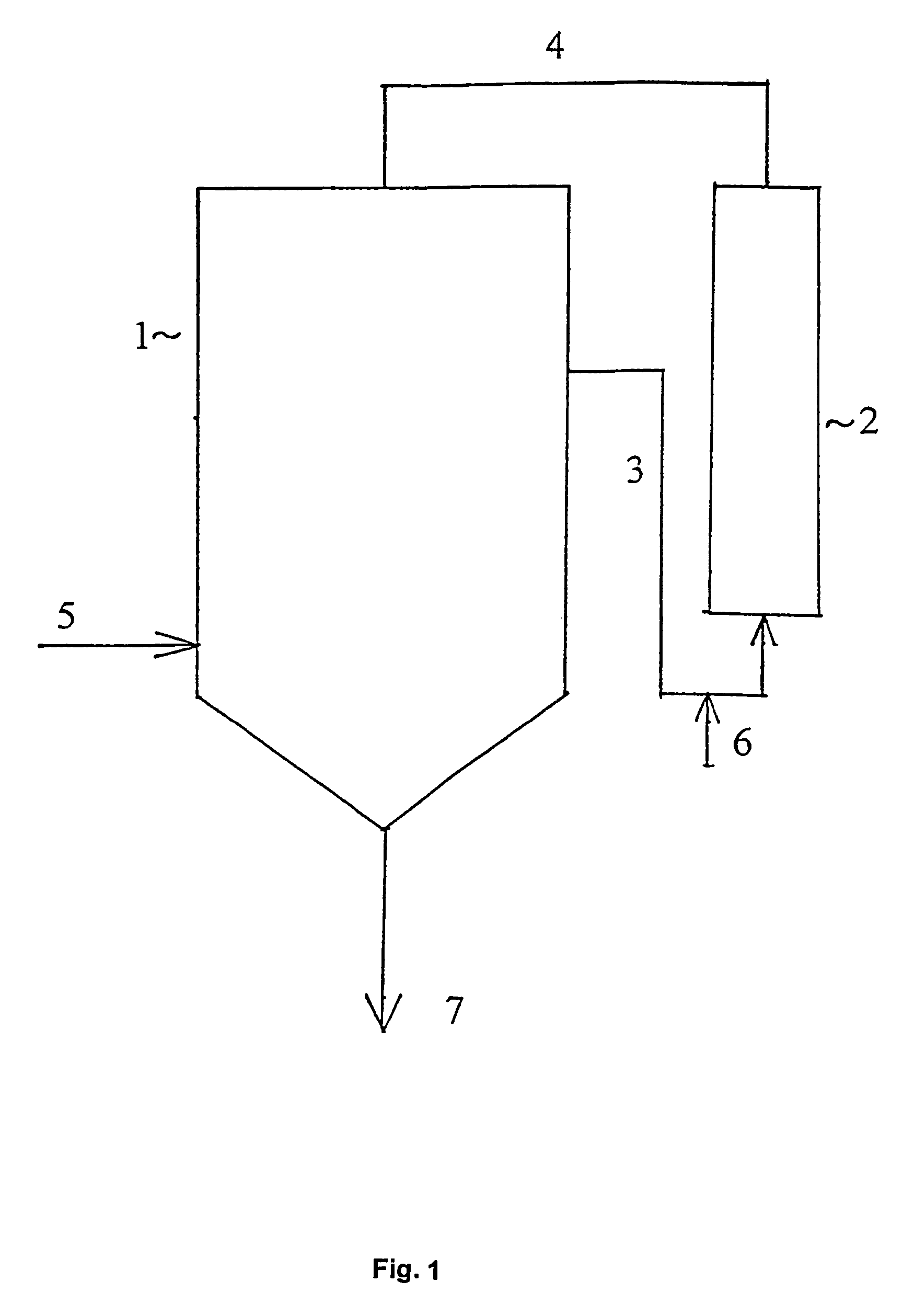
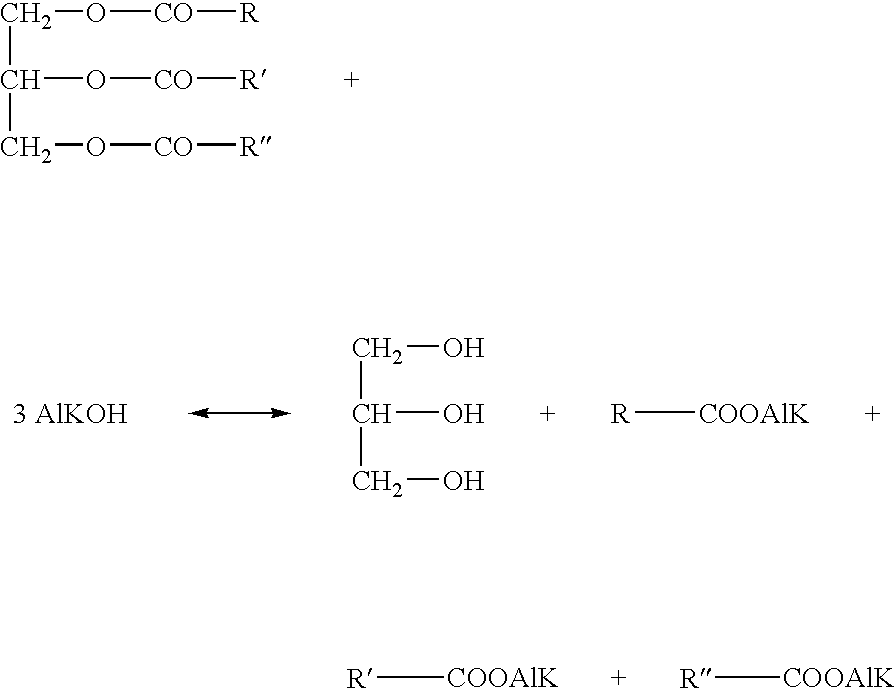
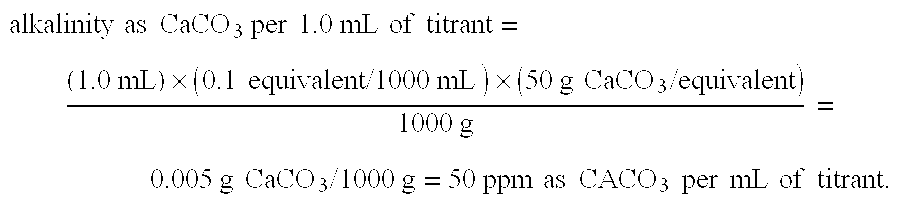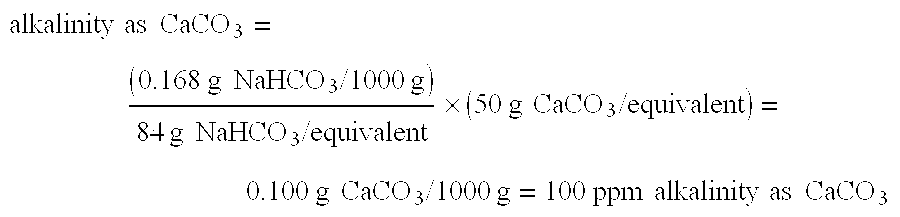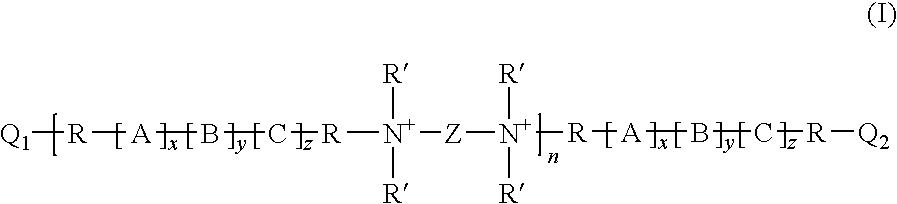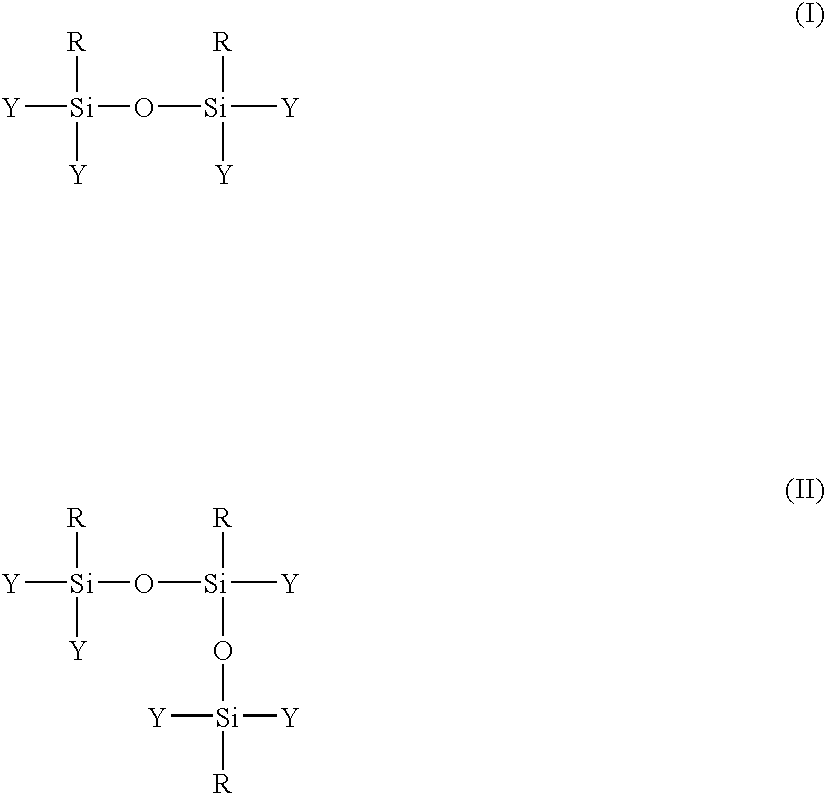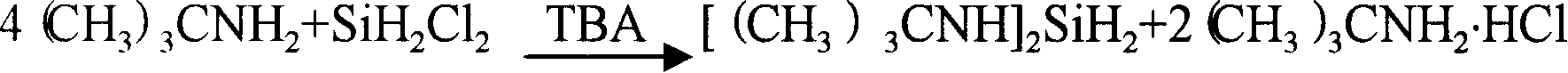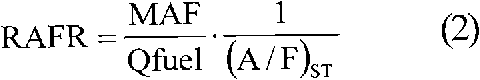Patents
Literature
69 results about "Chemical computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
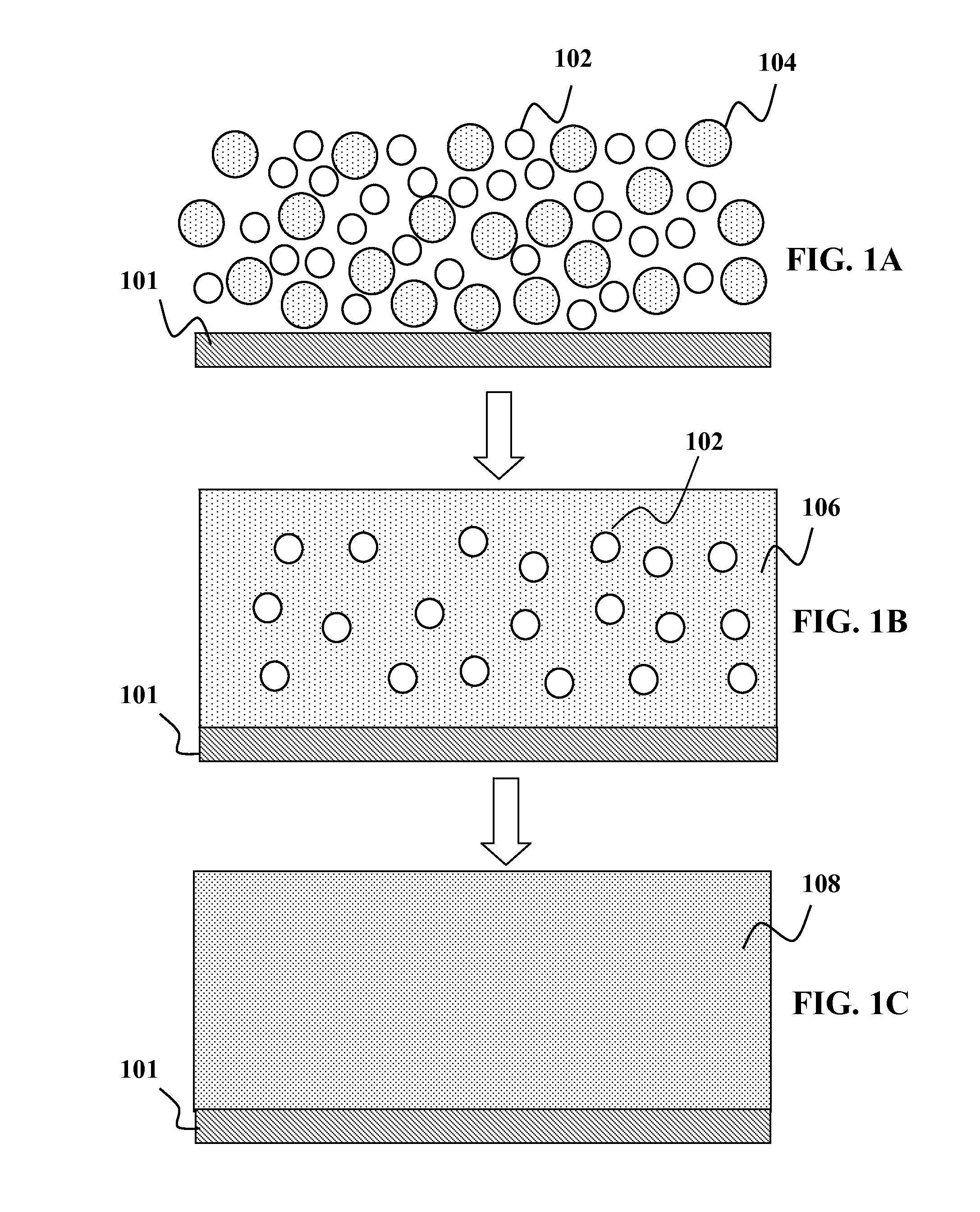
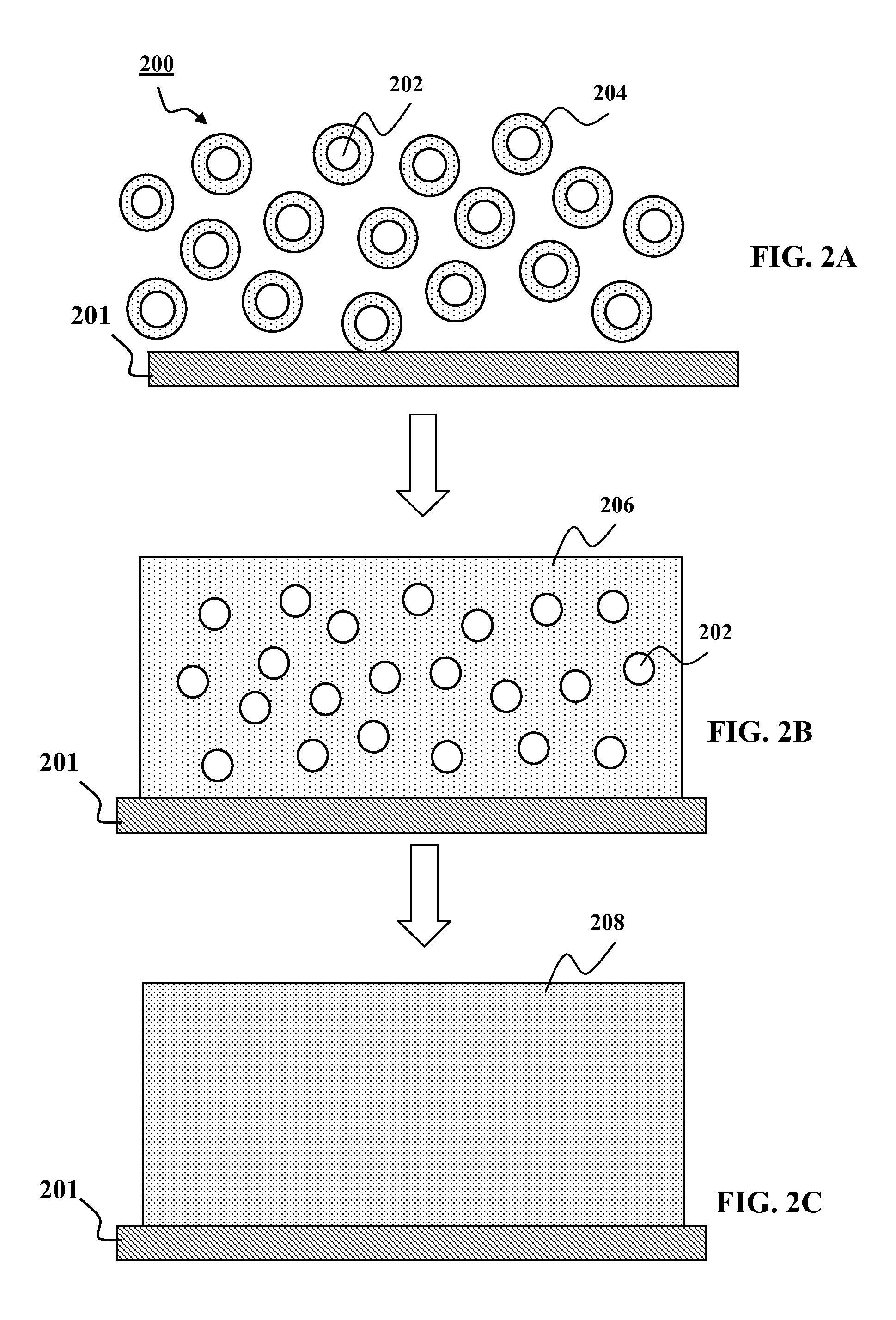
Chemical computing is an unconventional approach to computation that uses a "soup" where data is represented by different concentrations of chemicals. Chemcial computing can be used to solve a range of problems. Chemical computers can exploit several different kinds of reaction to carry out the computation.
