Cavity former
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
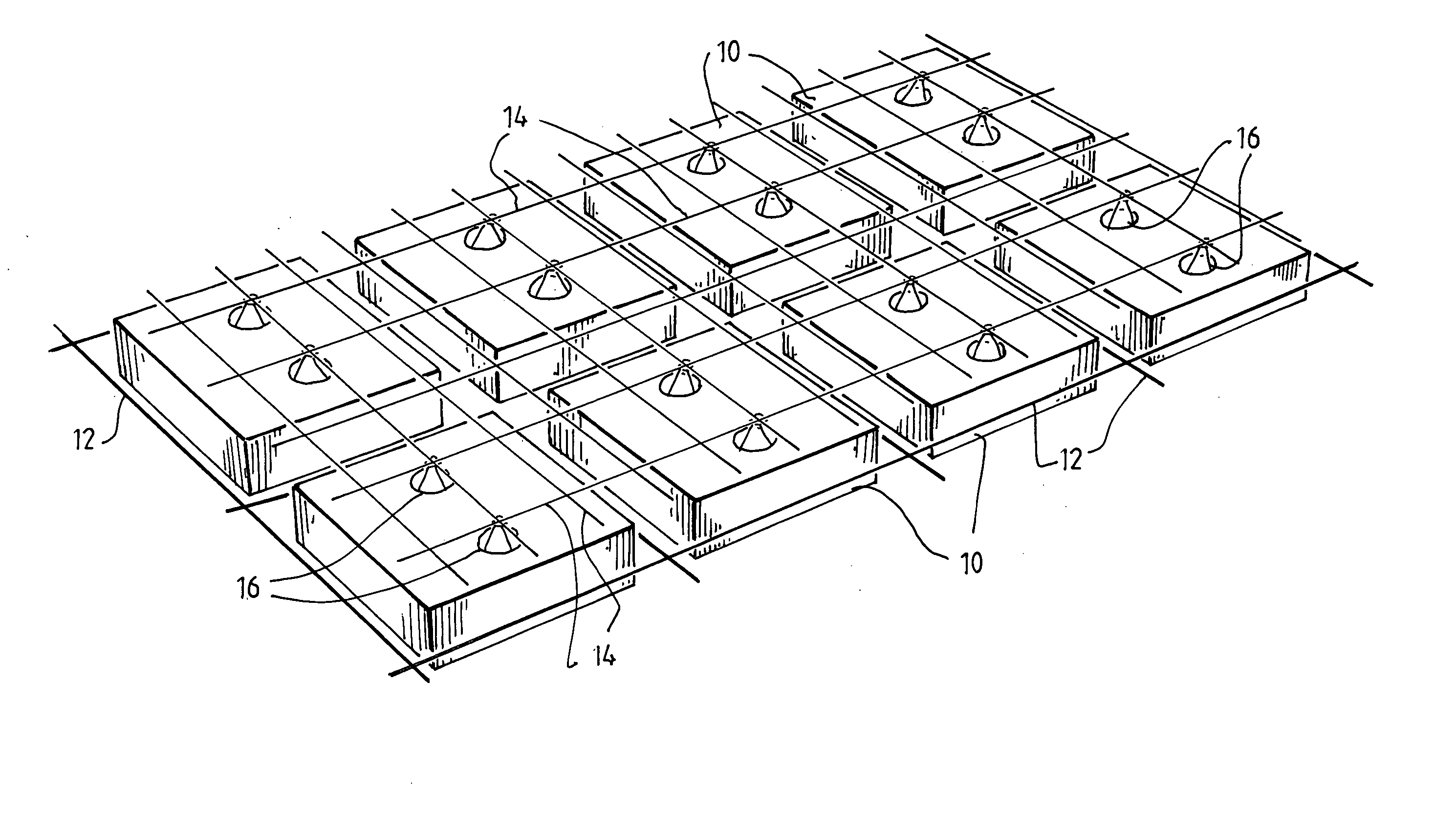
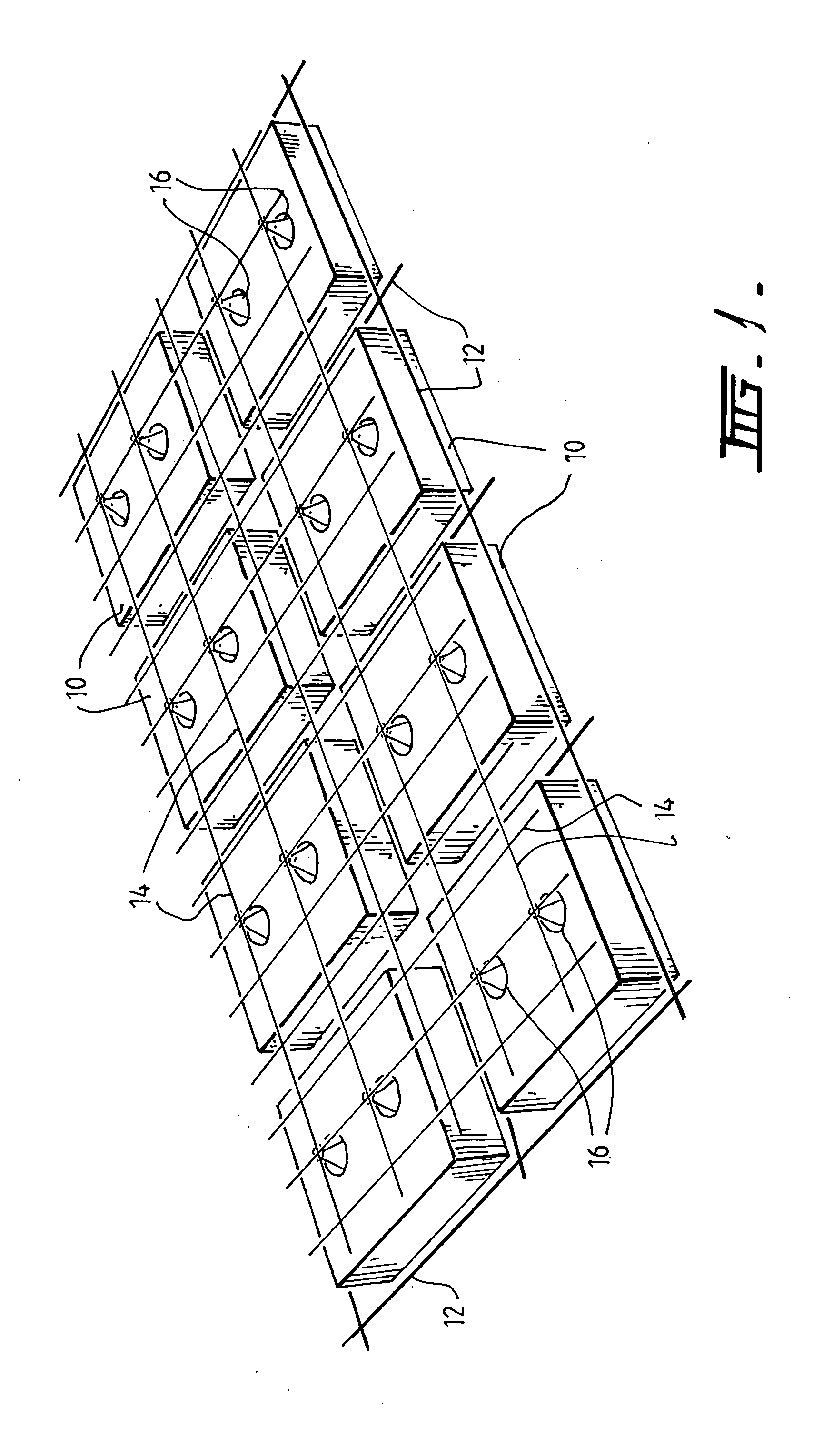
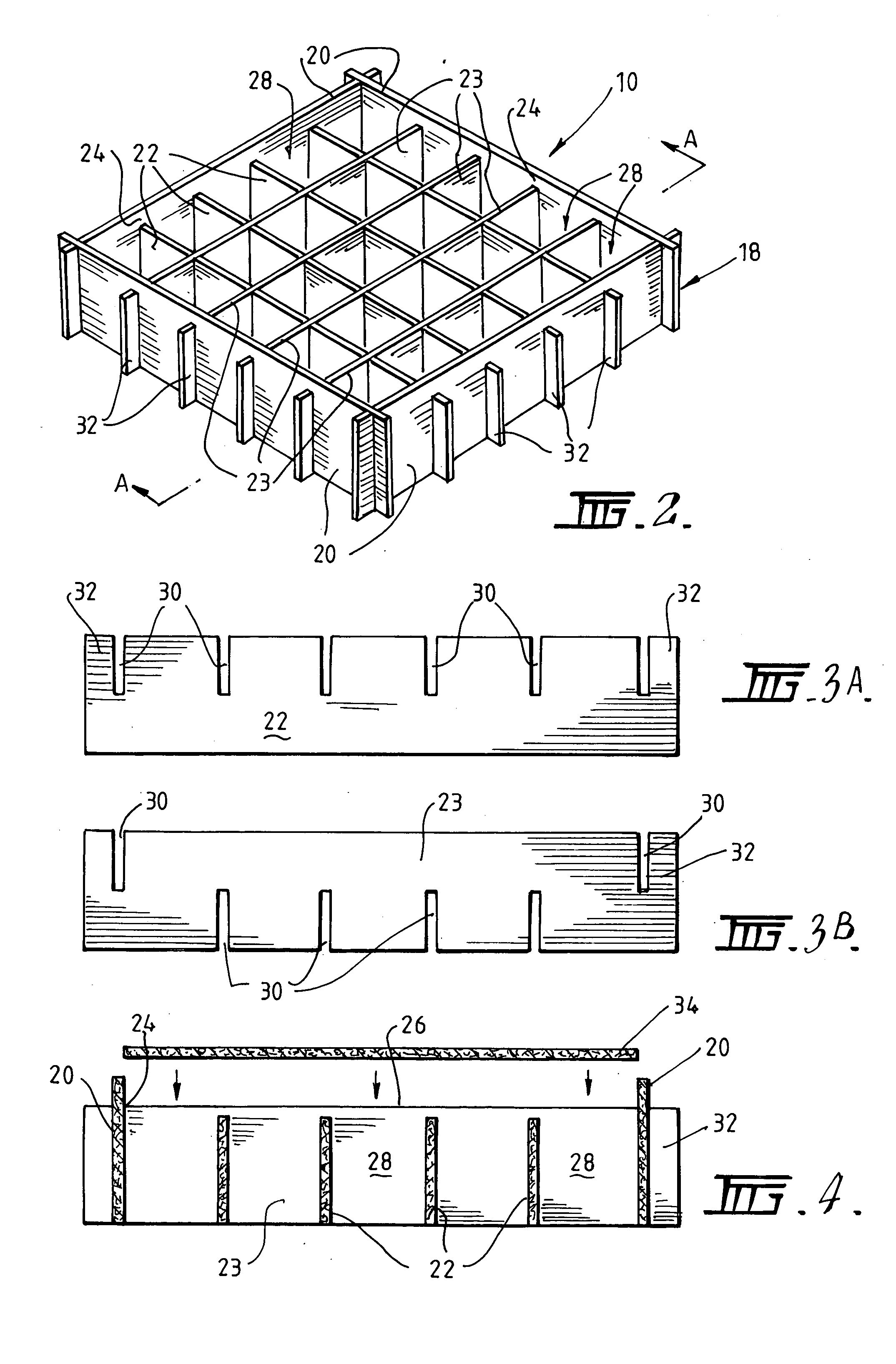
[0054] Referring to cavity former 10 illustrated in FIGS. 2 to 5, it can be seen that the base 18 of the cavity former 10 has a support member comprising an array of elements in the form of panels 22 and 23 for supporting the weight of wet concrete until it is sufficiently cured to support itself, and a rim 24 formed on the peripheral panels 20 which operates to locate and retain the cover means on the panels 22 and 23. The cover means is provided in the form of a lid 34 (FIG. 4). It will, therefore, be appreciated that the weight of wet concrete on the lid 34 will be distributed to the panels 22, 23 along their upper edges.
[0055] The panels 20, 22 and 23 are preferably formed from a degradable material, which disintegrates over time to leave a cavity within the slab. The panels 20, 22 and 23 may otherwise be formed from any material having the required strength to support the weight of a worker standing on the cavity former or of the wet concrete poured to form the slab.
