Method and kit for primer based amplification of nucleic acids
A nucleic acid and nucleotide technology, used in biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] In this example, nucleic acid sequences from each disease agent and the second disease agent were obtained and isolated as described herein. Nucleic acid from each pathogen was amplified by the Tem-PCR method described herein. The nucleic acid of each pathogen was placed in a separate reaction tube and the complete mix of primers specified in Table 2 was added along with the reagents for RT-PCR. For each pathogen, a separate reaction was performed at each of the three primer ratios specified in Table 5. Although any procedure known in the art for RT-PCR can be used, the following procedure was used in this example. Prepare a master rRT-PCR mix consisting of 5X RT-PCR buffer, a deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) mix (containing 400 μM of each dNTP), complete fractions of the primers shown in Table 2 at the ratios indicated in Table 5. mixture, and RT-PCR enzyme preparation. Ribonuclease inhibitors were also added at a concentration of 5-10 units / reaction if necessary...
Embodiment 2
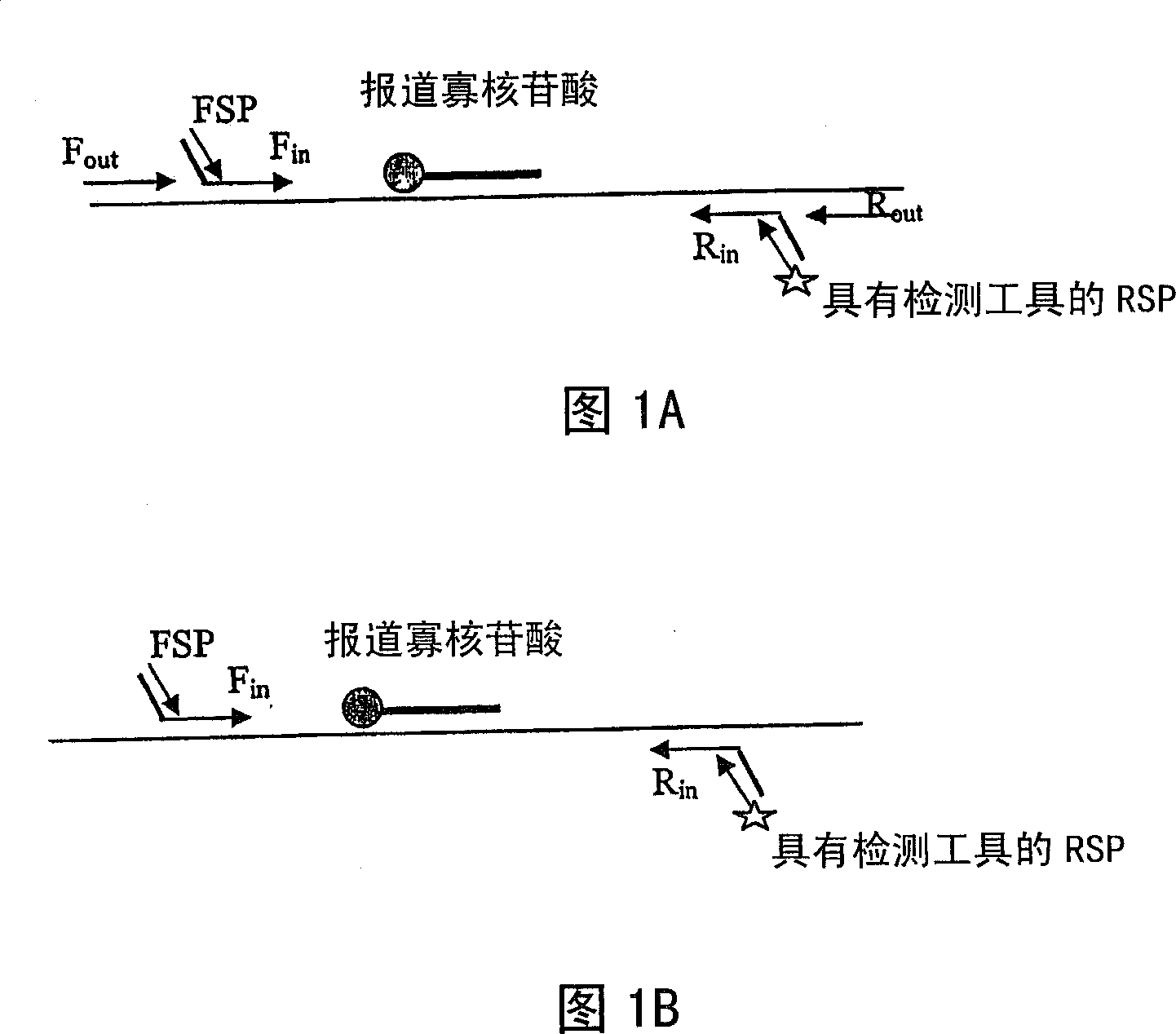
[0086] In this example, nucleic acid sequences from each disease agent and the second disease agent were obtained and isolated as described herein. Nucleic acid from each pathogen was amplified by the Tem-PCR method described herein. The nucleic acid of each pathogen was placed in a separate reaction tube and the complete mix of primers specified in Table 3 was added along with the reagents for RT-PCR. The conditions for RT-PCR were as described in Example 1 above. The primer ratio used in this example was 1:1:1:1:10:40 (F out :F in :R in :R out :FSP:RSP).
