Stabilized proteins
a technology of stabilized proteins and proteins, applied in the field of stabilized proteins, can solve the problems of potential undesirable reactive side-chain alteration, and achieve the effect of controlling the cross-link reaction and preventing undeirable cross-links
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
6. EXAMPLE I
Stabilized Fv Fragments
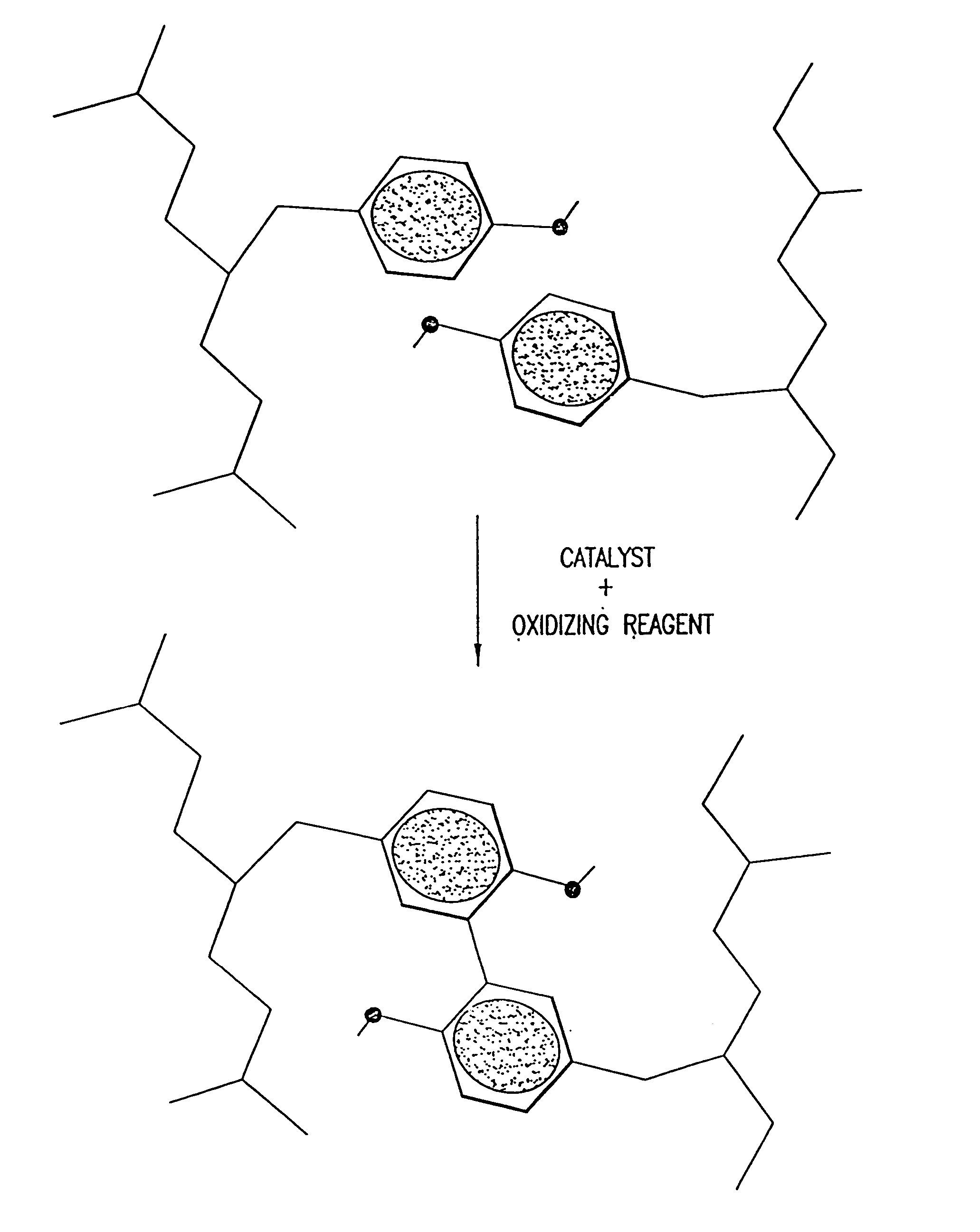
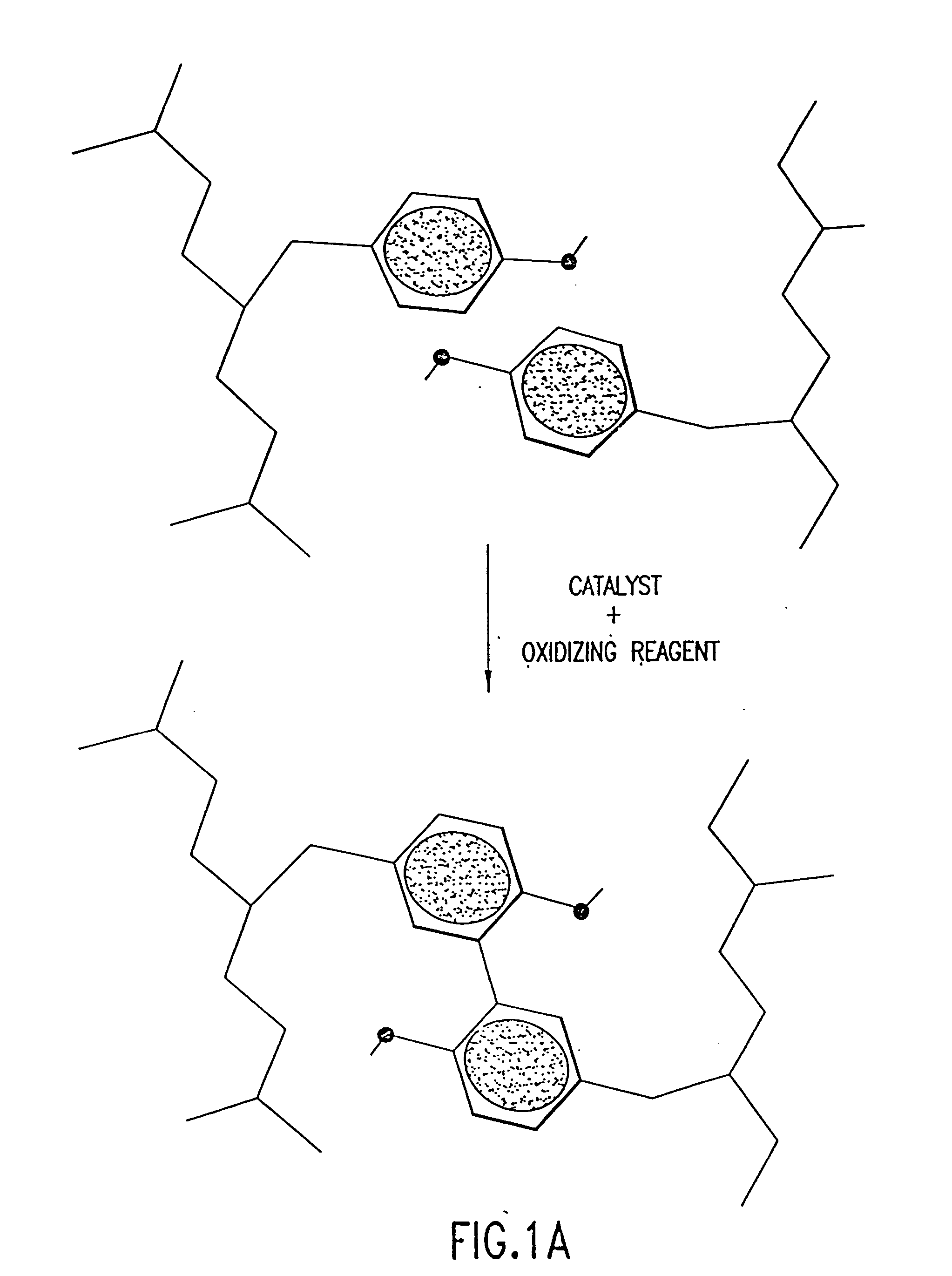
[0302] The following example illustrates certain variations of the methods of the invention for protein and protein complex stabilization. This example is presented by way of illustration and not by way of limitation to the scope of the invention.
6.1. Introduction
[0303] Several polypeptides and polypeptide complexes with significant commercial value have been identified in recent years, and furthermore, several modular domains have been identified that mediate protein-protein interactions: For many of these domains, the interaction sites with other proteins have also been mapped.
[0304] In the following section, methods of stabilizing one such complex, an Fv fragment complex, for which an abundance of data is available, are described in detail. Specifically, described below are the assembly of relevant databases for the selection process, the selection process itself, the introduction of point mutations, bacterial expression of the polypeptides ...
example ii
7. EXAMPLE II
Candida Antarctica Lipase B (CALB)
[0603] The following example illustrates certain variations of the methods of the invention for protein and protein complex stabilization. This example is presented by way of illustration and not by way of limitation to the scope of the invention.
[0604] Introduction
[0605] Several polypeptides with significant commercial value have been identified in recent years, and furthermore, for many of these polypeptides structural data is available. In the following section, methods of stabilizing one polypeptide, a biocatalyst, for which data is available only for the polypeptide itself, but not for other, structurally related polypeptides. Specifically, described below are the residue pair selection process, introduction of point mutations, expression of the polypeptides and their purification and deglycosylation, the cross-link reaction itself, and analysis of the resulting stabilized biocatalyst; for the description of the adjustment of th...
example iii
8. EXAMPLE III
[0693] The following example illustrates certain variations of the methods of the invention for protein and protein complex stabilization. This example is presented by way of illustration and not by way of limitation to the scope of the invention.