Solid electrolytic capacitor containing a conductive polymer
ActiveUS7515396B2Hybrid capacitor electrolytesSolid electrolytic capacitorsOligomerConductive polymer
A method for forming an electrolytic capacitor is disclosed. The method includes forming a conductive polymer coating by polymerizing a monomer in the presence of less than a stoichiometric amount of an oxidative polymerization catalyst. The present inventor has found that the use of less than the stoichiometric amount of the oxidative polymerization catalyst per mole of monomer can slow the polymerization of the monomer, creating oligomers that are shorter in length than if fully polymerized into a polymer. Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that these shorter oligomers provide better penetration into the porous anode. Thus, the resulting conductive polymer layer can be more intimately positioned with respect to the anode. As a result, the formed capacitor can exhibit better performance.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Solid electrolytic capacitor containing a conductive polymer
ActiveUS20080232037A1Hybrid capacitor electrolytesSolid electrolytic capacitorsOligomerConductive polymer
A method for forming an electrolytic capacitor is disclosed. The method includes forming a conductive polymer coating by polymerizing a monomer in the presence of less than a stoichiometric amount of an oxidative polymerization catalyst. The present inventor has found that the use of less than the stoichiometric amount of the oxidative polymerization catalyst per mole of monomer can slow the polymerization of the monomer, creating oligomers that are shorter in length than if fully polymerized into a polymer. Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that these shorter oligomers provide better penetration into the porous anode. Thus, the resulting conductive polymer layer can be more intimately positioned with respect to the anode. As a result, the formed capacitor can exhibit better performance.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
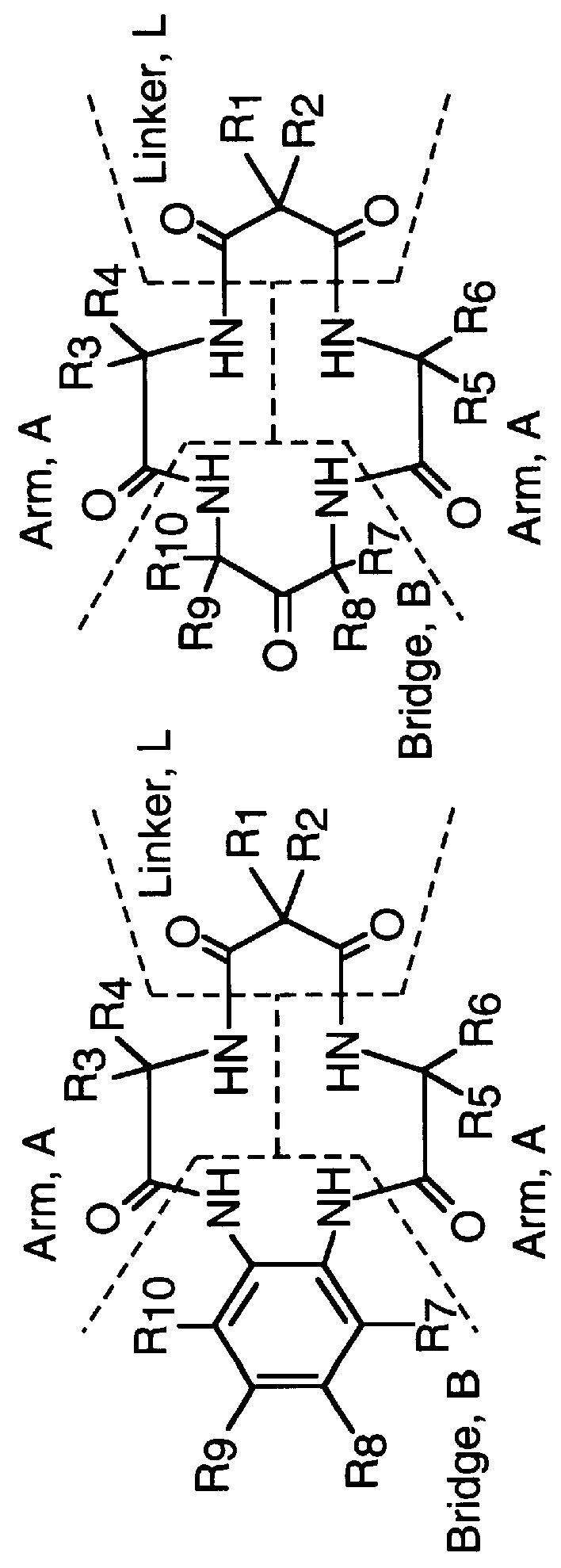
Synthesis of macrocyclic tetraamido-N ligands
InactiveUS6011152AIncrease productionLow costOrganic compound preparationIron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesArylCatalytic oxidation
New synthetic methods for the preparation of macrocyclic amido-N donor ligands are provided. The primary method of the present invention involves in general only two synthetic steps. In the first step, an alpha or beta amino carboxylic acid is allowed to react with an optimal (approximately stoichiometric) amount of an activated malonate or oxalate derivative with mild heating. Upon completion of the double coupling reaction, hydrolysis of the reaction mixture yields a diamide containing intermediate (a macro linker). In the second step, stoichiometric amounts of a diamine, preferably an orthophenylene diamine, are added to the macro linker intermediate in the presence of a coupling agent and heat. This second double coupling reaction, is allowed to proceed for a period of time sufficient to produce a macrocyclic tetraamido compound. The substituent groups on the alpha or beta amino carboxylic acid, the malonate, and the aryl diamine may all be selectively varied so that the resulting tetraamido macrocycle can be tailored to specific desired end uses. The macrocyclic tetraamide ligand may then be complexed with a metal, such as a transition metal, and preferably the middle and later transition metals, to form a robust chelate complex suitable for catalyzing oxidation reactions.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
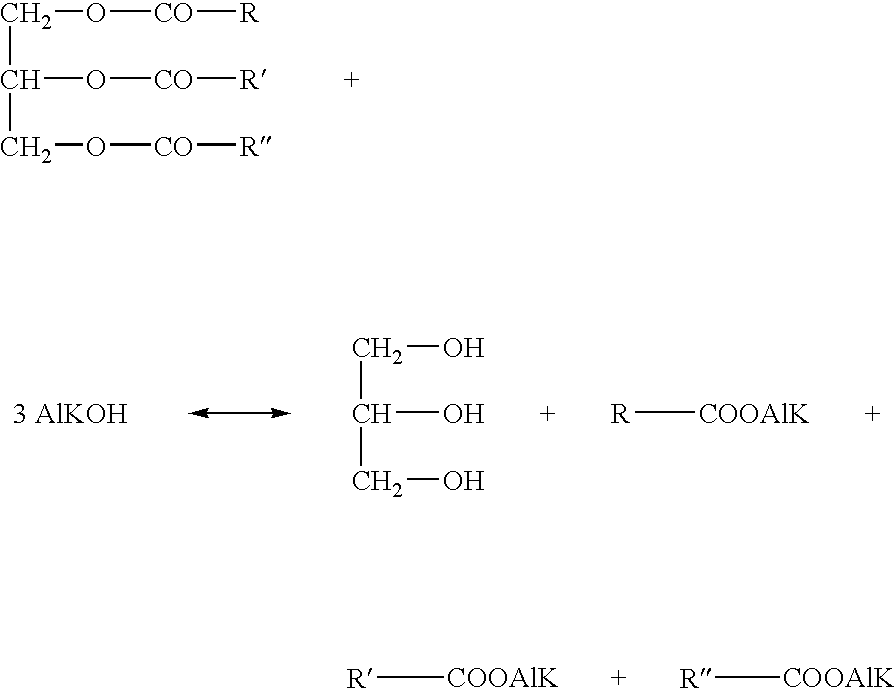
Method for transesterifying vegetable oils
ActiveUS7695533B2Reduce the amount requiredProceed very rapidlyFatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionVegetable oilAlcohol
The present invention relates to a method for producing Diesel grade fuel of plant origin by transesterifying a refined vegetable oil in a homogenous phase with a C1-C4 alkanol in the presence of an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent with a boiling point of 40-200° C. and a catalyst to form a first polar phase comprising glycerol by-product and a first apolar phase comprising transesterified fuel, non-transesterified vegetable oil, and aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent, separating the first polar phase and the first apolar phase, and refining the fuel from the first apolar phase, wherein the C1-C4 alcohol is used in an amount selected from the group consisting of: a stoichiometric amount; and an excess not exceeding 30% of an stoichiometric amount, and the aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent is used in an amount of at least 0.2 parts by volume relative to the unit volume of the refined vegetable oil.
Owner:QUIKSILVER
Adhesive of flexible epoxy resin and latent dihydrazide
Flexible epoxy-based adhesive compositions which remain Theologically stable at room temperature in an uncured state comprise: (a) at least one flexible polyepoxide resin having a hardness not exceeding a durometer Shore D reading of 45 when cured with a stoichiometric amount of diethylene triamine ("DETA"); and (b) a substantially stoichiometric amount of at least one latent epoxy resin curing agent. Optionally, the adhesive composition may also incorporate one or more semi-flexible resins. Other optional components include fillers, thixotropic agents, and flexibilizers. The adhesive composition provicdes an epoxy-based adhesive composition that is storable for weeks as a single component mixture at room temperature, curable at temperatures ranging from about 100° C. to 125° C. in less than two hours, and flexible upon curing to temperatures as low as minus 50° C., exhibiting a durometer Shore A of less than about 95.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
Silicone conveyor lubricant with stoichiometric amount of an acid
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Silicone conveyor lubricant with stoichiometric amount of an acid
The passage of a container along a conveyor is lubricated by applying to the container or conveyor a composition comprising a water-miscible silicone material wherein the composition comprises a stoichiometric amount of an organic acid. The compatibility of the lubricating composition with polyethylene terephthalate is increased because of the presence of a stoichiometric amount of acid.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Method for transesterifyng vegetable oils
ActiveUS20050016059A1Reduce the amount requiredProceed very rapidlyFatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionVegetable oilAlcohol
The present invention relates to a method for producing Diesel grade fuel of plant origin by transesterifying a refined vegetable oil in a homogenous phase with a C1-C4 alkanol in the presence of an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent with a boiling point of 40-200° C. and a catalyst to form a first polar phase comprising glycerol by-product and a first apolar phase comprising transesterified fuel, non-transesterified vegetable oil, and aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent, separating the first polar phase and the first apolar phase, and refining the fuel from the first apolar phase, wherein the C1-C4 alcohol is used in an amount selected from the group consisting of: a stoichiometric amount; and an excess not exceeding 30% of an stoichiometric amount, and the aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent is used in an amount of at least 0.2 parts by volume relative to the unit volume of the refined vegetable oil.
Owner:QUIKSILVER
Hydroxymethylfurfural ethers from sugars or hmf and branched alcohols
The current invention provides a method for the manufacture of an ether of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by reacting a hexose-containing starting material with a branched C3-C20 monoalcohol in the presence of a catalytic or sub-stoichiometric amount of an acid catalyst.
