Rotating axle of induction motor
A technology for induction motors and rotating shafts, applied in the direction of electric components, shafts, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of poor bearing position, increase the number of parts, and maintain bearings, so as to prevent poor position and reduce the number of parts Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
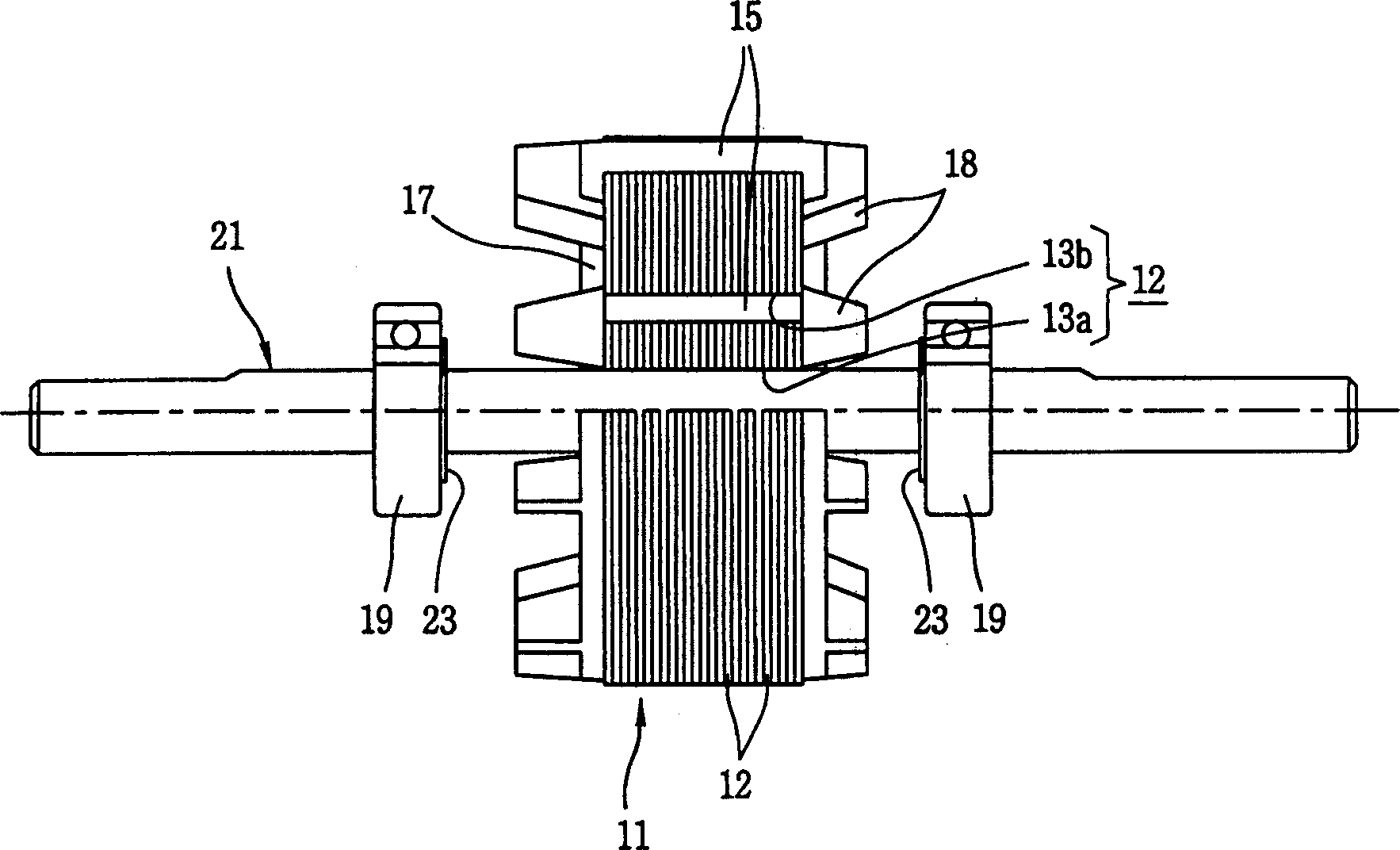
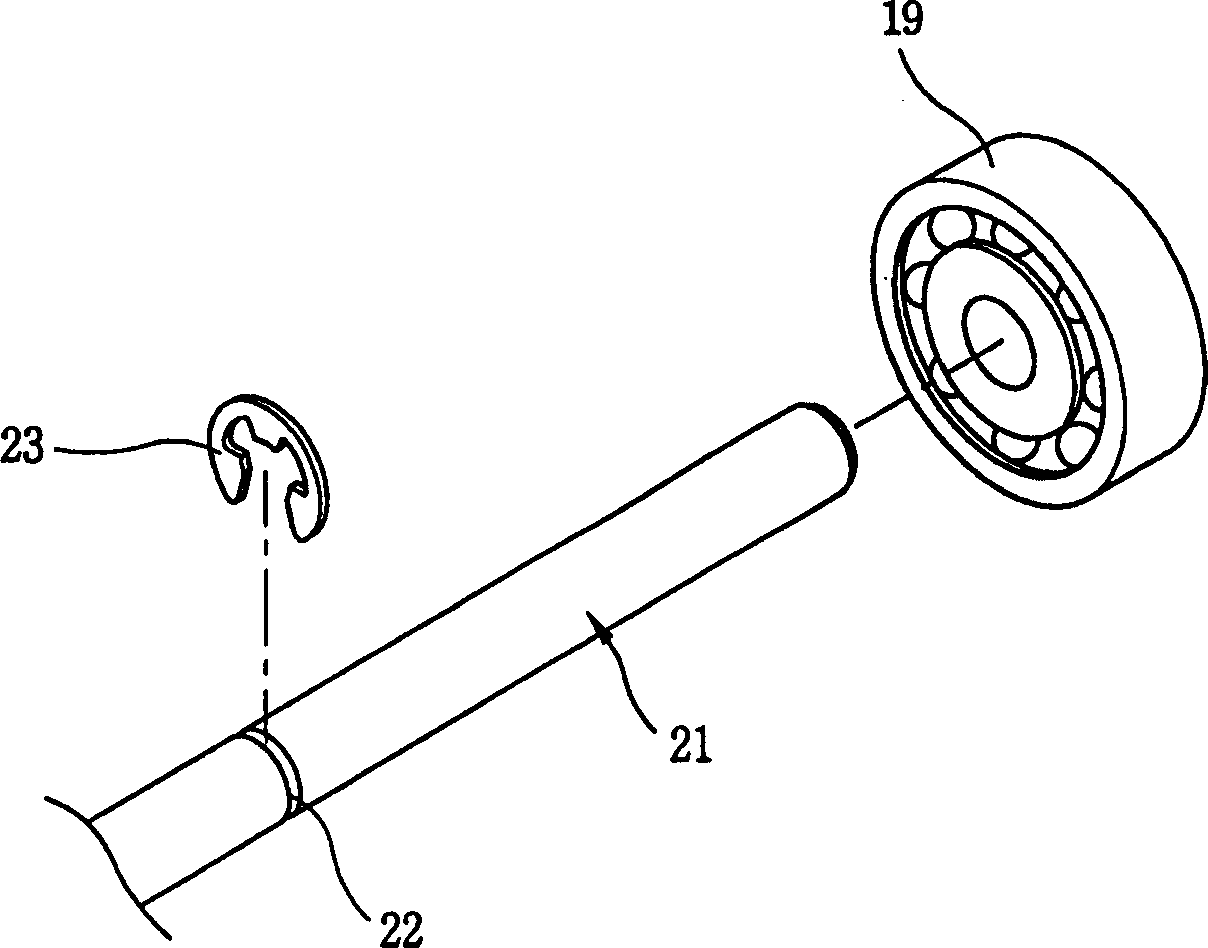
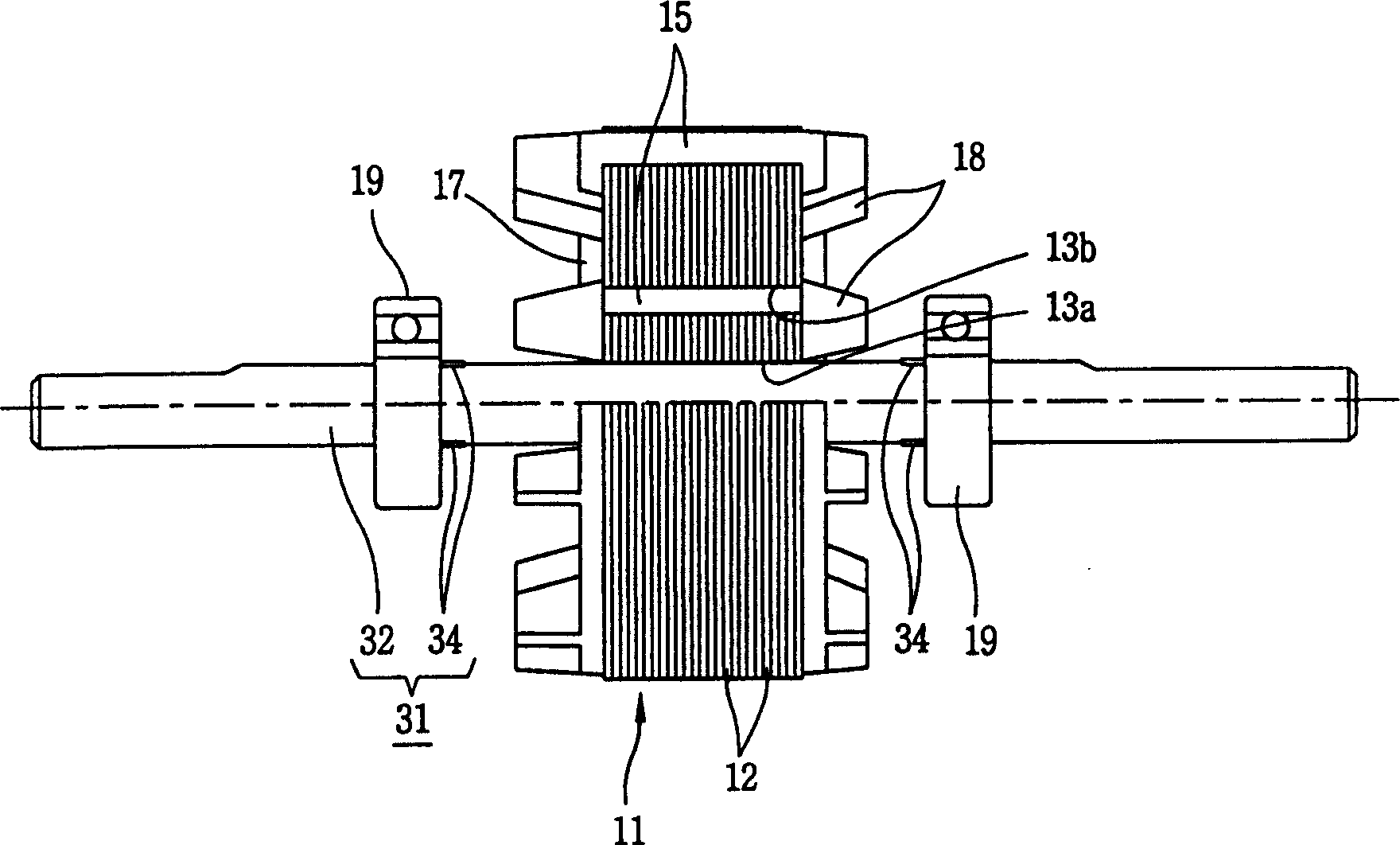
[0026] like image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Image 6 , Figure 7 As shown, the induction motor of the present invention includes a rotor core (11), a conductor bar (15), a locking (end ring) (17), and a rotating shaft (31). The above-mentioned rotor iron core (11) is formed by several silicon steel plates (12) insulated and laminated, and the silicon steel plate (12) has a shaft hole (13a) and several slots (13b), and each slot of the rotor iron core (11) ( 13b) Conductor rods (15) are formed inside; locking rings (17) are respectively provided at both ends of the rotor iron core (11), and the axis of the rotor iron core (11) is combined with the rotating shaft (31) of the induction motor of the present invention.
[0027] The rotating shaft (31) of the induction motor of the present invention includes a rotating shaft body (32) and a bearing stopper (stopper) (34). (11) Insert the rotor core (11) integrally; the bearing locking device (34) is integrally formed with th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com