In one aspect, the present invention may provide convenient, compatible, and portable computing device programs, devices, systems, and methods
usable with existing exercise equipment that vary recorded visual-image stream presentation rate in response to a user's
exertion level as indicated by the sensing of a repetitive
physical function of the user.
In one aspect of the invention, a computing device-readable medium is provided containing computing device-
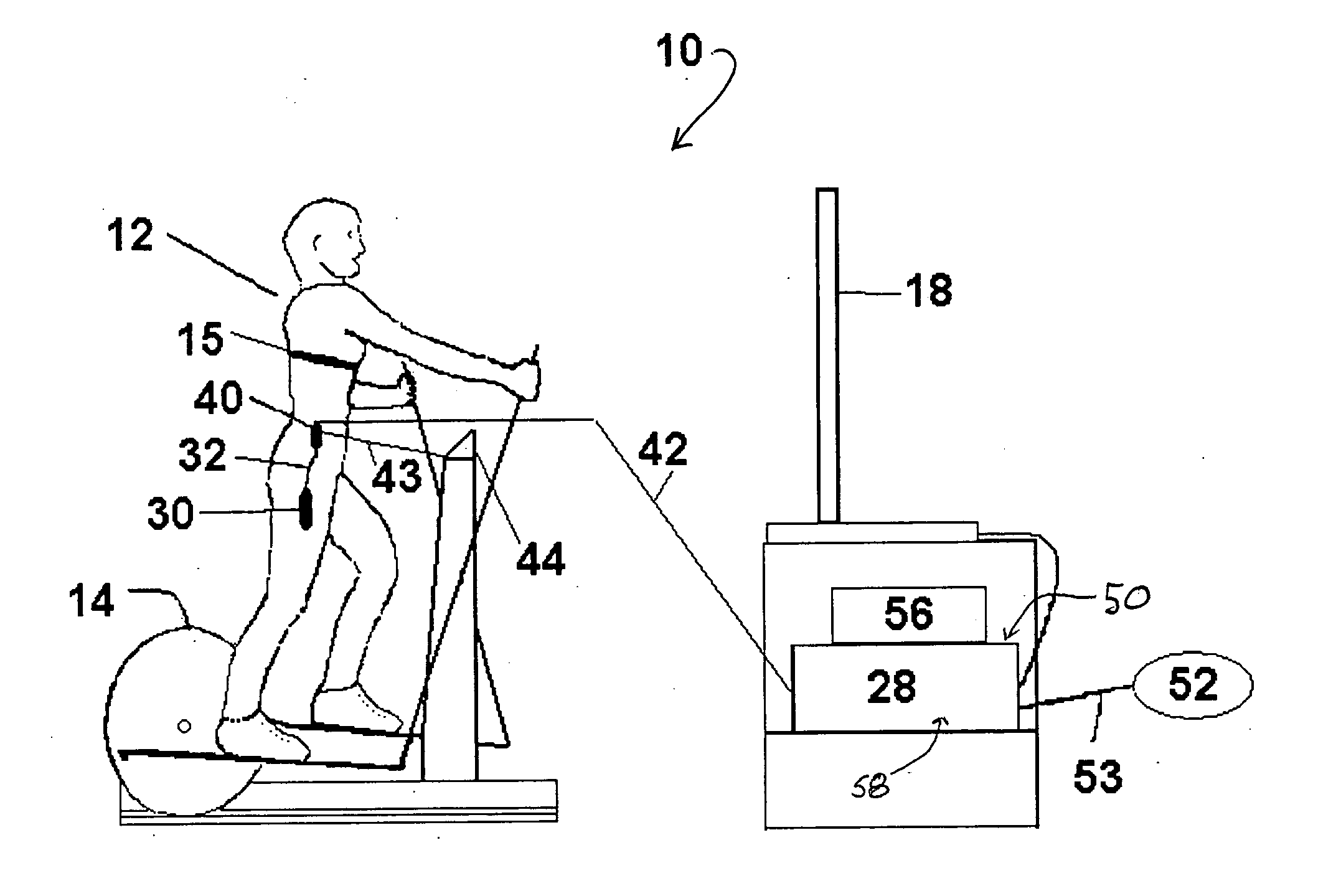
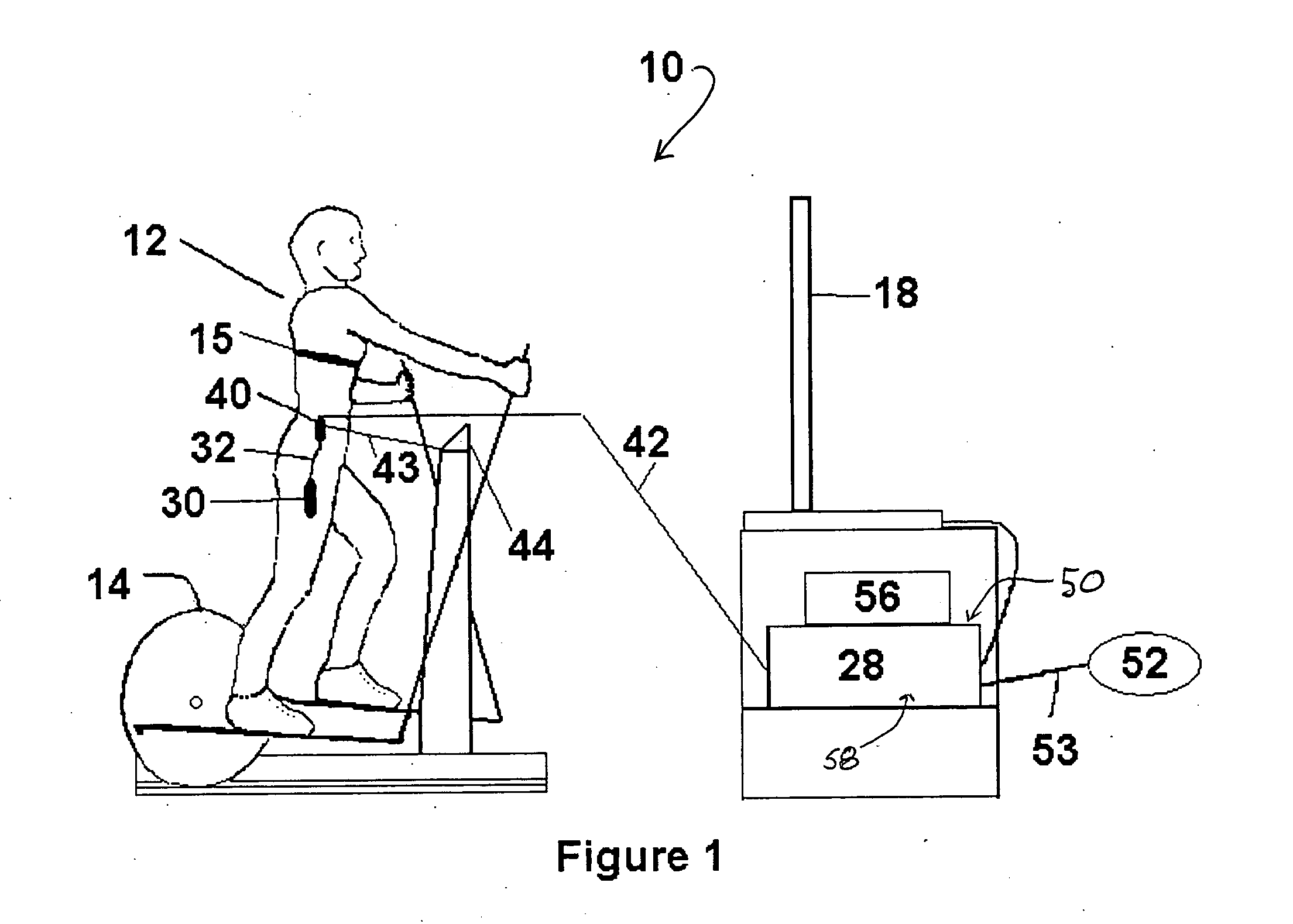
executable instructions which, when run on a computing device, cause the computing device to receive a user-exercise signal derived from the sensing of a repetitive
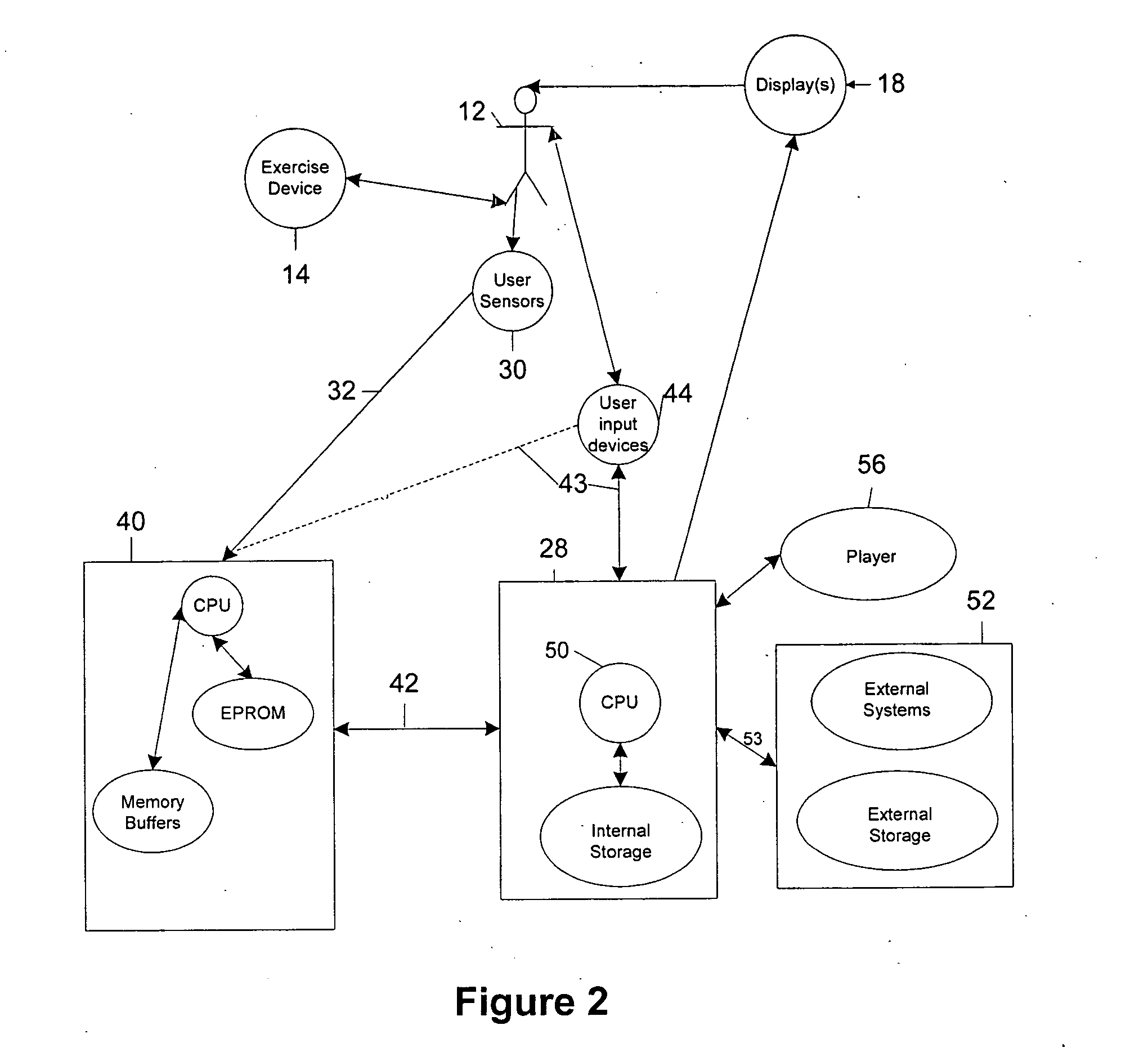
physical function of a user, relate the signal to a user-exercise level, determine a modified frame-display time for a visual-image stream in response to the user-exercise signal, and provide the modified frame-display time to a visual-image stream player. These instructions permit the visual-image stream player when playing the visual-image stream to dynamically change the frame-display time as a function of the user-exercise level. Determining the modified frame-display time may further include instructions that determine a user-exercise level in response to the user-exercise signal, receive a camera-
