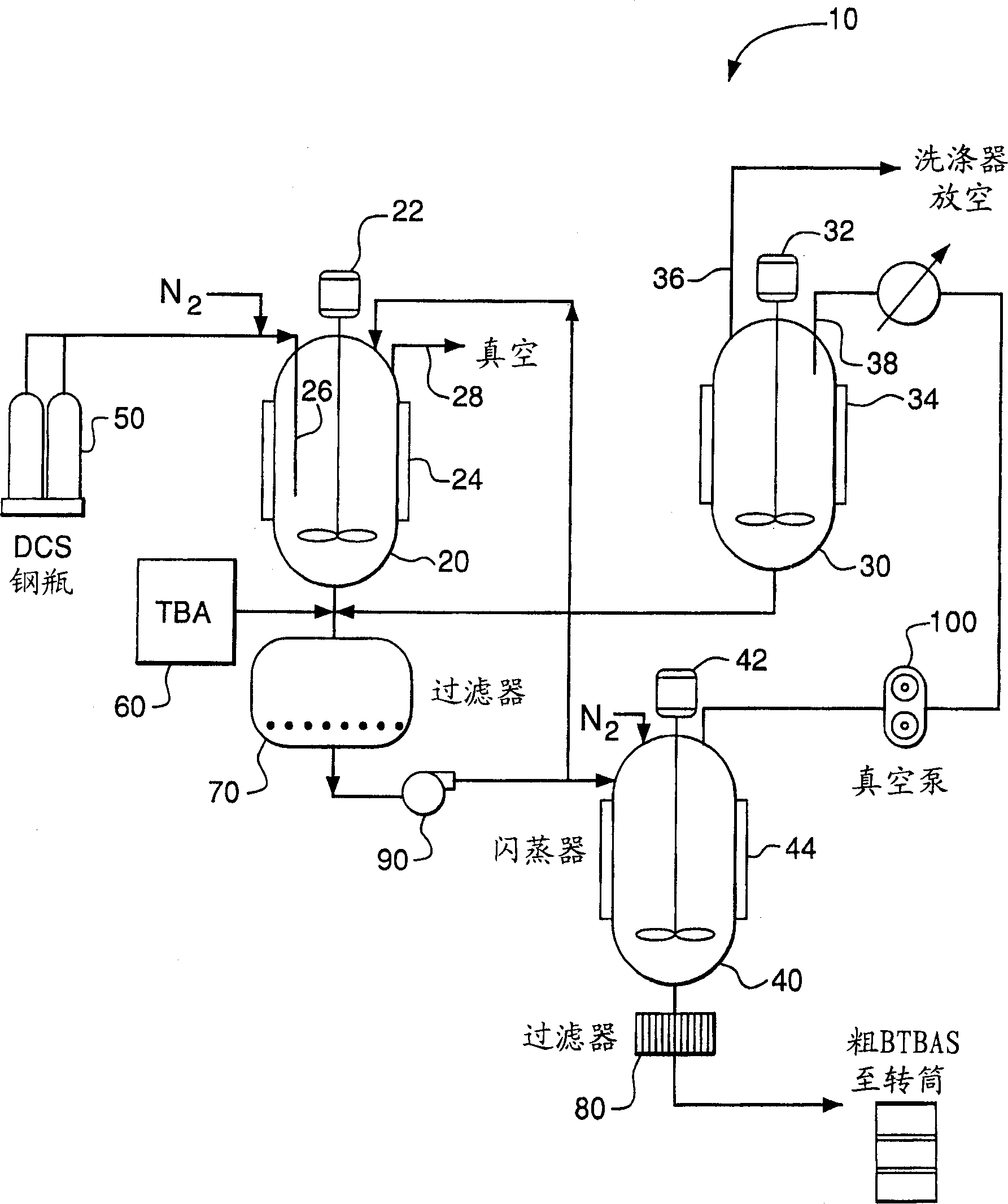
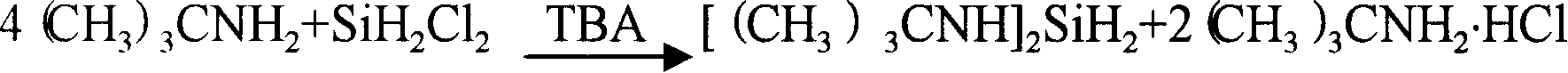Producing and purifying method of bi (Tert-butyl amino) silane
A technology of aminosilane and tert-butylamino, which is applied in the field of synthesis and production of aminosilane, which can solve the problems of poor film uniformity and no description of the production method of aminosilane compounds.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: adopt TBA reactant to synthesize two (tert-butylamino) silanes (BTBAS) as solvent
[0036] 250 ml of anhydrous liquid tert-butylamine (TBA) was added to a 300 ml stainless steel reactor manufactured by Parr Instruments, Moline, Illinois, equipped with a magnetic stirrer. The reactor was purged with nitrogen prior to adding the TBA reactant. The reactor was connected to a stainless steel vacuum line equipped with two 300cc stainless steel balancers, a pressure gauge, a soda-lime trap, and a vacuum pump. The reactor was cooled to -5°C with a dry ice / acetone bath. High purity (eg, 99.8%) DCS is continuously added as a vapor to the TBA liquid through a subsurface dip tube to provide the reaction mixture. The total amount of DCS consumed during the reaction was 8.2 g. The reaction mixture was stirred throughout the reaction. The reactor was sealed and the heat released by the reaction was removed through the reactor wall. After the reaction was complete, t...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Distillation of crude BTBAS product
[0040] The crude BTBAS product was prepared as described in Example 1. The crude product of BTBAS is distilled in about 7 sections of 1in×7in distillation tower, and the tower is equipped with 0.16″ stainless steel PROPACK TM, operating temperature 1,500 ppm chloride. Thus, the presence of the TBA.HCl salt adversely affects the distillation operation, and the BTBAS product obtained contains an undesired level of residual chloride impurities.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Distillation of filtered BTBAS crude product
[0042] The crude BTBAS product was prepared as described in Example 1. The TBA·HCl salt was removed from the liquid by passing the crude BTBAS product through a 0.45 μm glass frit filter manufactured by Ace Glass. Wash with TBA, filter and remove residual crude product from TBA.HCl. The TBA washes were captured and used in subsequent reactions.
[0043] After filtration, the crude BTBAS product was distilled in the same manner as described in Example 2. Negligible amounts of TBA.HCl salts were observed in the distillation column condenser, indicating that the 0.45 μm filter was only leaching a small amount of chloride precipitate. However, this amount of salt does not cause operational problems and the resulting product has a chloride content of <15 ppm. The comparison between Example 3 and Example 2 shows that effective filtering of the crude product can remove most of the TBA·HCl salt contained in the crude...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com