Optical modulator
A technology of optical modulator and modulation voltage, which is applied in the field of optical communication system, and can solve the problem of not teaching beam frequency chirp etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
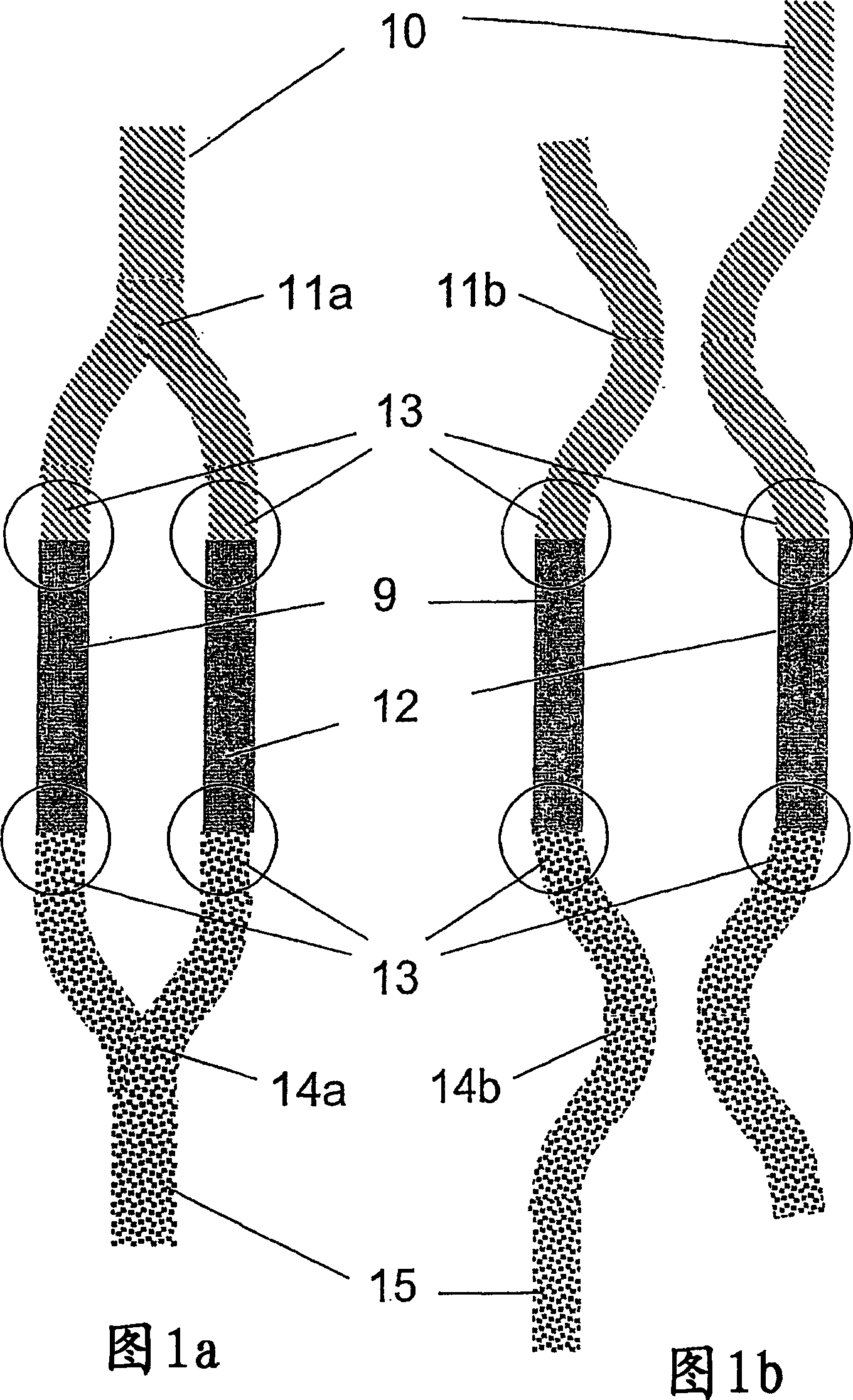
[0127] Figure 7 shows an embodiment of an optical modulator 1 according to the present invention, the optical modulator 1 comprising: a Mach-Zehnder structure, a first electrode structure 20, a second electrode structure 21, a third electrode structure 22, an optional A fourth electrode structure 23, and drive circuitry for driving the first, second, third, and fourth (if present) electrode structures 20, 21, 22, 23.
[0128] In the embodiment of FIG. 7 (see also FIG. 1a), the Mach-Zehnder structure includes an input waveguide 10; a beam splitter 11a that splits the input beam into two beams; Second waveguide arms 9 and 12; combiner 14a combining the two beams into an output beam; output waveguide 15; junction area 13 between waveguide arms 9, 12 and beam splitter 11a and optical combiner 14a.
[0129] In the optical modulator 1, the first electrode structure 20 is combined with the first waveguide arm 9, the second electrode structure 21 is combined with the second waveguide ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com