Owner:FURANIX TECH BV
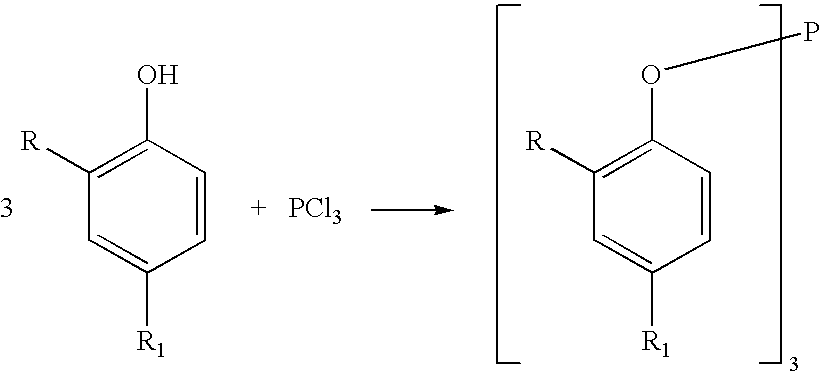
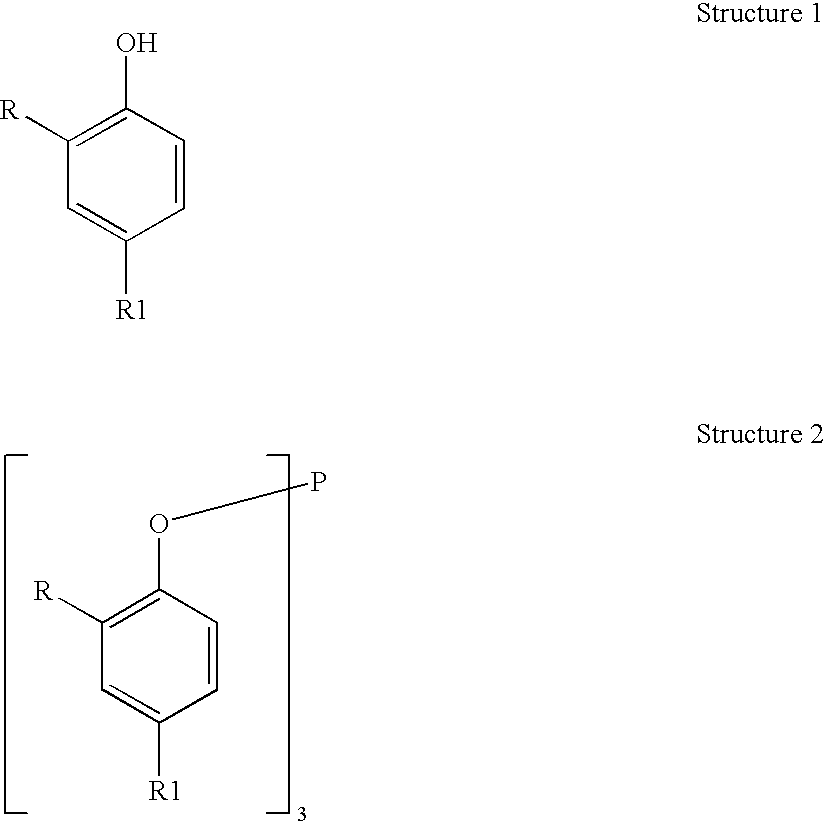
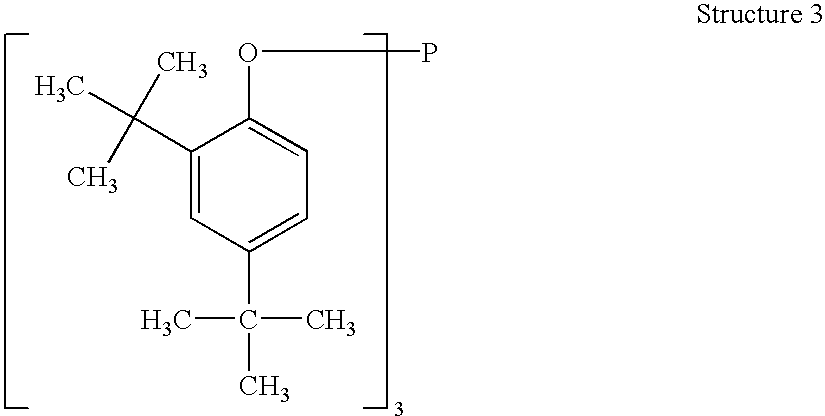
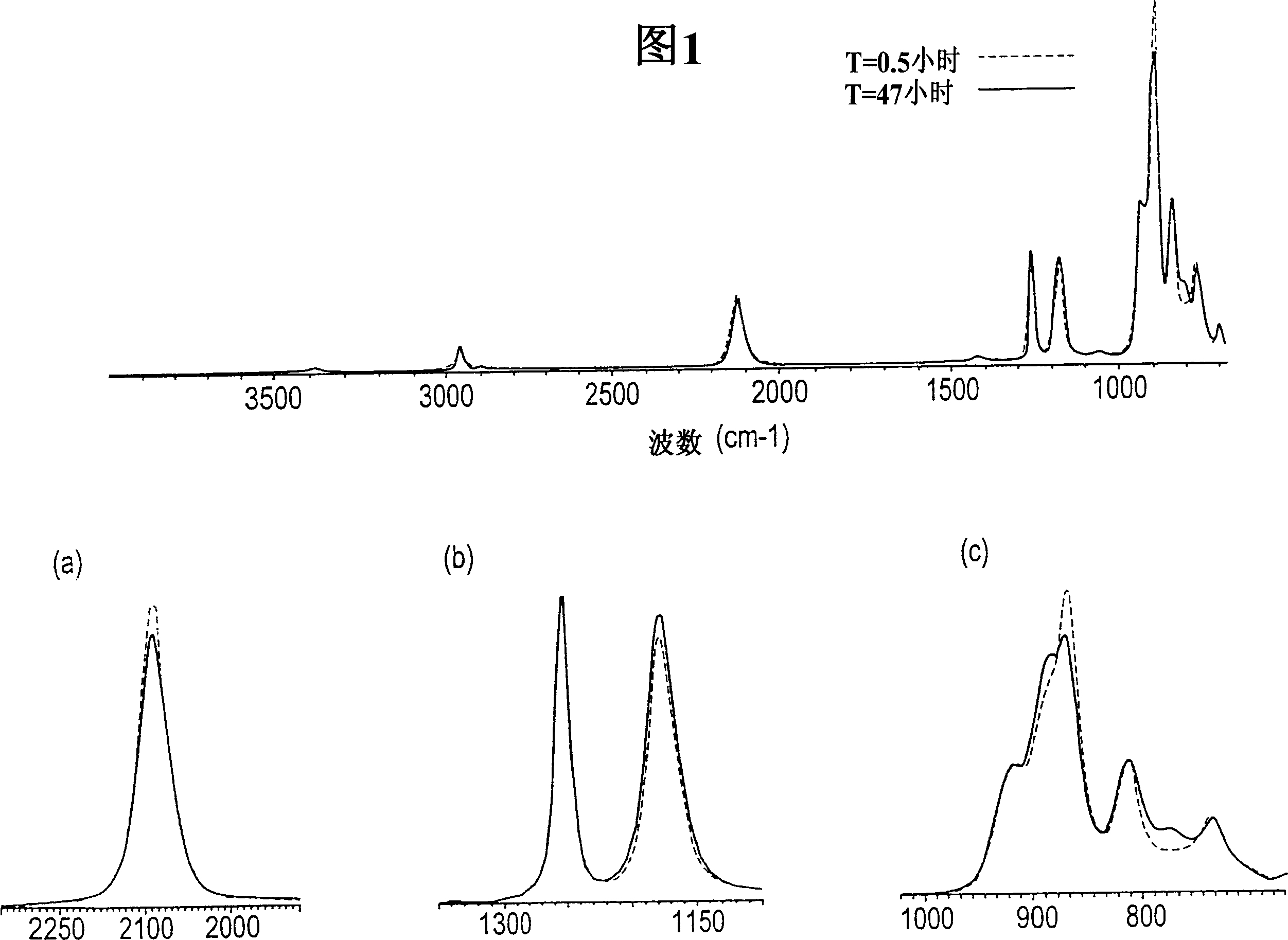
Processes for producing triaryl phospite
A one pot process for the preparation of sterically hindered triaryl phosphite is provided. The triaryl phosphite is of the formula P(OR)3 and is produced by reacting a hydroxyl-substituted aryl compound of formula ROH with phosphorus trihalide in a presence of a Lewis base, wherein R represents an aryl compound of a formula C6H3R1R2, wherein each R1 and R2 is an organic substituent. The process preferably comprises of mixing a substantial stoichiometric amount of 2,4-dialkyl phenol with phosphorous trihalide in methylene chloride with stoichiometric amount of pyridine. The reaction is preferably carried out at 0-5° C. and takes only 1 hr for the completion, followed by a precipitation out of isopropanol.
Owner:STRIDES INC
Novel silizane and/or polysilazane compounds and methods of making
This invention is directed to novel ammonolysis products including novel silazanes and polysilazanes characterized by repeating units of silicon-nitrogen in a polymeric compound having a reduced amount of Si-H bonds relative to the amount of Si-H bonds in the starting compound. Preparation of these novel ammonolysis products comprises introducing a starting compound containing at least one Si-H bond, such as a halosilane into a stoichiometric excess of anhydrous liquid ammonia wherein an ammonium halide is generated acting as an acid catalyst to provide an ionic and / or acidic environment for preparing the novel ammonolysis compounds. The prepared novel ammonolysis products are retained in a separated liquid-phase layer and distinct from the anhydrous liquid ammonia containing the ionized ammonium halide. Also provided are methods to purify ammonolysis products and to modify ammonolysis products by controllably increasing viscosity from a liquid to a solid and viscosities there between.
Owner:AZ ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LUXEMBOURG R L
Polyalkylene oxide polyquaternary ammonium biocides
ActiveUS20100158853A1High activityAmeliorating and reducing undesirable attributeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHalogenMedicinal chemistry
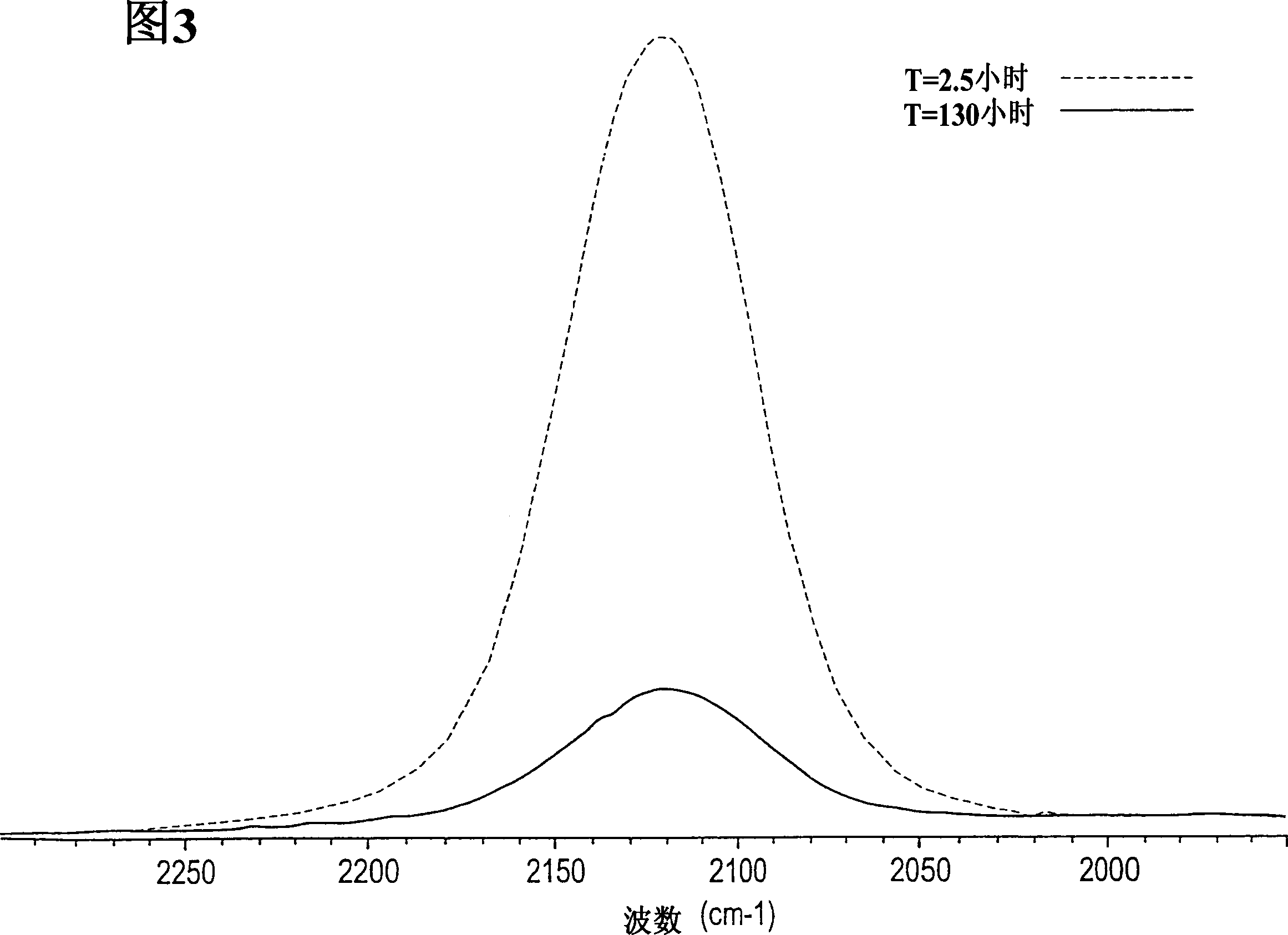
Disclosed are polyquaternary ammonium polymers containing polyalkylene oxide groups according to formula (I) wherein [A]x, [B]y and [C]z are poly(alkylene oxides) each independently selected from the group consisting of poly(ethylene oxide), poly(propylene oxide), and poly(butylene oxide); Z is selected from the group consisting of —CH2CH═CHCH2—, —CH2CH2CH2CH2—, —CH2—C≡C—CH2—, —CH2CH2—O—CH2CH2—, —CH2—N(CH2CH2)2N—CH2—, —CH2CH(OH)CH(OH)CH2— and —CH2—C6H4—CH2—; R is —(CR1R2)mCR3R4— wherein m is an integer from 0 to 3 and R1, R2, R3 and R4 are independently selected from the group consisting of H, CH3 and CH2CH3; n is an integer from 1 to 30; x is either 0 or an integer from 2 to 20; y is an integer from 2 to 20; z is either 0 or an integer from 2 to 20; R′ is a branched or unbranched alkyl group having from 1 to 3 carbon atoms and is optionally substituted by one or two hydroxyl groups; Q1 and Q2 are independently selected from the group consisting of —CH2CH═CHCH2—X, —CH2C≡C—CH2—X, —N(R′)2, —N(R′)3, —N(R′)(R″), and —N(R′)2(R″), wherein X is a halogen atom and R″ is a benzyl group; and a stoichiometric amount of a pharmaceutically acceptable anion. Also disclosed are suitable methods of making the polymers, and methods of using the polymers.
Owner:ALCON INC
Process for the production of organosilsesquioxanes
InactiveUS20070122636A1Controlled and rapid manufactureSilicon organic compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsWater useChemical reaction
A process for forming a composition comprising organosilsesquioxanes, comprises the following steps: 1. partially hydrolysing hydrolysable inorganic monomer precursors comprising at least 50 moles % of first hydrolysable inorganic monomer precursors having the formula RSiY3, in which R is an organic group, the R—Si bond is a non-hydrolysable bond, each Y group is the same as or different to one another and is selected from chemically-reactive groups such that each Si—Y bond is hydrolysable to form a Si—OH bond, to form inorganic monomers and allowing partial condensation of the inorganic monomers to form a liquid composition comprising inorganic oligomers; 2. prior to complete condensation of the inorganic monomers, quenching the liquid composition with an amount of water which, in combination with the water used in step (1) and any water liberated by condensation of the inorganic monomers in step (1), is in excess of the stoichiometric amount of water required to achieve complete hydrolysis of all the hydrolysable inorganic monomer precursors present; and 3. drying the composition.
