Method for bilateral filtering of digital images
a filtering and digital image technology, applied in image data processing, image enhancement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large relative cost of divide operation, large computational complexity required to implement, inclusion of integer division circuit,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
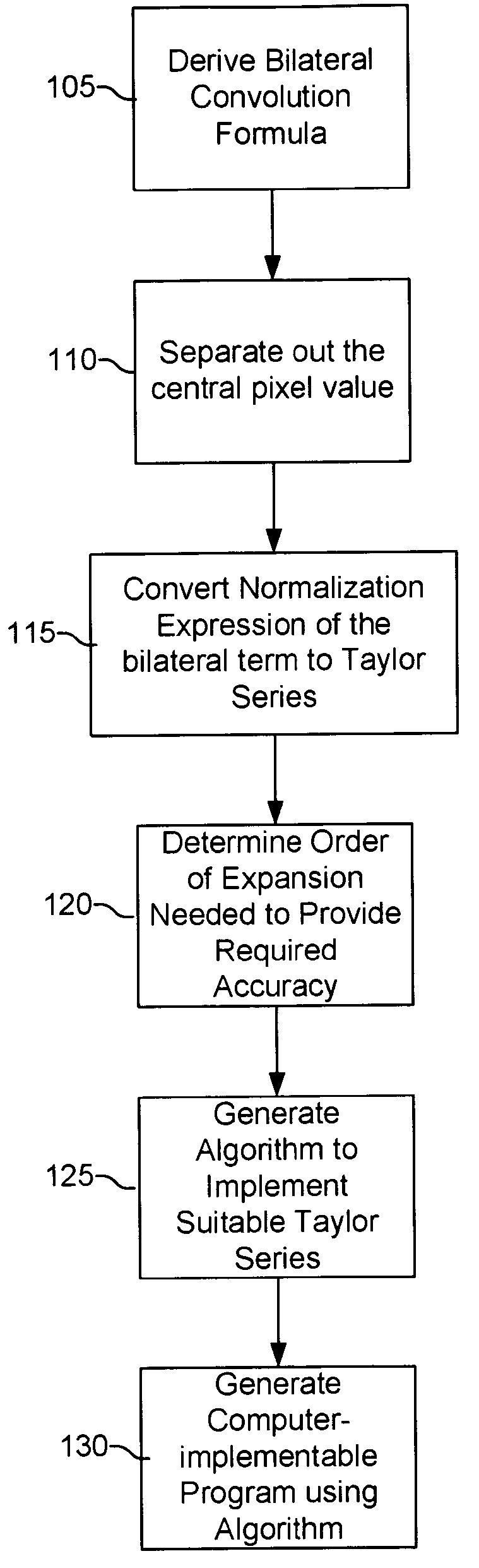
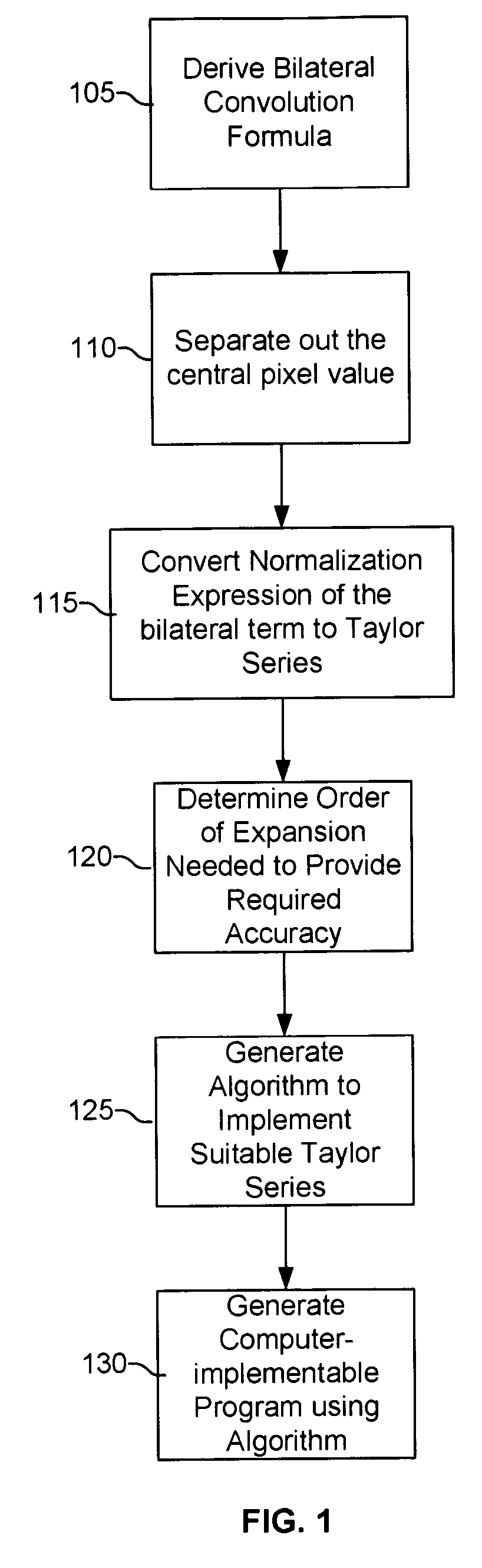
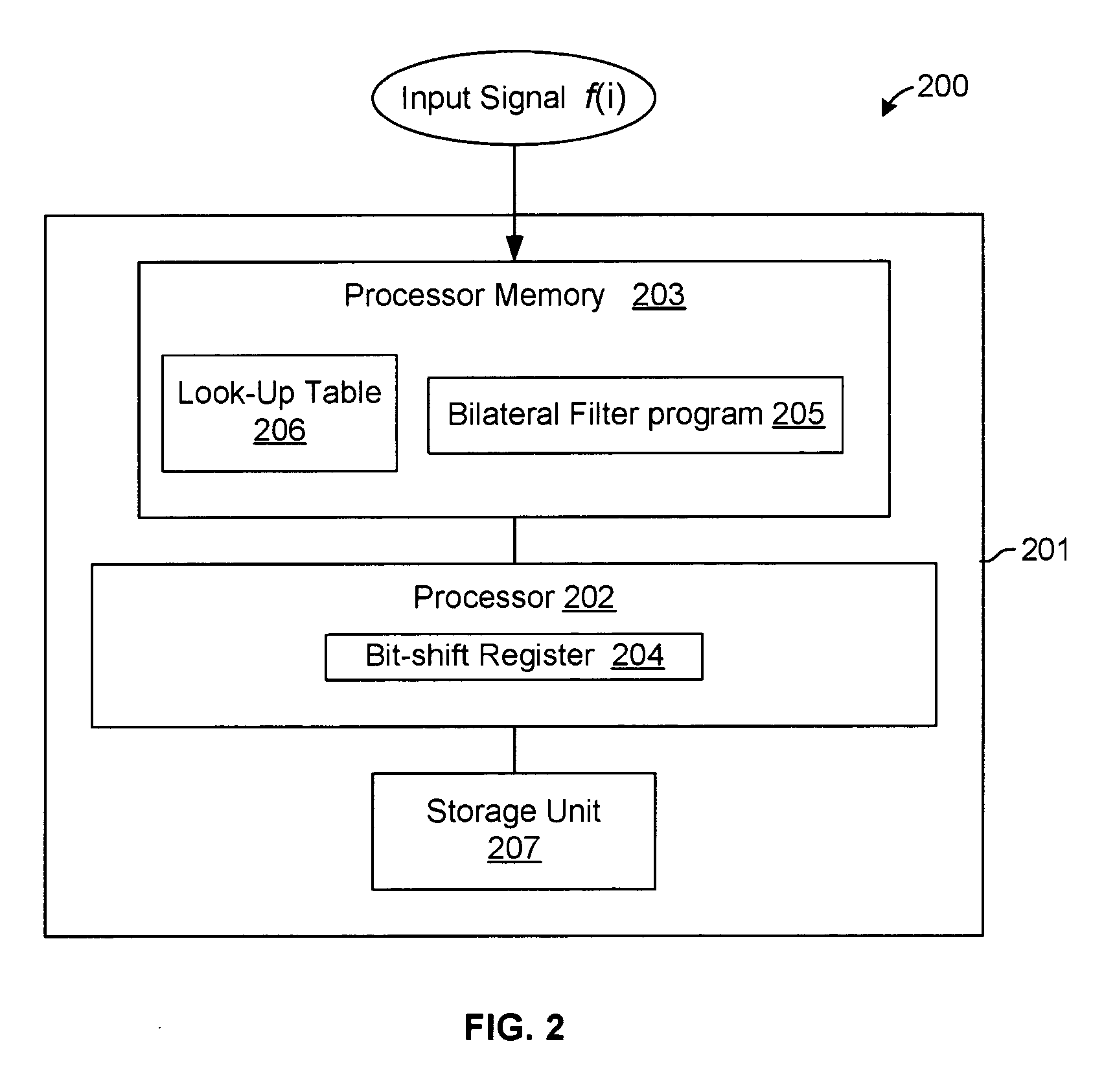
The present method eliminates the need for a division operation in the implementation of a bilateral filter. This division elimination speeds up software implementations and simplifies hardware implementations. A series expansion approximation is implemented using a formula for the normalization of filter weights. The formula employs multiplication and bit-shift operations instead of a division operation. The method provides for a well-controlled trade-off between computational complexity and accuracy of the approximation. The approximation used by the present method is based on a Taylor expansion of the normalization expression.
In order to reduce the potential normalization error, the bilateral filter is first reformulated at each pixel location into a sum of the original signal value at the pixel and a ‘bilateral correction term’ which depends only on local signal differences between the pixel and its neighbors, and is independent of the absolute intensity of the pixel. Hence, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com