Virtual time slot exchange method and its application circuit
A time slot switching and delay circuit technology, applied in time division multiplexing systems, time division multiplexing selection devices, electrical components, etc., to simplify complex logic, reduce PCB wiring area, and save time slot switching chips Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
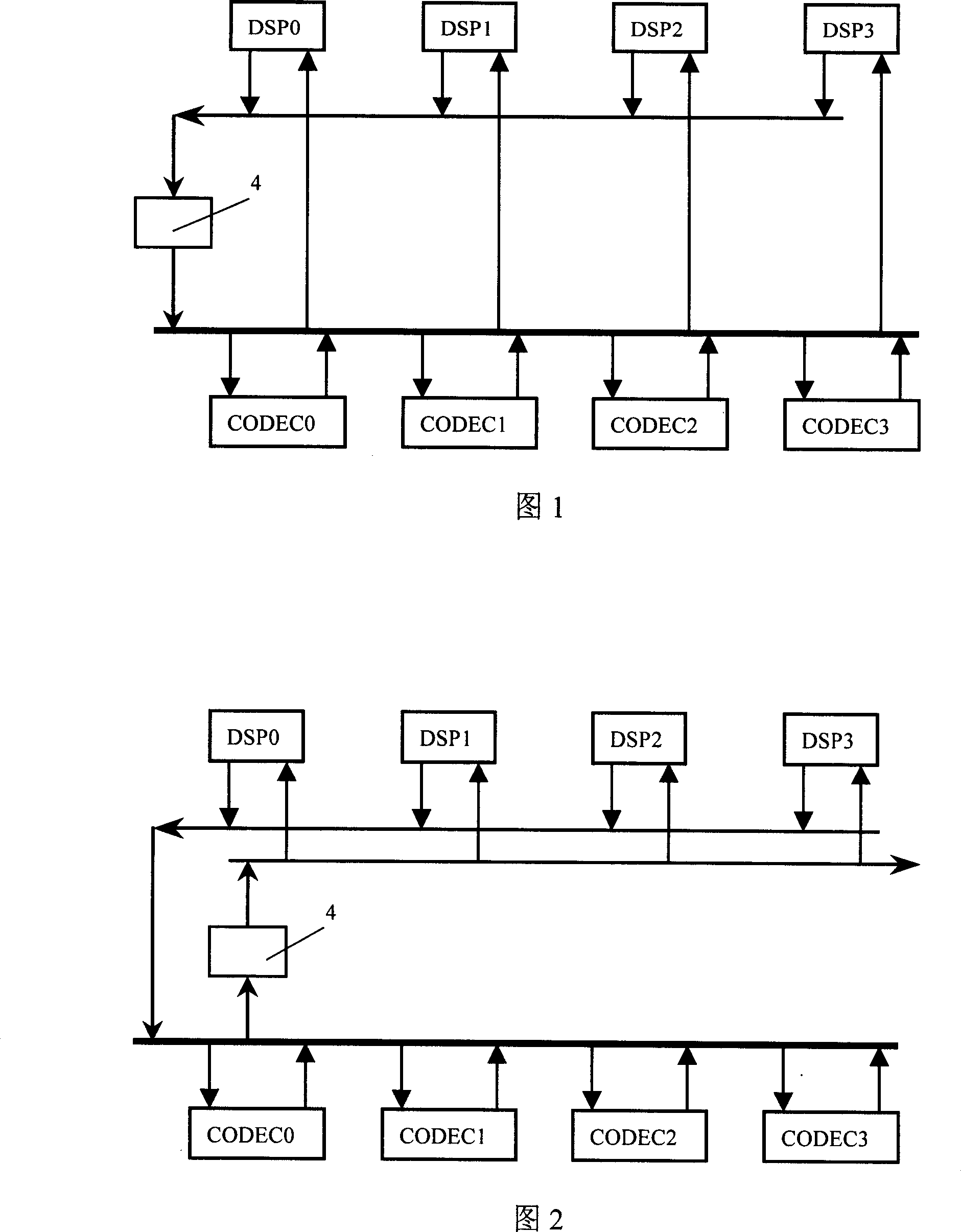
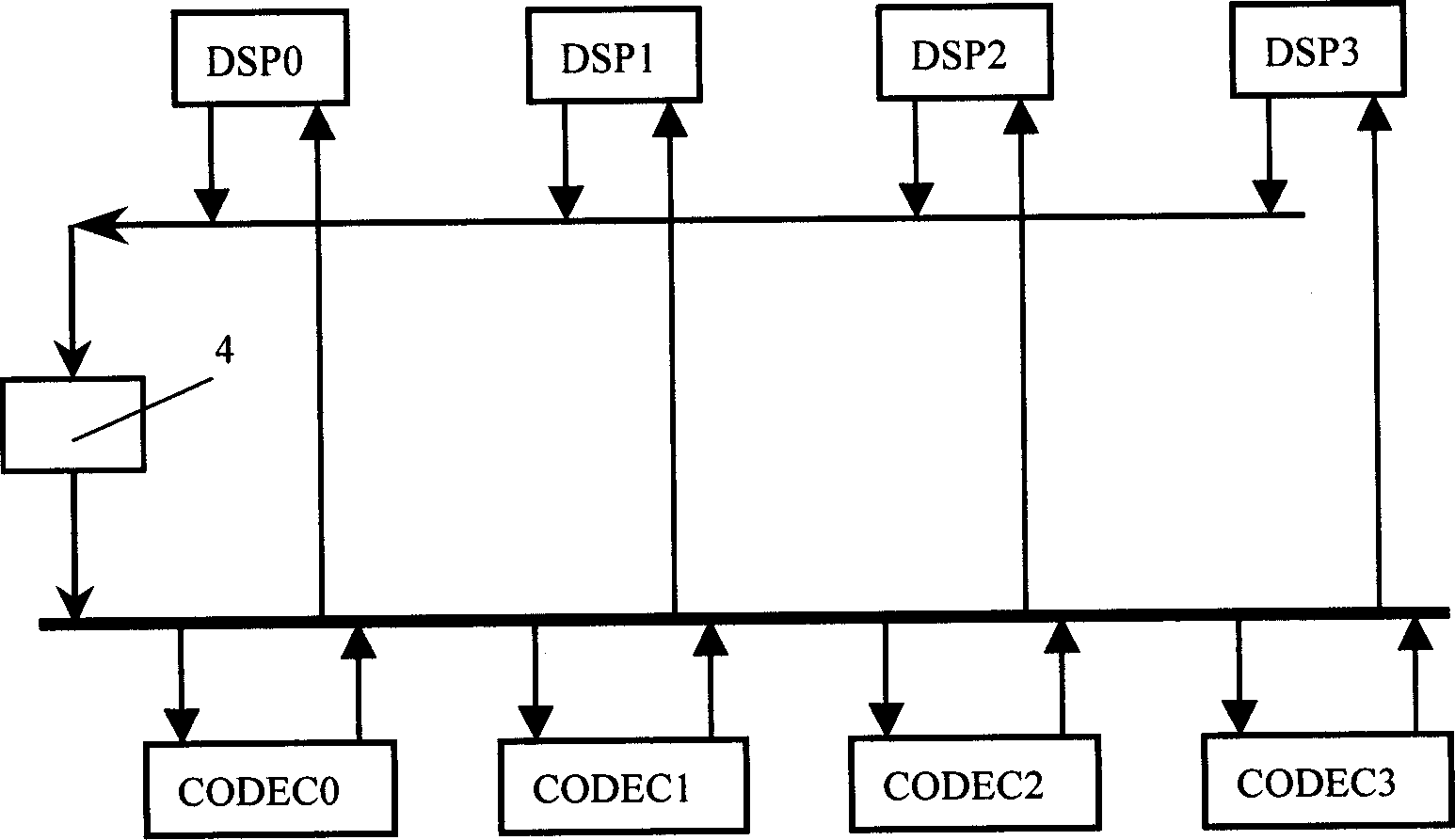
[0026] figure 1 It shows a schematic diagram of shifting the DSP transmission time slot by 1 time slot.
[0027] First of all, all DSPs in the system will not send data in the same time slot, and when the DSP is not sending data, its transmission line is in a high-impedance state, so the transmission lines of all DSPs can be connected in parallel, and then through an 8bit shift register 4 Access to the TDM bus. The effect of 8bit shift register 4 on this sending bus is to delay the data sent by DSP by 1 time slot. Assuming that the receiving time slot number of DSP0 is n, its corresponding sending time slot number is equivalent to n +1.
