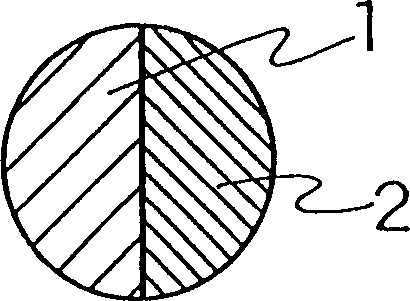
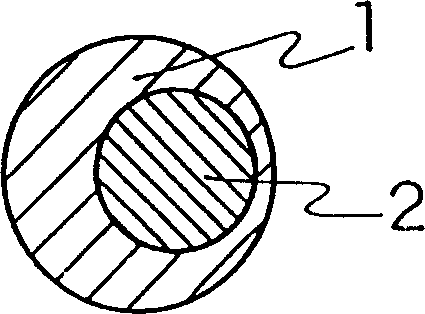
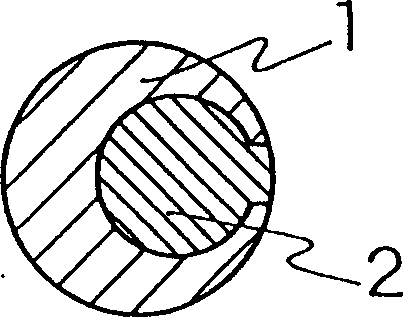
Spontaneously degradable fibers and goods made thereof
A fiber and single fiber technology, applied in the field of naturally degradable fibers and their products, can solve the problems of easy bonding of fibers, low heat resistance, slow solidification speed, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0203] 3 parts of polyethylene glycol (PEG), 98 parts of L-lactide, 100 ppm of tin octoate, and 0.1 part of antioxidant Irganox1010 of Ciba-Geigy Company are mixed with a molecular weight of 8000 and both ends are hydroxyl groups. At 190°C, it was melt-stirred and polymerized in a twin-screw extruder for 12 minutes. After cooling the slices, it was processed (solid-state polymerization) in a nitrogen atmosphere at 140°C for 4 hours to obtain a block copolymer P1 of polylactic acid and PEG. Polymer P1 has a molecular weight of 153,000, a PEG component content of about 3%, a melting point of 174°C, and a melting endothermic heat of 55 J / g when fully oriented and crystallized. Thereafter, polymer P2 was obtained in the same manner as polymer P1 except that a mixture consisting of 95.5 parts of L-lactide and 2.5 parts of D-lactide was used as lactide. The molecular weight of the polymer P2 is 158000, the melting point is 163° C., and the heat of melting is 27 J / g.
[0204] Polyme...
Embodiment 2
[0207] Polymer P5 was obtained in the same manner as the production of Polymer P1 in Example 1 except that 30 parts of polybutylene succinate having a molecular weight of 127,000 and having a hydroxyl group at the terminal was used instead of PEG. The molecular weight of the polymer P5 is 129000, the melting point is 162° C., and the heat of melting is 35 J / g.
[0208] Perform the same procedure as Polymer P1, but replace PEG with 10 parts of polybutylene succinate having a molecular weight of 12,700 and terminal hydroxyl groups, and replace L-lactide with 88.5 parts of L-lactide and 2.52 parts of D-lactide. Lactide, polymer P6 was obtained. The molecular weight of the polymer P6 is 134000, the melting point is 151° C., and the heat of melting is 26 J / g.
[0209] In the same manner as the drawn yarn F1 of Example 1, the drawn yarn F3 was obtained using the polymer P1 and the polymer P5. The drawn yarn F3 had a strength of 4.7 g / d, an elongation of 28%, a crimp elongation of ...
Embodiment 3
[0212] In the same manner as in Example 1, a block copolymer P1 of polylactic acid and PEG was produced. Polymer P1 is melted with a screw extruder at 230°C, spun out from a spinneret hole with a diameter of 0.2mm at 225°C, cooled in air, and wound at a speed of 1500m / min while oiling, at 80°C It was stretched to 4.5 times, and heat-treated at 110° C. under tension to obtain drawn yarn A1 of 40 deniers / 12 filaments. The drawn yarn A1 had a strength of 4.5 g / d, an elongation of 29%, and a boiling water shrinkage of 12%.
[0213] In addition, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and produced the polymer P2. Polymer P2 is melted with a screw extruder at 220°C, spun out from a spinneret hole with a diameter of 0.2mm at 225°C, cooled in air, and wound at a speed of 1500m / min while oiling, at 80°C It was drawn at 4.5 times without heat treatment to obtain drawn yarn B1 of 60 denier / 12 filaments. The tensile strength of the drawn yarn B1 was 4.4 g / d, the elongation was 33%, and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com