Owner:THE WELDING INST
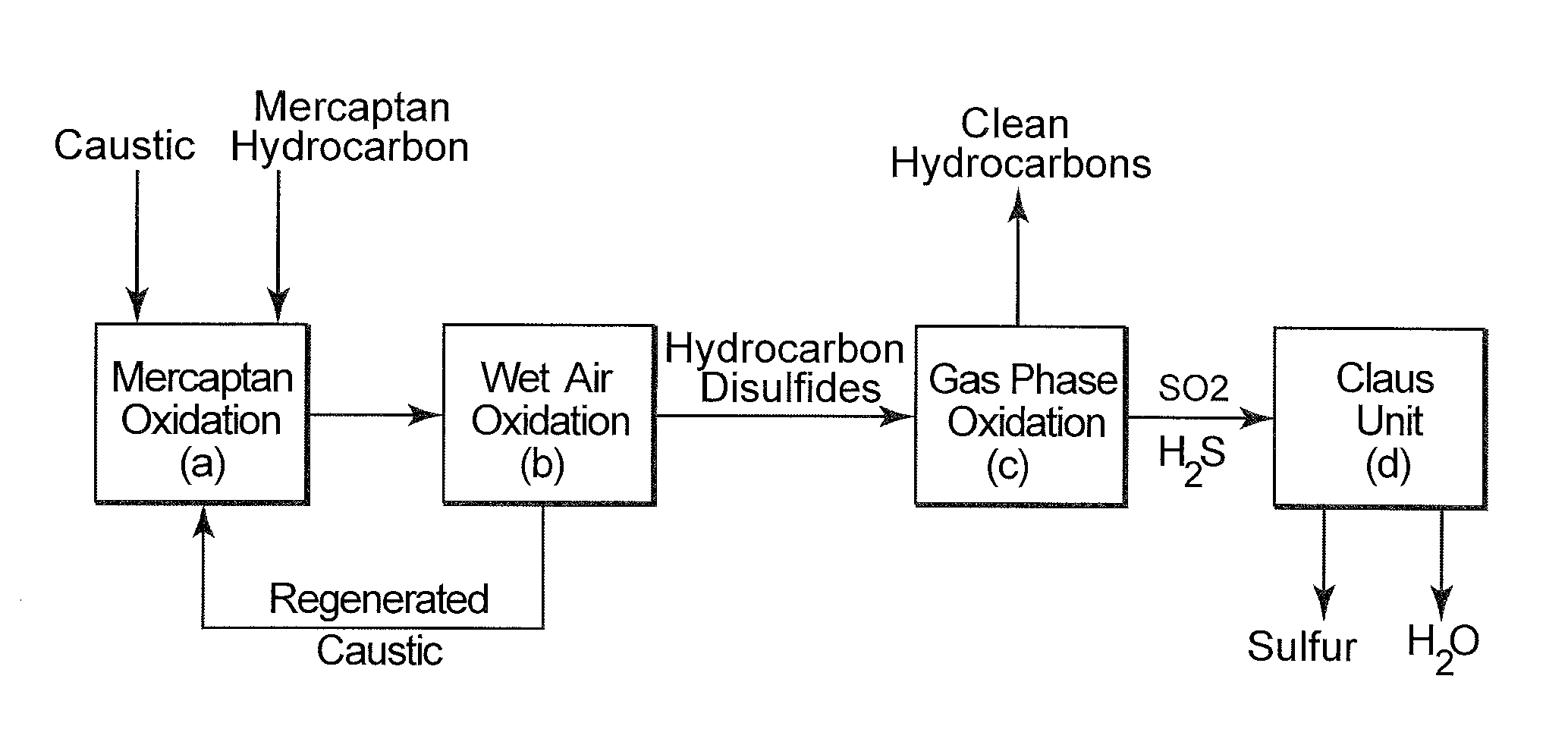
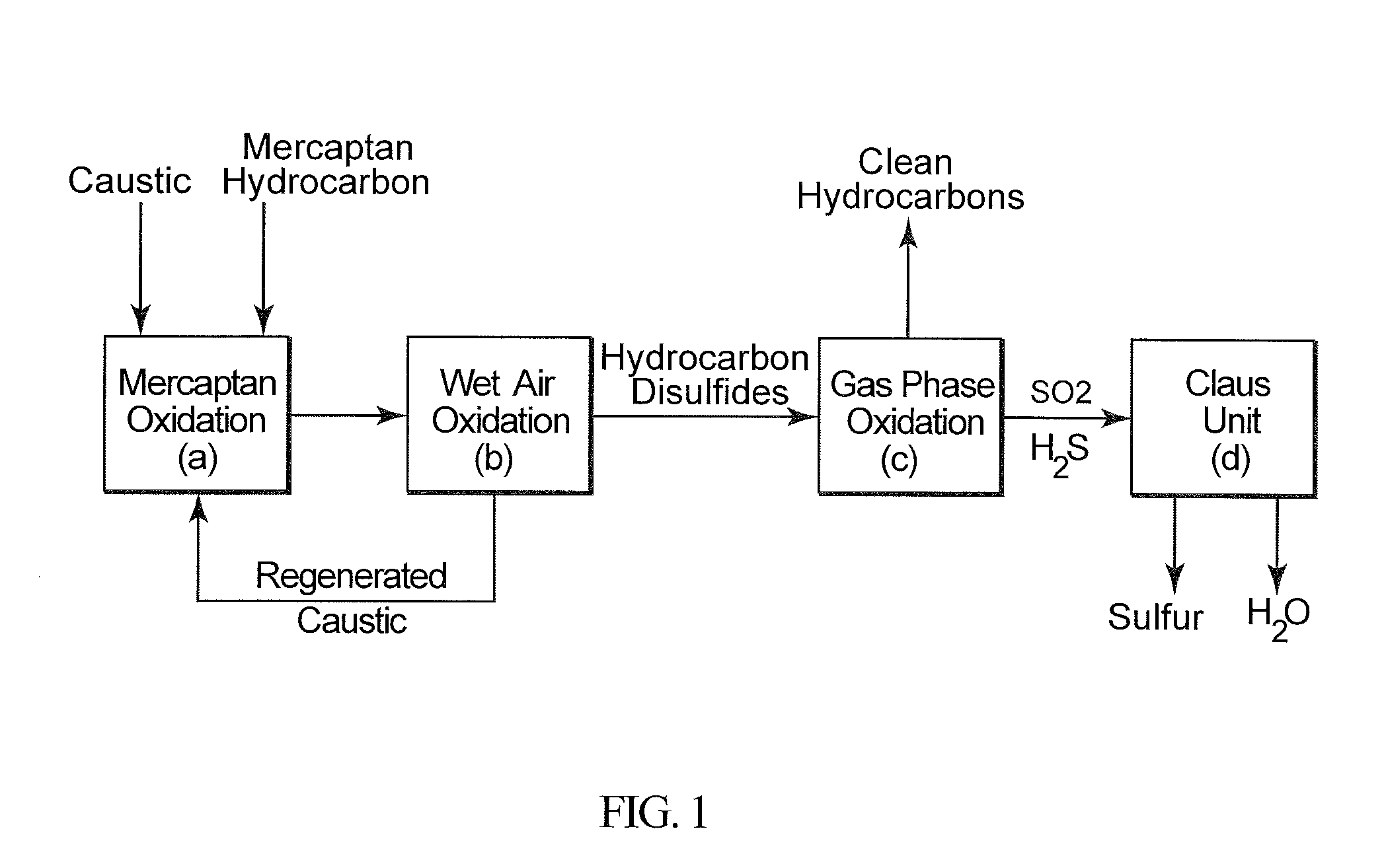
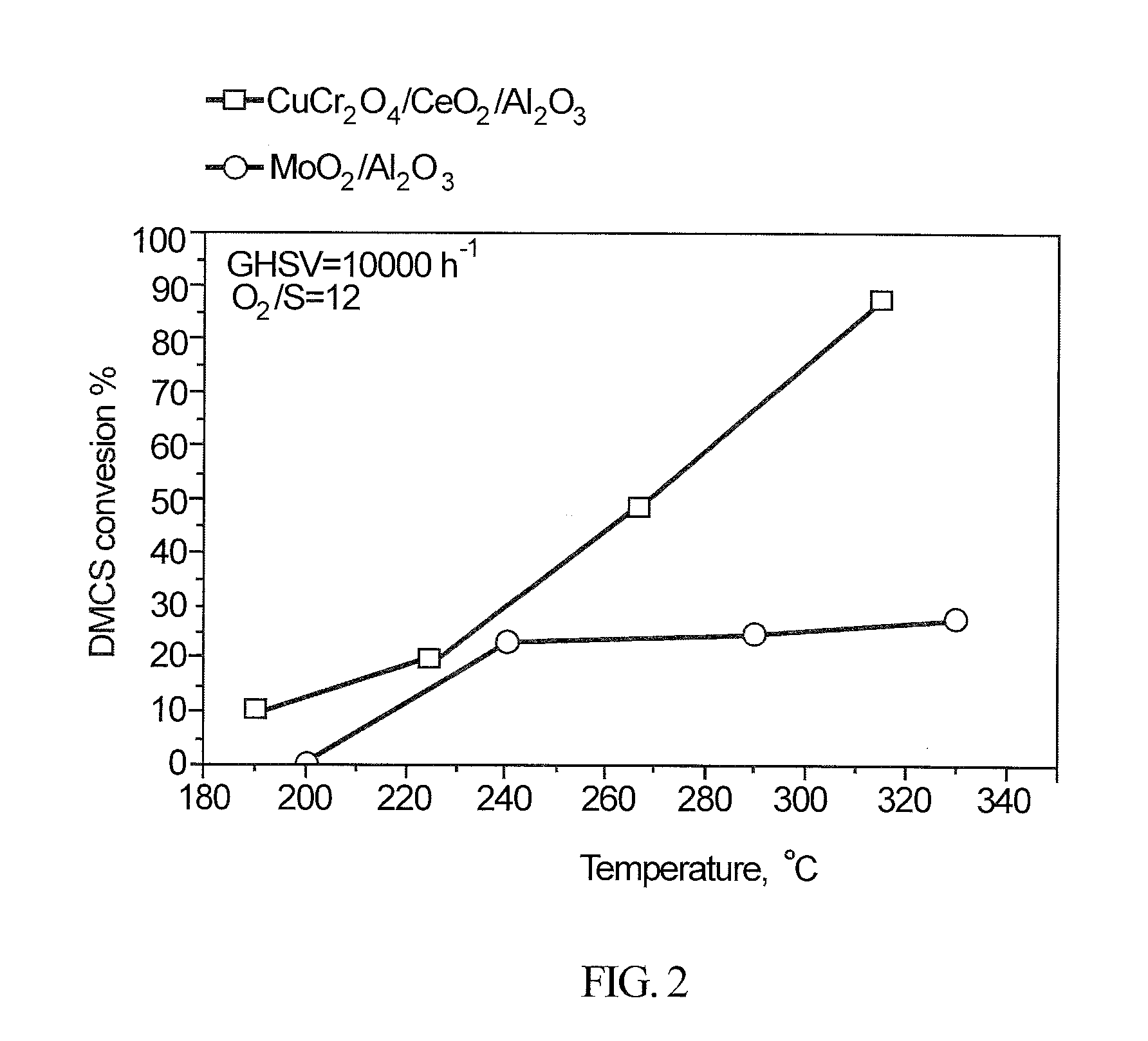
Integrated hydrocarbon desulfurization with oxidation of disulfides and conversion of so2 to elemental sulfur
ActiveUS20160145502A1Refining with oxygen compoundsDispersed particle separationLiquid hydrocarbonsCatalytic oxidation
A process to produce a sulfur-free hydrocarbon product stream from a liquid hydrocarbon disulfide product, e.g., of the Merox Process, includes subjecting the hydrocarbon disulfide to a catalytic oxidation step to produce SO2 which is separated from the remaining desulfurized hydrocarbons that form the clean sulfur-free hydrocarbon product stream; the SO2 is introduced into a Claus processing unit with the required stoichiometric amount of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas to produce elemental sulfur.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Process for preparing basic secondary Zn battery negative electrode active compound
InactiveCN1521876AElectrode manufacturing processesAlkaline accumulator electrodesZincateChemical computing
The present invention discloses a process for preparing zinc negative electrode active calcium zincate, wherein ZnO anc Ca(OH)2 are weighed by stoichiometric calculation and added into KOH solution for stirring, the temperature is controlled between the range of 70-100 degree C., stirring uninterruptedly for more than 72hrs, ageing for over 60 hrs in the environment of 70-95 degree C., cooling, filtering, washing to neutral, drying at the temperature of 105-110 degree C., grinding, screening by 300 mesh to obtain calcium zincate which can be used as the negative pole active compound for the Zn-Ni secondary cell.
Owner:江苏海四达集团有限公司
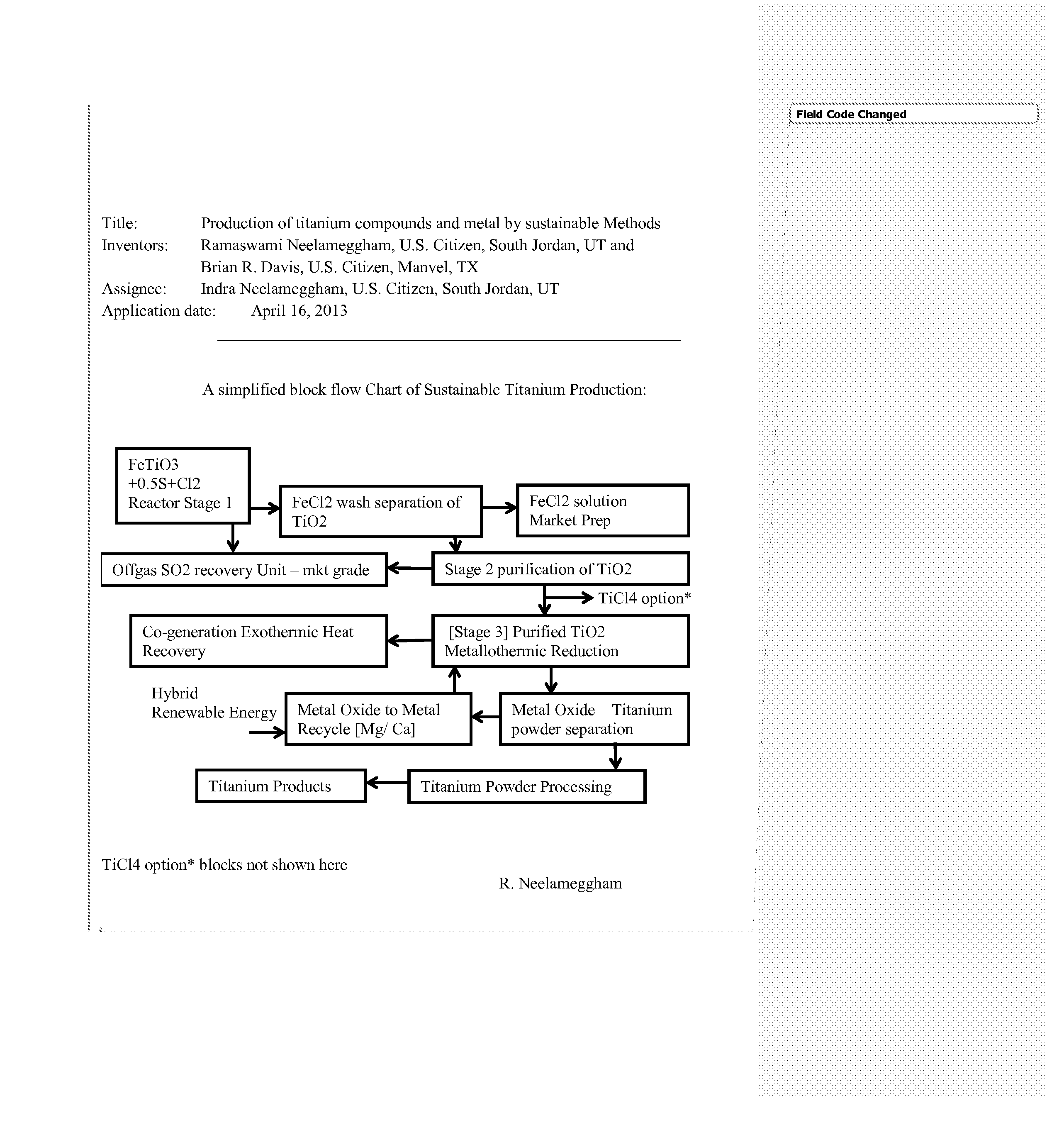
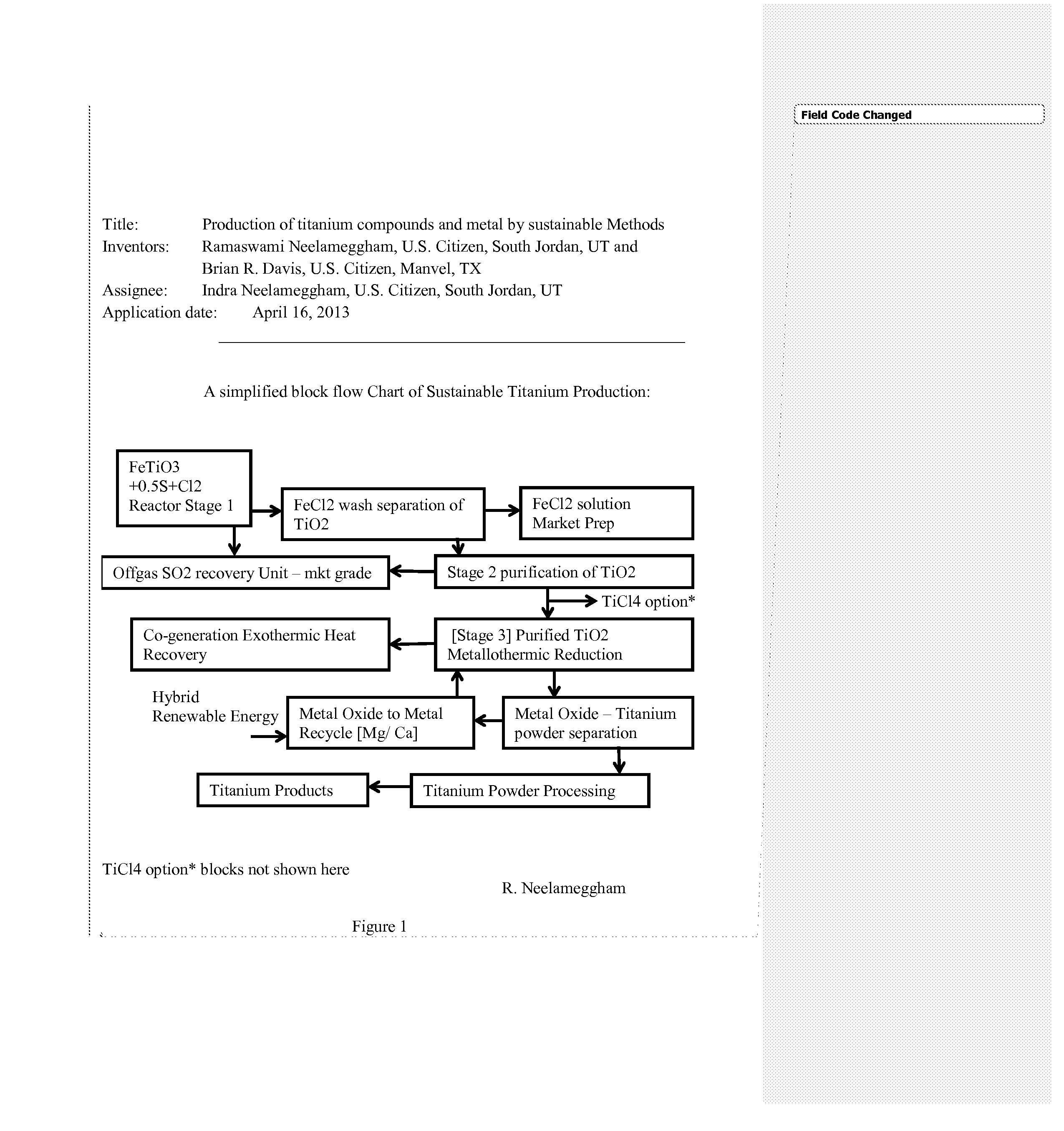
Production of titanium compounds and metal by sustainable Methods
InactiveUS20140308197A1Low carbon dioxide footprintLow costMagnesium chloridesBlast furnace detailsTitanium metalSustainable process
A unique production of titanium compounds and metal by sustainable methods using iron-titanium oxide starting material such as ilmenite, leucoxene, or rutile is described. Here the iron-titanium oxide compound is prepared by converting the iron portion of the compound to ferrous chloride at low temperatures by using close to stoichiometric amounts of sulfur and chlorine required for all the iron oxides and the other non-titanium oxides. The ferrous chloride thus formed is removed recovering a marketable product of ferrous chloride and the ‘sustainable’ titanium oxide starting material by additional process steps. This can be converted to ‘sustainable’ titanium metal, or titanium tetra-chloride by process shown herein for further conversions to titanium dioxide pigment by present chloride process or supplied to existing titanium sponge producers, benefitting them in having a ‘sustainable process’.