[0028] In the second step, usually the CODEC's sending and receiving time slot numbers can be configured independently, and the following points should be noted at the same time:
[0029] All CODECs will not send data in the same time slot;
[0030] When the CODEC does not send data, the sending line is high impedance;
[0031] The rece...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The shift register 4 in this example is connected to the receiving end of the DSP, and the effect produced is to move the receiving time slot of the DSP by one time slot. If the DSP transmits time slot is n, its receiving time slot is equivalent to n+1. The method for exchanging virtual time slots in this example is similar to that in Embodiment 1 and will not be repeated here. schematic diagram see figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
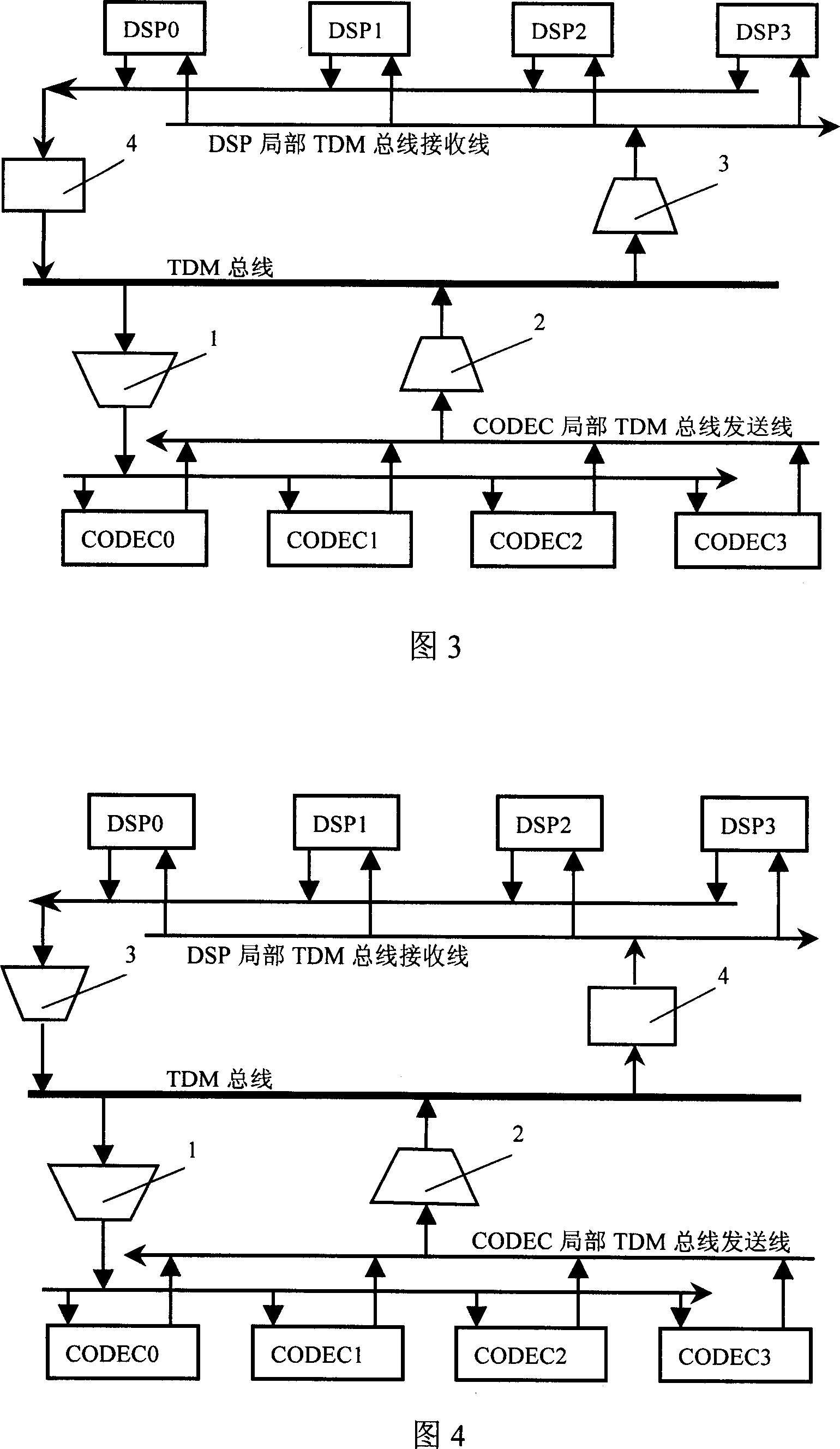
[0054] Considering the load capacity of the device, the hardware connection relationship of the implementation circuit is as follows: image 3 . In this case in figure 1 Based on the addition of 3 bus drivers. The bus driver 1 is connected between the receiving line of the CODEC local TDM bus and the TDM bus to solve the load capacity of the shift register 4. The bus driver 2 is connected between the CODEC local TDM bus sending line and the TDM bus to solve the load capacity of the CODEC. The driver 3 is connected between the DSP local TDM bus receiving line and the TDM bus, and is used to drive multiple DSPs, reducing the load of the bus driver 1 and the bus driver 2 . If the number of DSP and CODEC is not much, you can also follow figure 1 implement.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com