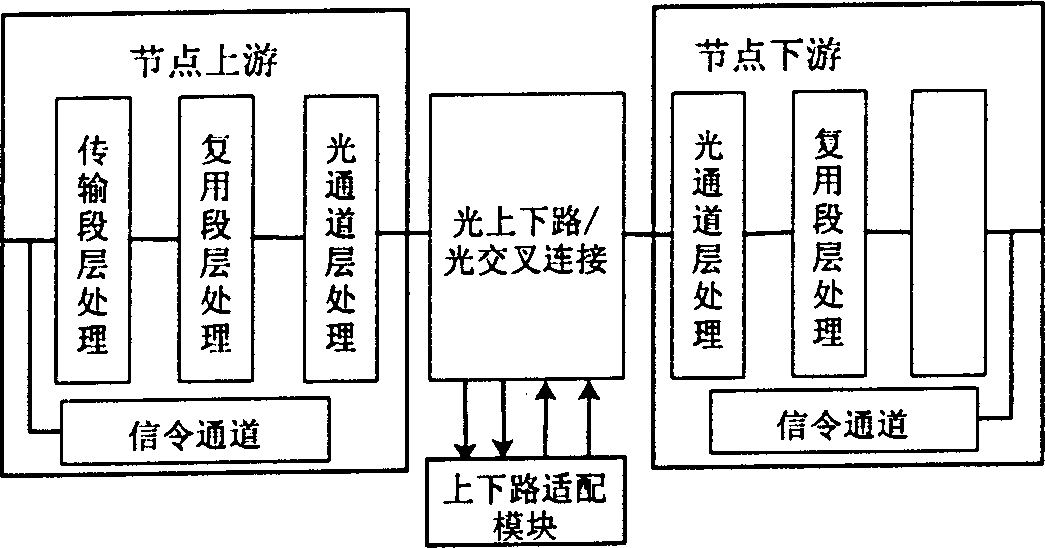
[0043] From the distributed fault location method described in the technical solution of the present invention, it can be seen that the fault monitoring point in the optical node needs to be set, and for the setting of the fault monitoring point, such as figure 1 As shown, the resources of the optical network correspond to three layers of OTS layer (transmission section layer), OMS layer (multiplex section layer), OCH layer (optical channel layer), and the client layer corresponds to specific end-to-end services (such as figure 2 ).
[0044] The same customer can occupy different resources, and the same resource can carry different customers. Resources are the carriers of customers. The ultimate purpose of protection and recovery is to protect and recover customer information, but these protection and recovery actions need to be completed through resources. Traditional The method does not separate resources and services, which makes the functions of fault location and protect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com