mount speed or other presentation rate value and a native frame-display time for a recorded visual-image stream, correlate the camera-mount speed and the user-exercise level, and modify the native frame-display time in response to the correlation to produce the modified frame-display time. In addition, where the user-exercise level correlates to a speed that exceeds the camera mount speed or other presentation rate value by a desired amount, the
system may omit the display of frames of the
video sequence to facilitate the smooth display of an apparent speed. This permits the use of a slower camera mount speed, and allows the video program to be used in conjunction with a variety of simulated outdoor exercise types having a wide range of desired apparent exercise speeds. This may also be important in the context of systems used in a
rehabilitation context.
In a further embodiment of the invention, a visual-image stream replay-
control system is provided that includes a computing device-readable medium containing computing device-
executable instructions which, when run on a computing device, cause the computing device to receive a user-exercise signal generated in response to a user's repetitive
physical function and related to a user-exercise level, determine a modified frame-display time for a visual-image stream in response to the user-exercise signal, and provide the modified frame-display time to a visual-image stream player. The system also includes a sensor for sensing a repetitive physical function of a user configured to provide the user-exercise signal when the user exercises. This system permits the visual-image stream player when playing the visual-image stream to dynamically change the frame-display time as a function of the user-exercise level. The system further includes a collector operable to receive a user-exercise signal from the sensor, and provide the user-exercise signal to a computing device. The collector may be further operable to store or buffer the user-exercise signal. Where the apparent speed of the video-image stream presentation is significantly greater than the camera mount speed, frame dropping may also be used to achieve the desired apparent speed of the video-image stream presentation.
In another aspect,
picture in picture,
video sequence branching, selection from multiple video streams (e.g., inserting a pacer or pacers into the
video image, or providing views to the rear or to the sides), frame dropping and periodic presentation of video stills based on, for example, location in the video stream, may be variously used to enhance the exercise experience. In addition, the apparent speed of the exerciser may be varied depending on grade information of the course so that, for example, the apparent speed of an exercise bicyclist exercising at a given rate on a steep uphill grade would be slower than for exercise at the same given rate on a flat or downhill segment.
In an aspect of the invention, the user may adjust the correlation between the exercise signal and the user exercise level so that he or she is capable, at the present fitness level, of achieving an apparent speed in the video-image stream that captures the user's interest. In another aspect, data is gathered by individual systems and transmitted over a
network connection, via a dial-up connection or the like to another system or systems so that an exercise specialist or medical person can monitor the user's progress. In another aspect, data is exchanged with other users of like systems. Where these users are also traversing the same virtual course, the location of the other riders can be marked by any of a variety of means, such as position markers along a line or bar indicating the percentage of the course that has been completed, or the use of picture-in-picture to show companion riders in a forward view or rear view mode. The position data along the course may be shared via peer-to-peer or
server-based
data exchange. Where data is shared over a network (including
the Internet) or over telephone lines via modem connections, physical proximity of the exercisers is not needed. The data shared may include
voice data to allow the exercisers to communicate verbally, thus enhancing the exercise experience.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More