Novel silizane and/or polysilazane compounds and methods of making
A technology for polysilazane and silazane is applied in the field of preparation of aminolysis products, and can solve the problems of difficult pyrolysis to form ceramic materials, low yield of polysilazane, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0139] Ammonolysis of methyl dichlorosilane using the inventive method
[0140] The 6 liter pressure reactor was filled with 2.5 liters of commercial grade anhydrous liquid ammonia. Ammonia was transferred directly from the bulk tank without additional purification. The pressure reactor is equipped with thermometer and pressure gauge. For mixing, a circulating reflux pump draws liquid from the bottom of the reactor and injects it below the surface of the liquid ammonia in the upper part of the reactor.
[0141] Methyldichlorosilane (237.2 g, 2.06 mol) was kept in a glass pressure tube, blanketed with nitrogen, and maintained at 100 psig above the expected reactor pressure.
[0142] The ammonia was vented from the reactor to cool the system to -6°F. Methyldichlorosilane was added to the reactor in batches until the heat released by the reaction raised the pressure in the reactor to a predetermined height (about 70 psi). The methyldichlorosilane feed was then stopped and the r...
Embodiment 3
[0152] Preparation and polymerization of tetramethyldisilazane using the method of the present invention
[0153] The 6 liter pressure reactor was filled with 4 liters of commercial grade refrigerated (-30°) anhydrous liquid ammonia. About 1 kg (7.5 moles) of dimethylchlorosilane was added to the addition tank, which was pressurized with nitrogen to about 160 psi. Dimethylchlorosilane is added to anhydrous liquid ammonia using the pressure difference between the two tanks. After about half of the halosilane had been charged with anhydrous liquid ammonia, the reactor was vented to reduce the pressure and further freeze the system. The remainder of the halosilane was added over about 30 minutes to complete the addition. The reaction vessel was stirred for about 10 minutes, then the stirring was stopped. The reaction mixture spontaneously separated into two distinct layers. Samples are taken from the upper layer and any dissolved ammonia is distilled off. A clean sample was ...
Embodiment 4