Owner:NEELAMEGGHAM INDRA
Preparation method of alkaline secondary zinc battery negative electrode active substance
InactiveCN1462083AGood formabilityImprove formingAlkaline accumulatorsZinc compoundsZincateChemical computing
An active substance (calcium zincate) for the negative electrode (Zn) of secondary alkaline battery is prepared from ZnO and Ca(OH)2 through proportioning, adding them to KOH solution, stirring at 75-95 deg.C for at least 72 hr. ageing at 75-95 deg.c for at least 60 hr, cooling, filtering, washing, baking at 105-110 deg.c, grinding and sieving by 300 meshes.
Owner:江苏海四达集团有限公司
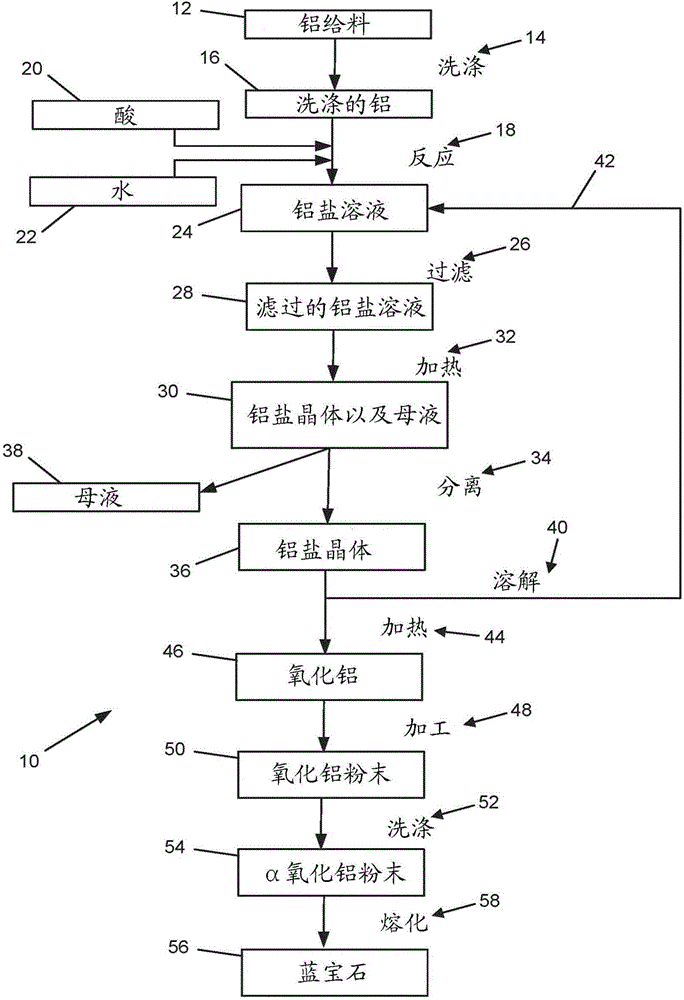
Process for making high-purity aluminum oxide
InactiveCN104903241AAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthCrucibleChemical computing
A method comprising contacting high-purity acid, high-purity aluminum, and high-purity water to form a first solution in a heated non-contaminating vessel, wherein the aluminum is employed in at least a stoichiometric amount relative to the acid, heating the first solution in a non-contaminating container, to provide a mother liquor and solid aluminum salts, separating the solid aluminum salts from the mother liquor, heating the solid aluminum salts in a non- contaminating crucible, to provide alpha aluminum oxide, and, optionally, washing the alpha aluminum oxide with high-purity water after some or all of the heating of the solid aluminum salts to provide the alpha aluminum oxide.
Owner:POLAR SAPPHIRE
High-throughput printing of semiconductor precursor layer by use of chalcogen-rich chalcogenides
A high-throughput method of forming a semiconductor precursor layer by use of a chalcogen-rich chalcogenides is disclosed. The method comprises forming a precursor material comprising group IB-chalcogenide and / or group IIIA-chalcogenide particles, wherein an overall amount of chalcogen in the particles relative to an overall amount of chalcogen in a group IB-IIIA-chalcogenide film created from the precursor material, is at a ratio that provides an excess amount of chalcogen in the precursor material. The excess amount of chalcogen assumes a liquid form and acts as a flux to improve intermixing of elements to form the group IB-IIIA-chalcogenide film at a desired stoichiometric ratio, wherein the excess amount of chalcogen in the precursor material is an amount greater than or equal to a stoichiometric amount found in the IB-IIIA-chalcogenide film.
Owner:VAN DUREN JEROEN K J +2
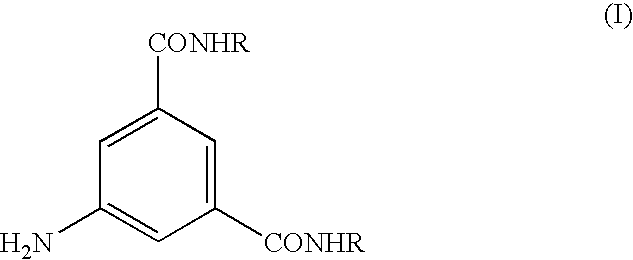
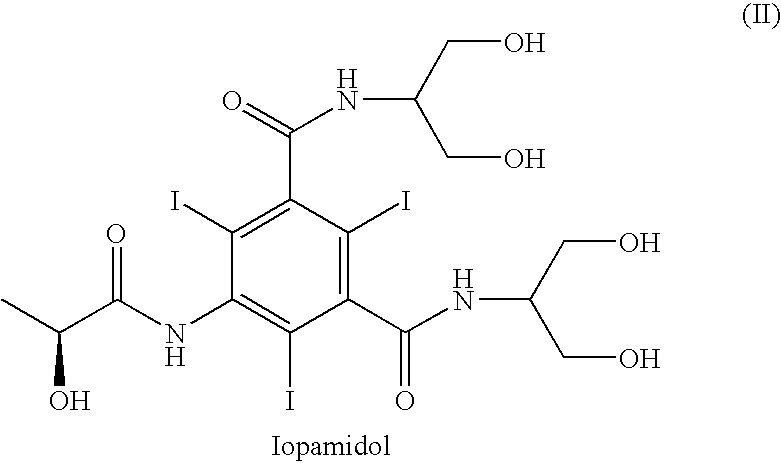
Process for the preparation of N,N-substituted 5-amino-1,3-benzenedicarboxamides