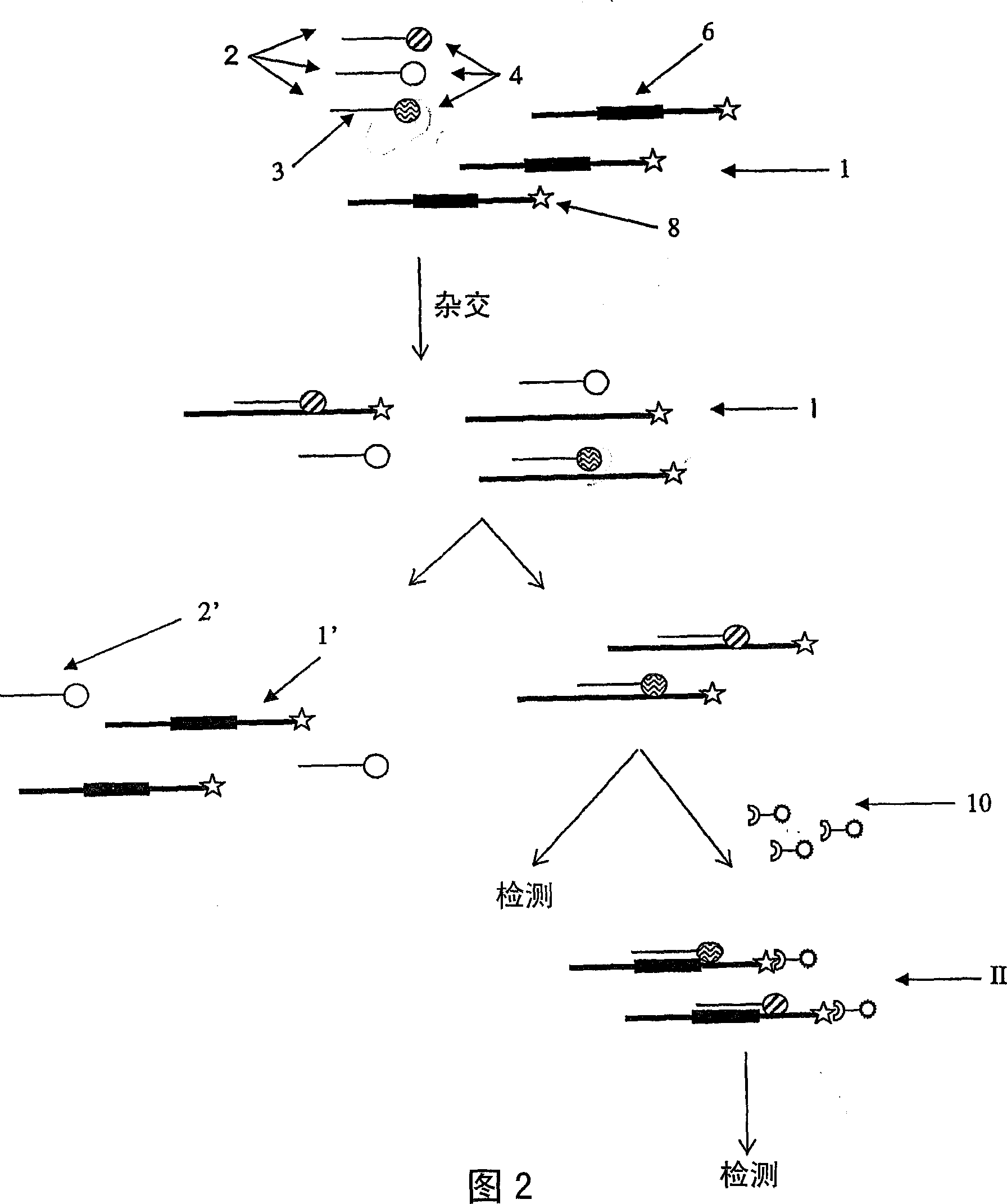
[0087] Detection of amplified products containing target sequences was performed as described for the direct detection method using the Luminex beads described in Example 1 . Add the detection oligonucleotides for each pathogen listed in Table 3 to each detection reaction.
[0088]Table 6 shows the results of this experiment using the target enrichment and target amplification primers disclosed in Table 3. The row ...
