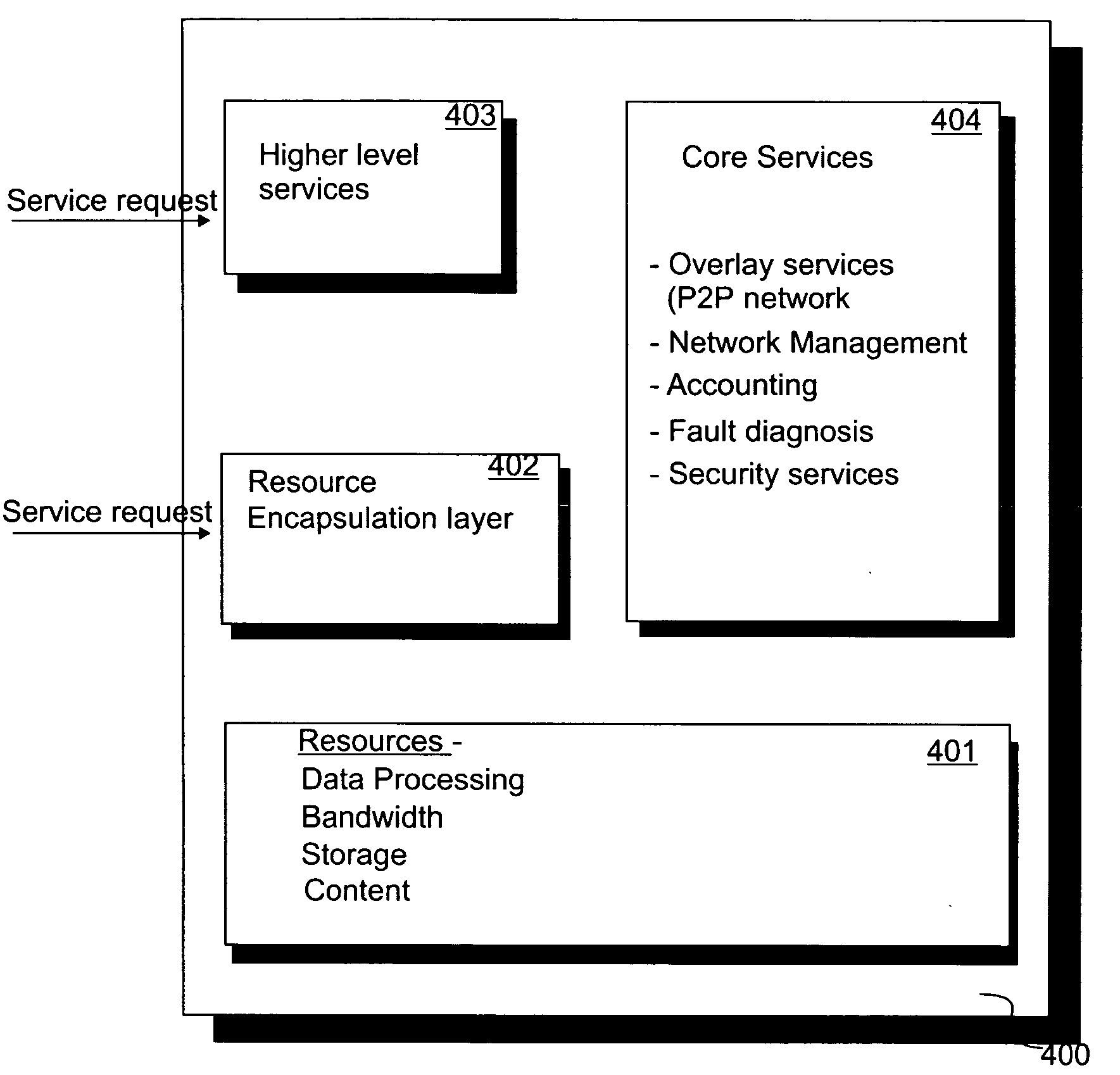
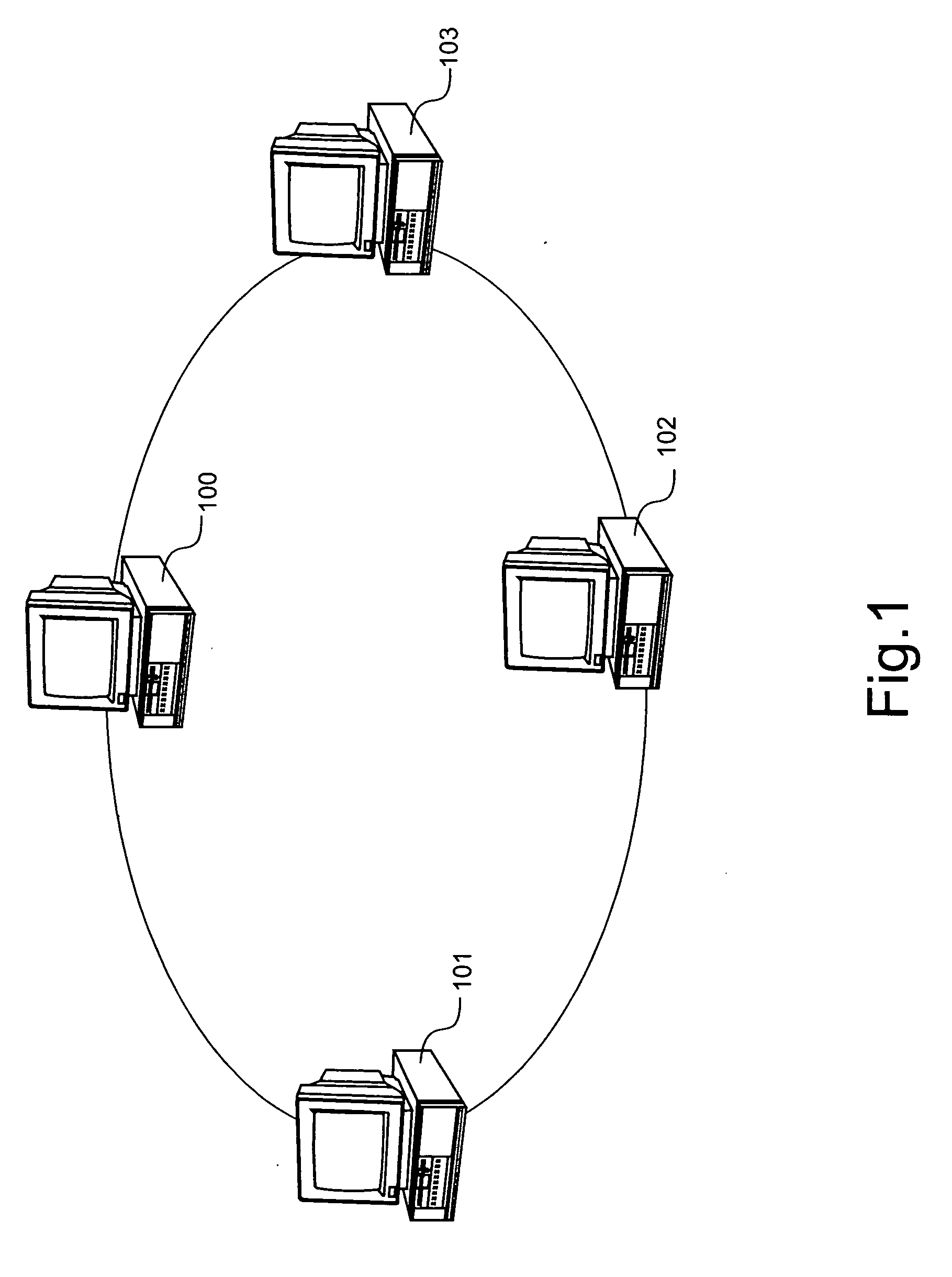
Use of nodes to monitor or manage peer to peer networks
a peer to peer network and node technology, applied in the field of computer science, can solve the problems of no centralised management system, no individual human network managers, no single computer entity has the capability to manage or monitor the whole peer to peer network
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] There will now be described by way of example a specific mode contemplated by the inventors for carrying out the invention. In the following description numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the present invention. It will be apparent however, to one skilled in the art, that the present invention may be practiced without limitation to these specific details. In other instances, well known methods and structures have not been described in detail so as not to unnecessarily obscure the present invention.
[0021] In this specification, the term computer entity is used to encompass many types of computer including personal computers, server computers, and other computing platforms such as personal digital assistant (PDA) devices, palmtop computers, laptop computers and the like. Communications links between computers may be local area network links, wide area network links and internet links, and may be carried on a variety of techno...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com