[0158] Further Polymerization of a Known Silazane - Methylhydromethylvinylpolysilazane
[0159] A sample of methylhydrogenatedmethylvinylpolysilazane with available Si-H bonds, as shown in the following structure, where R is methylvinyl, was prepared by the prior art method outlined in Example 2.
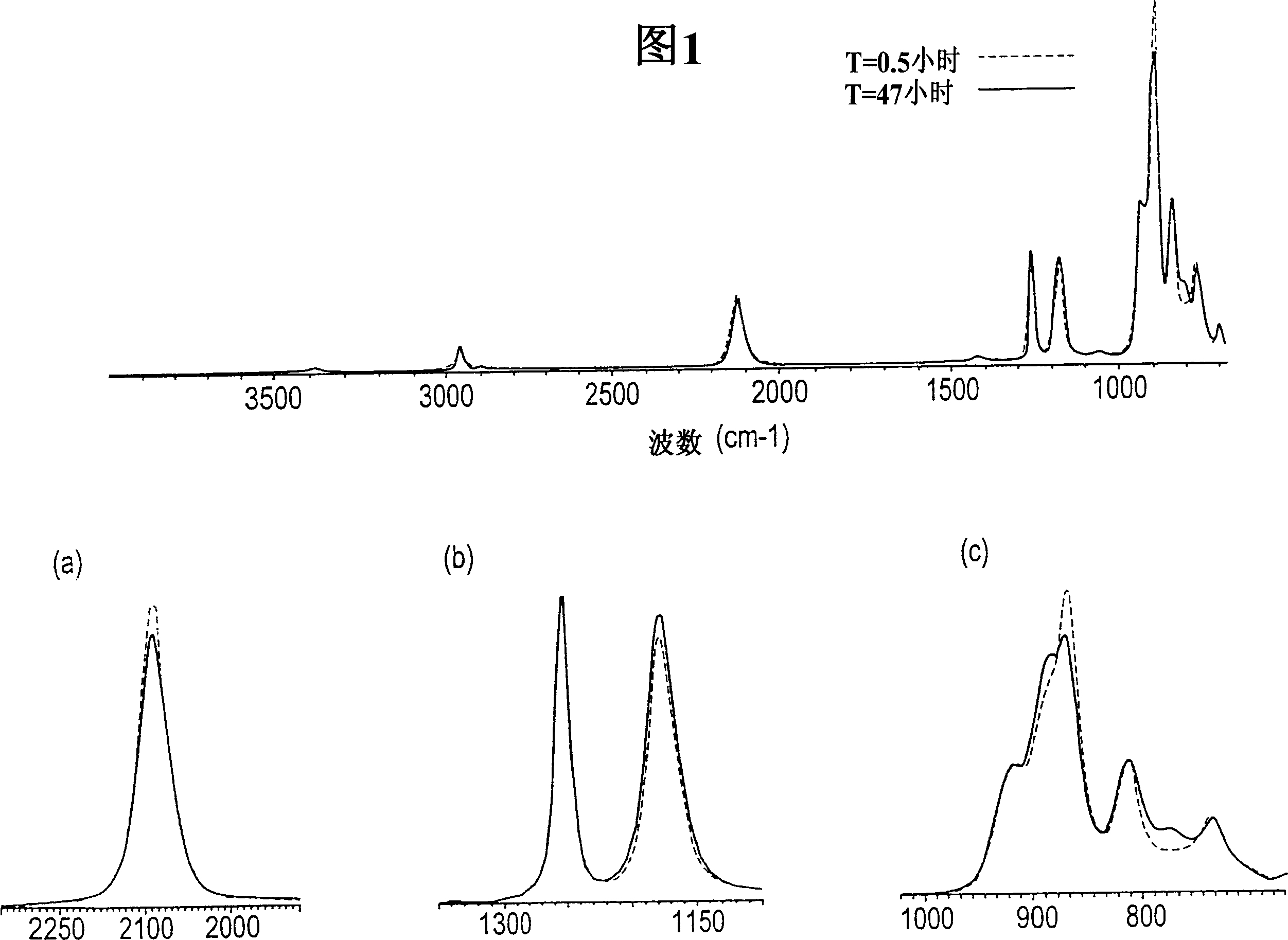
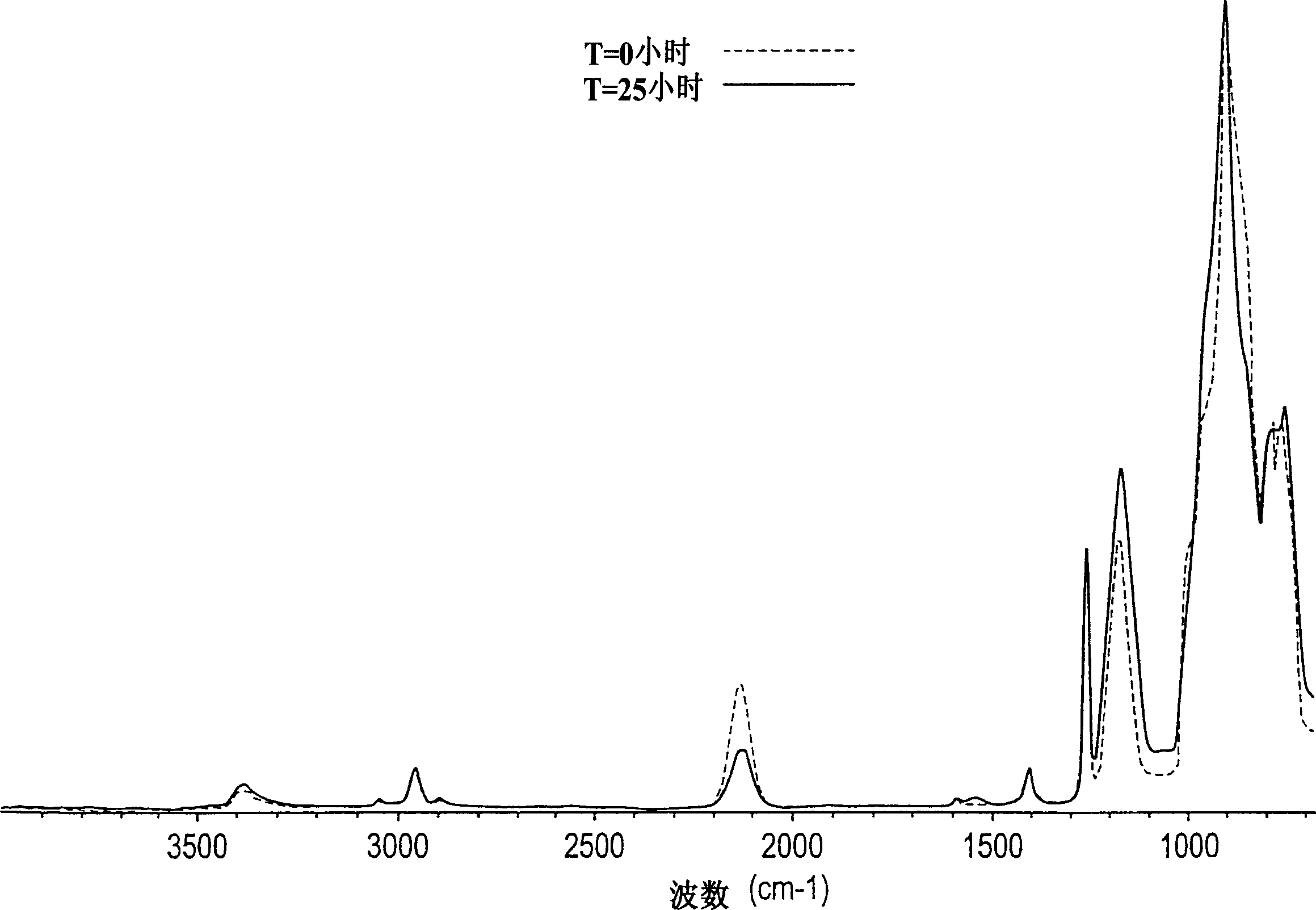
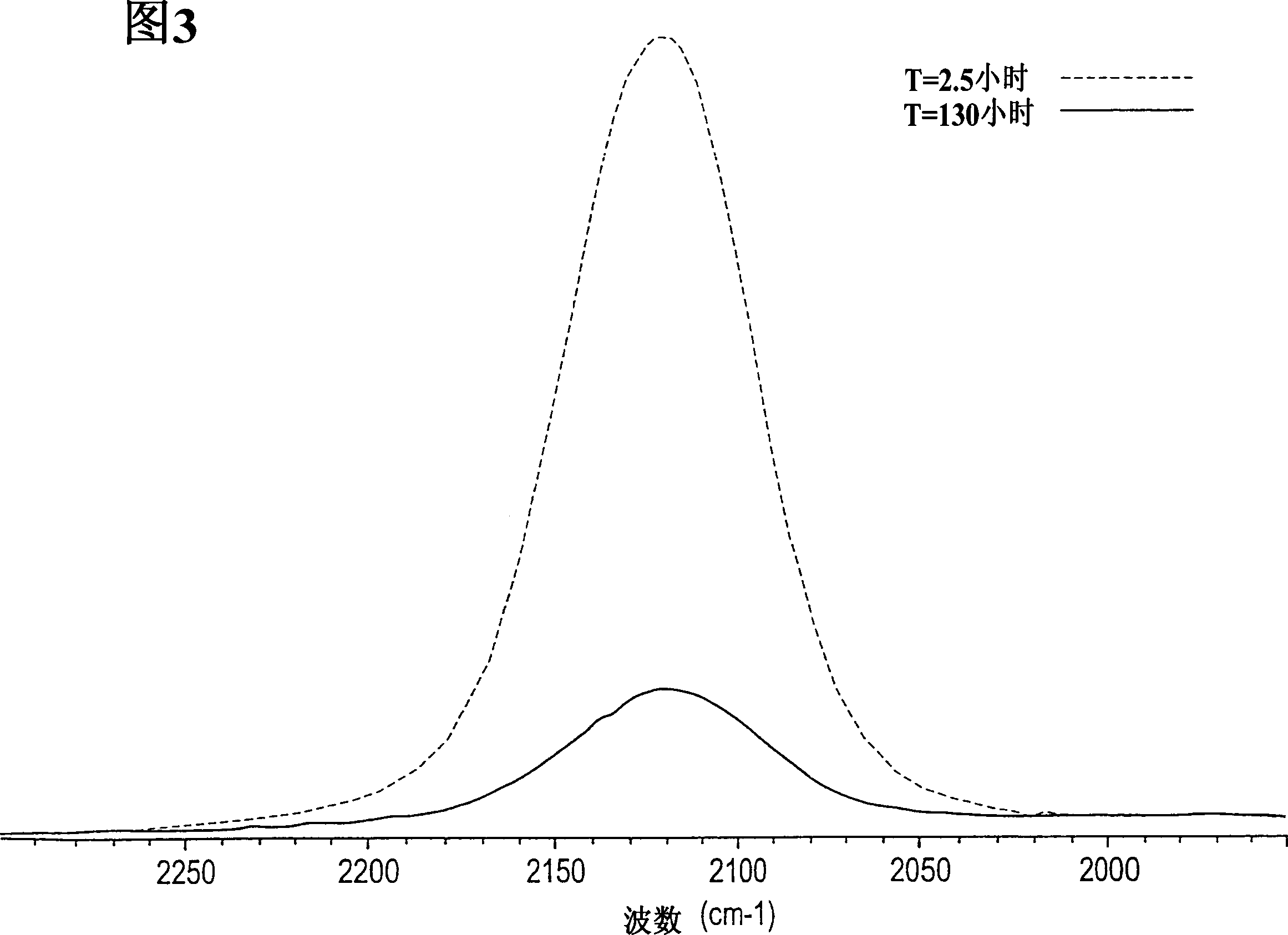
[0160] Add the prepared sample to anhydrous liquid ammonia and a catalytic amount of NH 4 Cl mixture to further polymerize the sample. figure 2 is the control FTIR spectrum of methylhydrogenmethylvinylpolysilazane before polymerization treatment and after 25 hours of treatment. observe figure 2 When the middle time is 0 ≈ 1500cm -1 (dotted line), it is clear that methylhydrogenmethylvinylpolysilazane is initially at ≈1500cm -1 With limited amine (NH 2 ) functionality. After 25 hours in liquid ammonia solution containing ionized acid catalyst (solid line), ≈1500cm -1 The amine functionality at the position increases significantly, such as ≈2120cm -1 Si-H bond reduction show...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com