InactiveUS7244864B2Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationChemical computingPhotochemistry
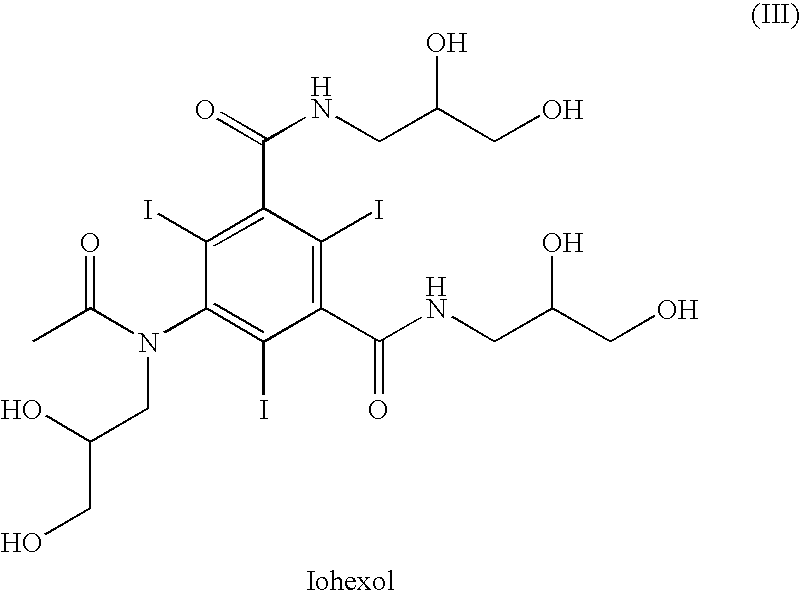
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of a compound of formula (I), wherein R represents a 2,3-dihydroxy-1-propyl or a 1,3-dihydroxy-2-propyl radical, via direct amidation of a dialkyl ester of 5-amino-1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid of formula (V), wherein R1 represents a straight or branched (C1-C4)-alkyl group, with at least the stoichiometric amount of an amine of formula H2NR.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Gas Turbine Topping in Sulfuric Acid Manufacture
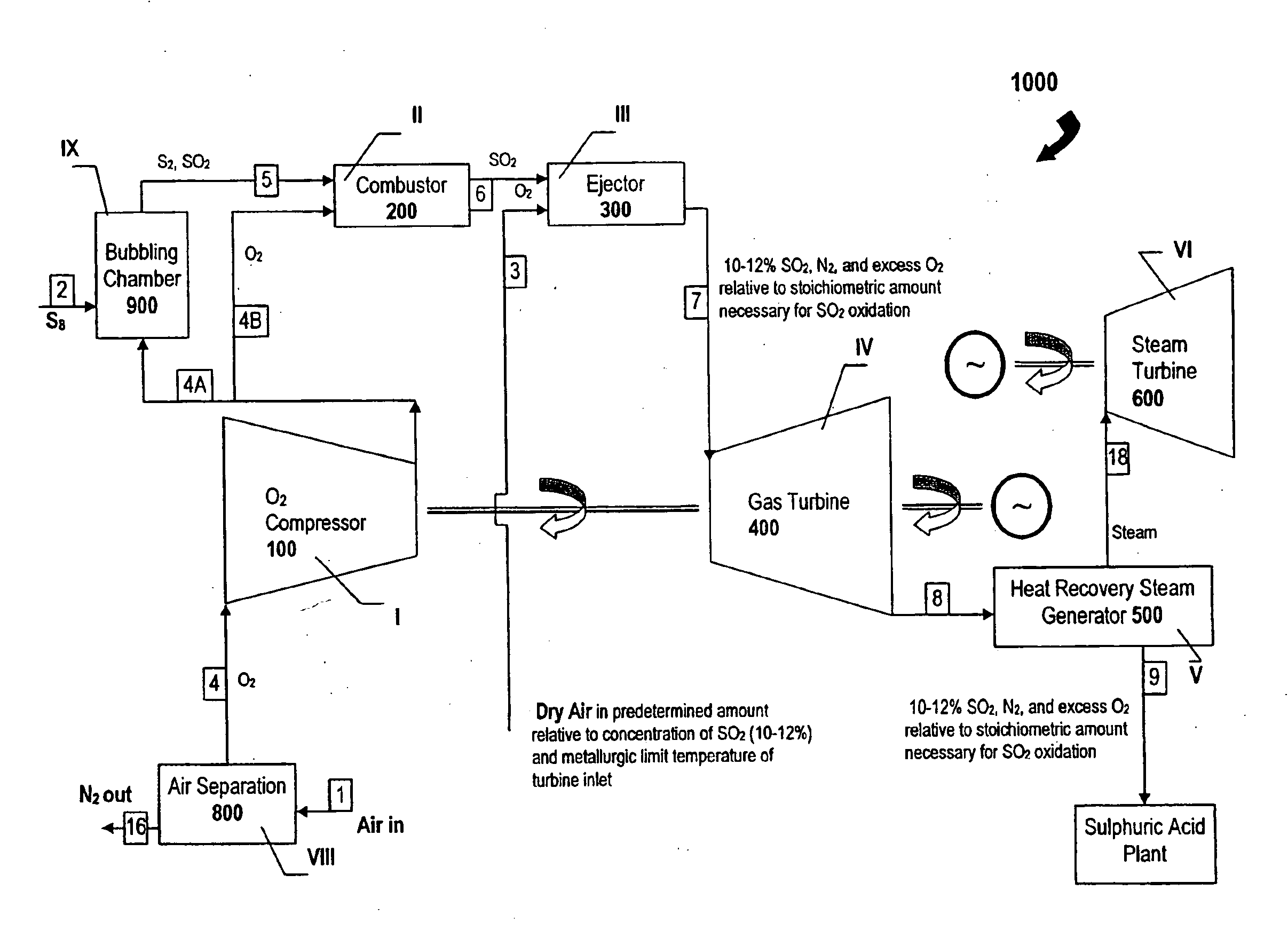
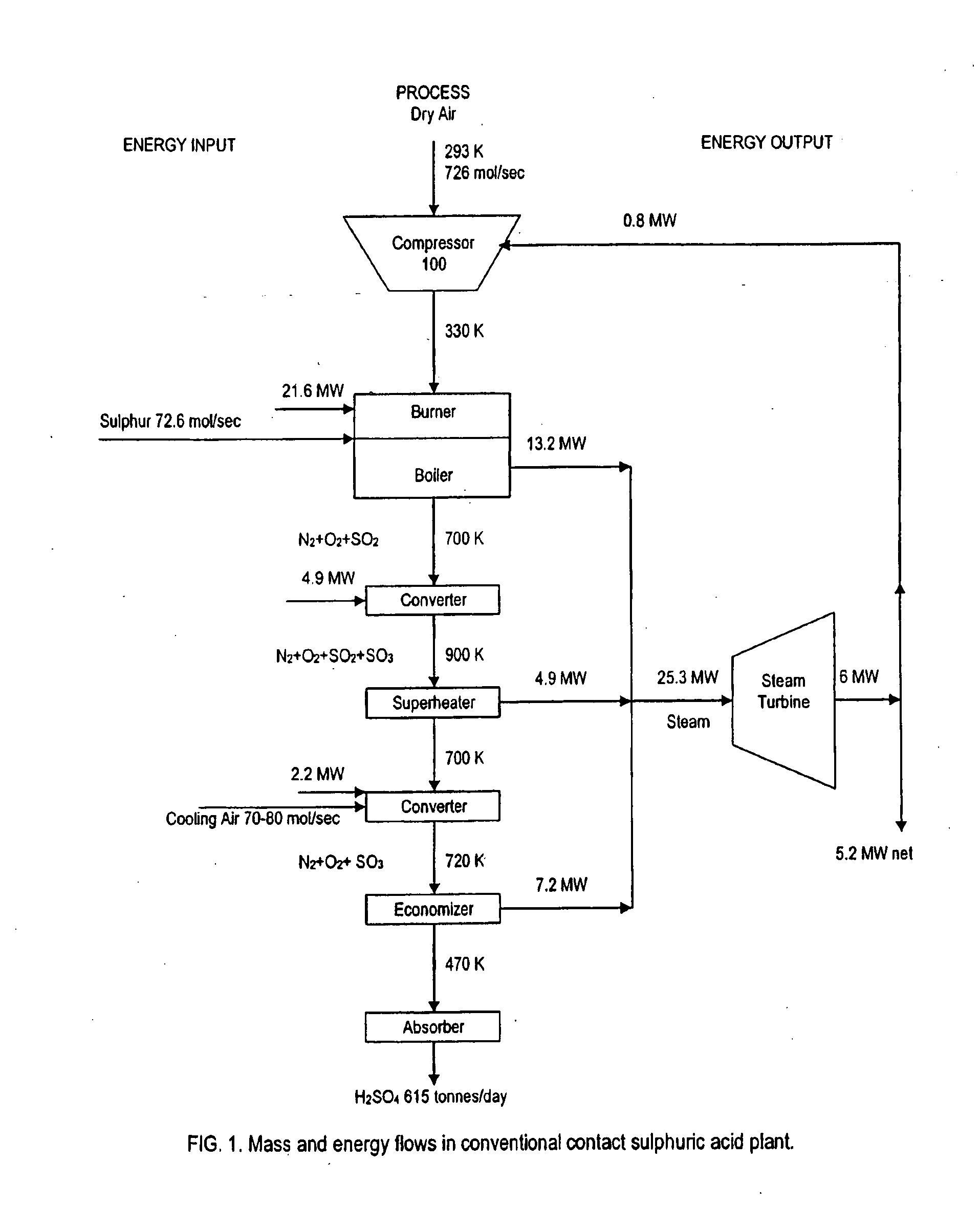
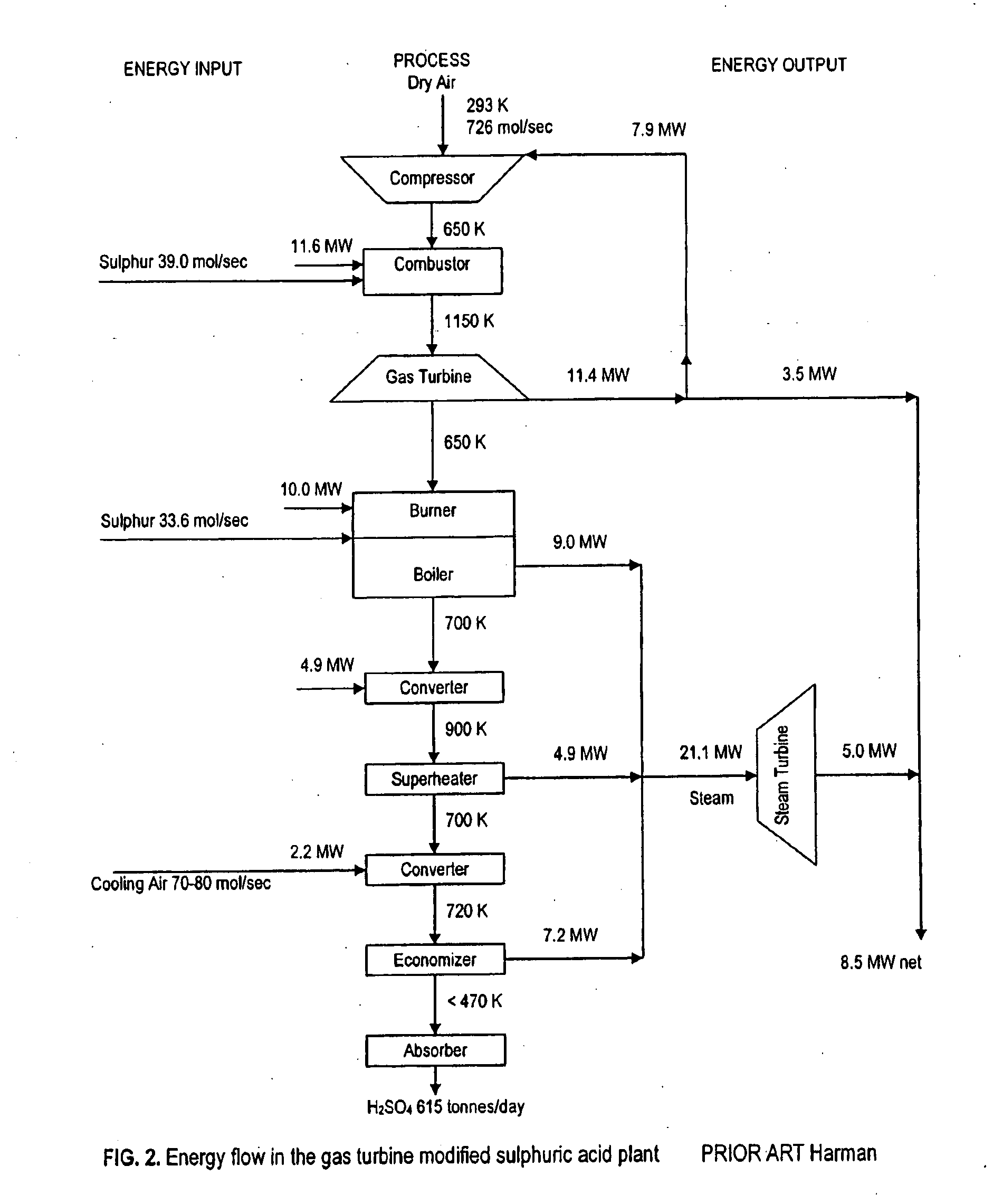
A method of generating electrical power using sulfur, the method having the steps of combusting oxygen with a stoichiometric quantity of sulfur comprising predominantly diatomic sulfur to generate hot sulfur dioxide gas; and mixing a cooling gas substantially cooler than the hot sulfur dioxide gas with the hot sulfur dioxide gas to produce a mixed working gas for driving a gas turbine, the mixed working gas having a temperature less than a maximum allowable temperature determined by a metallurgic limit of turbine blades in the gas turbine, whereby the gas turbine generates electrical power.
Owner:WOJAK BOGDAN
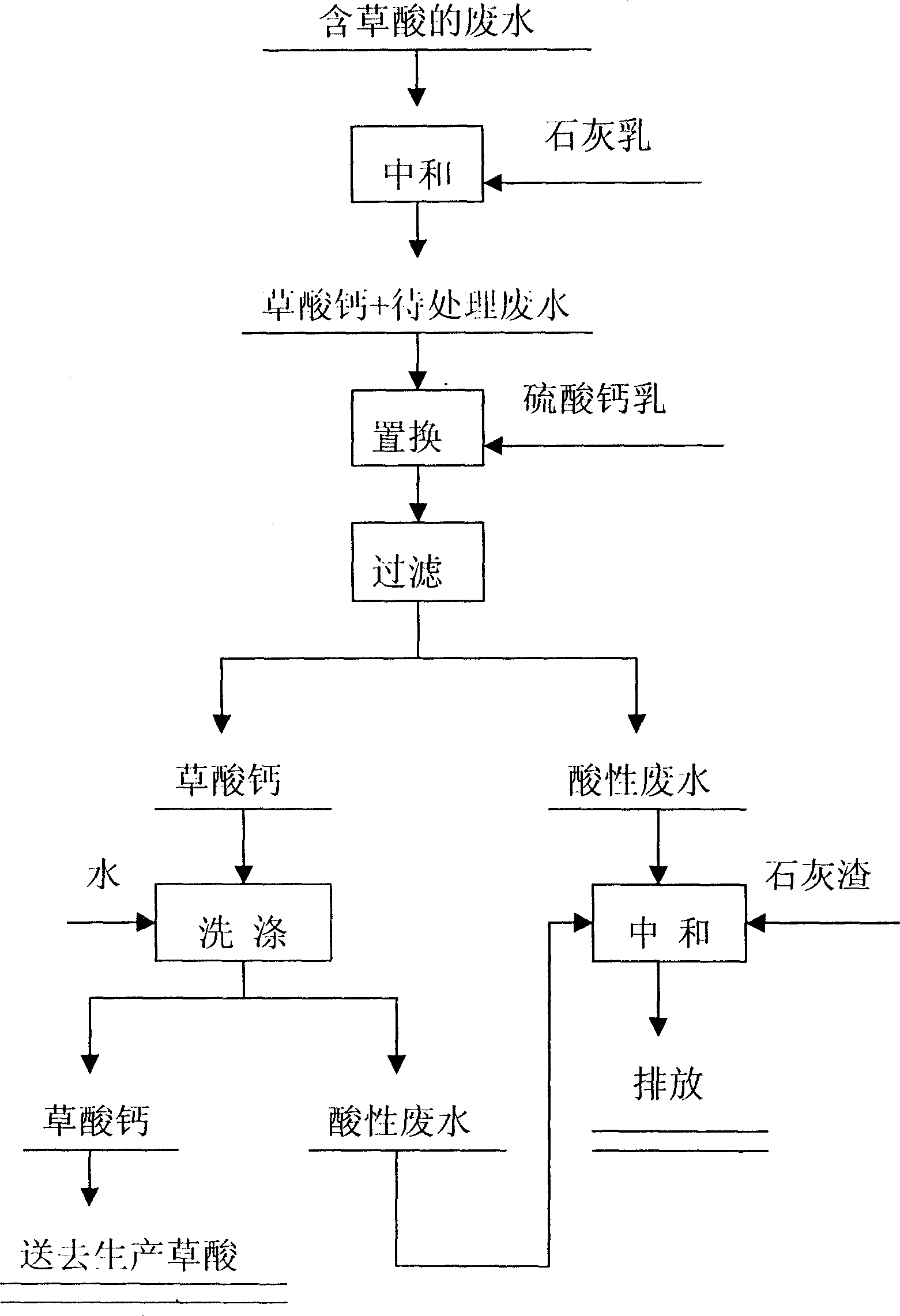
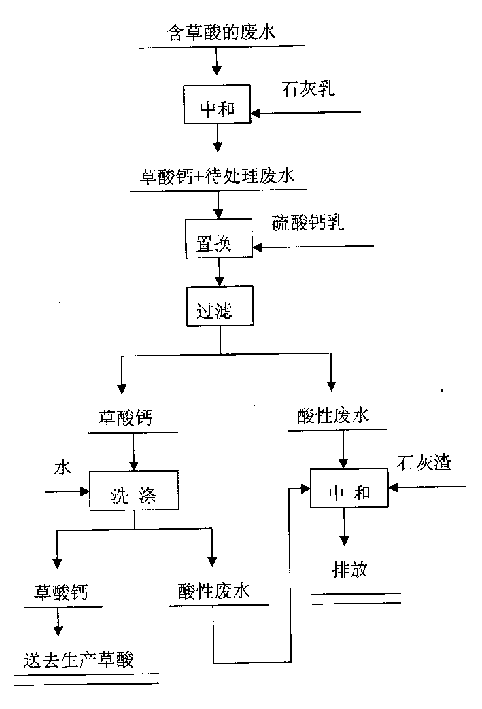
Method for reclaiming calcium oxalate from sewage comprising oxalic acid
InactiveCN1524841AHigh recovery rateAvoid pollutionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationSulfateReaction temperature
The invention relates to a process for reclaiming valuable substance from waste water, in particular a process for reclaiming calcium oxalate from waste water containing oxalic acid, characterized in that the process comprises the two steps of lime cream neutralization and calcium sulfate substitution, wherein the step of lime cream neutralization comprises charging lime cream into waste water containing oxalic acid for neutralization reaction, controlling the reaction temperature to be 80-90 deg. C, when the content of oxalic acid roots in the waste water amounts to 22-25 g / L, ceasing the charging of lime cream, while the calcium sulfate substitution step comprises charging calcium sulfate cream exceeding stoichiometric calculation amount into the waste water to be processed for displacement reaction, controlling the reaction temperature to be 95-98 deg. C, thus obtaining calcium oxalate and acid wastewater.