Embodiment 3
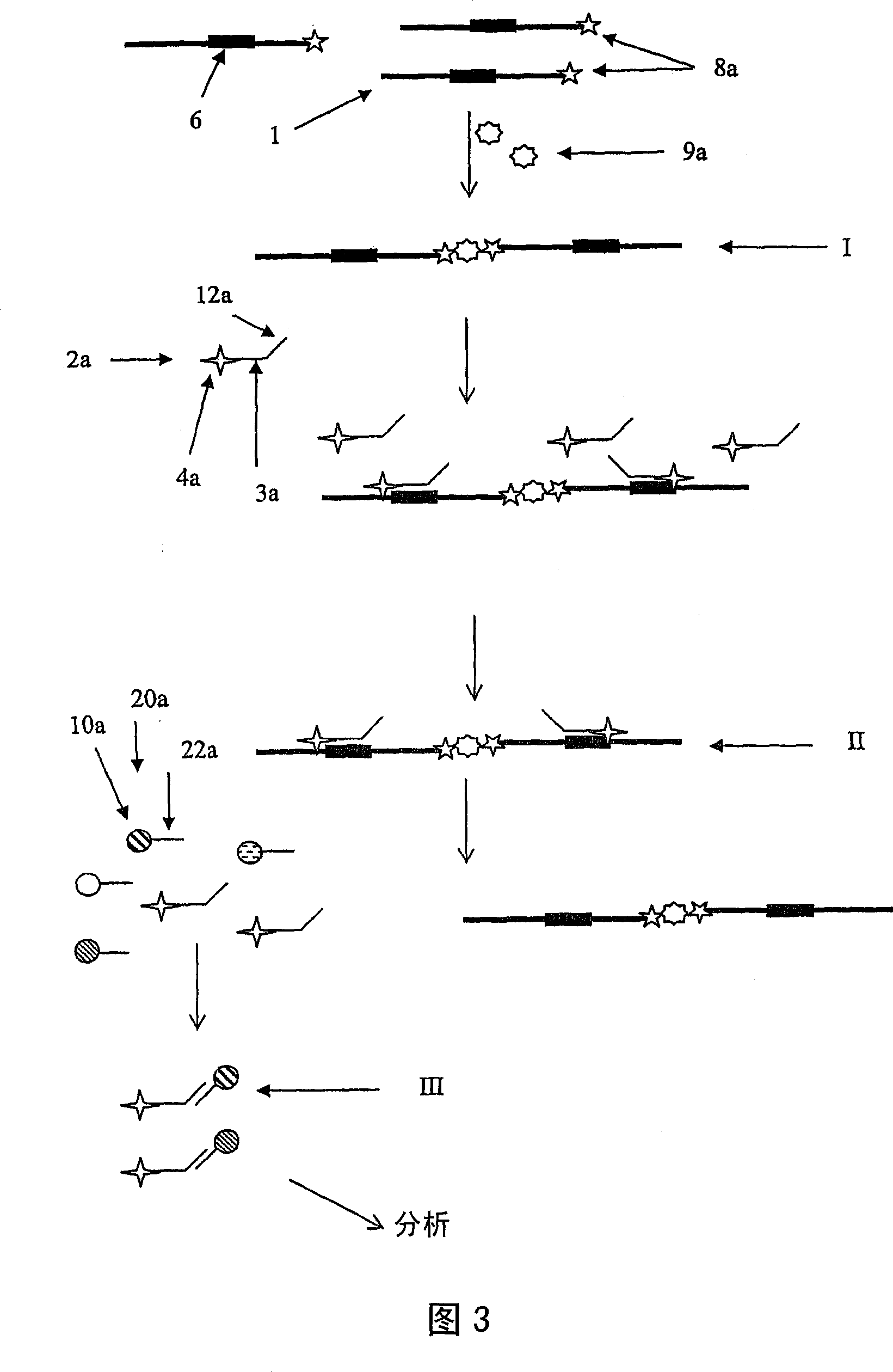
[0092] In Examples 1 and 2 above, only 1 nucleic acid sample was added to each reaction (albeit in the presence of target enrichment primers specific for multiple pathogens). Table 7 shows the specificity of the TemPCR amplification method when nucleic acid samples from multiple pathogens are included in a single sample for multiplex amplification and subsequent detection. In this example, target enrichment primers for each organism listed in Table 3, as well as target amplification primers and nucleic acids from the indicated pathogens were included in each sample. Rows in Table 7 indicate the detection oligonucleotides detected in the multiplex detection step (note that detection oligonucleotides specific to the target sequences of all organisms listed in Table 3 are included in each detection reaction ), while the row in Table 6 indicates the identity of the pathogenic nucleic acid that was added to each sample. TemPCR amplification conditions and multiplexing were perform...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com