Method for analyzing metabolites flux using converging ratio determinant and split ratio determinant
A metabolism and throughput technology, applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, analytical materials, etc., can solve problems such as user inconvenience, long calculation time, and inability to obtain actual values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
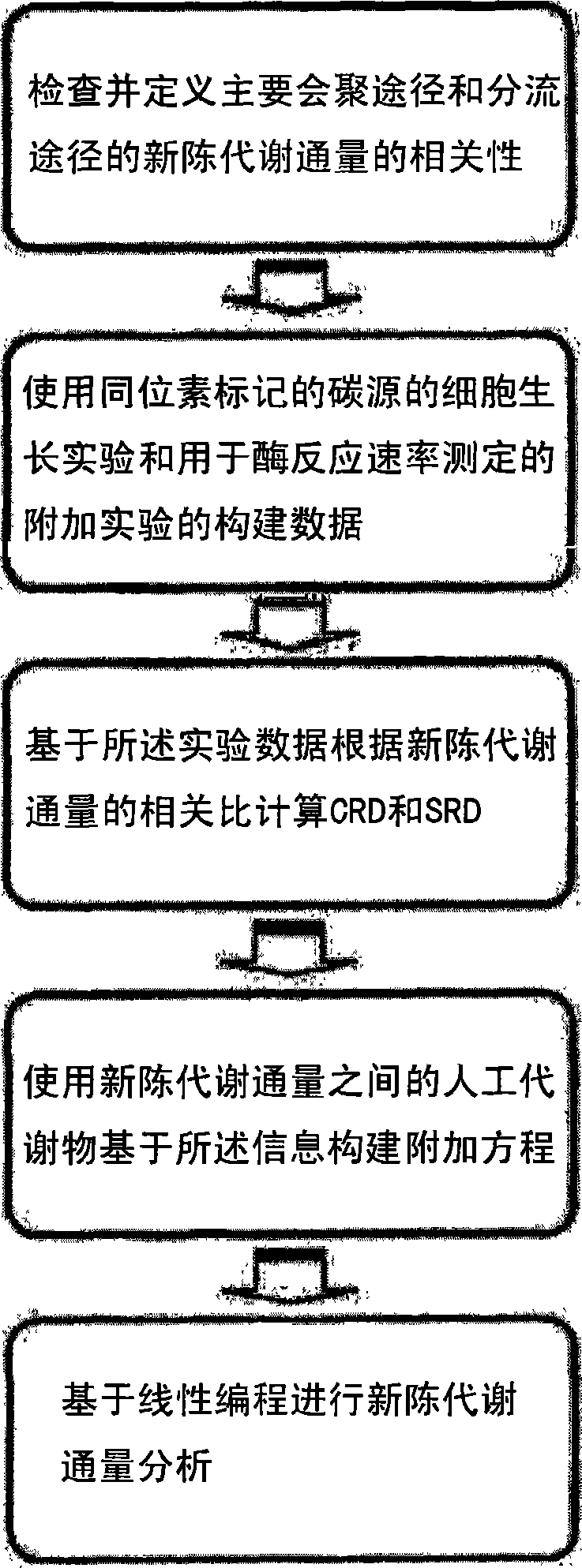
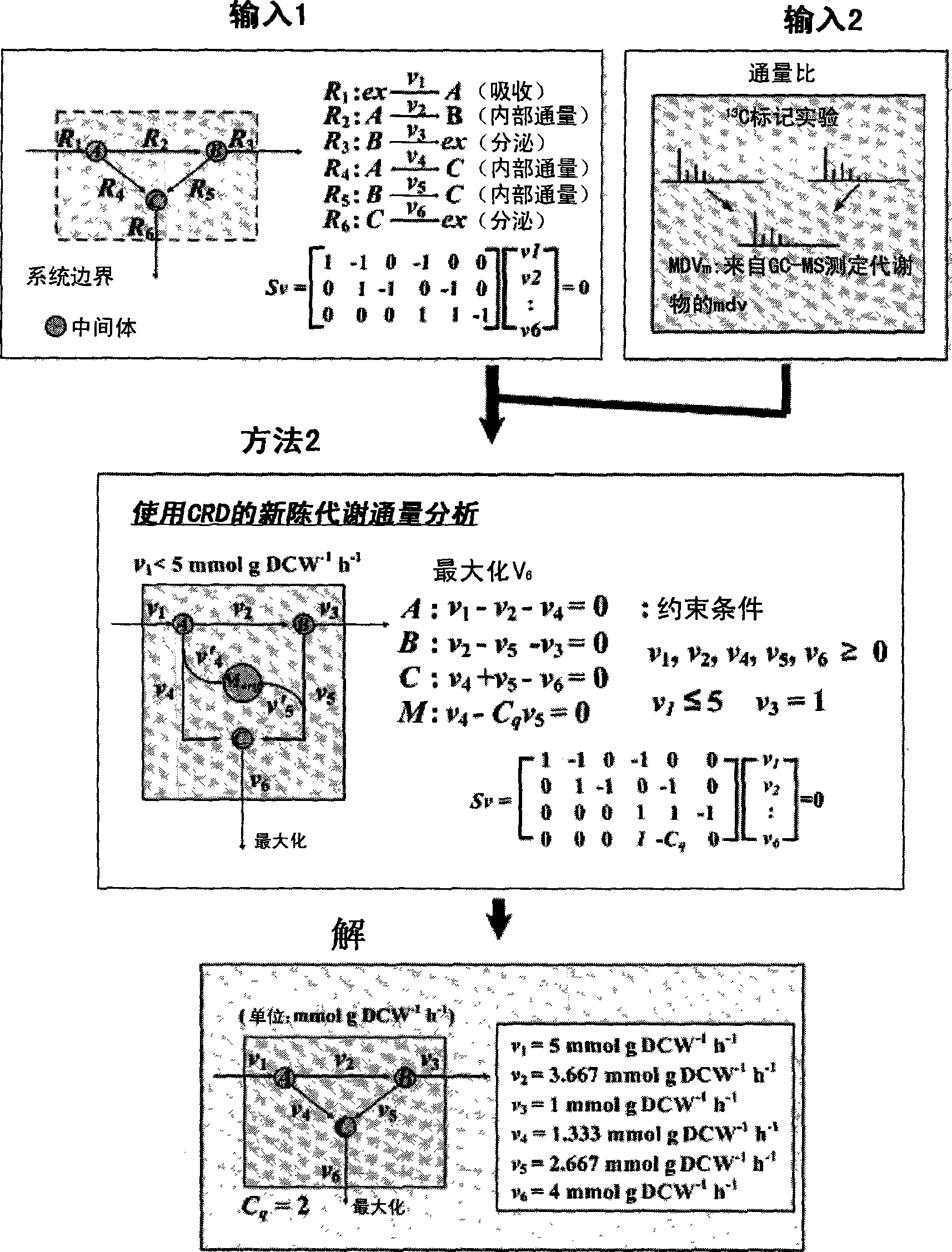
[0114]Example 1: Application of CRD and SRD in Exemplary Model
[0115] As an exemplary model for metabolic flux analysis, the image 3 system shown in . An exemplary model including 5 reaction equations, 3 metabolites and 1 uptake (uptake, R1 ) and maximum v6 as objective functions for metabolic flux analysis was set up. Stimulation was performed using MetaFluxNet 1.6, which can be downloaded at http: / / mbel.kaist.ac.kr / (Lee et al., Bioinformatics, 19:2144, 2003).
[0116] For comparison, a metabolic flux analysis excluding CRD and SRD was initially performed. When a quasi-steady state is assumed, the stoichiometric matrix for the exemplary model is as follows:
[0117] S · v = 1 - 1 0 - 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0150] Example 2: Example of CRD applied to E.coli. metabolic network model