Owner:周建华
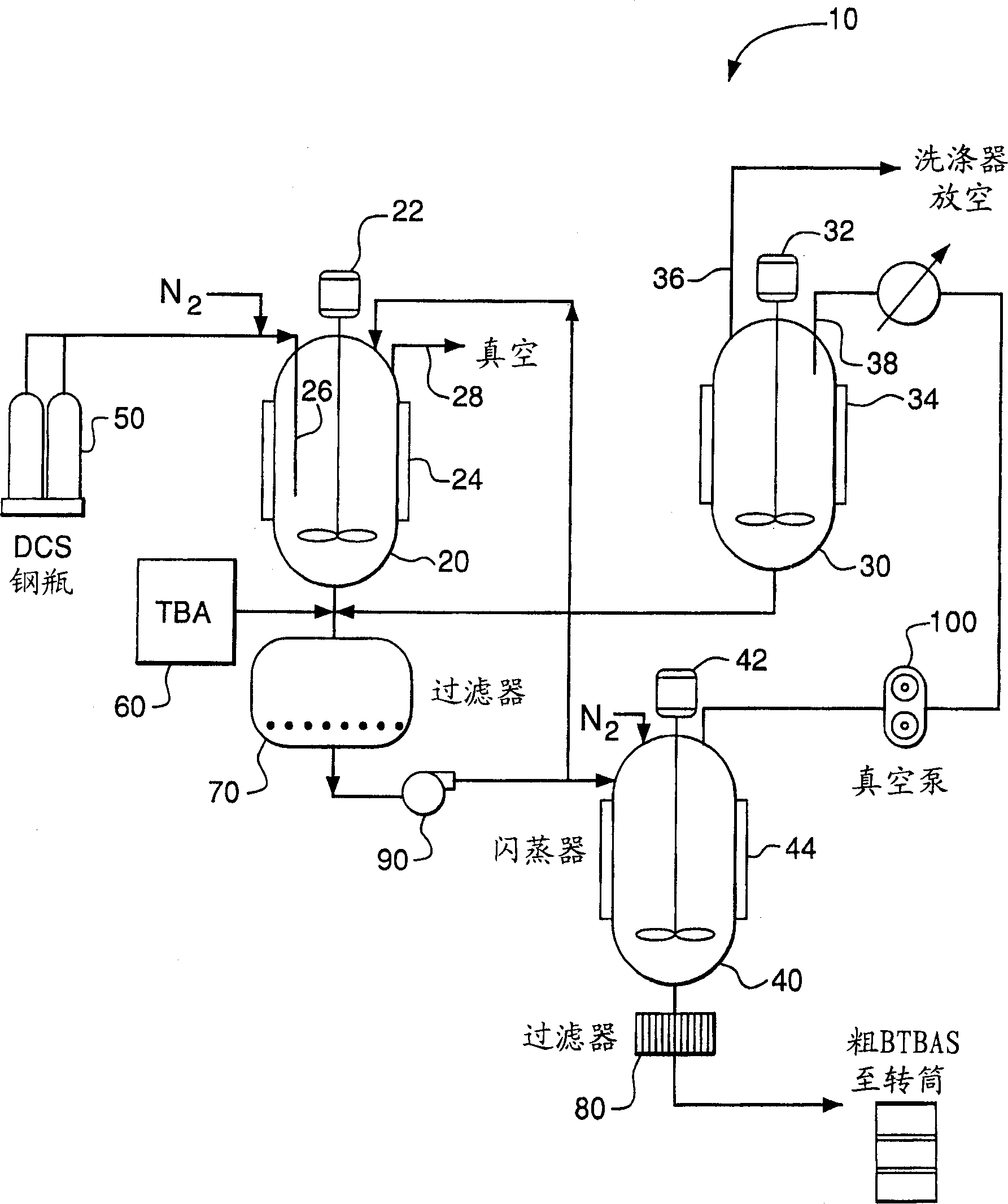
Producing and purifying method of bi (Tert-butyl amino) silane
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Preparation of Complex Metal Oxides
The present invention provides a process for making a complex metal oxide comprising the formula AxByOz. The process comprises the steps of: (a) reacting in solution at a temperature of between about 75° C. to about 100° C. at least one water-soluble salt of A, at least one water-soluble salt of B and a stoichiometric amount of a carbonate salt or a bicarbonate salt required to form a mole of a carbonate precipitate represented by the formula AxBy(CO3)n, wherein the reacting is conducted in a substantial absence of carbon dioxide to form the carbonate precipitate and wherein the molar amount of carbonate salt or bicarbonate salt is at least three times the stoichiometric amount of carbonate or bicarbonate salt required to form a mole of the carbonate precipitate; and (b) reacting the carbonate precipitate with an oxygen containing fluid under conditions to form the complex metal oxide.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
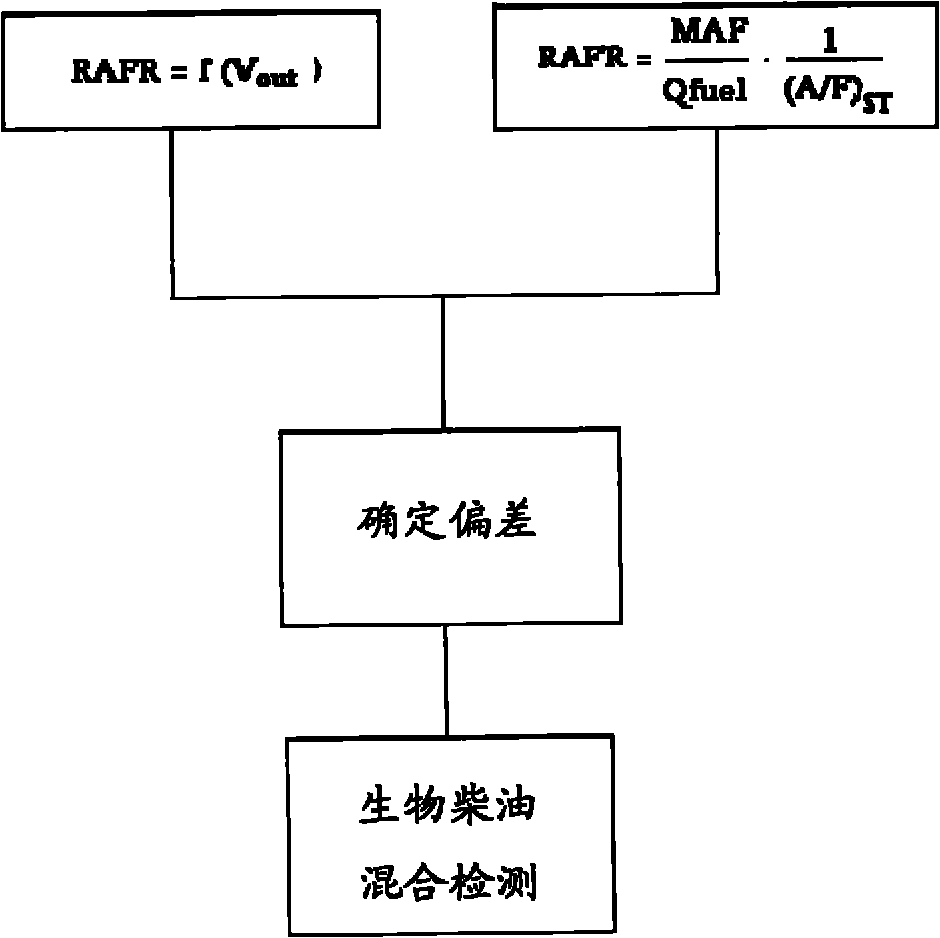
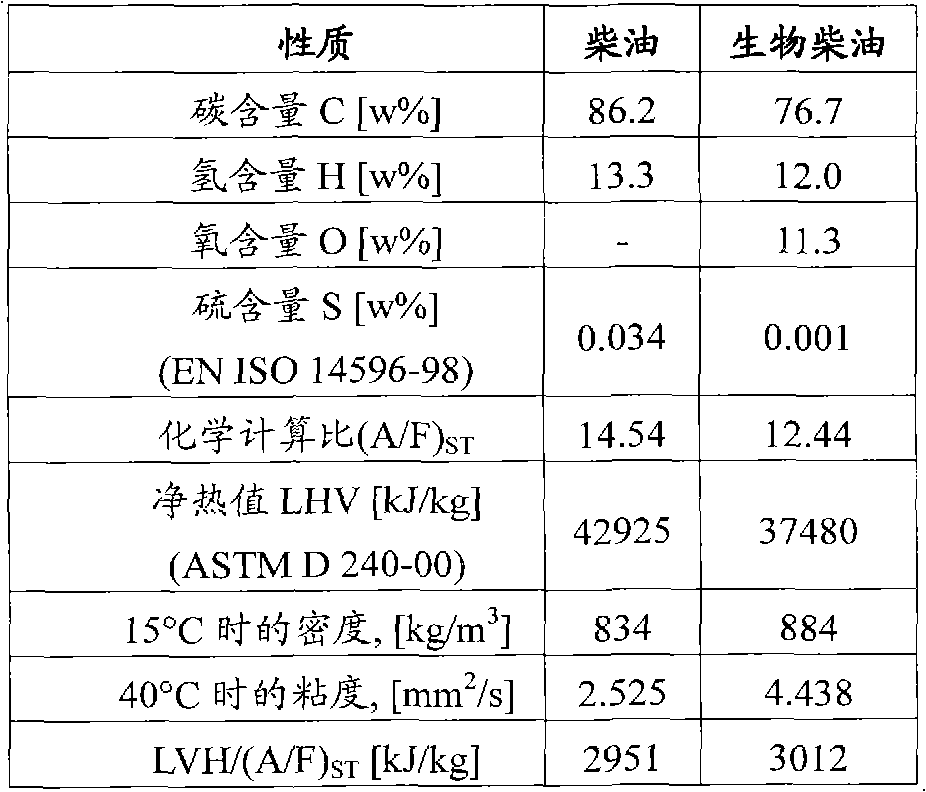
Method for biodiesel blending detection based on relative air-to-fuel ratio estimation
InactiveCN102042105AElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBiodieselInternal combustion engine
A method is provided for biodiesel blending detection in an internal combustion engine that includes, but is not limited to a first evaluation of the relative air-to-fuel ratio (RAFR) by means of a first sensor whose output whose output is representative of the actual RAFR value, in order to use such first evaluation as a reference value, a second evaluation of the relative air-to-fuel ratio (RAFR) performed measuring mass air flow (MAF), injected fuel quantity (Qfuel) and stoichiometric air-to-fuel (A / F)ST ratio of petrodiesel and carrying out said second evaluation by means of the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) of the engine, and determining discrepancies of values obtained from the second evaluation compared with values obtained from the first evaluation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for producing organosilicon compounds which have amino groups
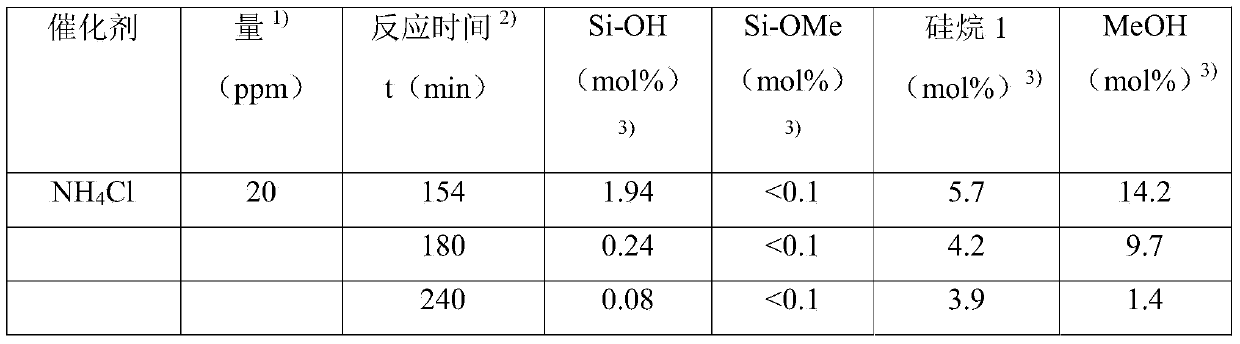
The invention relates to a method for producing amino-functional polyorganosiloxanes, wherein (A) organosiloxanes which contain Si-OH groups are reacted with (B) at least stoichiometric quantities of mono-alkoxy (amino-alkyl) silanes, with respect to the Si-OH groups, (C) in the presence of at least one acid as a catalyst.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Method for producing crude sodium L-ascorbate by recovering crude vitamin C mother liquor
InactiveCN103102335AHigh product yieldImprove product qualityOrganic chemistrySodium bicarbonateVitamin C
The invention discloses a method for producing crude sodium L-ascorbate by recovering crude vitamin C mother liquor. The method comprises the steps of: destaining crude vitamin C mother liquor through a macroporous adsorption resin, concentrating, crystallizing and centrifuging a destaining solution to obtain a crude vitamin C mother liquor recovered product, crushing and drying the mother liquor recovered product through a micro powder drying machine, performing esterification reaction with methanol, controlling the burdening ratio of mother liquor recovered product (weight) to methanol (volume) in the esterification reaction of 1: 7, reacting for 4 hours, wherein the esterification reaction temperature at the first hour is 68 DEG C, the esterification reaction temperature at the second hour is 60 DEG C, the esterification reaction temperature at the third hour is 55 DEG C and the esterification reaction temperature at the fourth hour is 50 DEG C, adding sodium bicarbonate with stoichiometric amount to perform conversion reaction to obtain intermediate crude sodium L-ascorbate, and then changing over to the production process of normal vitamin C. The production yield and quality of the crude sodium L-ascorbate are improved, the problem of the accumulation of a mother liquor recovered product is solved, and the production process is simplified.