[0694] Introduction
[0695] In the following section, methods of stabilizing one polypeptide, a biocatalyst, for which structural data is available for several structurally or functionally related polypeptides. Specifically, described below are the residue pair selection process, the introduction of point mutations, bacterial expression of the polypeptides and their purification, the cross-link reaction itself, and analysis of the resulting stabilized biocatalyst. For the description of the cross-link reaction and the adjustment of the cross-link reaction conditions, refer to Chapter 6.
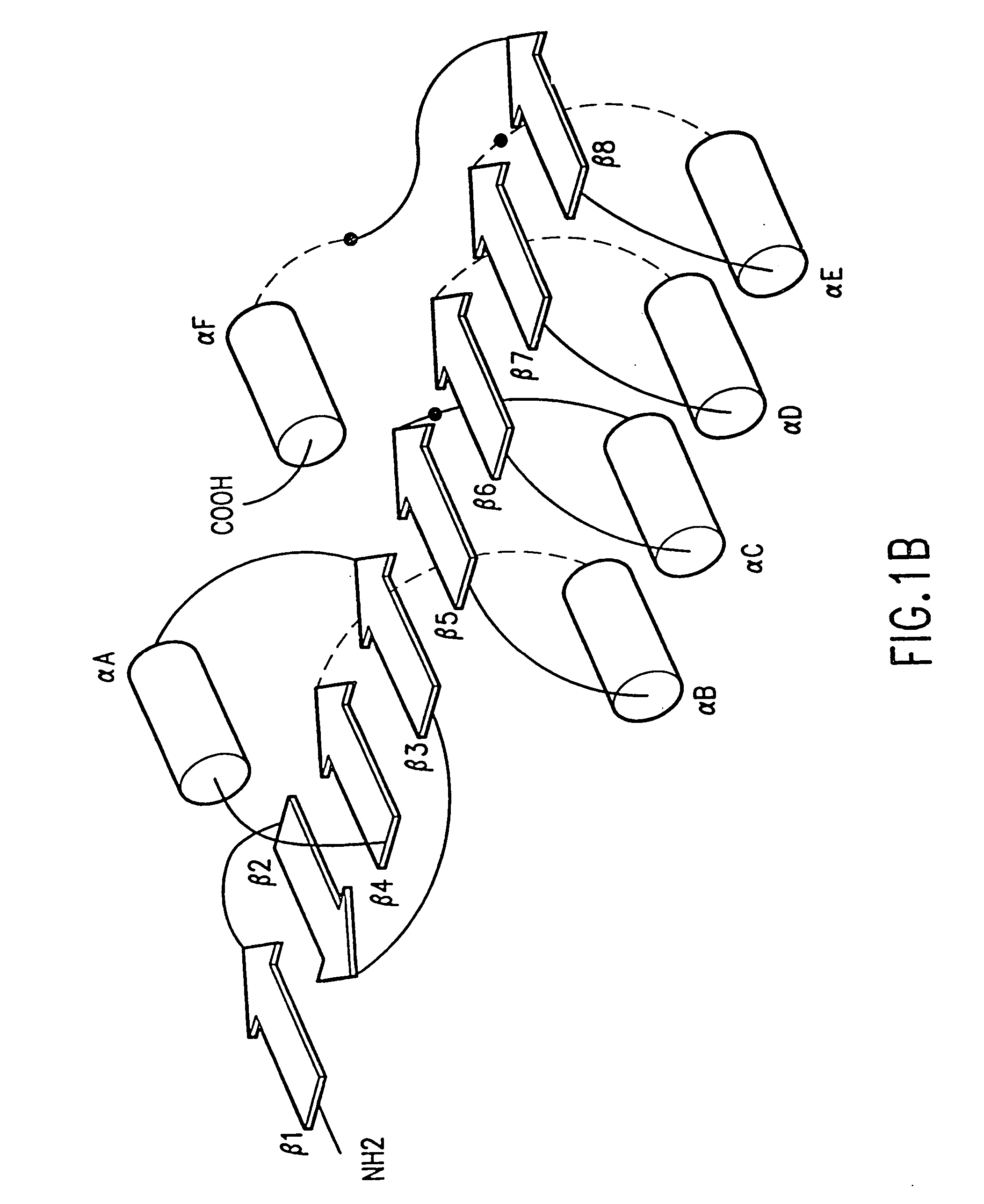
[0696] The biocatalyst stabilized in the below example is the serine endopeptidase Subtilisin E (FIG. 16A), which is one of the m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tetrahedral angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com