Apparatus and method for exchanging vehicular fluids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
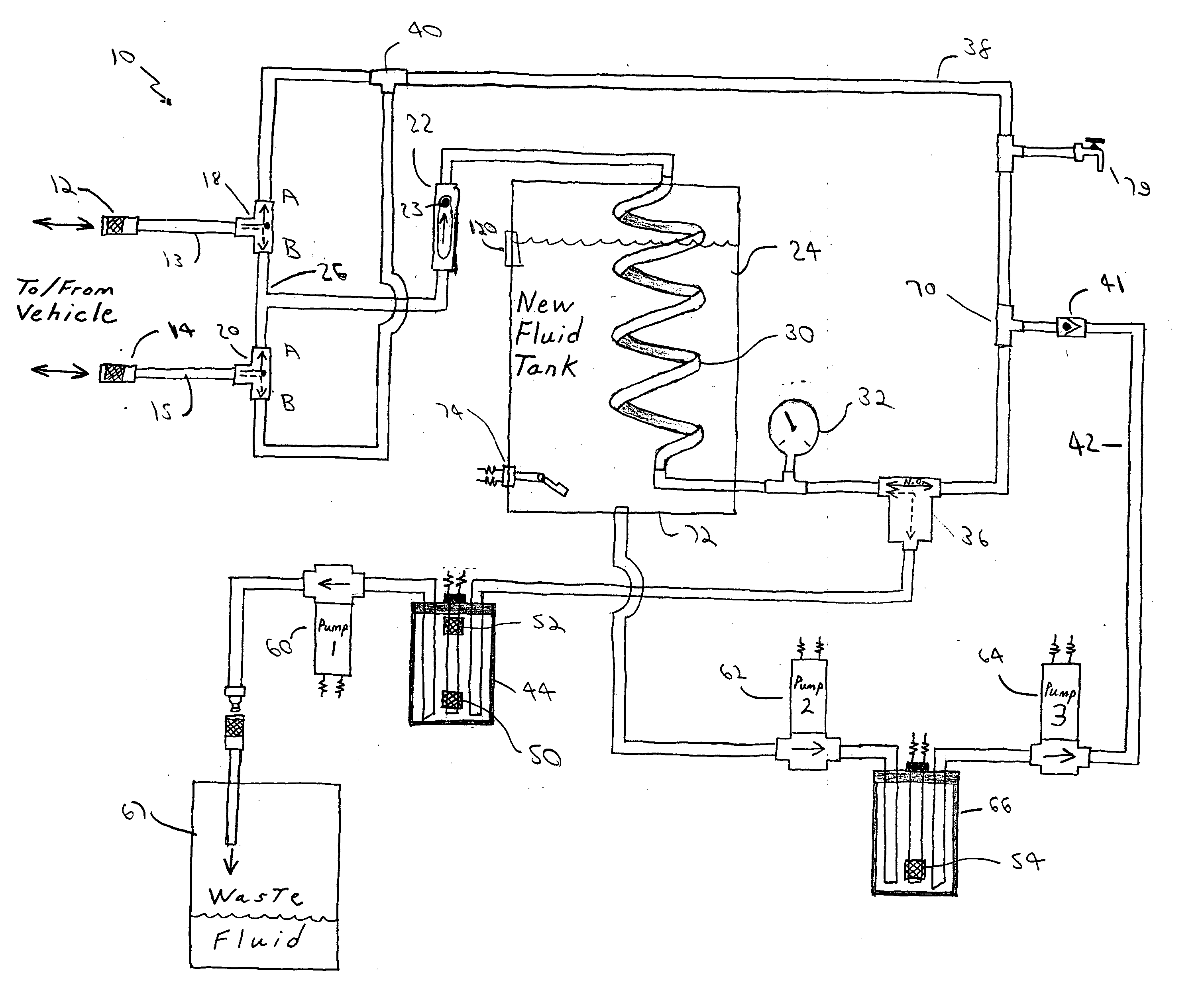
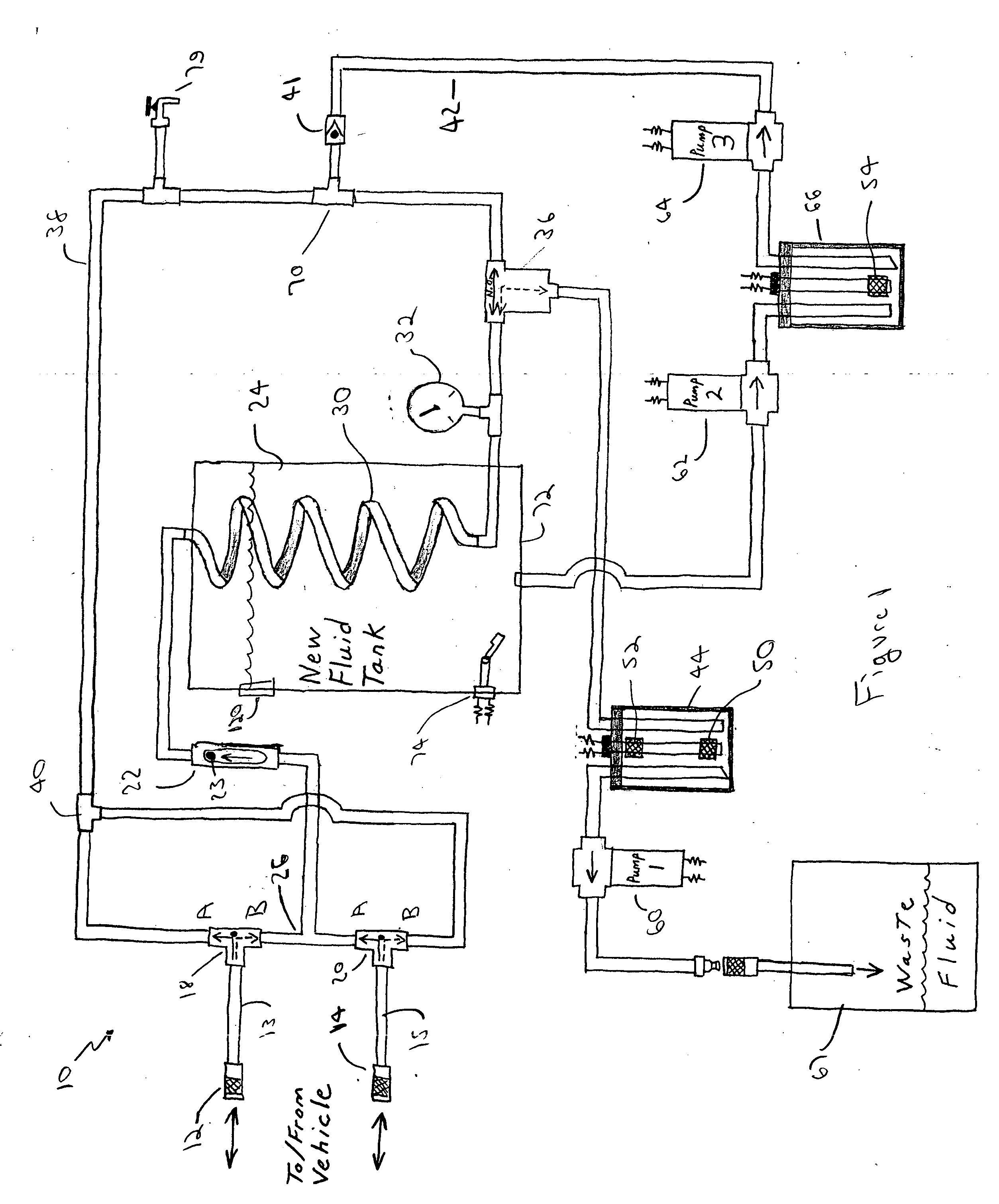
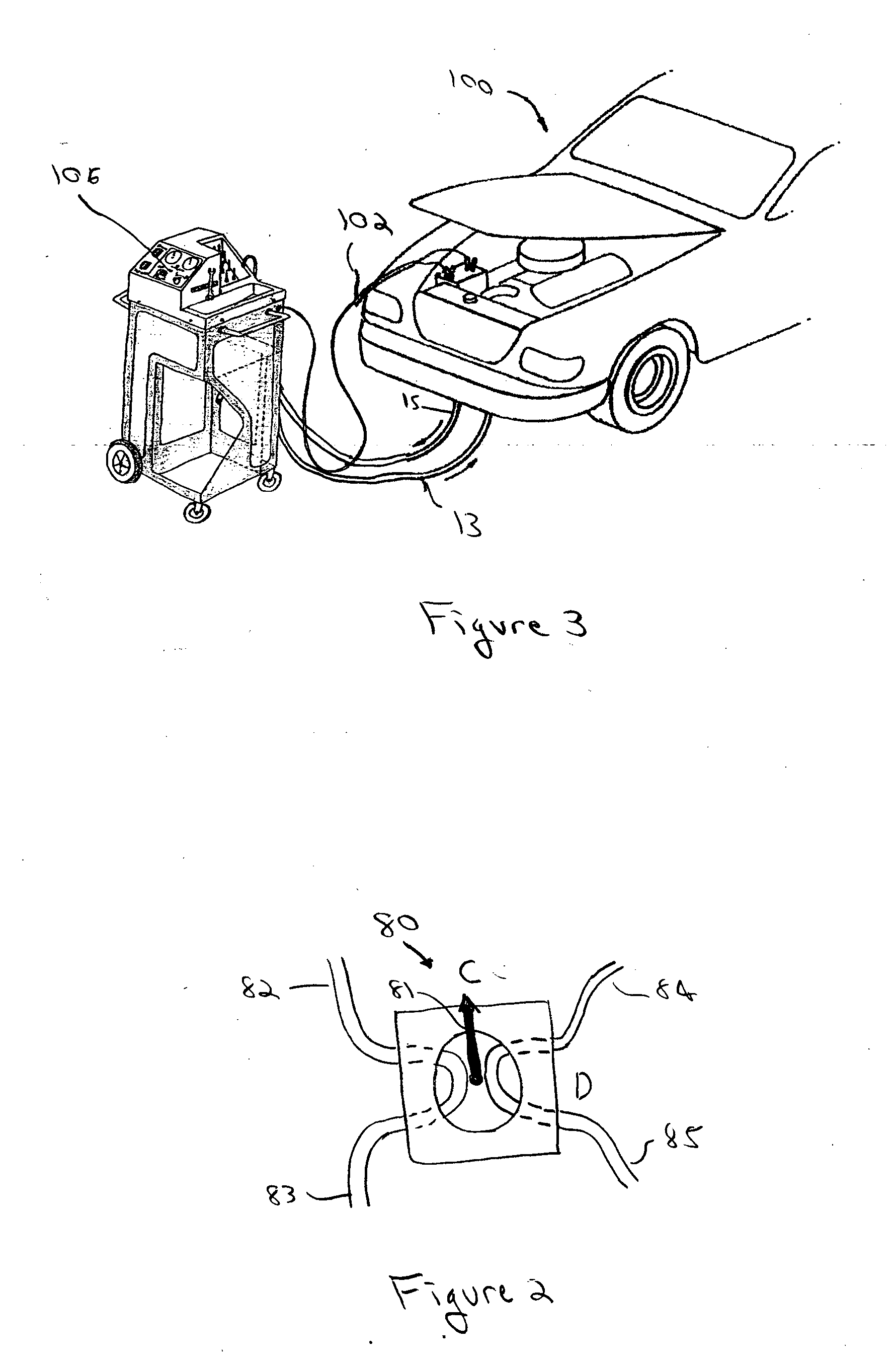
[0023] Before describing in detail the particular fluid replacement machine and a method for replacing fluid according to the teachings of the present invention, it should be observed that the present invention resides primarily in a novel and non-obvious combination of elements and method steps. Accordingly, the elements have been represented by conventional elements in the drawings, showing only those specific details that are pertinent to the present invention, so as not to obscure the disclosure with structural details that will be readily apparent to those skilled in the art having the benefit of the description herein.
[0024] One advantage of a machine and process according to the teachings of the present invention is use of the volume of used fluid evacuated from the system to control the exchange process. The use of pressure / force of the used fluid from the vehicle, as disclosed by the prior art, is not employed. As stated above, the exchange time is dictated by the speed at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com