[0056] Whi...
second embodiment
[0064] Reference is now made to a second embodiment illustrated in FIGS. 6A, 6B and 7, in which like parts are indicated by like numerals preceded by a 1. Cavity former 110 comprises a base 118 and a cover means in the form of a lid 134. The base 118 has end walls 40 and support elements 42 located between the end panels 40. The support panels 42 are formed from a number of sections 46 joined via fold lines 44 to enable the support panels to expand and contract in length in a concertina-type effect. As can be seen from FIG. 7, the contraction of the support panels 42 enables the base 118 to collapse to a reduced volume for conveniently transporting the cavity formers 110. The support panels 42 have a bias toward the collapsed state.
[0065] The lid 134 in FIG. 6A comprises a panel 56, in the shape of a square, having opposed depending side walls 54. The cavity former 110 is formed by moving the end walls 40 apart to configure the base 118 into an expanded state thereby allowing the li...
third embodiment
[0067] the present invention is illustrated in FIGS. 8 and 9. in which like parts are indicated with the numerals preceded by a 2. As shown in FIG. 8, the cavity former 210 comprises a base 218 to which may be fitted the lid 134 in FIG. 6A.
[0068] The base 218 comprises end walls 62 and intermediate support panels 64 all of which are generally parallel and connected at their respective ends by a pair of flexible webs 66. Furthermore, the upper edges 62 of the end walls 60 are spaced above the upper edges 68 of the support panels 64 by an amount equal to the thickness of the plate 56 of the lid 134.
[0069] The base 218 can be re-configured into a collapsed state as depicted in FIG. 9 by moving each adjacent panel closer to its neighbour such that there is substantially no space between the panels 60 and 64. In this configuration, the base218 has a substantially reduced volume relative to the expanded state shown in FIG. 8 and thereby enables the base 218 to be more conveniently transp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Lattice constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com