Owner:DSM JIANGSHAN PHARMACEUTICAL (JIANGSU) CO LTD
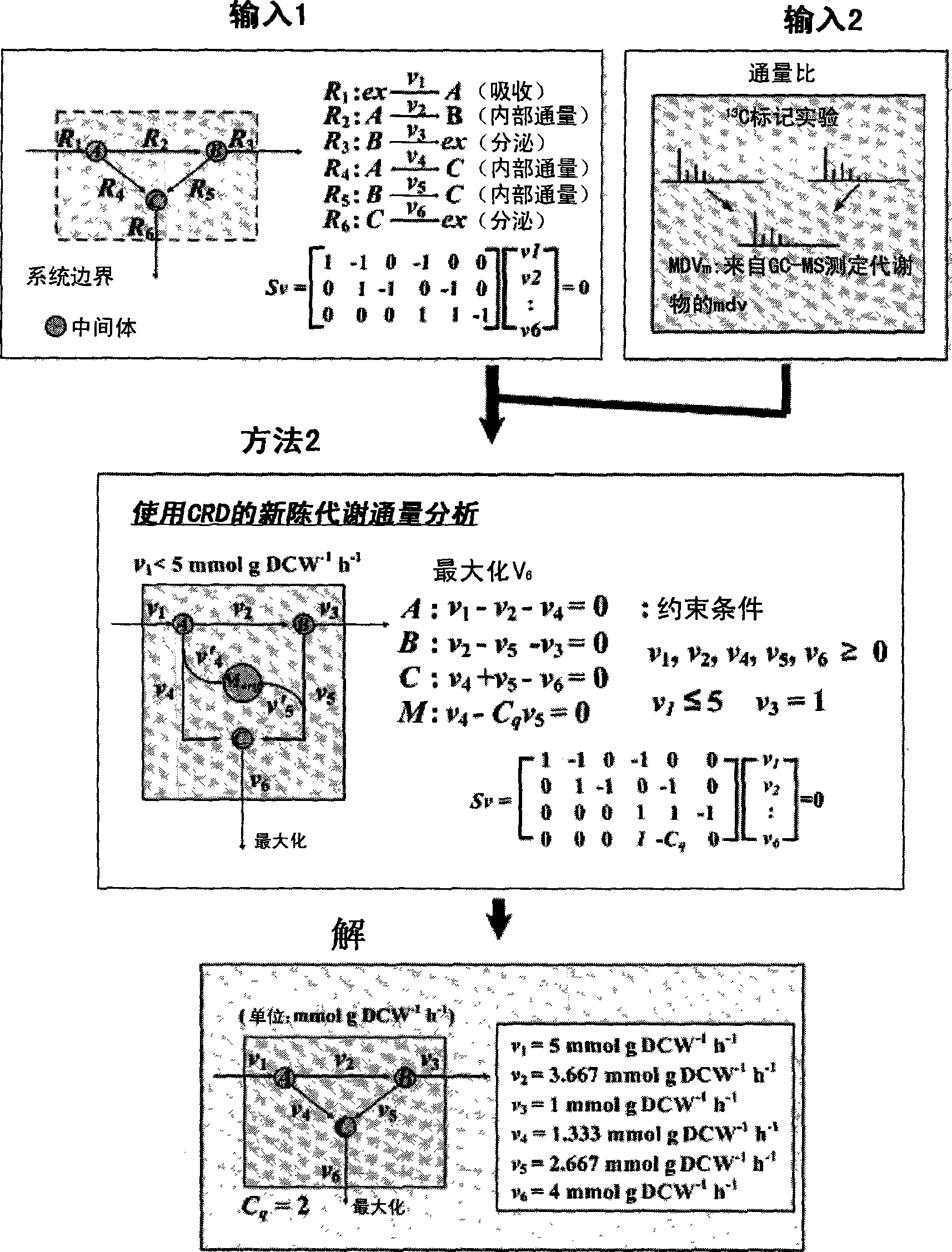
Method for analyzing metabolites flux using converging ratio determinant and split ratio determinant
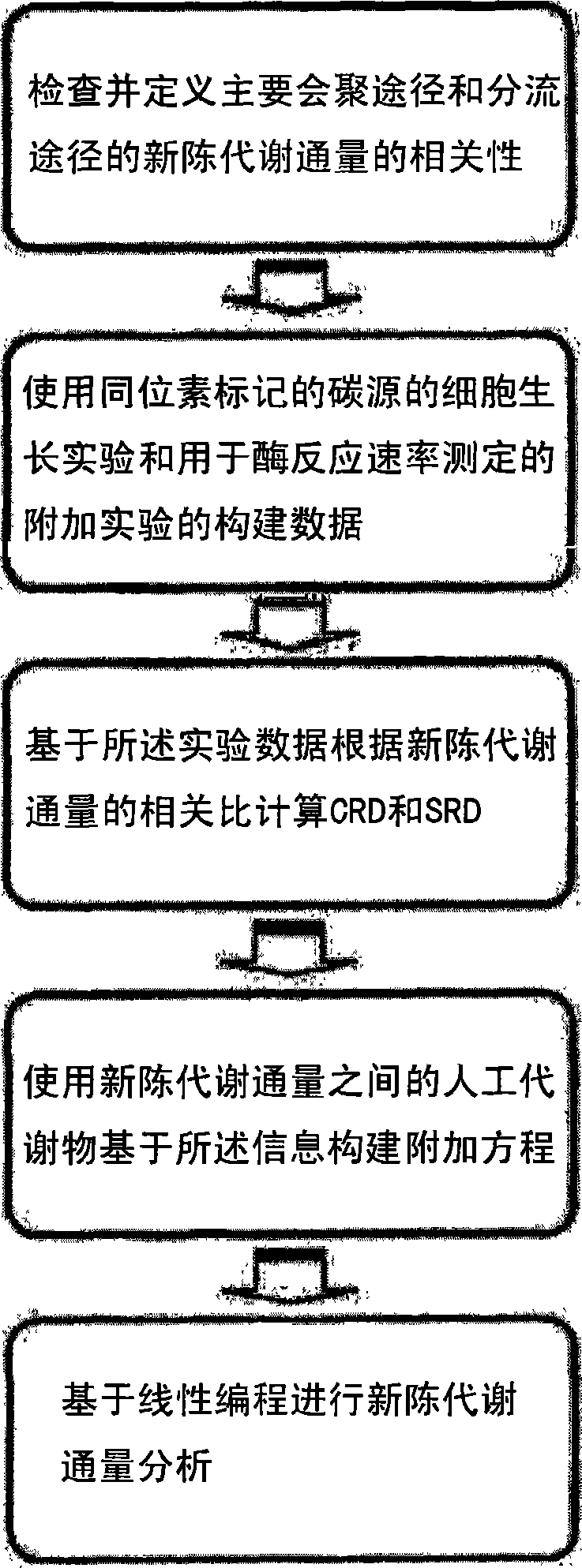
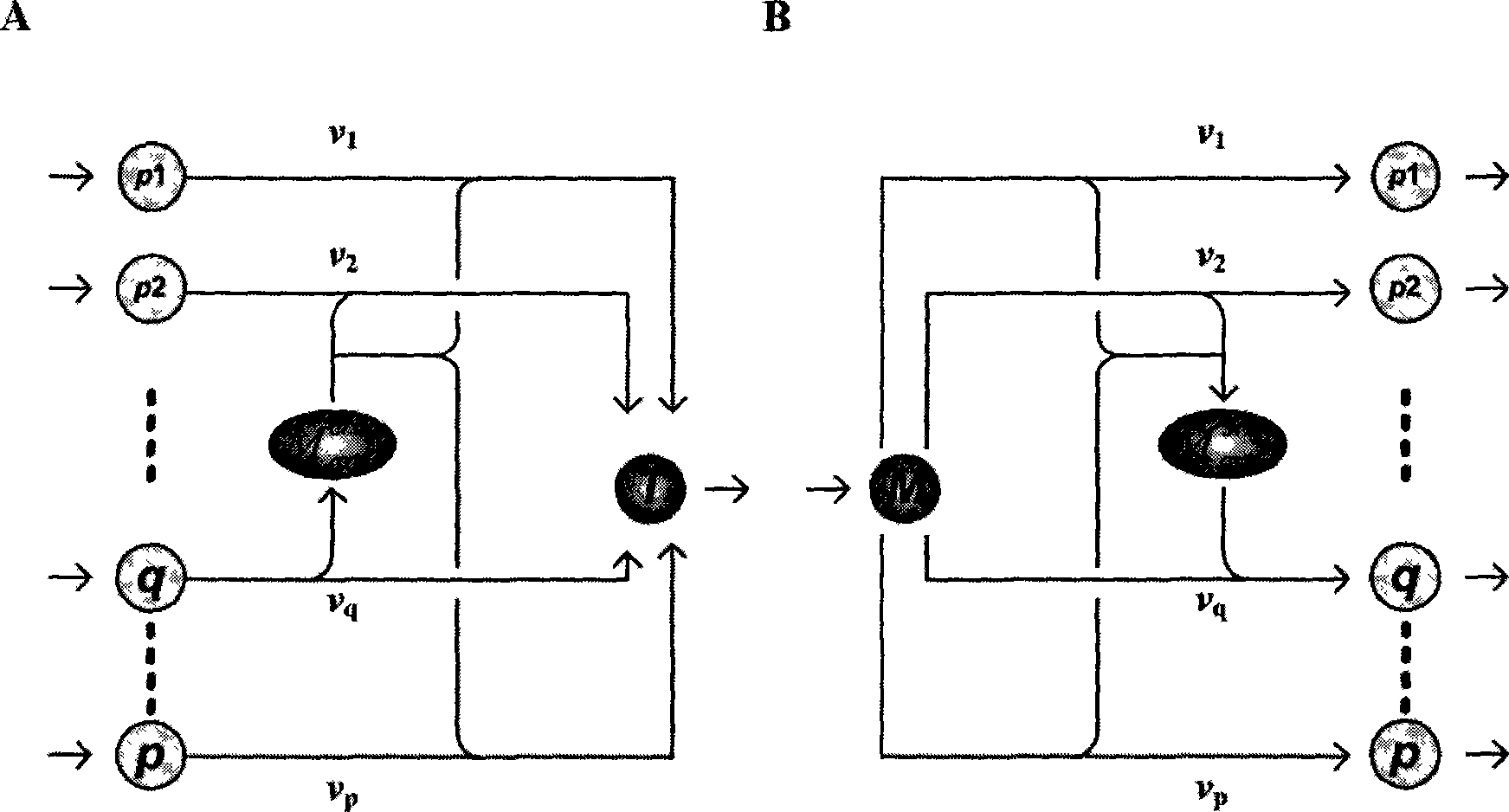
The present invention relates to a method for analyzing metabolic flux using CRD and SRD. Specifically, the method comprising: selecting a specific target organism, constructing the metabolic network model of the selected organism, identifying the correlations between specific metabolic fluxes in the metabolic network model, defining the correlation ratios as CRD and SRD, determining the correlation ratios of the metabolic fluxes through the experiment for measuring metabolic flux ratios, modifying a stoichiometric matrix with the determined CRD, SRD and correlation ratios, and applying the modified stoichiometric matrix of the metabolic network model for linear programming. According to the inventice method, the correlation between influent / effluent metabolic fluxes with respect to specific metabolites in target organisms (including E. coli), the genome-scale metabolic network model of which was constructed, can be determined as relative ratio using useful information obtained from various experiments, including a growth experiment using a radioactive isotope-labeled carbon source and an assay for measuring enzymatic reaction. Thus, limit values from various experiments can be effectively applied, so that internal metabolic flux can be quantified and analyzed in a more accurate and rapid manner.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing organosilicon compounds having amino groups
The object of the invention is therefore to provide a method for the preparation of amino-functional polyorganosiloxanes, in which (A) organosiloxanes containing Si—OH groups are reacted with (B) at least stoichiometric amounts of monoalkoxy(aminoalkyl) silanes with respect to the Si—OH groups, wherein catalytically active additives selected from acid, base or metal-organic compound are used in amounts of less than 0.1 ppm acid, less than 30 ppm base and less than 0.4% metal-organic compound.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
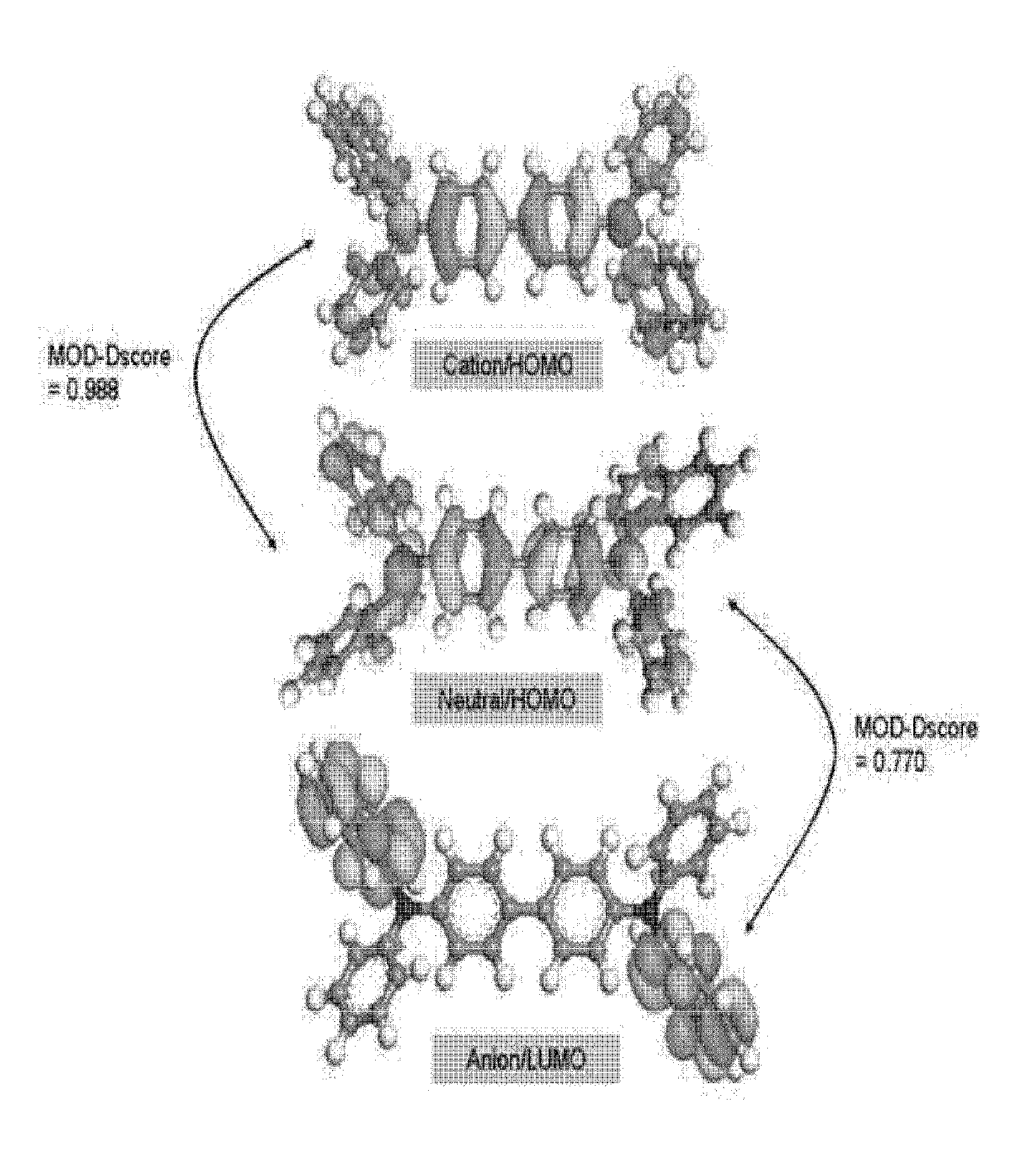
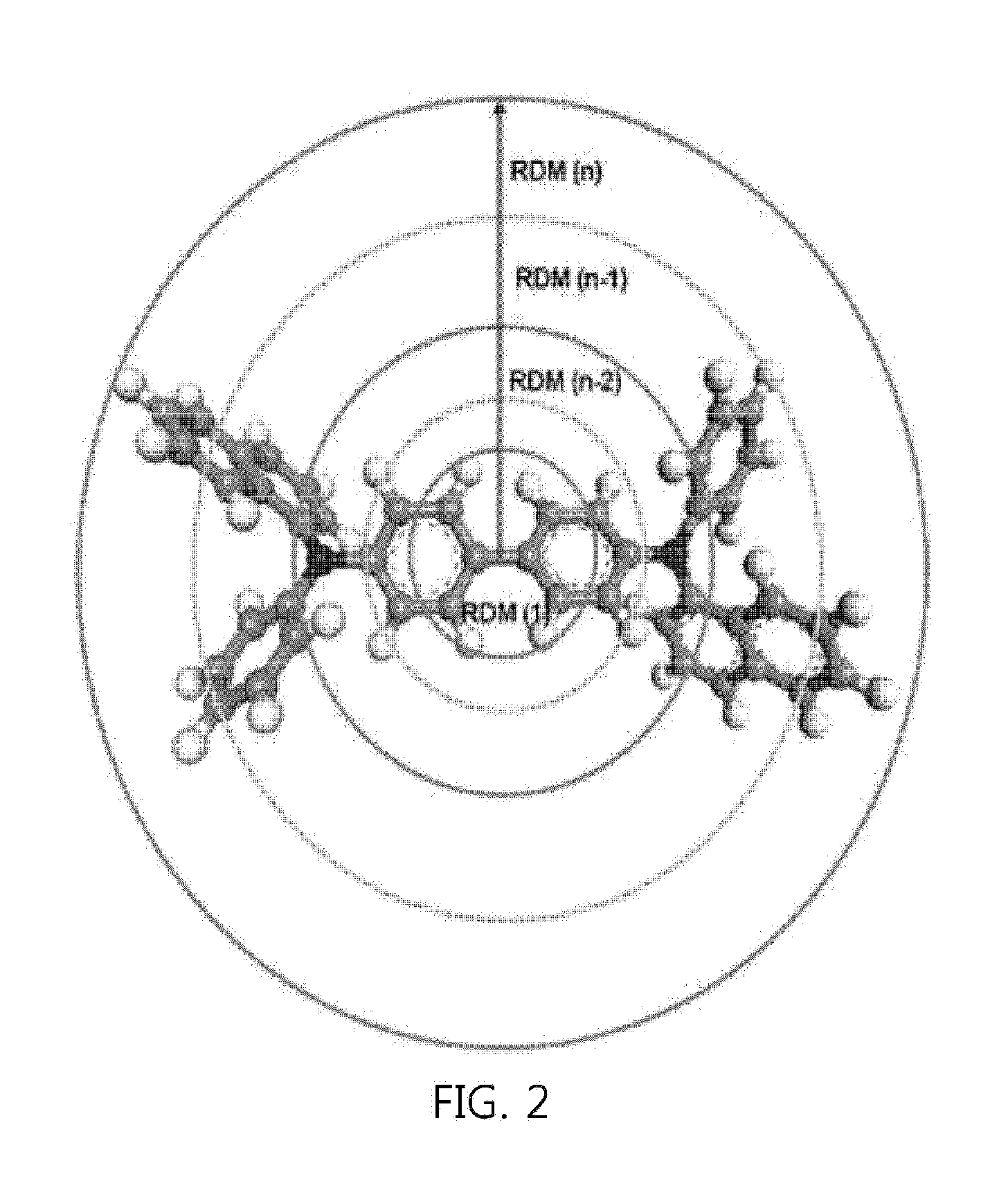
Quantitative comparative analysis method for molecular orbital distribution, and system using same
InactiveUS20160371467A1Organic chemistry methodsComputational theoretical chemistryQuantum chemistryUsage analysis
Disclosed herein are a method for quantitatively analyzing a molecular orbital distribution, and a quantitative analysis system of molecular orbital distributions using the same. The method comprise a) selecting two molecular orbitals to be compared for molecular orbital distributions and computing molecular orbital distributions by quantum chemistry calculation; b) calculating structural properties of each molecular orbital by means of an RDM (radially discrete mesh) calculation method, followed by matching with the molecular orbital distributions computed in step a) to obtain molecular orbital distributions according to the structural properties; and c) comparing the two molecular orbital distributions according to structural properties, obtained by RDM in step b), using a profiling method.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com