[0151] In the case of E. coli., a new metabolic network consisting of 979 biochemical reactions and 814 metabolites was taken as the metabolic network. Such a system including all E. coli biochemical reactions and most of the biomass composition for forming E. coli to be used as the objective function using the biomass formation equation is as follows (Neidhardt et al., Cellular and Molecular Biology, 1996): 55% protein, 20.5% RNA, 3.1% DNA, 9.1% lipid, 3.4% lipopolysaccharide, 2.5% peptidoglycan, 2.5% glycogen, 0.4% polyamine and 3.5% other metabolites, cofactors and ion.
[0152] In general, E. coli. seem to grow using a maximal cell fraction, which is expressed as a specific growth rate. Therefore, metabolic flux analysis was performed according to linear programming using a specific growth rate as the objective function.
[0153] First, in E. coli., experimental values for definable correlat...
Embodiment 3
[0178] Example 3: Genetic Screening and Organism Improvement Using the Present Invention to Increase the Yield of Useful Substances
[0179] In order to increase the yield of useful substances, the genes to be amplified that increase the yield of useful substances were screened using the optimal value of the total metabolic flux and the spectrum obtained according to Examples 1 and 2. The screening of the gene to be amplified was performed according to the method described in Korean Patent Document Publication No. 10-2005-0086119.
[0180] Also, the gene to be amplified screened according to the method in Korean Patent Publication No. 10-2005-0086119 may be introduced into or amplified in a related organism to construct a mutant of the related organism.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com